Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (29): 4617-4622.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.29.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Tolerance of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing human heme oxygenase 1 to ischemia/hypoxia injury
Deng Ning-bo1, Han Teng-long2, Zeng Yuan-qing3, Jiang Zhi-xin2
- 1Zhuhai Hospital of Guangdong Provincial TCM Hospital, Zhuhai 519015, Guangdong Province, China; 2the 305 Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100017, China; 3the First People’s Hospital of Chenzhou, Chenzhou 423000, Hunan Province, China
-
Revised:2017-06-06Online:2017-10-18Published:2017-11-08 -
Contact:Jiang Zhi-xin, Master, Chief technician, the 305 Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100017, China -
About author:Deng Ning-bo, Master, Zhuhai Hospital of Guangdong Provincial TCM Hospital, Zhuhai 519015, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30971235; the Medical Research Fund of PLA during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan Period, No. 2013XL010
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Deng Ning-bo, Han Teng-long, Zeng Yuan-qing, Jiang Zhi-xin. Tolerance of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing human heme oxygenase 1 to ischemia/hypoxia injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(29): 4617-4622.
share this article
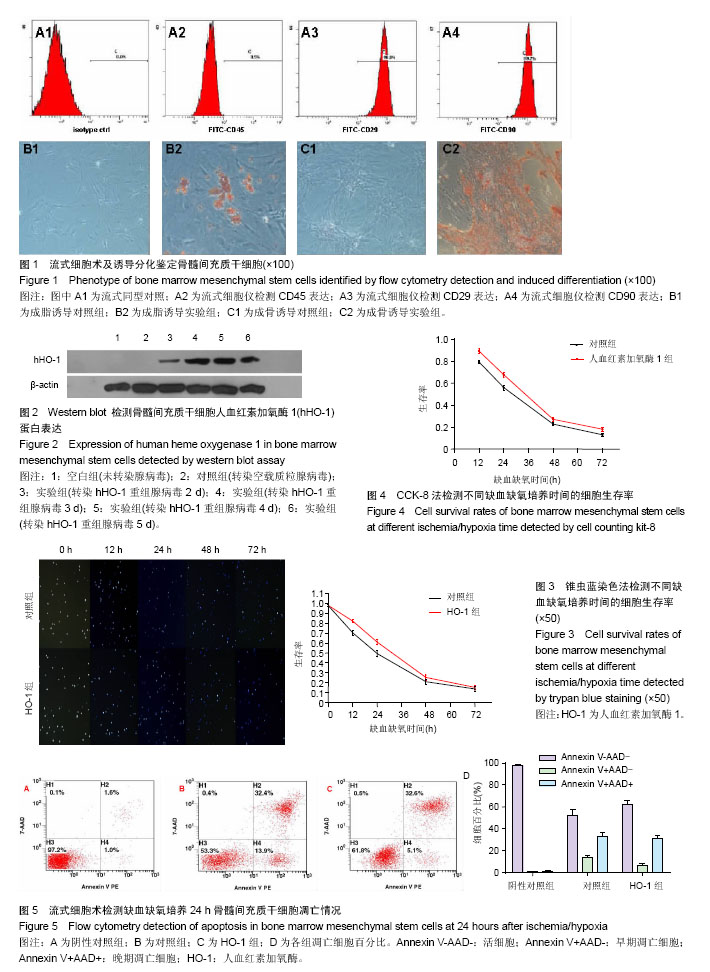
2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞鉴定结果 经流式细胞仪检测,结果显示第3代骨髓间充质干细胞的特异性表面标志物CD45阴性,阳性率为0.5%(图1A2);CD29阳性,阳性率为98.0%(图1A3);CD90阳性,阳性率为99.2%(图1A4)。 成脂诱导3周后,骨髓间充质干细胞有脂滴形成,油红O染色呈红色(图1B2),成骨诱导3周后,骨髓间充质干细胞有钙结节形成,茜素红染色呈红色(图1C2)。 2.2 hHO-1蛋白表达 空白组(未转染腺病毒)及对照组(转染空载质粒腺病毒)未见明显条带,HO-1组(转染hHO-1重组腺病毒)随着时间延长目的蛋白的表达量增加,在第4天达到最大表达量(图2)。 2.3 锥虫蓝染色法检测细胞存活率 正常培养条件下的对照组和HO-1组的生存率分别为(98.02±0.78)%,(98.33± 0.77)%(n=30,t=-1.535,P=0.130),差异无显著性意义。缺血缺氧培养12,24,48,72 h的对照组和HO-1组的生存率分别为(70.37±2.28)% vs. (82.32±1.61)%(n=30,t=-23.358,P=0.000),(49.41±3.27)% vs. (60.90±2.58)% (n=30,t=-15.107,P=0.000),(20.93±2.67)% vs. (25.17± 2.61)%(n=30,t=-6.182,P=0.000),(13.60±2.21)% vs. (15.20±1.74)%(n=30,t=-3.121,P=0.003),差异有显著性意义(图3)。 2.4 CCK-8法检测细胞存活率 对照组和HO-1组缺血缺氧12 h生存率分别为(79.32±1.26)%,(89.31±2.06)% (n=60,t=-32.030,P=0.000),缺氧24 h生存率分别为(55.95±2.27)%,(67.73±2.38)%(n=60,t=-27.734,P=0.000),缺血缺氧48 h生存率分别为(22.69±1.54)%,(27.24±1.80)%(n=60,t=-14.858,P=0.000),缺血缺氧72 h生存率分别(13.15±1.30)%,(18.06±1.89)% (n=60,t=-16.554,P=0.000),差异均有显著性意义(图4)。 2.5 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡 阴性对照生存率为(97.39±1.15)%(图5A),缺血缺氧24 h后对照组及HO-1组生存率分别为(52.72±4.66)%,(62.15±3.88)%(n=27,t= -8.076,P=0.000)(图5B,C),差异有显著性意义。"
| [1] Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131(4):e29-322.[2] Young PP, Schäfer R. Cell-based therapies for cardiac disease: a cellular therapist's perspective. Transfusion. 2015; 55(2):441-451.[3] Gerbin KA, Murry CE. The winding road to regenerating the human heart. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2015;24(3):133-140.[4] Tian T, Chen B, Xiao Y, et al. Intramyocardial autologous bone marrow cell transplantation for ischemic heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Atherosclerosis. 2014;233(2):485-492.[5] Telukuntla KS, Suncion VY, Schulman IH, et al. The advancing field of cell-based therapy: insights and lessons from clinical trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2(5):e000338.