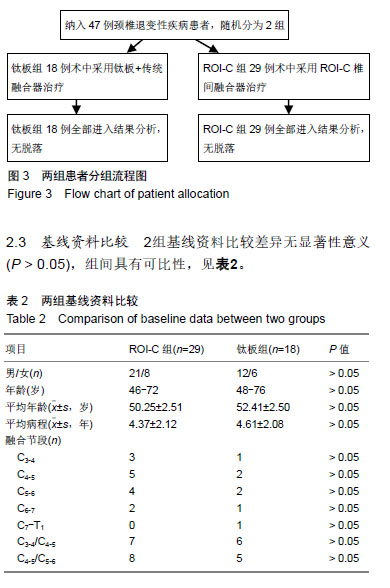
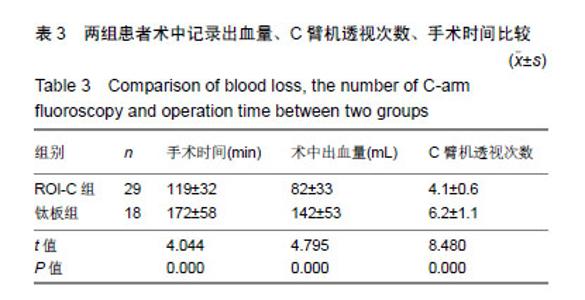
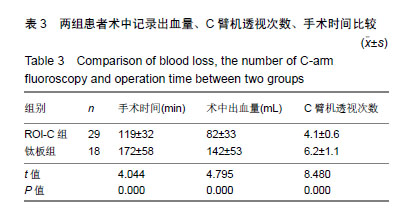
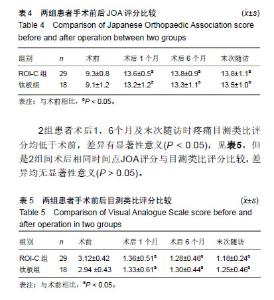
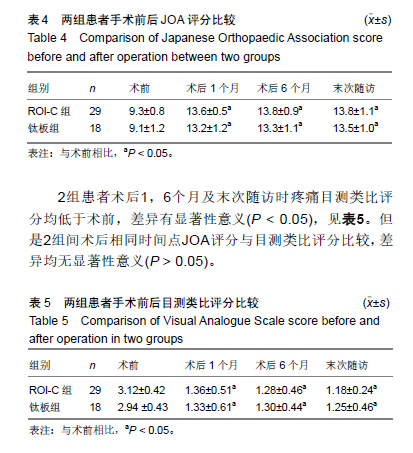
| [1]Hetdecke V,Ramov NG,Marx T,et al.Outcome in cloward anterior fusion for degenerative cervical spinal disease.Acta Neurochir. 2000;142(3):283-291.[2]Sampath P,Bendebba M,Davis JD,et al.Outcome in patients with cervical radiculopathy,prospective multicenter study with indepentent clinical review. Spine. 1999;24(6):591-597.[3]Yonenobu K,Wada E,Tanaka T,et al.Japanese orthopaedic association cervical myelopathy evaluation quesionnaire(JOACMEQ):Part 2.Endorsement of the alternative item. J Orthop Sci. 2007;12(3): 241-248.[4]Ikenaga M,Shikata J,Tanaka C. Long-term results over 10 years of anterior corpectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy. Spine. 2006;31(14):1568-1575.[5]Papadopoulos EC,Huang RC,Girardi FP,et al. Three-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with plate fixation:radiographic and clinical results. Spine. 2006;31(8):897-902.[6]Kaiser MG, Haid RW, Subach BR, et al. Anterior cervical plating enhances arthrodesis after discectomvy and fusion with cortical allograft. Neurosurgery. 2002;50(2):229-238.[7]Joseph T,King J,John JM,et al.Muhimodal assessment after surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurgery. 2005;2(5): 526-534.[8]Kim SW,Limson MA,Kim SB,et al. Comparison of radiographic changes after ACDF versus bryan disc athroplasty in sigle and bi-level cases. J Eur Spine. 2009;18(2):218-231.[9]Goffin J,Geusens E,Vantomme N,et al. Long-term follow-up after interbody fusion of the cervical spine. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17: 79-85.[10]Chen Y, Lu G, Wang B, et al. A comparison of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion(ACDF) using self-locking stand-alone polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cage with ACDF using cage and plate in the treatment of three-level cervical degenerative spondylopathy: a retrospective study with 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(7):2255-2262.[11]Song KJ ,Choi BW ,Kim JK. Adjacent segment pathology following anterior decompression and fusion using cage and plate for the treatment of degenerative cervical spinal diseases. Asian Spine J. 2014; 8(6):720-728.[12]陈博来,林涌鹏,赵帅,等,零切迹自稳型颈椎融合器在颈椎前路减压融合术中的应用研究[J].中华外科杂志, 2013,51(11):1046-1048.[13]Liu W, Hu L, Wang J, et al. Comparison of zero-profile anchored spacer versus plate-cage construct in treatment of cervical spondylosis with regard to clinical outcomes and incidence of major complications: a meta-analysis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;(11):1437-1447.[14]陈德玉,贾连顺,袁文,等. 颈椎前路带锁钢板临床应用的并发症及预防[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2001,21(5):287-289.[15]夏展,赵兴,范顺武.颈椎前路手术并发食管瘘的诊治进展[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2011,31(4):384-386.[16]Riley LH 3rd,Skolasky RL,Albert TJ,et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical decompression and fusion:prevalence and risk factors from a longitudinal cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(22): 2564-2569. [17]Lee MJ,Bazaz R,Furey CG, et al. Influence of anterior cervical plate design on Dysphagia:a 2-year prospective longitudinal follow-up study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005; 18(5):406-409.[18]张宗余,姜为民,李雪峰,等.桥形椎间锁定融合器(ROI-C)在颈椎病前路减压融合术中应用的临床研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(6):510-516.[19]Cannada LK, Scherping SC, Yoo JU, et al. Pseudarthrosis of the cervical spine:a comparison of radiographic diagnostic measures. Spine. 2003;28:46-51.[20]Gok B,Sciubba DM,McLoughlin GS,et al. Revision surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy:surgical results and outcome. Neurosurgery. 2008;63:292-298.[21]蒋富贵,瞿东滨,朱志刚,等.颈椎前路减压及内固定的解剖学问题[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2000,18(4):314-315. |