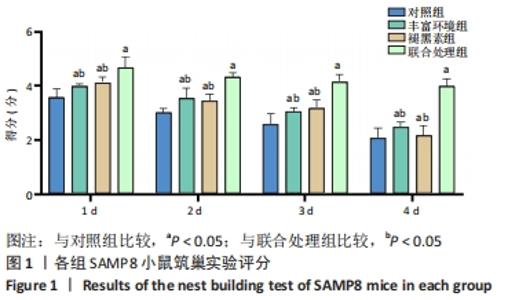
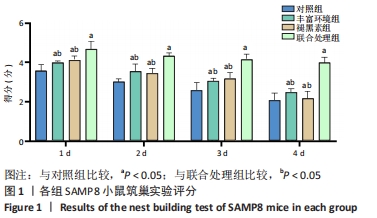
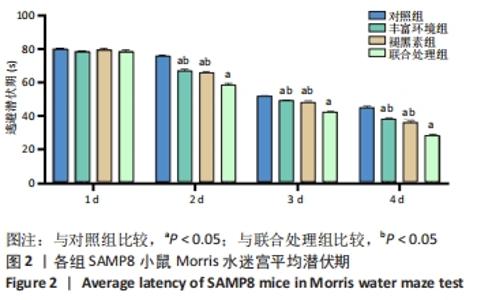
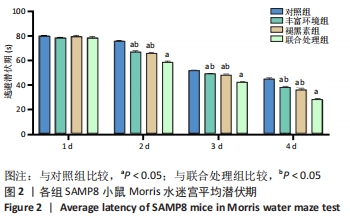
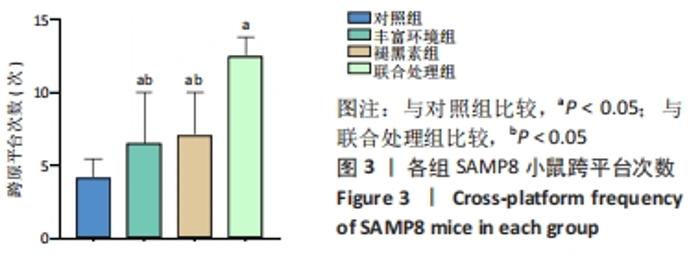
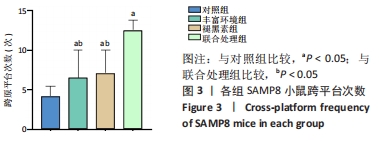
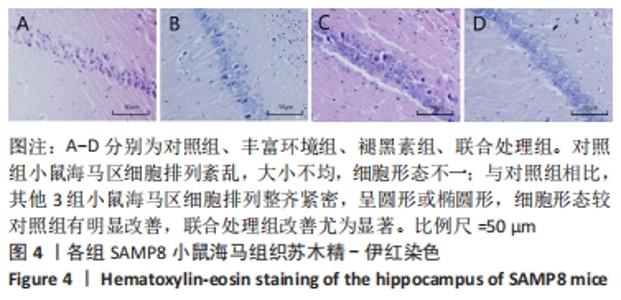
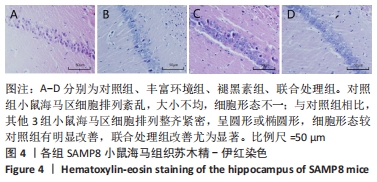
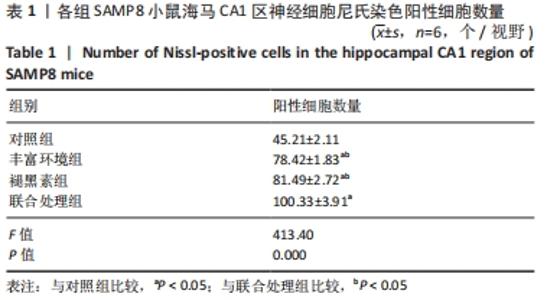
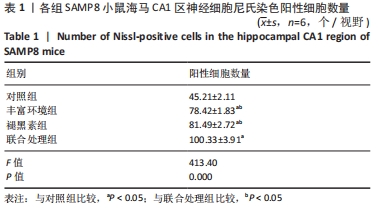
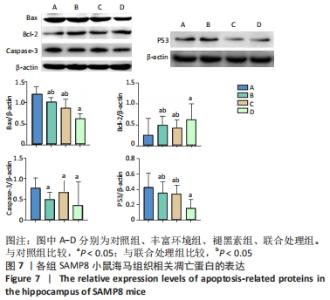
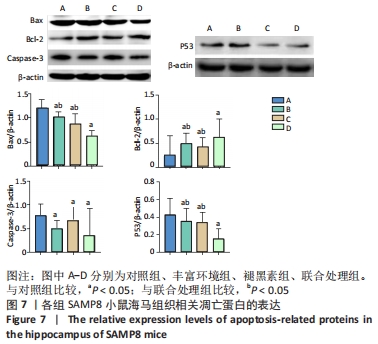
[1] 李艳丽.肠道微生态在脑老化认知功能减退中的作用及机制研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2019.
