Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 1202-1209.doi: 10.12307/2022.224
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research
Li Zhiyi1, He Pengcheng1, Bian Tianyue1, Xiao Yuxia1, Gao Lu2, Liu Huasheng1
- 1Department of Hematology, 2Medical Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an JiaoTong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-19Revised:2021-03-22Accepted:2021-05-17Online:2022-03-18Published:2021-11-02 -
Contact:Liu Huasheng, MD, Chief physician, Department of Hematology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an JiaoTong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Zhiyi, MD, Department of Hematology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an JiaoTong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:University Joint Project of Shaanxi Provincial Key R&D Program, No. 2020GXLH-Y-006 (to LHS); Shaanxi Provincial Key R&D Program Project, No. 2018ZDCXL-SF-01-02-01 (to HPC); Clinical Research Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an JiaoTong University, No. HX201826 (to LHS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhiyi, He Pengcheng, Bian Tianyue, Xiao Yuxia, Gao Lu, Liu Huasheng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1202-1209.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
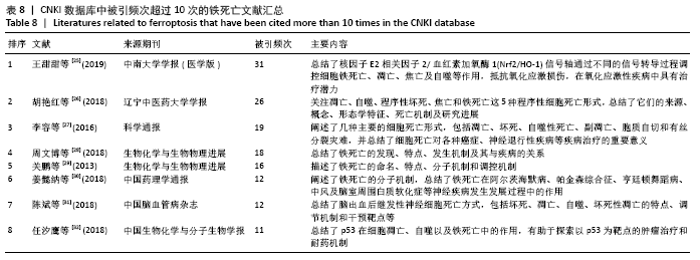
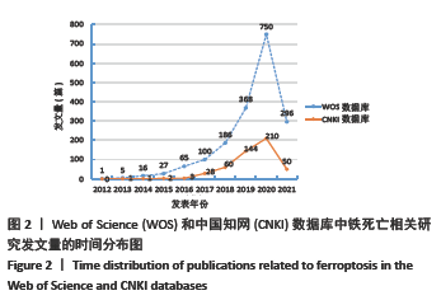
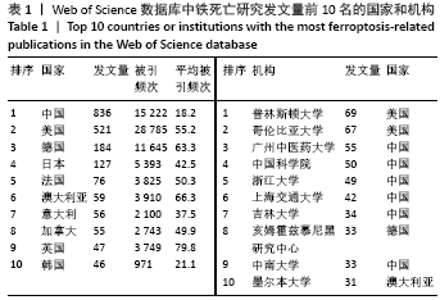
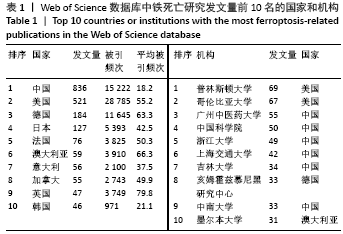
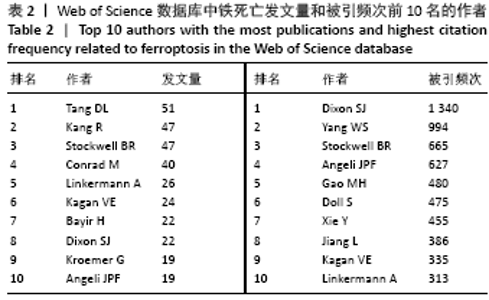
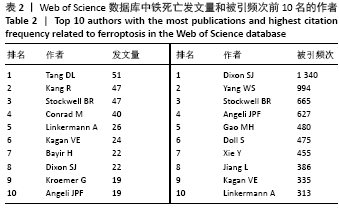
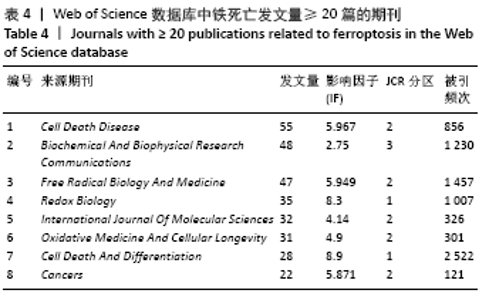
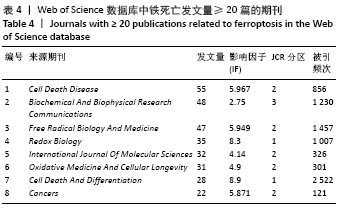
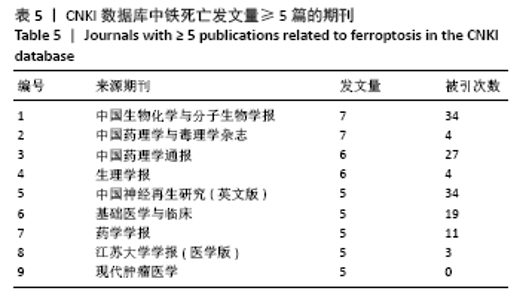
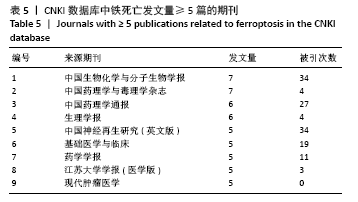
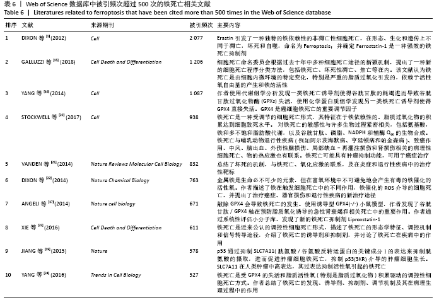
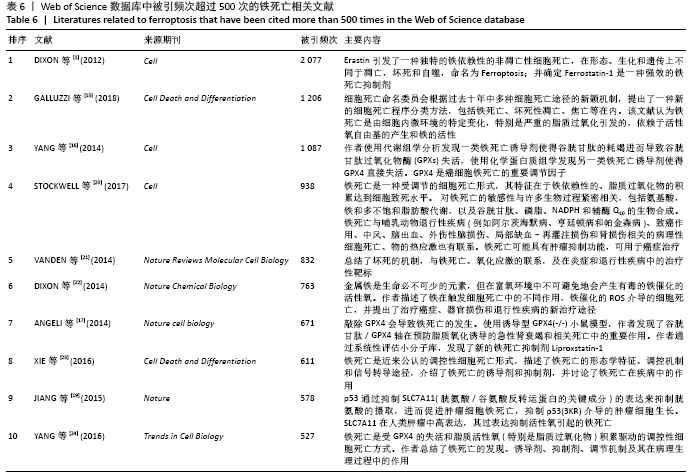
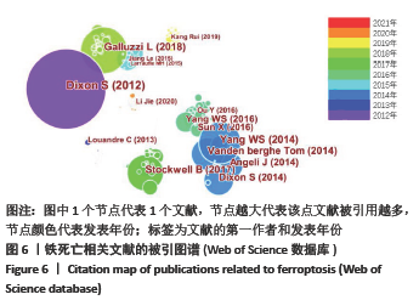
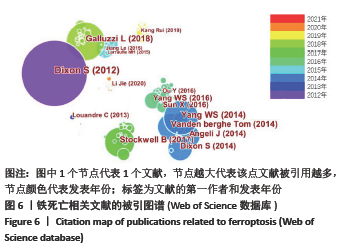
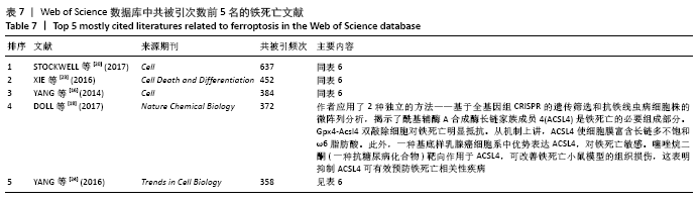
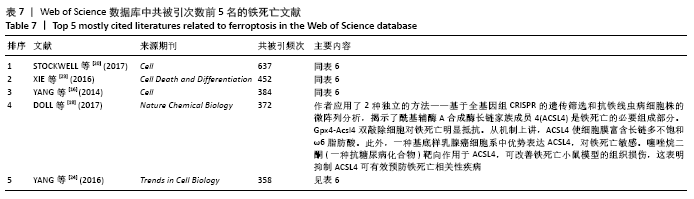
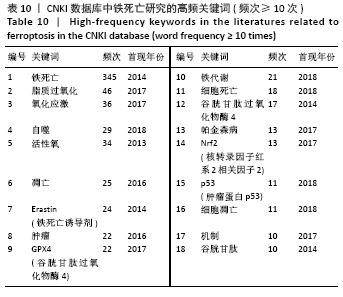
