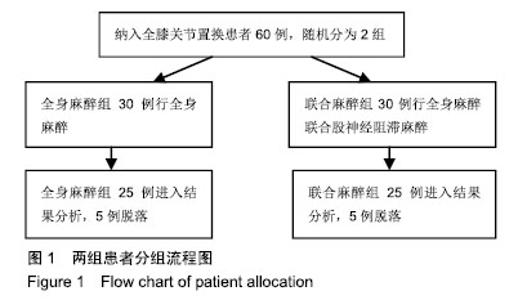
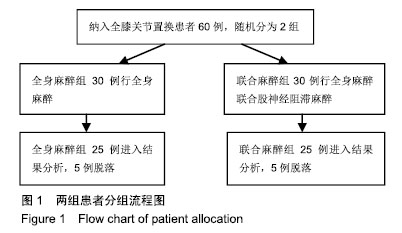
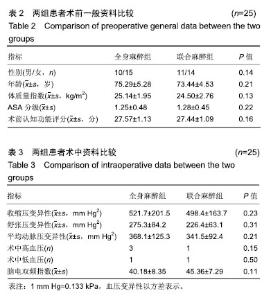
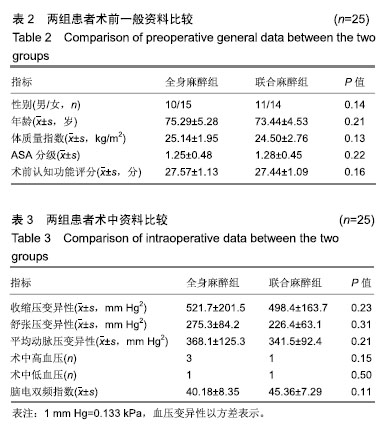
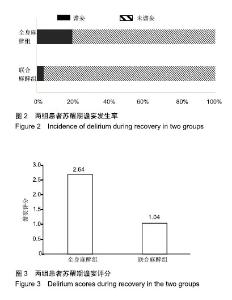
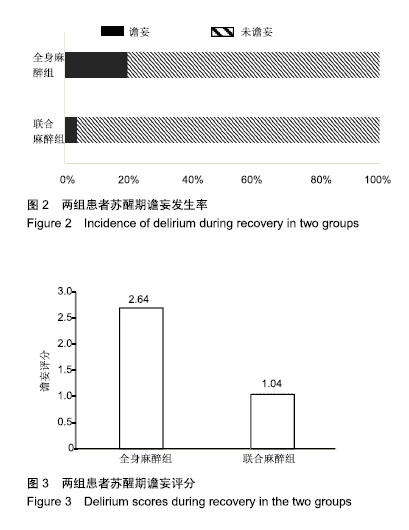
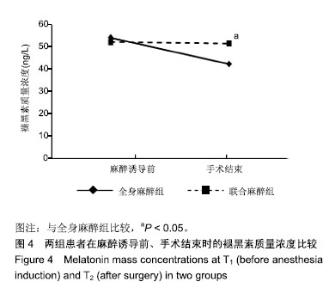
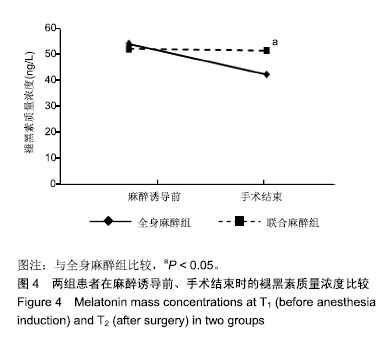
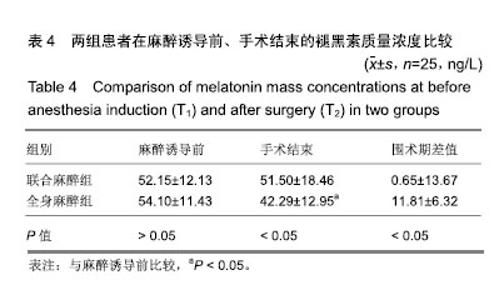
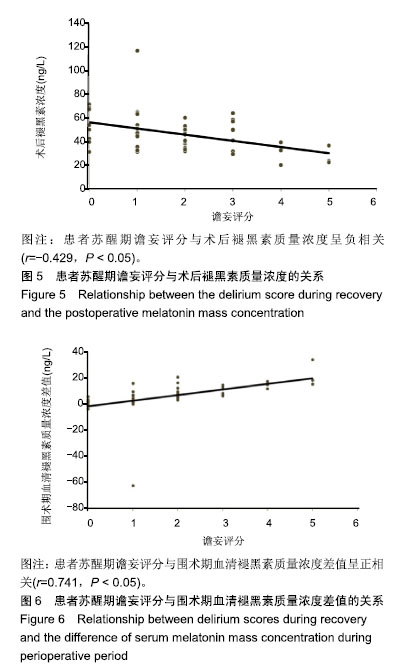
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (28): 4468-4473.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1467
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation of anesthesia methods with serum melatonin mass concentration and delirium during recovery in elderly patients undergoing knee arthroplasty
Jiao Yuxia, Zhou Qun, Fan Kaile, Li Dongbai
- Department of Anesthesiology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Online:2019-10-08Published:2019-10-08 -
Contact:Li Dongbai, Master, Chief physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Jiao Yuxia, MD, Attending physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 2013023009 (to LDB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiao Yuxia, Zhou Qun, Fan Kaile, Li Dongbai. Correlation of anesthesia methods with serum melatonin mass concentration and delirium during recovery in elderly patients undergoing knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4468-4473.
share this article
| [1]Munk L, Ersen G, Moller AM. Post-anaesthetic emergence delirium in adults: incidence, predictors and consequences. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016;60(8): 1059-1066.[2]Marseglia L, D'Angelo G, Manti S, et al. Analgesic, anxiolytic and anaesthetic effects of melatonin: new potential uses in pediatrics. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(1):1209-1220.[3]Hansen MV, Andersen LT, Madsen MT, et al. Effect of melatonin on depressive symptoms and anxiety in patients undergoing breast cancer surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;145(3):683-695. [4]Hansen MV, Halladin NL, Rosenberg J, et al. Melatonin for pre- and postoperative anxiety in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; 4(4):CD009861.[5]De Rooij SE, van Munster BC. Melatonin deficiency hypothesis in delirium: a synthesis of current evidence. Rejuvenation Res. 2013; 16(4):273-278.[6]Ciesielska N, Soko?owski R, Mazur E, et al. Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) test better suited than the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) detection among people aged over 60? Meta-analysis. Psychiatria Polska. 2016;50(5):1039-1052.[7]Winter A, Steurer M, Dullenkopf A. Postoperative delirium assessed by post anesthesia care unit staff utilizing the Nursing Delirium Screening Scale: a prospective observational study of 1000 patients in a single Swiss institution. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015;15:184.