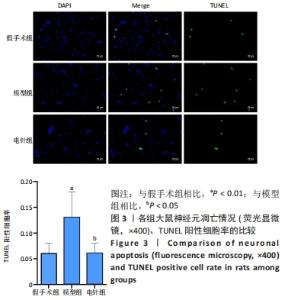
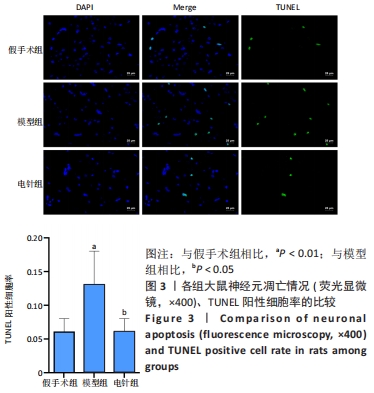
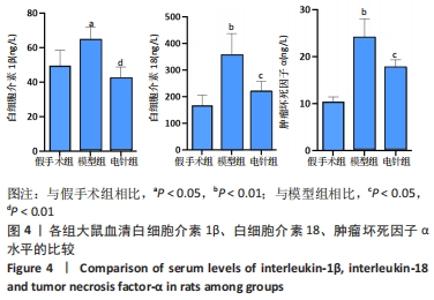
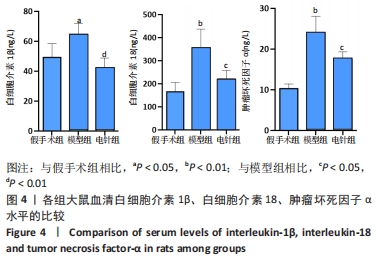
[1] YUAN Y, ZHAI Y, CHEN J, et al. Kaempferol Ameliorates Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Neuronal Ferroptosis by Activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Axis. Biomolecules. 2021;11(7):923.
[2] WANG L, XU L, DU J, et al. Nose-to-brain delivery of borneol modified tanshinone IIA nanoparticles in prevention of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):1363-1375.
[3] LIU L, ZHENG B, WANG Z. Protective effects of the knockdown of lncRNA AK139328 against oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury in PC12 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(3):621.
[4] ZHOU Y, YANG L, BO C, et al. MicroRNA-9-3p Aggravates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 (FGF19) to Inactivate GSK-3β/Nrf2/ARE Signaling. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021;17:1989-2002.
[5] HENTZEN NB, MOGAKI R, OTAKE S, et al. Intracellular Photoactivation of Caspase-3 by Molecular Glues for Spatiotemporal Apoptosis Induction. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(18):8080-8084.
[6] QI G, SUN D, TIAN Y, et al. Fast Activation and Tracing of Caspase-3 Involved Cell Apoptosis by Combined Electrostimulation and Smart Signal-Amplified SERS Nanoprobes. Anal Chem.2020;92(11):7861-7868.
[7] NICHANI K, LI J, SUZUKI M, HOUSTON JP. Evaluation of Caspase-3 Activity During Apoptosis with Fluorescence Lifetime-Based Cytometry Measurements and Phasor Analyses. Cytometry A. 2020;97(12):1265-1275.
[8] TUMMERS B, GREEN DR. Caspase-8: regulating life and death. Immunol Rev. 2017;277(1):76-89.
[9] FRITSCH M, GÜNTHER SD, SCHWARZER R, et al. Caspase-8 is the molecular switch for apoptosis, necroptosis and pyroptosis. Nature. 2019;575(7784):683-687.
[10] YIN F, ZHOU H, FANG Y, et al. Astragaloside IV alleviates ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the activation of key factors in death receptor pathway and mitochondrial pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;248:112319.
[11] 龚彪,李长清,黄剑. SD大鼠线栓法局灶性脑缺血/再灌注模型的改进[J].重庆医学,2006,35(4):313-315.
[12] 华兴邦,周浩良.大鼠穴位图谱的研制[J].实验动物与动物实验,1991,3(1):1-5.
[13] CHAI Z, GONG J, ZHENG P, et al. Inhibition of miR-19a-3p decreases cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting IGFBP3 in vivo and in vitro. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):17.
[14] 尹正录,孟兆祥,葛晟,等.互动式头针结合任务导向性镜像疗法治疗缺血性脑卒中偏瘫上肢功能障碍临床观察[J].中国针灸,2020,40(9):918-922.
[15] 任彩丽,付娟娟,王红星,等.早期康复临床路径对缺血性脑卒中患者功能恢复影响的多中心、单盲、随机对照研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017, 32(3):275-282.
[16] LEE D, CHOI JI. Hydrogen-Rich Water Improves Cognitive Ability and Induces Antioxidative, Antiapoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in an Acute Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Mouse Model. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:9956938.
[17] 王兴,尤苗苗,刘文文,等.针刺改善脑卒中后患者生活自理能力评定指数的Meta分析[J].中国老年学杂志,2018,38(13):3090-3093.
