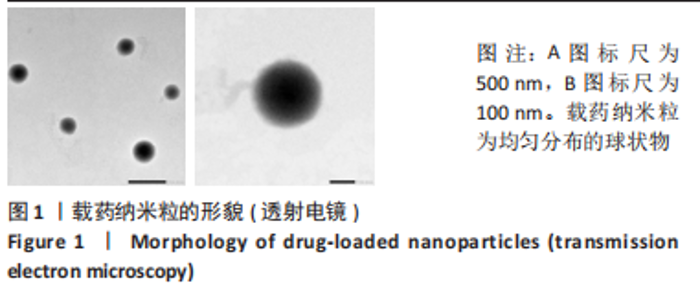
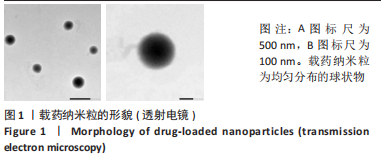
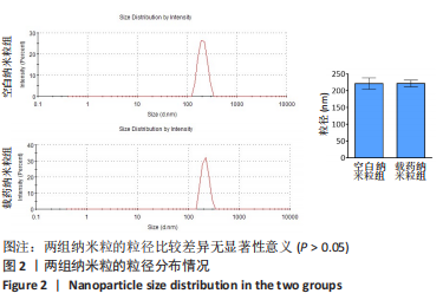
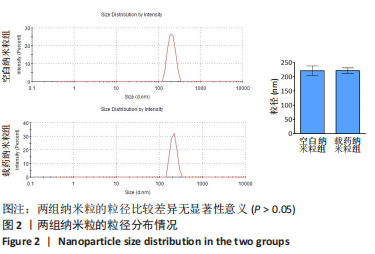
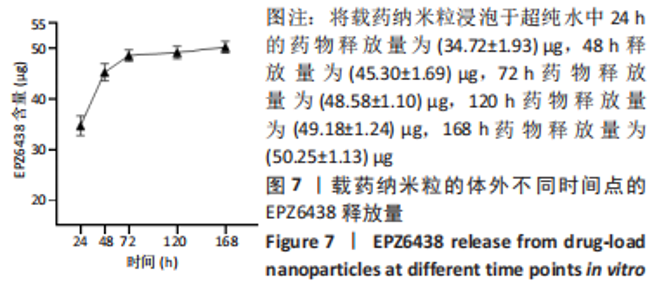
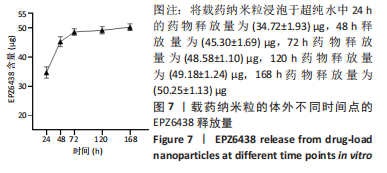
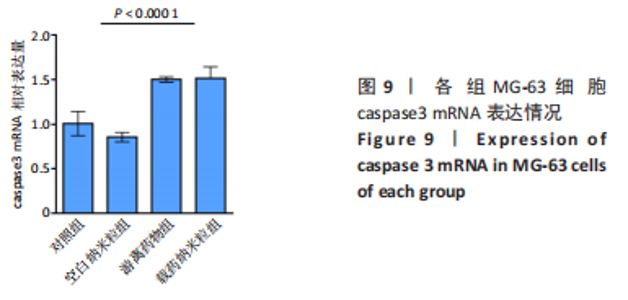
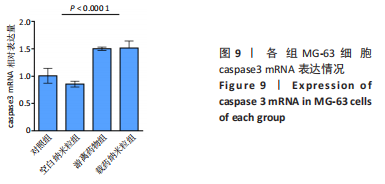
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1512-1518.doi: 10.12307/2024.368
Previous Articles Next Articles
Inhibitory effect of bovine serum albumin-chitosan nanoparticles loaded with EPZ6438 on osteosarcoma
Liu Chang1, 2, Zhang Wen1, 2, Zhu Can1, 2, Sun Jie1, 2, Ding Yicheng3, Shi Qin1, 2
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Orthopedic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-04-09Accepted:2023-05-25Online:2024-04-08Published:2023-08-17 -
Contact:Shi Qin, MD, Professor, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China; Orthopedic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Liu Chang, Master candidate, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China; Orthopedic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82172485 (to SQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Chang, Zhang Wen, Zhu Can, Sun Jie, Ding Yicheng, Shi Qin. Inhibitory effect of bovine serum albumin-chitosan nanoparticles loaded with EPZ6438 on osteosarcoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1512-1518.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
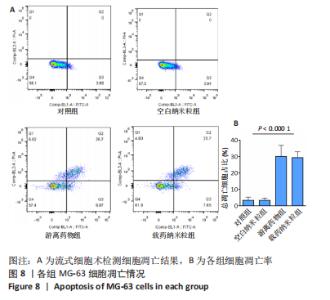
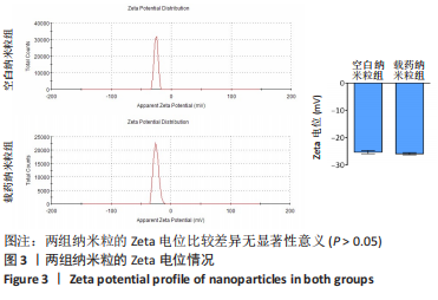
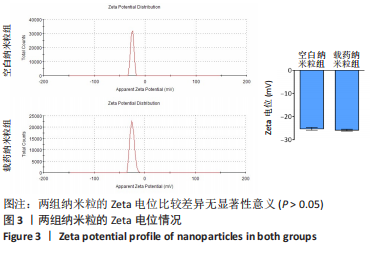
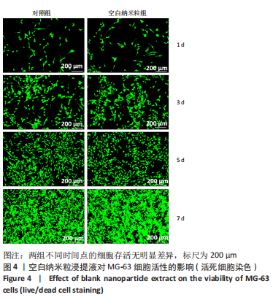
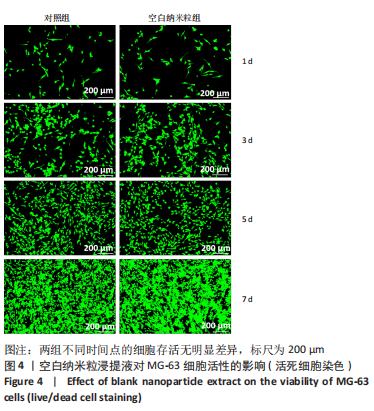
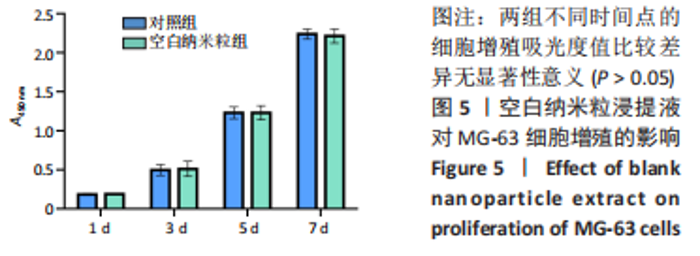
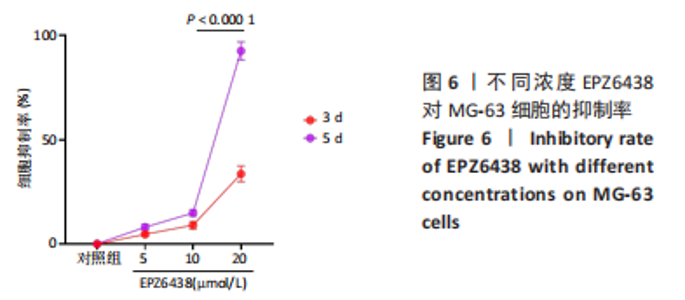
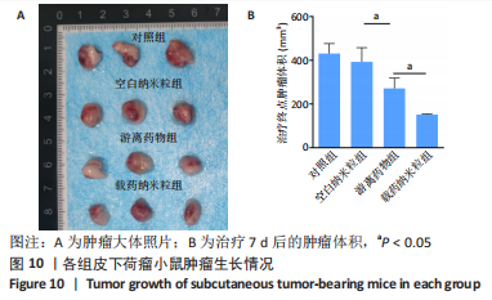
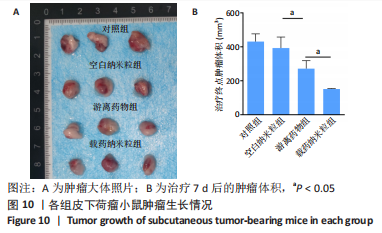
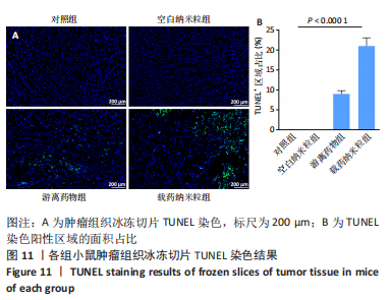
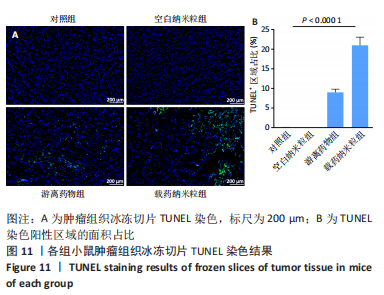
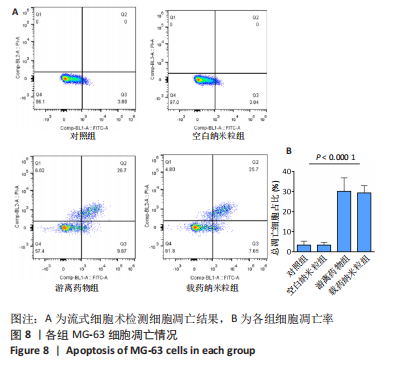
2.5 载药纳米粒对MG-63细胞凋亡及凋亡基因表达的影响 流式细胞术检测MG-63细胞凋亡结果如图8所示,对照组、空白纳米粒组细胞凋亡率分别为(3.33±1.97)%,(3.35±1.38)%,两组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),可以认为单纯纳米粒材料无法诱导MG-63细胞凋亡进而杀伤骨肉瘤细胞。游离药物组、载药纳米粒组细胞凋亡率分别为(30.07±6.71)%,(29.31±3.59)%,两组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),该两组细胞凋亡率高于对照组、空白纳米粒组(P < 0.001)。可以认为游离EPZ6438和载药纳米粒组浸提液都可以诱导MG-63细胞凋亡,进而杀伤骨肉瘤细胞。"