被引频次超过1 000次的2篇文献是DIXON等[1]和GALLUZZI等[15]发表的文献,命名并确立了铁死亡作为一种新型调控性细胞死亡方式。YANG等[16]发现GPX4是最关键的抑制肿瘤铁死亡的抗氧化酶,ANGELI等[17]发现抑制GPX4活性可促进急性肾损伤,这2篇文献揭示了GPX4是抑制铁死亡至关重要的抗氧化酶。DOLL等[18]发现ACSL4在RSL3诱导的铁死亡发生过程中是必不可少的。JIANG等[19]首次发现抑癌基因p53可通过调节铁死亡抑制肿瘤细胞活性。YANG等[16](2014)、STOCKWELL等[20](2017)、XIE等[23](2016)和YANG等[24](2016)这4篇文献均在表6,7中出现,提示此4篇文献是铁死亡研究领域中具有高度中心性的、公认的经典文献。 在CNKI数据库被引频次超过10次的铁死亡中文文献有8篇,见表8,多为综述类文献,介绍了铁死亡的命名、分子机制和调节机制,及其在神经系统疾病和肿瘤中的作用。"
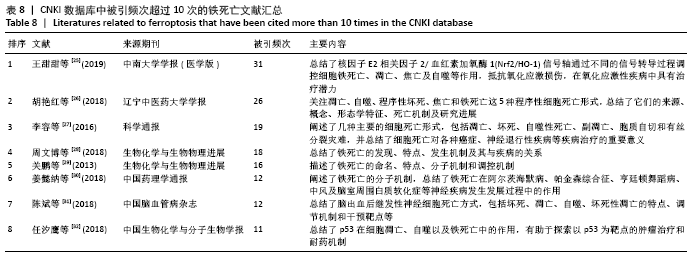

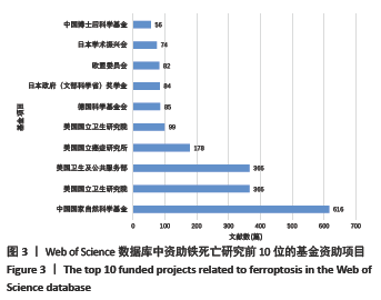
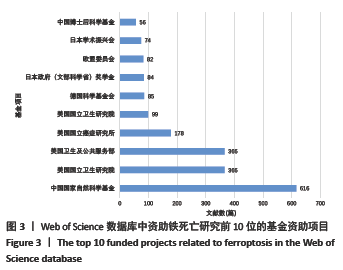
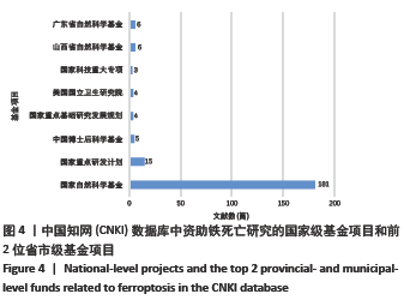
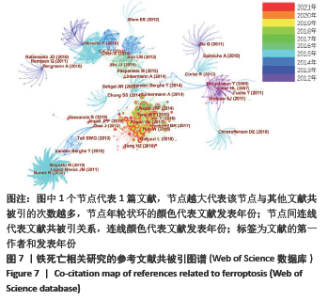
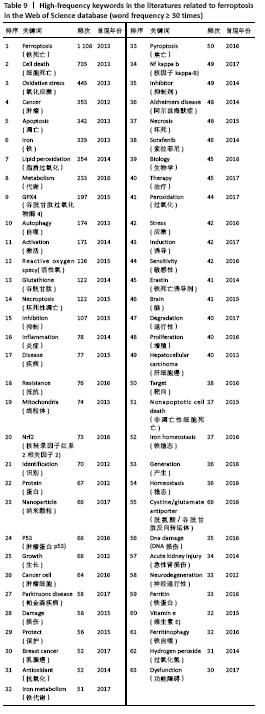
2.5 关键词分析 文献的关键词是用来表达学术论文主题内容必不可少的词语,是一篇学术论文中最核心、最重要的术语,具有索引、快速导读及突出重点的功能[33],因此通过分析关键词可迅速了解文献的核心内容。Web of Science和CNKI数据库中铁死亡领域的高频关键词分别见表9,10,Web of Science数据库铁死亡相关关键词的爆发图谱见图8。 高频关键词显示:铁死亡领域关注的代谢热点是铁代谢、脂质代谢和谷胱甘肽代谢。铁死亡的发生依赖亚铁与过氧化氢反应生成活性氧的芬顿反应,故铁的转运、存储和释放等代谢过程与铁死亡密切相关[34]。多不饱和脂肪酸被氧化生成的脂质过氧化物是铁死亡发生的必要,故脂质的合成、降解、酯化、去酯化和氧化等代谢过程也与铁死亡密切相关。谷胱甘肽是细胞内关键的抗氧化短肽,能强有力地抑制铁死亡,它的合成、降解及其底物的转运也与铁死亡密切相关[35]。 铁死亡领域的热点基因是GPX4,NRF2,p53,NF-κb。GPX4是合成谷胱甘肽的催化酶,是抑制铁死亡最为关键的抗氧化酶,它的活性和数量直接影响铁死亡[16]。NRF2,p53和NF-κb是3个著名的转录因子,调控多种基因表达,参与众多细胞过程。NRF2能感知细胞氧化应激水平,目前认为其能抑制铁死亡发生[2]。p53是研究最多的抑癌基因,其编码的p53蛋白调控上百种基因表达,能通过调控其不同靶基因的转录促进或抑制铁死亡[2]。NF-κb能激活促炎细胞因子的表达,促进铁死亡的发生[36]。 铁死亡在肿瘤、神经系统疾病和心血管疾病被广泛研究,索拉菲尼、爱拉斯汀(Erastin)和维生素E是铁死亡领域受到关注的药物。在肿瘤细胞中,多种癌蛋白、肿瘤抑制因子和致癌信号转导通路可调控铁死亡[37]。原癌基因RAS基因的突变是癌症中最常见的基因突变,铁死亡诱导剂爱拉斯汀在体外试验中能促进RAS突变的肿瘤细胞死亡[2]。索拉菲尼是RAS-G12C突变蛋白的直接抑制剂,除靶向原癌蛋白RAS的直接抗肿瘤作用,也可促进肿瘤细胞铁死亡发挥抗肿瘤作用[38]。神经退行性病(阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病等)的一个共同特征是神经细胞的早期和进行性丢失,研究发现阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型的病变区神经元细胞出现铁死亡,缺乏铁死亡抑制剂维生素E可加重小鼠的神经退行性变[39]。铁死亡是缺血再灌注疾病的关键驱动因素,如脑卒中、心肌梗死、急性肾损伤和手术或器官移植时的缺血再灌注损伤,铁死亡抑制剂能有效保护脑、心脏、肝肠肾等多种器官[40]。线粒体通透性改变和内质网应激是铁死亡中重要的亚细胞器改变[41-42],并介导与细胞凋亡间的相互作用[43]。 Web of Science数据库中高频关键词的首现时间多为2014-2016年,提示该时间段铁死亡研究发展迅速且不断受到全球研究者的关注。Web of Science数据库的关键词包含CNKI数据库的,但CNKI数据库的关键词时间略晚于Web of Science数据库,提示中国的铁死亡中文研究稍晚但紧跟国际热点研究。"
| [1] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072. [2] CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(5):280-296. [3] 任全娥.大数据背景下的文献计量学研究进展与学科融合[J].情报理论与实践,2019,42(1):48-52. [4] 潘颖,孙瑜峥,刘岩.科技文献阅读中语素意识研究的可视化分析[J].情报科学,2019,37(12):123-127. [5] CHEN C, IBEKWE SJF, HOU J. The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: a multiple‐perspective cocitation analysis. J Am Soc Inform Sci Tech. 2010;61(7):1386-1409. [6] CHEN C. Cascading citation expansion. J Inf Sci Theory Pract. 