Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (21): 3375-3381.doi: 10.12307/2023.178
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and mechanism of polyphosphate in bone tissue regeneration
Cao Jin1, Wang Ansu1, Huang Nijiao1, Wu Fujun1, Chen Ping1, Li Chengmei2, Wang Xin1
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, 2Medical Case Unit, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-05-12Accepted:2022-07-02Online:2023-07-28Published:2022-11-24 -
Contact:Wang Xin, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Cao Jin, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31960209; Basic Research Program of Guizhou Science and Technology Department (Guizhou Science and Technology Foundation), No. [2020]1Y093 (to WX); Graduate Research Fund of Zunyi Medical University, No. ZYK63 (to CJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Jin, Wang Ansu, Huang Nijiao, Wu Fujun, Chen Ping, Li Chengmei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of polyphosphate in bone tissue regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3375-3381.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
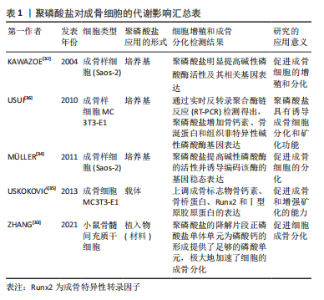
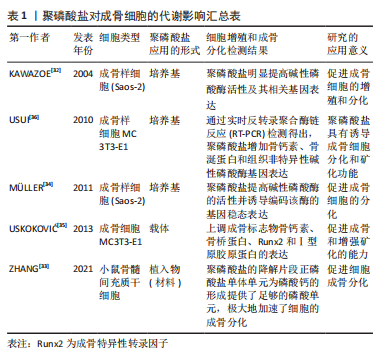
2.1 聚磷酸盐对间充质干细胞分化的影响 间充质干细胞作为一种多能干细胞。具有强大的增殖能力和多向分化潜能,在适宜的体内、外环境下可分化为造血细胞、肌细胞、肝细胞、成骨细胞、软骨细胞和基质细胞等多种细胞。研究表明,聚磷酸盐具有诱导间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞,促进骨组织再生的功能[23]。间充质干细胞的分化和成熟不仅受到骨形态发生蛋白2的调节,还受Runt相关转录因子2(runt-related transcription factor,Runx2)的影响[24]。Runx2的成骨性表达,使得一系列编码骨组织结构和功能的基因依赖性增加,如碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ 型胶原蛋白、骨桥蛋白、骨唾液蛋白、骨钙素和核转录因子κB配体受体激活剂(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)等相关基因[25-26]。Müller等[27]研究表明,将CaCl2溶液与聚磷酸钠(Na-Poly)溶液混合形成无定形聚磷酸钙微粒 (Ca-Poly-MPs)并将其用于骨缺损研究,结果发现,Ca-Poly-MPs上调了鼠股骨外植体中骨髓干细胞转录因子Runx2的表达,促进细胞成骨分化。 细胞增殖作为骨组织再生的重要活动之一,受到诸多细胞及因子调控,其中成纤维细胞生长因子在骨组织再生过程中扮演着重要的角色[28]。有研究显示,聚磷酸盐通过促进成纤维细胞生长因子2与受体之间的结合,激活成纤维细胞生长因子介导的细胞信号通路,促进人牙髓细胞增殖[29]。同时,聚磷酸盐诱导人牙髓细胞细胞增殖与人间充质干细胞中基质金属蛋白酶1、骨桥蛋白、骨钙素和骨保护素相关基因表达相关。通过PCR检测也证实了基质金属蛋白酶1、骨桥蛋白和骨钙素基因在细胞增殖过程中的重要作用,茜素红染色显示细胞矿化也得到一定程度的提高,免疫组织化学染色结果也显示了Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的形成也有进一步增加。并通过提高碱性磷酸酶及基质金属蛋白酶13的活性,上调碱性磷酸酶、骨桥蛋白、骨钙素和骨唾液蛋白相关基因的表达,诱导脂肪组织来源的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[30]。 2.2 聚磷酸盐对成骨细胞的代谢影响 成骨细胞主要由内外骨膜和骨髓中基质内的间充质始祖细胞分化而来,能特异性分泌多种生物活性物质,调节并影响骨的形成和重建过程。来源于间充质干细胞的成骨细胞,最终分化为骨细胞,参与骨组织修复与再生[31]。将人成骨肉瘤细胞(Saos-2)培养于含聚磷酸盐和CaCl2 的培养基中,观察到碱性磷酸酶活性明显提高并诱导其相关基因表达,促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化[32]。体外骨整合研究表明,作为聚磷酸盐降解片段的正磷酸盐单体单元为磷酸钙的形成提供了足够的磷酸单元,显著加速了细胞的成骨分化[33]。甘油磷酸盐作为传统成骨诱导培养基中的必需物质。MüLLER等[34]的研究发现:即使在低浓度条件下,聚磷酸盐/Ca2+复合物的成骨诱导效果也优于有机磷酸盐及甘油磷酸盐。该研究表明:作为羟基磷灰石形成的供体并不是有机磷酸盐及甘油磷酸盐,而是聚磷酸盐水解后的无机磷酸盐(Pi)单元。在骨组织再生模型中,聚磷酸盐诱导MC3T3-E1细胞系成骨样细胞矿化[35],并通过不同途径诱导成骨样细胞的细胞学行为:首先,poly分解产物无机磷酸盐(Pi)单元,作为细胞矿化的磷酸盐来源;其次,聚磷酸盐水解后产生焦磷酸(PPi)以调节PPi和Pi之间的平衡促进细胞矿化[34];再次,聚磷酸盐促进成纤维细胞因子与其受体的结合,促进成骨细胞增殖与分化;最后,聚磷酸盐还诱导降钙素、成骨相关转录因、骨唾液酸蛋白、组织非特异性碱性磷酸酶相关基因的表达,促进骨组织再生与修复[36]。聚磷酸盐对成骨细胞的代谢影响汇总表,见表1。"