[8]Gaudreau JD, Gagnon P, Harel F, et al. Fast, systematic, and continuous delirium assessment in hospitalized patients: the nursing delirium screening scale. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2005;29(4):368-375.[9]Deoleveira TD,Tatsch DM,Levandovski RM,et al.The concept of the immune-pineal axistested in patients undergoing an abdominal hysterectomy. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2013; 20(4):205-212.[10]Kärkelä J, Vakkuri O, Kaukinen S, et al. The influence of anaesthesia and surgery on the circadian rhythm of melatonin. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 2010; 46(1):30-36.[11]Simons SS, Beijers R, Cillessen AH, et al. Development of the cortisol circadian rhythm in the light of stress early in life. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015; 62(1):292-300.[12]Ramachandran N, Smyth N, Thorn L, et al. Relationship between post-awakening salivary cortisol and melatonin secretion in healthy participants. Stress. 2016;19(2):260-263.[13]Gögenur I, Ocak U, Altunpinar O, et al. Disturbances in melatonin, cortisol and core body temperature rhythms after major surgery. World J Surg. 2007;31(2):290-298.[14]Aller MA, Arias JI, Prieto I, et al. Surgical inflammatory stress: the embryo takes hold of the reins again. Theor Biol Med Model. 2013;10:6.[15]Zhang M, Wang T, Chen HM, et al. Serum levels of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and melatonin over summer and winter in kidney deficiency syndrome in Bizheng rats. Chin Med Sci J. 2014; 29(2):107-111.[16]Hill-Venning C, Belelli D, Peters JA, et al. Subunit-dependent interaction of the general anaesthetic etomidate with the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;120(5):749-756.[17]Wang F, Li J, Wu C, et al. The GABA(A) receptor mediates the hypnotic activity of melatonin in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003;74(3):573-578.[18]Dispersyn G, Pain L, Touitou Y. Propofol anesthesia significantly alters plasma blood levels of melatonin in rats. Anesthesiology. 2010;112(2):333-337.[19]Mowafi HA, Ismail SA. Melatonin improves tourniquet tolerance and enhances postoperative analgesia in patients receiving intravenous regional anesthesia. Anesthesia Analgesia. 2008;107(4):1422-1426.[20]Ranjit S, Pradhan BB. Ultrasound guided femoral nerve block to provide analgesia for positioning patients with femur fracture before subarachnoid block: comparison with intravenous fentanyl. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2016;14(54): 125-129.[21]Shigeta H, Yasui A, Nimura Y, et al. Postoperative delirium and melatonin levels in elderly patients. Am J Surg. 2001; 182(5):449-454.[22]Yon JH, Carter LB, Reiter RJ, et al. Melatonin reduces the severity of anesthesia-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;21(3): 522-530.[23]Rashiq S, Vandermeer B, Abou-Setta AM, et al. Efficacy of supplemental peripheral nerve blockade for hip fracture surgery: multiple treatment comparison. Can J Anaesth. 2013; 60(3):230-243.