2018;6(2): 6-13. [7] 黄茂茂,胡月,王彬川,等.缺血性脑卒中康复近10年国际文献计量学及可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23):3725-3733. [8] NG JY. Global research trends at the intersection of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and traditional, integrative, and complementary and alternative medicine:a bibliometric analysis. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020;20(1):353. [9] GUO S, WANG L, XIE Y, et al. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of stem cells therapy for spinal cord injury based on web of science and citespace in the last 20 years. World Neurosurg. 2019;132:246-258. [10] SEDANI A, YAKKANTI R, ALLEGRA P, et al. Thromboprophylaxis across orthopaedic surgery: bibliometric analysis of the most cited articles. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;16:157-167. [11] ZHENG H, JIANG J, XU S, et al. Nanoparticle-induced ferroptosis: detection methods, mechanisms and applications. Nanoscale. 2021; 13(4):2266-2285. [12] COZZI A, ORELLANA DI, SANTAMBROGIO P, et al. Stem cell modeling of neuroferritinopathy reveals iron as a determinant of senescence and ferroptosis during neuronal aging. Stem Cell Rep. 2019;13(5):832-846. [13] LI X, ZENG J, LIU Y, et al. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of action of quercetin and quercetin diels-alder anti-dimer on erastin-induced ferroptosis in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(3):205-223. [14] NOBUTA H, YANG N, NG YH, et al. Oligodendrocyte death in pelizaeus-merzbacher disease is rescued by iron chelation. Cell Stem Cell. 2019; 25(4):531-541. [15] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541. [16] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1-2):317-331. [17] FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, SCHNEIDER M, PRONETH B, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(12):1180-1191. [18] DOLL S, PRONETH B, TYURINA YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017; 13(1):91-98. [19] JIANG L, KON N, LI T, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 