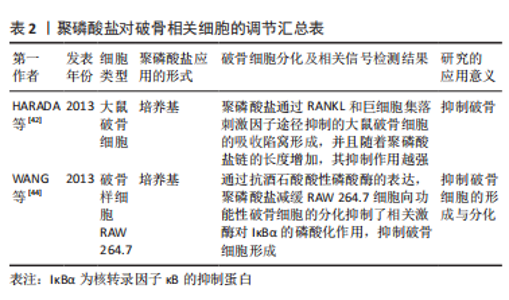
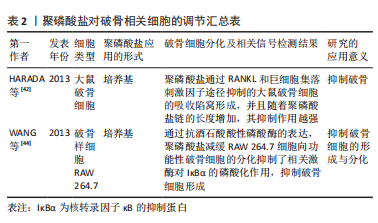
2.3 聚磷酸盐对破骨相关细胞的调节 破骨细胞是骨吸收的主要功能细胞,在骨发育、生长、修复及重建中具有重要的作用[37]。破骨细胞起源于血系单核-巨噬细胞系统,是一种特殊的终末分化细胞,它可由其单核前体细胞通过多种方式融合形成巨大的多核细胞,主要分化阶段包括成骨细胞前体和具有骨吸收活性的成熟破骨细胞[38]。在骨吸收过程中,成熟破骨细胞诱导游离磷酸盐离子合成聚磷酸盐,使其体内聚集大量聚磷酸盐颗粒[39]。作为破骨细胞分化成熟的标志物抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶,在骨组织重吸收扮演着重要角色[40]。成熟破骨细胞的骨吸收活性依赖于抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶,该酶由哺乳动物的Acp5基因编码,水解过程中产生22 kD的N端和16 kD 的C端片段,并通过二硫键连接成活性异二聚体酶[41]。在骨吸收过程中抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶从基底外侧释放到细胞外,并从褶边进入吸收陷窝参与骨吸收[42]。同时,由于抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶的聚磷酸酶活性,使其在酶解聚磷酸盐过程中被消耗。聚磷酸盐竞争性抑制破骨细胞中抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶的酶活性,抑制成熟破骨细胞的骨吸收活性,在维持机体骨量过程中起着重要作用。此外,长链聚磷酸盐(Poly300,300个磷酸残基)比短链聚磷酸盐(Poly15,15个磷酸残基)具有更高的亲和力,且酶竞争性抑制作用明显强于短链聚磷酸盐。同时,聚磷酸盐降解还为机体代谢活动提供充足的能量来源[42]。 IκBα激酶介导核转录因子κB激活作为RANKL诱导破骨前体细胞分化过程中的关键分子[43]。在含RANKL培养基中,IκBα在破骨细胞样RAW 264.7细胞上广泛磷酸化。然而,即使是在低浓度的聚磷酸盐复合物培养基中,IκBα激酶的磷酸化依然受到强烈抑制,阻碍破骨细胞形成[44]。因此,聚磷酸盐通过抑制IκBα激酶磷酸化,降低核转录因子κB进入细胞核,阻碍破骨细胞向成熟破骨细胞分化,抑制破骨。聚磷酸盐对破骨相关细胞的调节汇总表,见表2。"
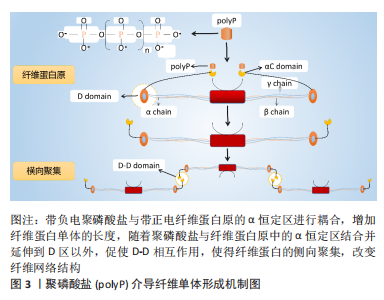
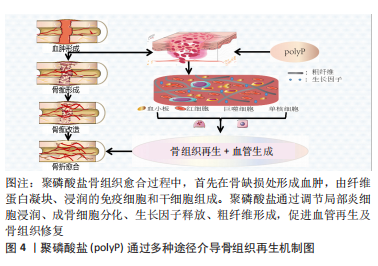
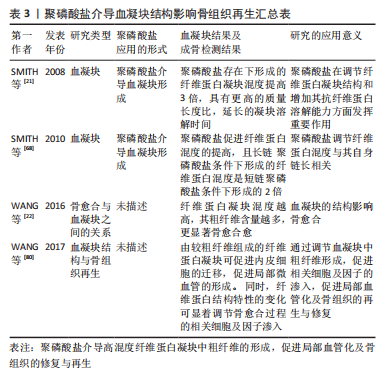
2.4 聚磷酸盐介导局部炎症对骨代谢的调节 骨组织再生修复均经历3个连续的阶段:炎症、再生和重塑[45]。炎症反应通过炎症细胞及炎症因子对骨缺损部位早期骨愈合起着关键性作用[46-47]。 自然杀伤性细胞不仅可以间接清除细胞碎片,这有助于启动骨折愈合,并通过分泌趋化因子CXCL7增强间充质干细胞的迁移促进骨愈合[48]。在单核细胞系中,巨噬细胞通过分泌趋化因子(如MCP-1和MIP-1α)促进间充质干细胞迁移,并在骨组织修复阶段直接诱导间充质干细胞成骨和骨基质形成[49-50]。此外,单核巨噬细胞谱系通过释放细胞因子(如骨形态发生蛋白2和转化生长因子β1等)对成骨细胞分化和增殖起着促进作用[51-52],并维持骨骼在重塑过程中的形成与吸收平衡,为骨组织修复与再生提供有利的微环境[53]。尽管炎症反应对组织修复至关重要,但炎症的失调,对骨组织再生及愈合却是不利的[54]。同样,炎症持续的时间对骨组织修复也至关重要。正常情况下:炎症反应在骨组织修复早期刺激成骨相关细胞及血管生成相关因子的释放,并随着骨折愈合的进展而逐渐退散,以确保骨组织的再生与修复[55]。 聚磷酸盐通过激活核转录因子κB信号通路上调血管细胞黏附分子1、细胞间黏附分子1和选择素E的表达,增强了单核细胞(THP-1)与内皮细胞的黏附[56]。当免疫细胞激活时:分泌高迁移率族蛋白B1和组蛋白4等核蛋白,促使炎症细胞向抗炎细胞转化[57-58]。此外,长链聚磷酸盐(Poly700,700个磷酸残基)较短链聚磷酸盐(Poly70,70个磷酸残基)拥有更高的亲和力与组蛋白4和高迁移率族蛋白B1结合,有效地提高了炎症信号的传导[59]。同时,组蛋白4和高迁移率族蛋白B1介导的血管通透性信号因子、细胞表面黏附因子、炎症细胞迁移因子的表达提高,并通过对内皮细胞PI3K/AKT和PLC/PKC/Ca2+信号通路的调节激活哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路,调节炎症反应[60]。缓激肽作为一类促炎物质,其机制是通过破坏内皮细胞膜的完整性达到增加血管通透性的目的[61]。 聚磷酸盐促进激肽释放酶-激肽系统的激活有效促使了缓激肽的产生,并显著增加小鼠皮肤微血管的通透性,有利于细胞及相关因子渗透[62]。相关研究也表明:存在于肥大细胞和嗜碱性粒细胞中的聚磷酸盐,促使血液中产生更多的缓激肽参与炎症反应[63]。聚磷酸盐介导的激肽释放酶-激肽系统激活还可启动经典补体途径,诱导巨噬细胞迁移至炎症区域协助并完成炎症反应。同时,聚磷酸盐通过末端途径降低补体C5b6的稳定性,从而降低膜攻击复合物的裂解能力,调节炎症反应[64]。综上,聚磷酸盐介导炎症因子的调节对于骨组织再生有着重大影响。在骨缺损早期:炎症的发生对于骨组织再生的作用不可或缺。尽管目前并没有相关研究对其进行深入阐述,但这将可能成为未来的一大研究热点。 2.5 聚磷酸盐介导血凝块结构影响骨再生 当骨缺损发生时,外源性凝血途径被激活,局部形成的血凝块充当“天然支架”作用,为骨组织再生与修复提供适宜条件[65]。该途径依赖于3个主要成分之间的相互作用,即凝血因子、活化的血小板和血细胞[66]。正常生理条件下,机体释放组织因子与凝血因子Ⅶ结合,启动外源性凝血途径[67]。研究表明:随着聚磷酸盐的链长增加,其促凝效率也有所提升[68]。在凝血过程中,血凝块结构通过血小板的回缩并释放聚磷酸盐使得血凝块结构发生改变[69],血小板中聚磷酸盐的释放促使血凝块中粗纤维的形成,并减少纤维蛋白的分支,延长纤维蛋白长度[70],见图3。"
