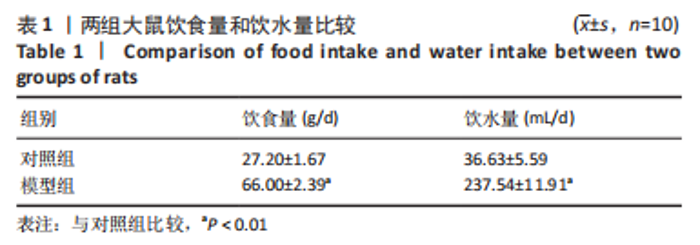
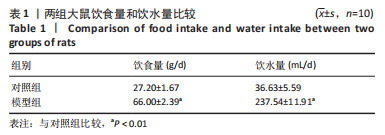
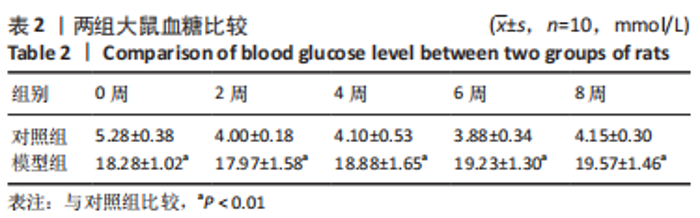
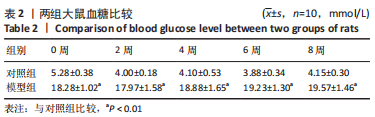
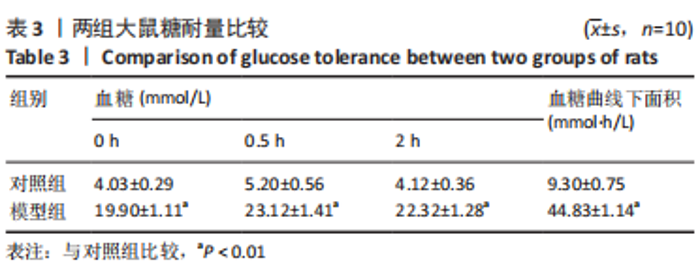
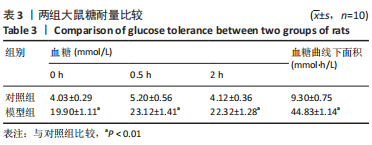
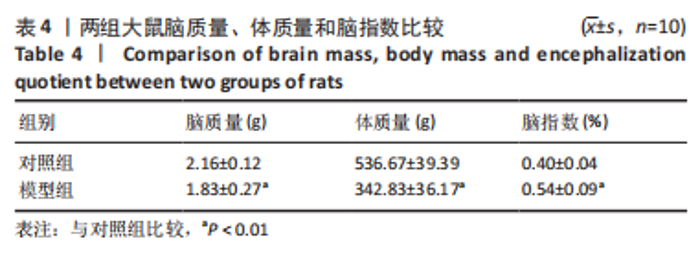
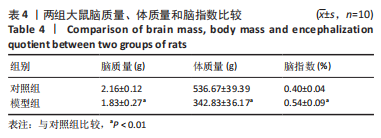
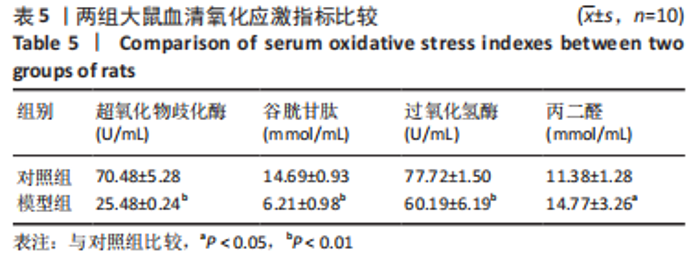
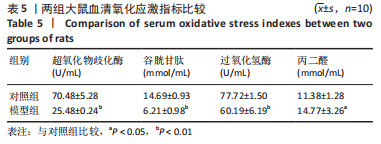
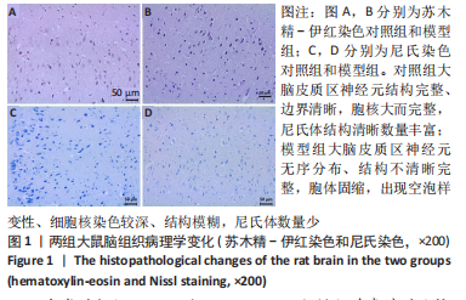
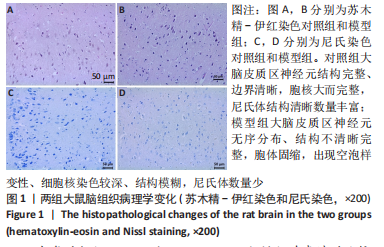
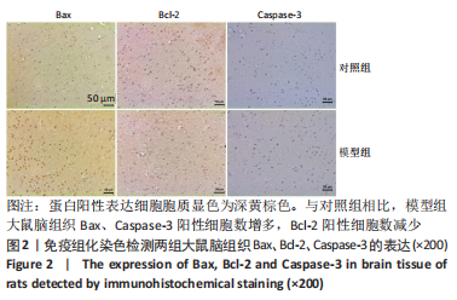
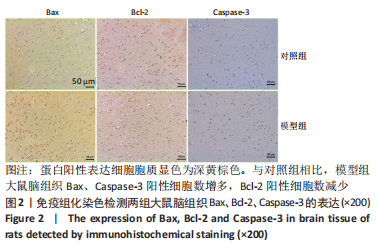
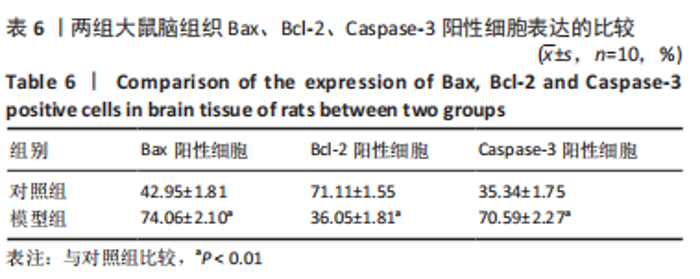
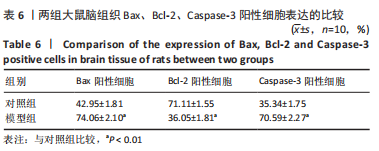
[1] 付玉, 尚画雨, 李顺昌. 有氧和抗阻运动可缓解2型糖尿病模型大鼠的肝脏炎症反应[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(29):4666-4671.
[2] ZIMATH PL, DALMAGRO AP, MOTA DA SILVA L, et al. Myrsinoic acid B from Myrsine coriacea reverses depressive-like behavior and brain oxidative stress in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2021;347:109603.
[3] CHEN YJ, TANG ZZ, DU L, et al. A novel compound AB-З8b improves diabetes-associated cognitive decline in mice via activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway. Brain Res Bull. 2019;150:160-167.
[4] RAWLINGS AM, SHARRETT AR, ALBERT MS, et al. The association of late-life diabetes status and hyperglycemia with incident mild cognitive impairment and dementia: The ARIC Study. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(7):1248-1254.