| [1] GILL J, GORLICK R. Advancing therapy for osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 202;18(10):609-624. [2] MELTZER PS, HELMAN LJ. New Horizons in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(22):2066-2076. [3] ZHAO X, WU Q, GONG X, et al. Osteosarcoma: a review of current and future therapeutic approaches. Biomed Eng OnLine. 2021;20(1):24. [4] KANSARA M, TENG MW, SMYTH MJ, et al. Translational biology of osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(11):722-735. [5] CHEN S, ZENG J, HUANG L, et al. RNA adenosine modifications related to prognosis and immune infiltration in osteosarcoma. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):228. [6] NACEV BA, SANCHEZ-VEGA F, SMITH SA, et al. Clinical sequencing of soft tissue and bone sarcomas delineates diverse genomic landscapes and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3405. [7] SHI D, MU S, PU F, et al. Integrative analysis of immune-related multi-omics profiles identifies distinct prognosis and tumor microenvironment patterns in osteosarcoma. Mol Oncol. 2022;16(11): 2174-2194. [8] YUAN Y, YAN G, HE M, et al. ALKBH5 suppresses tumor progression via an m(6)A-dependent epigenetic silencing of pre-miR-181b-1/YAP signaling axis in osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(1):60. [9] WAN D, HAN X, ZHANG C, et al. EZH2 promotes the progression of osteosarcoma through the activation of the AKT/GSK3β pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;49(11):1179-1186. [10] SUN R, SHEN J, GAO Y, et al. Overexpression of EZH2 is associated with the poor prognosis in osteosarcoma and function analysis indicates a therapeutic potential. Oncotarget. 2016;7(25):38333-38346. [11] ZHANG H, WANG T, GONG H, et al. A novel molecular classification method for osteosarcoma based on tumor cell differentiation trajectories. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):1. [12] YAN G, LV Y, LAI X, et al. Expressions of EZH2 and NOTCH3 pathway in osteosarcoma and their roles in osteosarcoma stem cells. Pol J Pathol. 2022;73(4):343-351. [13] HOY SM. Tazemetostat: First Approval. Drugs. 2020;80(5):513-521. [14] YAN Q, WENG J, WU X, et al. Characteristics, Cryoprotection Evaluation and In Vitro Release of BSA-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles. Mar Drugs. 