[24]Perras B, Kurowski V, Dodt C. Nocturnal melatonin concentration is correlated with illness severity in patients with septic disease. Int Care Med. 2006;32(4):624-625.[25]Steiner LA. Postoperative delirium. Part 1: pathophysiology and risk factors. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2011;28(9):628-636.[26]Hardland R. Melatonin in aging and disease -multiple consequences of reduced secretion, options and limits of treatment. Aging Dis. 2012;3(2):194-225. |
| [1] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [2] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [3] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [4] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [5] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [6] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [7] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [8] | Wang Dasai, Zhang Yang, Cheng Yin, Wang Qiang. Efficacy and safety of staged versus simultaneous unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3929-3936. |
| [9] | Mieralimu•Muertizha, Ainiwaerjiang•Damaola, Lin Haishan, Wang Li . Relationship between tibio-femoral mechanical axis deviation on coronal plane and early joint function recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3300-3304. |
| [10] | Yu Yinghao, Zhao Jijun, Liu Dongcheng, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Clinical significance of preoperative planning assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with digital imaging system for fixed-bearing prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3324-3331. |
| [11] | Deng Zhibo, Li Zhi, Wu Yahong, Mu Yuan, Mu Yuexi, Yin Liangjun. Local infiltration anesthesia versus femoral nerve block for pain control and safety after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3401-3408. |
| [12] | Huang Chenyu, Tang Cheng, Wei Bo, Li Jiayi, Li Xuxiang, Zhang Huikang, Xu Yan, Yao Qingqiang, Wang Liming. Application of three-dimensional printing guide plate in total knee arthroplasty for patients with varus and valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2789-2793. |
| [13] | Li Shangzhi, Zheng Dezhi, Liu Jun. Early analgesia of cocktail therapy after total knee arthroplasty with enhanced recovery after surgery program [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2794-2798. |
| [14] | Liu Jinlei, Yin Li, Zhang Yi, Wang Haitao, Li Zhuangyan, Xia Peige, Qiao Renqiu. Effects of intravenous tranexamic acid combined with periarticular multipoint injection of tranexamic acid cocktail on blood loss and pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2833-2839. |
| [15] | Xu Hui, Kang Bingxin, Gao Chenxin, Zhao Chi, Xu Xirui, Sun Songtao, Xie Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Effectiveness of Tuina in the treatment of pain after total knee arthroplasty in patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2840-2845. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||