[5] BIESSELS GJ, STAEKENBORG S, BRUNNER E, et al. Risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(1):64-74.
[6] 武翠玲, 刘弘毅, 范源, 等. 糖尿病脑病的发病机制研究进展[J].昆明医科大学学报,2022,43(7):145-151.
[7] WANG Z, HUANG Y, CHENG Y, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal inflammatory response and apoptosis likely plays a key role in the development of diabetic encephalopathy. Oncotarget. 2016;7(48):78455-78472.
[8] 于丽, 严利君, 权青云. 浅析糖尿病脑病研究进展[J].糖尿病新世界,2022, 25(6):195-198.
[9] LUO Z, WAN Q, HAN Y, et al. CAPE-pNO2 ameliorates diabetic brain injury through modulating Alzheimer’s disease key proteins, oxidation, inflammation and autophagy via a Nrf2-dependent pathway. Life Sci. 2021;287:119929.
[10] LEE JY, PARK CS, CHOI HY, et al. Ginseng extracts, GS-KG9 and GS-E3D, prevent blood–brain barrier disruption and thereby inhibit apoptotic cell death of hippocampal neurons in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Nutrients. 2020;12(8):2383.
[11] KIMURA N. Diabetes Mellitus induces alzheimer’s disease pathology: histopathological evidence from animal models. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(4):503.
[12] SHI S, YIN HJ, LI J, et al. Studies of pathology and pharmacology of diabetic encephalopathy with KK-Ay mouse model. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020;26(3):332-342.
[13] 刘申贝, 古小云, 钟志江,等. KKAy糖尿病脑病模型的探索及相关机制研究[J].中药药理与临床,2020,36(1):210-218.