2020;18(6):315. [15] QI J, YAO P, HE F, et al. Nanoparticles with dextran/chitosan shell and BSA/chitosan core--doxorubicin loading and delivery. Int J Pharm. 2010;393(1-2):176-184. [16] RITTER J, BIELACK SS. Osteosarcoma. Ann Oncol. 2010;21 Suppl 7: vii320-325. [17] BEIRD HC, BIELACK SS, FLANAGAN AM, et al. Osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8(1):77. [18] SMRKE A, ANDERSON PM, GULIA A, et al. Future Directions in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma. Cells. 2021;10(1):172. [19] JAFARI F, JAVDANSIRAT S, SANAIE S, et al. Osteosarcoma: A comprehensive review of management and treatment strategies. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2020;49:151654. [20] KNUTSON SK, KAWANO S, MINOSHIMA Y, et al. Selective inhibition of EZH2 by EPZ-6438 leads to potent antitumor activity in EZH2-mutant non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(4):842-854. [21] ILANGO S, PAITAL B, JAYACHANDRAN P, et al. Epigenetic alterations in cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020;25(6):1058-1109. [22] SUN L, ZHANG H, GAO P. Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer. Protein Cell. 2022;13(12):877-919. [23] ZHENG C, TANG F, MIN L, et al. PTEN in osteosarcoma: Recent advances and the therapeutic potential. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020;1874(2):188405. [24] ZHANG Y, SUN T, JIANG C. Biomacromolecules as carriers in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018;8(1):34-50. [25] Montero N, Pérez E, Benito M, et al. Biocompatibility studies of intravenously administered ionic-crosslinked chitosan-BSA nanoparticles as vehicles for antitumour drugs. Int J Pharm. 2019;554: 337-351. [26] ZHANG R, LIU T, LI W, et al. Tumor microenvironment-responsive BSA nanocarriers for combined chemo/chemodynamic cancer therapy. J Nanobiotechnol. 2022;20(1):223. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [3] | Wang Wu, Fan Xiaolei, Xie Jie, Hu Yihe, Zeng Min. Hydroxyapatite-polyvinyl alcohol/collagen-chitosan-gelatin composite hydrogel for repairing rabbit osteochondral defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 682-689. |