[2] WARDLAW JM, SMITH C, DICHGANS M. Small vessel disease: mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(7):684-696.
[3] LUO F, SANDHU AF, RUNGRATANAWANICH W, et al. Melatonin and Autophagy in Aging-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7174.
[4] 邹陈君.非药物干预中丰富环境治疗老年期痴呆有效性的临床研究[D].宁波:宁波大学,2017.
[5] WANG C, ZHANG Q, YU K, et al. Enriched Environment Promoted Cognitive Function via Bilateral Synaptic Remodeling After Cerebral Ischemia. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1189.
[6] BEUCKMANN CT, SUZUKI H, MUSIEK ES, et al. Evaluation of SAMP8 Mice as a Model for Sleep-Wake and Rhythm Disturbances Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease: Impact of Treatment with the Dual Orexin (Hypocretin) Receptor Antagonist Lemborexant. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;81(3):1151-1167.
[7] 何依帆,成绍武,马春媚,等.褪黑素对不同年龄SAM-P8小鼠学习记忆相关脑区的影响[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2014,35(6):830-838.
[8] NGUYEN LD, FISCHER TT, EHRLICH BE. Pharmacological rescue of cognitive function in a mouse model of chemobrain. Mol Neurodegener. 2021;16(1):41.
[9] NEELY CLC, PEDEMONTE KA, BOGGS KN, et al. Nest Building Behavior as an Early Indicator of Behavioral Deficits in Mice. J Vis Exp. 2019; (152).doi: 10.3791/60139.
[10] WU Y, GONG Y, LUAN Y, et al. BHBA treatment improves cognitive function by targeting pleiotropic mechanisms in transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2020;34(1):1412-1429.
[11] SEKI T, YAMAGATA H, UCHIDA S, et al. A novel mouse model of postpartum depression using emotional stress as evaluated by nesting behavior. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):22615.
[12] DINEL AL, LUCAS C, GUILLEMET D, et al. Chronic Supplementation with a Mix of Salvia officinalis and Salvia lavandulaefolia Improves Morris Water Maze Learning in Normal Adult C57Bl/6J Mice. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1777.
[13] 刘心朗,周丽丽,杨占君,等.肉苁蓉总苷对SAMP8小鼠学习记忆能力及突触可塑性的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2022(1):110-115.
[14] 谌勤,罗洪斌,谢文执.板桥党参通过PP2A信号通路改善AD模型大鼠认知功能障碍[J].中国药理学通报,2019,35(9):1232-1239.
[15] ZHOU HY, HUAI YP, JIN X, et al. An enriched environment reduces hippocampal inflammatory response and improves cognitive function in a mouse model of stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(11):2497-2503.
[16] 李敏,陶陶,张继荣.丰富环境对脑缺血再灌注损伤后相关凋亡基因的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2018,33(10):1238-1241.