[18] 田亮,杜小正,王金海,等.手针与电针治疗急性缺血性脑卒中偏瘫的对比研究[J].中国针灸,2016,36(11):1121-1125.
[19] 董苗苗,赖涵,李曼玲,等.电针干预脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3/半胱天冬氨酸蛋白酶1表达的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(5):781-787.
[20] 赖涵,王娇,董苗苗,等.电针干预大鼠大脑中动脉栓塞缺血再灌注模型丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(2):233-239.
[21] ZHAO B, SUN LK, JIANG X, et al. Genipin protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the UCP2-SIRT3 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;845:56-64.
[22] ZENG J, ZHU L, LIU J, et al. Metformin Protects against Oxidative Stress Injury Induced by Ischemia/Reperfusion via Regulation of the lncRNA-H19/miR-148a-3p/Rock2 Axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:8768327.
[23] CUI Y, WANG JQ, SHI XH, et al. Nodal mitigates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(13):5923-5933.
[24] YANG JL, MUKDA S, CHEN SD. Diverse roles of mitochondria in ischemic stroke. Redox Biol. 2018;16:263-275.
[25] ZAMORANO S, ROJAS-RIVERA D, LISBONA F, et al. A BAX/BAK and cyclophilin D-independent intrinsic apoptosis pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e37782.
[26] WANG W, XU J. Curcumin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury Through Regulating Mitophagy and Preserving Mitochondrial Function. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020;17(2):113-122.
[27] QI G, YU N, XU K, et al. Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) Bcl-xl: transcriptional regulation and anti-apoptosis analysis. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2020;46(2):483-500.
[28] MA X, YU M, HAO C, et al. Shikonin induces tumor apoptosis in glioma cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress, and Bax/Bak mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeability. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;263:113059.
[29] DEWSON G. Investigating the Oligomerization of Bak and Bax during Apoptosis by Cysteine Linkage. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015;2015(5):481-484.
[30] PORTER AG, JÄNICKE RU. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6(2):99-104.
[31] YIN F, ZHOU H, FANG Y, et al. Astragaloside IV alleviates ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the activation of key factors in death receptor pathway and mitochondrial pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;248:112319.
[32] SHALINI S, DORSTYN L, DAWAR S, et al. Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(4):526-539.
[33] LI J, PENG L, BAI W, et al. Biliverdin Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Regulating the miR-27a-3p/Rgs1 Axis. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021;17:1165-1181.
[34] HUANG Y, WANG Y, DUAN Z, et al. Restored microRNA-326-5p Inhibits Neuronal Apoptosis and Attenuates Mitochondrial Damage via Suppressing STAT3 in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021;16(1):63.
[35] WANG P, HE Y, LI D, et al. Class I PI3K inhibitor ZSTK474 mediates a shift in microglial/macrophage phenotype and inhibits inflammatory response in mice with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):192.
[36] XIAN W, WU Y, XIONG W, et al. The pro-resolving lipid mediator Maresin 1 protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating the pro-inflammatory response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;472(1):175-181.
[37] ZHANG Y, WEI X, LIU L, et al. TIPE2, a novel regulator of immunity, protects against experimental stroke. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(39):32546-32555.
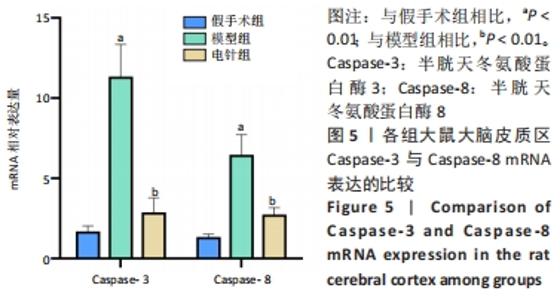
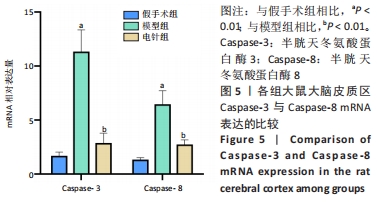
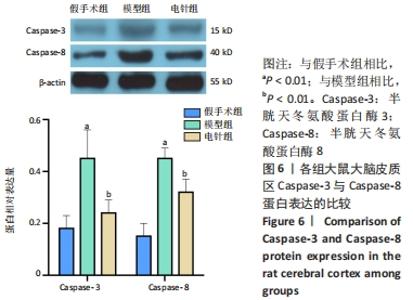
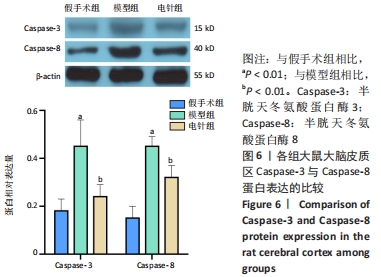
[38] 王博,张晓明,吴松,等.标本配穴电针预处理对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马神经元p53与caspase-3表达的影响[J].中国针灸,2019,39(9):957-962.
|