| [4] | Zhu Liwei, Wang Jiangyue, Bai Ding. Application value of nanocomposite gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels in different bone defect environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [5] | Chen Zepeng, Hou Yonghui, Chen Shudong, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treats spinal cord injury by reducing apoptosis of spinal cord neurons under glucose and oxygen deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [6] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [7] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Changcheng, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Guo Lin. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a three-dimensional porous cartilage scaffold made of silk fibroin/gelatin/chitosan [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [8] | Chen Pinrui, Pei Xibo, Xue Yiyuan. Function and advantages of magnetically responsive hydrogel in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [9] | Ran Lei, Han Haihui, Xu Bo, Wang Jianye, Shen Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Molecular docking analysis of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Cibotium barometz and Epimedium for rheumatoid arthritis: animal experiment validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 208-215. |
| [10] | Zuo Jun, Ma Shaolin. Mechanism of beta-sitosterol on hypertrophic scar fibroblasts: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 216-223. |
| [11] | Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230. |
| [12] | Chen Simin, Hu Yingjun, Yan Wenrui, Ji Le, Shao Mengli, Sun Ze, Zheng Hongxing, Qi Shanshan. Establishment and evaluation of a streptozotocin-induced diabetic encephalopathy rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 237-241. |
| [13] | Zhang Shasha, Wang Na, Li Yongjun. Grape seed extract inhibits apoptosis of rat growth plate chondrocytes and promotes tibial bone growth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2494-2499. |
| [14] | Xie Wenguan, Liu Yutao, Cui Wenbo, Kuang Mingye. Melatonin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced injury of human nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2180-2185. |
| [15] | Zhuang Zhikun, He Mincong, Lin Tianye, Wu Rongkai, Guo Jinhua, Wu Zhaoke, Wei Qiushi. Exploration and clinical validation of the repair mode of the sclerotic zone of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on Tandem Mass Tags technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2191-2196. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||