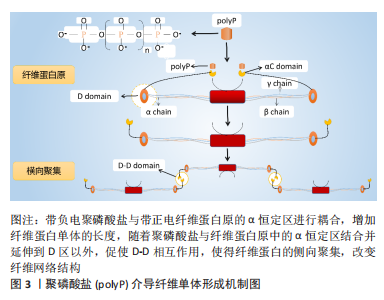
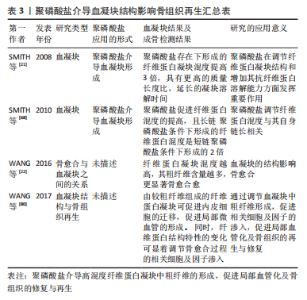
在大鼠股骨骨折模型中,去除骨折部位血凝块后(形成于骨折后2-4 d)将显著影响骨的自然愈合能力[71]。此外,在绵羊胫骨缺损模型中,去除骨折部位血凝块(4-7 d),骨折早期愈合显著延迟。因此,骨缺损部位早期血凝块的形成对于骨愈合至关重要[72]。 有研究显示,聚磷酸盐激活凝血因子Ⅻ(FXII)启动凝血途径,并通过下列几个步骤提高凝血酶的生成速率[62]:①增强凝血因子V向Va转化[73];②加速因子XI活化[74];③拮抗抗凝活性组织因子途径抑制剂(tissue factor pathway inhibitor,TFPI)[75]。带负电聚磷酸盐与带正电纤维蛋白原的α恒定区进行藕合,增加纤维蛋白单体的长度,随着聚磷酸盐与纤维蛋白原中的α恒定区结合并延伸到D区以外,促使D-D相互作用,使得纤维蛋白的侧向聚集,改变纤维网络结构[76-77],见图3。 SMITH等[21]研究发现,聚磷酸盐存在条件下形成的纤维蛋白凝块混度及纤维粗细比例更高、抗弹性拉伸及抗纤维蛋白溶解能力也更强。值得注意的是,聚磷酸盐存在条件下形成的纤维蛋白混度提高,且长链聚磷酸盐(700个磷酸盐残基,聚磷酸盐700)条件下形成的纤维蛋白混度是短链聚磷酸盐 (70个磷酸盐残基,聚磷酸盐70)条件下形成的2倍[68]。纤维蛋白原质长比与聚磷酸盐的浓度相关,在聚磷酸盐的环境中纤维蛋白原质长比增加了15%,而聚磷酸盐使得质长比增加了3倍[21]。扫描电子显微镜观察结果显示:血凝块中的纤维直径随着聚磷酸盐浓度的增加而增加。同时,纯化的纤维蛋白原和凝血酶形成的纤维蛋白凝块混度主要与纤维的直径相关,纤维直径随着凝块混度的增加而变粗[78]。有研究表明,由较粗纤维组成的纤维蛋白凝块可促进内皮细胞的迁移,促进局部微血管的形成[79]。同时,纤维蛋白结构特性的变化可显着调节骨愈合过程的相关细胞及因子渗入[80]。该课题组在大鼠股骨骨缺损模型中的前期研究发现,正常骨愈合组和骨延迟愈合组中的早期血凝块存在显著的结构性差异[22],正常骨愈合组中的血凝块由较粗纤维(直径> 400 nm)的纤维结构组成,而骨延迟愈合组中的血凝块由较细纤维(直径约 200 nm)的纤维结构组成。聚磷酸盐介导血凝块结构影响骨再生汇总表,见表3。"
| [1] WANG X, SCHRöDER HC, MüLLER WEG. Amorphous polyphosphate, a smart bioinspired nano-/bio-material for bone and cartilage regeneration: towards a new paradigm in tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(16):2385-2412. [2] MüLLER WEG, SCHRöDER HC, WANG X. Inorganic Polyphosphates As Storage for and Generator of Metabolic Energy in the Extracellular Matrix. Chem Rev. 2019;119(24):12337-12374. [3] BROWN MR, KORNBERG A. Inorganic polyphosphate in the origin and survival of species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(46):16085-16087. [4] EZAWA T, CAVAGNARO TR, SMITH SE, et al. Rapid accumulation of polyphosphate in extraradical hyphae of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus as revealed by histochemistry and a polyphosphate kinase/luciferase system. New Phytol. 2004;161(2):387-392. [5] FLEISH H, NEUMAN WF. Mechanisms of calcification: role of collagen, polyphosphates, and phosphatase. Am J Physiol. 1961;200:1296-1300. [6] XIE L, JAKOB U. Inorganic polyphosphate, a multifunctional polyanionic protein scaffold. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(6):2180-2190. [7] RAO NN, LIU S, KORNBERG A. Inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli: the phosphate regulon and the stringent response. J Bacteriol. 1998;180(8):2186-2193. [8] AHN K, KORNBERG A. Polyphosphate kinase from Escherichia coli. Purification and demonstration of a phosphoenzyme intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(20):11734-11739. [9] RAO NN, GóMEZ-GARCíA MR, KORNBERG A. Inorganic polyphosphate: essential for growth and survival. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:605-647. [10] ITOH H, KAWAZOE Y, SHIBA T. Enhancement of protein synthesis by an inorganic polyphosphate in an E. coli cell-free system. J Microbiol Methods. 