[17] 刘佳雨,严萍,张瑜,等.代谢型谷氨酸受体在丰富环境改善卒中后认知功能障碍中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(23):3676-3682.
[18] 黄俊,吴帆帆,贺旭,等.丰富环境对血管性痴呆模型大鼠梨状皮质未成熟神经元表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(27):4006-4012.
[19] 袁颖,常宏,袁弘琼,等.褪黑素对大鼠前额叶皮层缺血诱发认知功能障碍的影响及其受体机制[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2021,41(12):1514-1517.
[20] 王敏,张峰,李晓红,等.褪黑素对Alzheimer病模型大鼠认知功能和海马tau蛋白过度磷酸化的影响[J].临床神经病学杂志,2007,20(5):374-376.
[21] 张良.褪黑素对放疗后大鼠卵巢功能的保护作用及其机制的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2014.
[22] 刘阳阳,梁国标,甄恩迪,等.褪黑素通过沉默信息调节因子1减轻线粒体氧化应激对脑缺血-再灌注小鼠的作用[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2017,14(10): 519-524.
[23] XU D, LIU L, ZHAO Y, et al. Melatonin protects mouse testes from palmitic acid-induced lipotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress and DNA damage in a SIRT1-dependent manner. J Pineal Res. 2020;69(4):e12690.
[24] YOKOMIZO S, NISHIMURA M, MORIOKA T, et al. Environmental Enrichment Increases Radiation-induced Apoptosis Not Spontaneous Apoptosis in Mouse Intestinal Crypt Cells. In Vivo. 2022;36(2):618-627.
[25] BAYAT M, KOHLMEIER KA, HAGHANI M, et al. Co-treatment of vitamin D supplementation with enriched environment improves synaptic plasticity and spatial learning and memory in aged rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021; 238(8):2297-2312.
[26] 王传杰,吴毅,陶峰,等.丰富环境对缺血性脑卒中小鼠海马区Bcl-2和Bax蛋白表达和认知功能的效果 [J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(5):539-543.
[27] 李敏,陶陶,张继荣.丰富环境对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后缺血半暗带区凋亡蛋白的影响[J].重庆医学,2019,48(10):1661-1664.
[28] CHANGIZI Z, MOSLEHI A, ROHANI AH, et al. Chlorogenic acid induces 4T1 breast cancer tumor’s apoptosis via p53, Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 signaling pathways in BALB/c mice. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(2):e22642.
[29] 程晓晖.PGRN在AD模型小鼠海马内的表达及与凋亡相关因子Bax/Bcl-2/Caspase-3关系的研究[D]. 广州:广东药科大学,2016.
[30] 谢婷婷,张爱华.p53介导的线粒体凋亡通路在燃煤型砷中毒大鼠肝损伤中的作用[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2014,28(2):210-215.
[31] VILBORG A, WILHELM MT, WIMAN KG. Regulation of tumor suppressor p53 at the RNA level. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010;88(7):645-652.
[32] LI Z, ZHAO J, LIU H, et al. Melatonin inhibits apoptosis in mouse Leydig cells via the retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor α/p53 pathway. Life Sci. 2020; 246:117431.
[33] 李文新,陈怡然,伊娜,等.电针不同频率对坐骨神经损伤大鼠脊髓Bcl-2、Bax及p53表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(8):75-78+267-268.
[34] LI YY, HUANG NQ, FENG F, et al. Icaritin Improves Memory and Learning Ability by Decreasing BACE-1 Expression and the Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8 (SAMP8) Mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020; 2020:8963845.
[35] 杨志虹,杨孝芳,易玮,等.艾灸神阙穴对衰老模型小鼠脑组织凋亡相关因子bcl-2、bax、caspase-3和p53表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(2): 321-324.
[36] 单博颖,薛亚然,梁思,等.何首乌饮对衰老生精细胞p53、Bcl-2和Bax mRNA表达的影响[J].承德医学院学报,2019,36(3):185-189.
|