[6] Trounson A, McDonald C. Stem Cell Therapies in Clinical Trials: Progress and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17(1): 11-22.[7] Gao F, Chiu SM, Motan DA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and immunomodulation: current status and future prospects. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2062.[8] Miura Y. Basics and clinical application of human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2015;56(10):2195-2204. [9] Kawashiri MA, Nakanishi C, Tsubokawa T, et al. Impact of Enhanced Production of Endogenous Heme Oxygenase-1 by Pitavastatin on Survival and Functional Activities of Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015;65(6):601-606.[10] Hao BB, Pan XX, Fan Y, et al. Oleanolic acid attenuates liver ischemia reperfusion injury by HO-1/Sesn2 signaling pathway. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2016;15(5):519-524.[11] Kawashiri MA, Nakanishi C, Tsubokawa T, et al. Impact of Enhanced Production of Endogenous Heme Oxygenase-1 by Pitavastatin on Survival and Functional Activities of Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015;65(6):601-606.[12] Zhang L, Chan C. Isolation and enrichment of rat mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and separation of single-colony derived MSCs. J Vis Exp. 2010;(37): 1852.[13] Briguori C, Reimers B, Sarais C, et al. Direct intramyocardial percutaneous delivery of autologous bone marrow in patients with refractory myocardial angina. Am Heart J. 2006;151(3): 674-680.[14] Wu TW, Wu J, Li RK, et al. Albumin-bound bilirubins protect human ventricular myocytes against oxyradical damage. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991;69(10-11):683-688.[15] Memon IA, Sawa Y, Miyagawa S, et al. Combined autologous cellular cardiomyoplasty with skeletal myoblasts and bone marrow cells in canine hearts for ischemic cardiomyopathy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;130(3):646-653.[16] Lu H, Li Y, Zhang T, et al. Salidroside Reduces High-Glucose- Induced Podocyte Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via Upregulating Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) Expression. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:4067-4076.[17] 邓宁波,曾元清,韩腾龙,等.hHO-1联合GATA-4修饰大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞抗凋亡及向心肌分化的实验研究[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2017,42(4):314-319.[18] Fan X, Mu L.The role of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in the regulation of inflammatory reaction, neuronal cell proliferation and apoptosis in rats after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016;13:77-85. [19] Li C, Zhang C, Wang T, et al. Heme oxygenase 1 induction protects myocardiac cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation- induced apoptosis : The role of JNK/c-Jun/Caspase-3 inhibition and Akt signaling enhancement. Herz. 2016; 41(8): 715-724. [20] Ma T, Chen T, Li P, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) protects human lens epithelial cells (SRA01/04) against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Exp Eye Res. 2016;146:318-329.[21] Hamedi-Asl P, Halabian R, Bahmani P, et al. Adenovirus-mediated expression of the HO-1 protein within MSCs decreased cytotoxicity and inhibited apoptosis induced by oxidative stresses. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2012;17(2): 181-190.