2006;64(2):241-249. [11] RASHID MH, RAO NN, KORNBERG A. Inorganic polyphosphate is required for motility of bacterial pathogens. J Bacteriol. 2000;182(1): 225-227. [12] VARAS MA, RIQUELME-BARRIOS S, VALENZUELA C, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate is essential for salmonella typhimurium virulence and survival in dictyostelium discoideum. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018;8:8. [13] ARIGANELLO MB, OMELON S, VARIOLA F, et al. Osteogenic cell cultures cannot utilize exogenous sources of synthetic polyphosphate for mineralization. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(12):2089-2102. [14] MüLLER WE, TOLBA E, SCHRöDER HC, et al. Polyphosphate: a morphogenetically active implant material serving as metabolic fuel for bone regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2015;15(9):1182-1197. [15] GRAY MJ, WHOLEY WY, WAGNER NO, et al. Polyphosphate is a primordial chaperone. Mol Cell. 2014;53(5):689-699. [16] STOTZ SC, SCOTT LO, DRUMMOND-MAIN C, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate regulates neuronal excitability through modulation of voltage-gated channels. Mol Brain. 2014;7:42. [17] DHIVYA S, KESHAV NARAYAN A, LOGITH KUMAR R, et al. Proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on scaffolds containing chitosan, calcium polyphosphate and pigeonite for bone tissue engineering. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(1):e12408. [18] WANG X, SCHRöDER HC, MüLLER WE. Enzymatically synthesized inorganic polymers as morphogenetically active bone scaffolds: application in regenerative medicine. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014;313:27-77. [19] WANG Y, LI M, LI P, et al. Progress and applications of polyphosphate in bone and cartilage regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5141204. [20] YUAN Q, KUBO T, DOI K, et al. Effect of combined application of bFGF and inorganic polyphosphate on bioactivities of osteoblasts and initial bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(5):1716-1724. [21] SMITH SA, MORRISSEY JH. Polyphosphate enhances fibrin clot structure. Blood. 2008;112(7):2810-2816. [22] WANG X, FRIIS TE, MASCI PP, et al. Alteration of blood clot structures by interleukin-1 beta in association with bone defects healing. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35645. [23] PHELIPE HATT L, THOMPSON K, MüLLER WEG, et al. Calcium polyphosphate nanoparticles act as an effective inorganic phosphate source during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5801. [24] XI Y, MIAO X, LI Y, et al. BMP2-mimicking peptide modified with E7 coupling to calcined bovine bone enhanced bone regeneration associating with activation of the Runx2/SP7 signaling axis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(1):80-93. [25] LIU XW, MA B, ZI Y, et al. Effects of rutin on osteoblast MC3T3-E1 differentiation, ALP activity and Runx2 protein expression. Eur J Histochem. 