2015;520(7545):57-62. [20] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171(2):273-285. [21] VANDEN BT, LINKERMANN A, JOUAN LS, et al. Regulated necrosis:the expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(2):135-147. [22] DIXON SJ, STOCKWELL BR. The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10(1):9-17. [23] XIE Y, HOU W, SONG X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(3):369-379. [24] YANG WS, STOCKWELL BR. Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26(3):165-176. [25] 王甜甜,陈淳媛,杨雷,等.Nrf2/HO-1信号轴在氧化应激性疾病中的机制[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2019,44(1):74-80. [26] 胡艳红,张凡,张楚焌,等.程序性细胞死亡形式研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2018,20(12):85-89. [27] 李容,王新文,杨晓辉,等.细胞命运之终点—细胞死亡[J].科学通报,2016,61(18):1983-1987. [28] 周文博,孔晨飞,秦高伟,等.铁死亡发生机制的研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2018,45(1):16-22. [29] 关鹏,石振华,李亚青,等.铁死亡:一种新的细胞死亡方式[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2013,40(2):137-140. [30] 姜懿纳,阳松威,张欣,等.铁死亡的机制及其在神经疾病中的作用[J].中国药理学通报,2018,34(2):166-170. [31] 陈斌,成宜军,陈正鸿,等.脑出血后神经细胞死亡机制的研究进展[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2018,15(3):153-156. [32] 任汐鹰,刘勤献,王海英.p53与细胞死亡[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2018,34(6):588-594. [33] 姜昕.学术论文关键词标引研究[J].辽宁师专学报(自然科学版), 2020,22(3):104-108. [34] HASSANNIA B, VANDENABEELE P, BERGHE TV. Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer Cell. 2019;35(6):830-849. [35] ZHENG J, CONRAD M. The metabolic underpinnings of ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 2020;32(6):920-937. [36] OH BM, LEE SJ, PARK GL, et al. Erastin inhibits septic shock and inflammatory gene expression via suppression of the NF-κB pathway. J Clin Med. 2019;8(12):2210-2222. [37] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282. [38] LACHAIER E, LOUANDRE C, GODIN C, et al. Sorafenib induces ferroptosis in human cancer cell lines originating from different solid tumors. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(11):6417-6422. [39] HAMBRIGHT WS, FONSECA RS, CHEN L, et al. Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox Biol. 2017;12: 8-17. [40] CONRAD M, LORENZ SM, PRONETH B. Targeting ferroptosis: new hope for as-yet-incurable diseases. Trends Mol Med. 2021;27(2):113-122. [41] LINKERMANN A, SKOUTA R, HIMMERKUS N, et al. Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(47):16836-16841. [42] LEE YS, LEE DH, CHOUDRY HA, et al. Ferroptosis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress:cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16(7):1073-1076. [43] LEE Y-S, KALIMUTHU K, PARK YS, et al. BAX-dependent mitochondrial pathway mediates the crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2020;25(9):625-631. [44] JIANG X, HE C, LIN W. Supramolecular metal-based nanoparticles for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021;61: 143-153. [45] XU Y, QIN Z, MA J, et al. Recent progress in nanotechnology based ferroptotic therapies for clinical applications. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020; 880:173198-173206. [46] GAO M, DENG J, LIU F, et al. Triggered ferroptotic polymer micelles for reversing multidrug resistance to chemotherapy. Biomaterials. 2019;223:119486-119496. [47] YANG Y, TIAN Q, WU S, et al. Blue light-triggered Fe(2+)-release from monodispersed ferrihydrite nanoparticles for cancer iron therapy. Biomaterials. 2021;271:120739-120749. [48] MO Y, DUAN L, YANG Y, et al. Nanoparticles improved resveratrol brain delivery and its therapeutic efficacy against intracerebral hemorrhage. Nanoscale. 2021;13(6):3827-3840. |
| [1] | LIU Danni, SUN Guanghua, ZHOU Guijuan, LIU Hongya, ZHOU Jun, TAN Jinqu, HUANG Xiarong, PENG Ting, FENG Wei-bin, LUO Fu. Effect of electroacupuncture on apoptosis of neurons in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury at "Shuigou" and "Baihui" points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Yang Shenglin, Pu Xingwei, Luo Chunshan, Yang Jianwen. Neuroprotective effects of tetrandrine preconditioning in rabbits with spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1223-1227. |
| [3] | Zhao Jing, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Yue, Zhang Jiaming, Zhong Dongling, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy based on CiteSpace: therapeutic effects, hot spots, and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1234-1241. |