[14] 霍明轩, 刘伟, 王倩, 等. 糖尿病脑病动物模型制备方法的研究进展[J].山东医药,2021,61(15):103-106.
[15] 祁珊珊, 何佳, 孙泽, 等. 糖尿病肾病SD大鼠模型的建立和评价[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2021,37(9):1114-1116+1125.
[16] 何嘉玲, 王天奇, 张长勇, 等. 大、小鼠CO2安乐死方法研究[J].实验动物科学, 2019,36(5):81-84.
[17] 祁珊珊, 何佳, 龚帅, 等. 黑米花青苷对糖尿病大鼠视网膜病变的保护作用[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(22):3751-3754.
[18] ZHENG HX, QI SS, HE J, et al. Cyanidin-3-glucoside from black rice ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via reducing blood glucose, suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation, and regulating transforming growth factor β1/smad expression. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68(15):4399-4410.
[19] 孙晶, 魏静, 杨洋, 等.茄皮提取物对糖尿病小鼠的降血糖作用[J].现代食品科技,2022,38(9):10-17.
[20] 董秀娟, 曹亚磊, 李芹, 等.白藜芦醇对妊娠期糖尿病大鼠脑组织氧化应激和细胞凋亡的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2016,32(1):61-64.
[21] 陈丹丹, 彭成, 万峰, 等. 氢溴酸樟柳碱对抗大鼠急性脑缺血/再灌注损伤的作用机制研究[J].中国药理学通报,2017,33(8):1096-1102.
[22] 吴岚, 周素娴, 刘开祥, 等. 青藤碱对糖尿病大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后Bcl-2和Caspase-3表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(11):1543-1545.
[23] 胡新国, 李娜, 程玲, 等. 糖尿病性认知功能障碍的研究进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2012,14(3):343-344.
[24] SRIKANTH V, SINCLAIR ALAN J, HILL-BRIGGS F, et al. Type 2 diabetes and cognitive dysfunction-towards effective management of both comorbidities. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8:535-545.
[25] 杨晓晖,田文杨.糖尿病脑病的诊断及处理[J].中华全科医学,2017,15(2):186-187.
[26] WU J, YAN LJ. Streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes in rodents as a model for studying mitochondrial mechanisms of diabetic β cell glucotoxicity. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2015;8:181-188.
[27] GRIEB P. Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin injections as a model of alzheimer’s disease: in search of a relevant mechanism. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(3):1741-1752.
[28] ZHANG Y, DING R, WANG S, et al. Effect of intraperitoneal or intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin on learning and memory in mice. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(3):2375-2380.
[29] RAVELLI KG, ROSARIO BD, CAMARINI R, et al. Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin as a model of alzheimer’s disease: neurochemical and behavioral characterization in mice. Neurotox Res. 2017;31(3):327-333.
[30] SAMARGHANDIAN S, AZIMI-NEZHAD M, SAMINI F. Ameliorative effect of saffron aqueous extract on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and oxidative stress on diabetic encephalopathy in streptozotocin induced experimental diabetes mellitus. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:920857.
[31] 贺青华,李勇超,王文娟, 等. 雨生红球藻虾青素对糖尿病大鼠脑损伤的干预作用[J].中国食品学报,2019,19(5):33-38.
[32] 李钊至, 吕敏, 梁魏, 等.糖尿病大鼠模型的建立及评价[J]. 基层医学论坛, 2017,21(1):4-5.
[33] LAWSON CM, RENTRUP KFG, CAI X, et al. Using multimodal MRI to investigate alterations in brain structure and function in the BBZDR/Wor rat model of type 2 diabetes. Animal Model Exp Med. 2020;3(4):285-294.
[34] SRISUKSAI K, PARUNYAKUL K, PHAONAKROP N, et al. The effect of cordycepin on brain oxidative stress and protein expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J Vet Med Sci. 2021;83(9):1425-1434.
[35] MA XJ, SONG M, YAN YS, et al. Albiflorin alleviates cognitive dysfunction in STZ-induced rats. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13:18287-18297.
[36] GORGICH EAC, PARSAIE H, YARMAND S, et al. Long-term administration of metformin ameliorates age-dependent oxidative stress and cognitive function in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2021;410:113343.
[37] 周丽丽, 莫超然, 刘心朗, 等. 蒙药香青兰总黄酮对帕金森病模型小鼠的神经保护作[J].中国比较医学杂志,2021,31(5):41-46.
|