[22] Zeng B, Ren X, Lin G, et al. Paracrine action of HO-1-modified mesenchymal stem cells mediates cardiac protection and functional improvement. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(10):1256-1264.[23] Mancuso C, Bonsignore A, Di Stasio E, et al. Bilirubin and S-nitrosothiols interaction: evidence for a possible role of bilirubin as a scavenger of nitric oxide. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66(12):2355-2363.[24] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[25] Hamedi-Asl P, Halabian R, Bahmani P, et al. Adenovirus- mediated expression of the HO-1 protein within MSCs decreased cytotoxicity and inhibited apoptosis induced by oxidative stresses. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2012;17(2): 181-190.[26] 刘楠梅,王会玲,韩国锋,等. HO-1基因修饰对急性肾损伤微环境下骨髓间充质干细胞增生分化的影响[J].中华肾病研究电子杂志, 2015,4(4):200-207.[27] Serafini R, Longobardi V, Spadetta M, et al. Trypan blue/giemsa staining to assess sperm membrane integrity in salernitano stallions and its relationship to pregnancy rates. Reprod Domest Anim. 2014;49(1):41-47.[28] Shi XL, Gu JY, Han B, et al. Magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells after autologous transplantation into acutely injured liver. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(29): 3674-3679.[29] Ercan E, Bagla AG, Aksoy A, et al. In vitro protection of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by erythropoietin. Acta Histochem. 2014;116(1):117-125.[30] 白海,王存邦,张玲,等.血红素加氧酶1在骨髓间充质干细胞中抗凋亡作用研究[J].中华医学杂志, 2012,92(32):2292-2294.[31] 王艾丽,曾彬,程新耀,等.血红素氧合酶-1基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞培养上清液对心肌梗死治疗作用的实验研究[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(18):8270-8274.[32] Liang OD, Mitsialis SA, Chang MS, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells expressing heme oxygenase-1 reverse pulmonary hypertension. Stem Cells. 2011;29(1):99-107.[33] Cremers NA, Lundvig DM, van Dalen SC, et al. Curcumin-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression prevents H2O2-induced cell death in wild type and heme oxygenase-2 knockout adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(10):17974-17999.[34] Peng Y, Pan W, Ou Y, et al. Extracardiac-Lodged Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Propel an Inflammatory Response Against Myocardial Infarction via Paracrine Effects. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(5):929-935.[35] Hao J, Zhang Y, Jing D, et al. Mechanobiology of mesenchymal stem cells: Perspective into mechanical induction of MSC fate. Acta Biomater. 2015;20:1-9.[36] Wang L, Xu X, Kang L, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Mitochondria Damage Induced by Hypoxia in Mouse Trophoblasts. PLoS One. 2016;11(4): e0153729. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [5] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [6] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [7] | Cui Xing, Sun Xiaoqi, Zheng Wei, Ma Dexin. Huangqin Decoction regulates autophagy to intervene with intestinal acute graft-versus-host disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1057-1062. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [11] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [12] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [13] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [14] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [15] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||