2021;65(1):3195. [26] ZHAO J, LIU R, ZHU J, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation through their immunosuppressive function. J Oral Biosci. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2021.07.003. [27] MüLLER WEG, NEUFURTH M, WANG S, et al. Amorphous, smart, and bioinspired polyphosphate nano/microparticles: a biomaterial for regeneration and repair of osteo-articular impairments in-situ. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):427. [28] MOSSAHEBI-MOHAMMADI M, QUAN M, ZHANG JS, et al. FGF signaling pathway: a key regulator of stem cell pluripotency. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:79. [29] KAWAZOE Y, KATOH S, ONODERA Y, et al. Activation of the FGF signaling pathway and subsequent induction of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by inorganic polyphosphate. Int J Biol Sci. 2008;4(1):37-47. [30] OZEKI N, MOGI M, HASE N, et al. Polyphosphate-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 is required for osteoblast-like cell differentiation in human adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biosci Trends. 2016;10(5):365-371. [31] GARG P, MAZUR MM, BUCK AC, et al. Prospective review of mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into osteoblasts. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):13-19. [32] KAWAZOE Y, SHIBA T, NAKAMURA R, et al. Induction of calcification in MC3T3-E1 cells by inorganic polyphosphate. J Dent Res. 2004;83(8): 613-618. [33] ZHANG M, QIAN T, DENG Z, et al. 3D printed double-network alginate hydrogels containing polyphosphate for bioenergetics and bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;188;639-648. [34] MüLLER WE, WANG X, DIEHL-SEIFERT B, et al. Inorganic polymeric phosphate/polyphosphate as an inducer of alkaline phosphatase and a modulator of intracellular Ca2+ level in osteoblasts (SaOS-2 cells) in vitro. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(6):2661-2671. [35] USKOKOVIĆ V, HOOVER C, VUKOMANOVIĆ M, et al. Osteogenic and antimicrobial nanoparticulate calcium phosphate and poly-(D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) powders for the treatment of osteomyelitis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(6):3362-3373. [36] USUI Y, UEMATSU T, UCHIHASHI T, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate induces osteoblastic differentiation. J Dent Res. 2010;89(5):504-509. [37] WANG X, YU Y, JI L, et al. Calcium phosphate-based materials regulate osteoclast-mediated osseointegration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12): 4517-4530. [38] WANG X, SCHRöDER HC, SCHLOßMACHER U, et al. Inorganic polyphosphates: biologically active biopolymers for biomedical applications. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2013;54:261-294. [39] OMELON S, GEORGIOU J, HENNEMAN ZJ, et al. Control of vertebrate skeletal mineralization by polyphosphates. PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5634. [40] VASIKARAN SD, MIURA M, PIKNER R, et al. Practical considerations for the clinical application of bone turnover markers in osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s00223-021-00930-4. [41] LJUSBERG J, WANG Y, LåNG P, et al. Proteolytic excision of a repressive loop domain in tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase by cathepsin K in osteoclasts. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(31):28370-28381. [42] HARADA K, ITOH H, KAWAZOE Y, et al. Polyphosphate-mediated inhibition of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase and suppression of bone resorption of osteoclasts. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e78612. [43] LEE ZH, KIM HH. Signal transduction by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003; 305(2):211-214. [44] WANG X, SCHRöDER HC, DIEHL-SEIFERT B, et al. Dual effect of inorganic polymeric phosphate/polyphosphate on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in vitro. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(10):767-776. [45] MARSELL R, EINHORN TA. The biology of fracture healing. Injury. 2011; 42(6):551-555. [46] FROST HM. The biology of fracture healing. An overview for clinicians. Part I. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(248):283-293. [47] XIAO L, MA YP, CRAWFORD R, et al. The interplay between hemostasis and immune response in biomaterial development for osteogenesis. Materials Today. 2022;54: 202-224. [48] ALMEIDA CR, CAIRES HR, VASCONCELOS DP, et al. NAP-2 secreted by human nk cells can stimulate mesenchymal stem/stromal cell recruitment. Stem Cell Rep. 2016;6(4):466-473. [49] OMAR OM, GRANéLI C, EKSTRöM K, et al. The stimulation of an osteogenic response by classical monocyte activation. Biomaterials. 2011;32(32):8190-8204. [50] NIU Y, LI Q, XIE R, et al. Modulating the phenotype of host macrophages to enhance osteogenesis in MSC-laden hydrogels: design of a glucomannan coating material. Biomaterials. 2017;139;39-55. [51] CHAMPAGNE CM, TAKEBE J, OFFENBACHER S, et al. Macrophage cell lines produce osteoinductive signals that include bone morphogenetic protein-2. Bone. 2002;30(1):26-31. [52] FROMIGUé O, MARIE PJ, LOMRI A. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-beta2 interact to modulate human bone marrow stromal cell proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 1998;68(4):411-426. [53] CHO SW. Role of osteal macrophages in bone metabolism. J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(2):102-104. [54] WHEATLEY BM, NAPPO KE, CHRISTENSEN DL, et al. Effect of NSAIDs on bone healing rates: a meta-analysis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019; 27(7):e330-e336. [55] BAHNEY CS, ZONDERVAN RL, ALLISON P, et al. Cellular biology of fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(1):35-50. [56] BAE JS, LEE W, REZAIE AR. Polyphosphate elicits pro-inflammatory responses that are counteracted by activated protein C in both cellular and animal models. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10(6):1145-1151. [57] WANG H, BLOOM O, ZHANG M, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999;285(5425):248-251. [58] XU J, ZHANG X, PELAYO R, et al. Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nat Med. 2009;15(11):1318-1321. [59] DINARVAND P, HASSANIAN SM, QURESHI SH, et al. Polyphosphate amplifies proinflammatory responses of nuclear proteins through interaction with receptor for advanced glycation end products and P2Y1 purinergic receptor. Blood. 2014;123(6):935-945. [60] HASSANIAN SM, DINARVAND P, SMITH SA, et al. Inorganic polyphosphate elicits pro-inflammatory responses through activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin complexes 1 and 2 in vascular endothelial cells. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(5):860-871. [61] OSCHATZ C, MAAS C, LECHER B, et al. Mast cells increase vascular permeability by heparin-initiated bradykinin formation in vivo. Immunity. 2011;34(2):258-268. [62] MüLLER F, MUTCH NJ, SCHENK WA, et al. Platelet polyphosphates are proinflammatory and procoagulant mediators in vivo. Cell. 2009; 139(6):1143-1156. [63] MORENO-SANCHEZ D, HERNANDEZ-RUIZ L, RUIZ FA, et al. Polyphosphate is a novel pro-inflammatory regulator of mast cells and is located in acidocalcisomes. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(34):28435-28444. [64] WAT JM, FOLEY JH, KRISINGER MJ, et al. Polyphosphate suppresses complement via the terminal pathway. Blood. 2014;123(5):768-776. [65] GU JT, JIAO K, LI J, et al. Polyphosphate-crosslinked collagen scaffolds for hemostasis and alveolar bone regeneration after tooth extraction. Bioact Mater. 2022;15:68-81. [66] EINHORN TA, GERSTENFELD LC. Fracture healing: mechanisms and interventions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):45-54. [67] LAZZARO MA, ZAIDAT OO. Multimodal endovascular reperfusion therapies: adjunctive antithrombotic agents in acute stroke. Neurology. 2012;78(7):501-506. [68] SMITH SA, CHOI SH, DAVIS-HARRISON R, et al. Polyphosphate exerts differential effects on blood clotting, depending on polymer size. Blood. 2010;116(20):4353-4359. [69] BAHAMMAM MA, ATTIA MS. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor using platelet rich fibrin (PRF) and nanohydroxyapatite(nano-HA) in treatment of periodontal intra-bony defects - a randomized controlled trial. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(1):870-878. [70] MUTCH NJ, ENGEL R, UITTE DE WILLIGE S, et al. Polyphosphate modifies the fibrin network and down-regulates fibrinolysis by attenuating binding of tPA and plasminogen to fibrin. Blood. 2010;115(19):3980-3988. [71] GRUNDNES O, REIKERåS O. The importance of the hematoma for fracture healing in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 1993;64(3):340-342. [72] VAN DER ENDE J, VAN BAARDEWIJK LJ, SIER CF, et al. Bone healing and mannose-binding lectin. Int J Surg. 2013;11(4):296-300. [73] CHOI SH, SMITH SA, MORRISSEY JH. Polyphosphate accelerates factor V activation by factor XIa. Thromb Haemost. 2015;113(3):599-604. [74] CHOI SH, SMITH SA, MORRISSEY JH. Polyphosphate is a cofactor for the activation of factor XI by thrombin. Blood. 2011;118(26):6963-6970. [75] PUY C, TUCKER EI, IVANOV IS, et al. Platelet-derived short-chain polyphosphates enhance the inactivation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor by activated coagulation factor XI. PLoS One. 2016;11(10): e0165172. [76] SMITH SA, MORRISSEY JH. Polyphosphate as a general procoagulant agent. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6(10):1750-1756. [77] WHYTE CS, CHERNYSH IN, DOMINGUES MM, et al. Polyphosphate delays fibrin polymerisation and alters the mechanical properties of the fibrin network. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116(5):897-903. [78] CARR ME JR, HERMANS J. Size and density of fibrin fibers from turbidity. Macromolecules. 1978;11(1):46-50. [79] COLLEN A, KOOLWIJK P, KROON M, et al. Influence of fibrin structure on the formation and maintenance of capillary-like tubules by human microvascular endothelial cells. Angiogenesis. 1998;2(2):153-165. [80] WANG X, FRIIS T, GLATT V, et al. Structural properties of fracture haematoma: current status and future clinical implications. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(10):2864-2875. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [3] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [4] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [5] | Long Guiyue, Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing. Calcium phosphate cement/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation products promote osteoclast differentiation of mouse monocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [6] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [7] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [8] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [9] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [10] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [11] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [12] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [13] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [14] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [15] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||