| [4] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [5] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [6] | Xiakeerzhati•Xiaohalati, Wang Xiaobei, Wang Lin. Nanoparticles: a novel strategy for the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3566-3572. |
| [7] | Xu Xinzhi, Zhang Yue, Jin Ying, Jin Chunxiang. Preparation and imaging experiment of a new type of safe near-infrared luminescent nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3450-3454. |
| [8] | Yang Kang, Zhao Huimin, Fan Haojun, Su Xie, Wu Guojun. Preparation of a polydopamine modified hemerythrin-based nano-oxygen carrier and performance testing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3369-3374. |
| [9] | Li Wanhai, Dong Yuhang, Shi Chao, Jiang Yiyao, Liu Ge, Diao Wenjie, Wu Zhen. Ligustrazine furoxan complex protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 205-210. |
| [10] | Guo Junfu, Li Xiangnan, Ma Tianchi, Miao Lanying. Effects of miR-7-5p on stem cell-like properties of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3030-3035. |
| [11] | Dong Jiale, Wei Yuanhao, Zhang Hongwu. Visualization analysis of bone defect treatment based on knowledge map [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2906-2913. |
| [12] | Guo Junfu, Gao Xia, Chang Jiarong, Gao Shiqi, Miao Lanying. Effects of nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 on migration, invasion and cell cycle of human gastric cancer MGC803 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2732-2737. |
| [13] | Ma Ziyu, Zhang Yuntao, Ma Xiangrui, Qiao Luhui, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Surface treatment of iron oxide nanoparticles in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2570-2575. |
| [14] | Chen Keyi, Wang Dingxuan, Zhao Sike, Xia Zhangrong. Research hotspots of pressure training in rehabilitation and visualized analysis of relevant literature data in the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2406-2411. |
| [15] | Li Zhishuai, Zhang Hongqian, Li Li, Han Xinwen, Feng Jing. Finite element analysis of the knee joint: research hotspots and trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2412-2418. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||