Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 224-230.doi: 10.12307/2023.873
Previous Articles Next Articles
Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells
Wang Qian1, Lu Ziang2, Li Lihe1, Lyu Chaoliang1, Wang Meng3, Zhang Cunxin1
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, 3Clinical Medical Experiment Center, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China; 2School of Clinical Medicine, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-29Accepted:2023-01-29Online:2024-01-18Published:2023-06-30 -
Contact:Zhang Cunxin, Master, Attending physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang Qian, Master, Department of Spine Surgery, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Province Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project, No. Q-2022025 (to ZCX); Jining Key R&D Program Projects, Nos. 2020JKNS008 (to ZCX) and 2019SMNS003 (to WM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
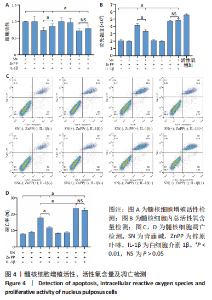
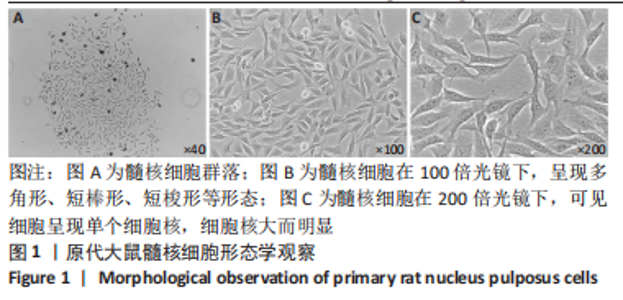
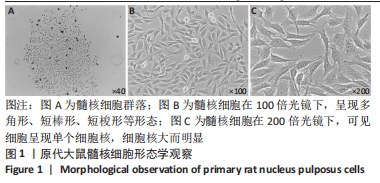
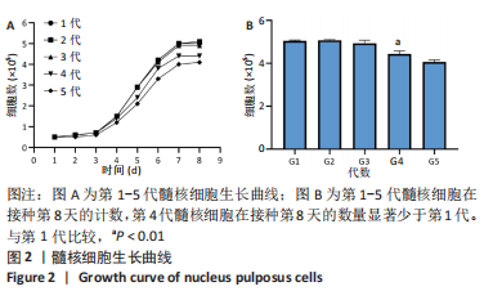
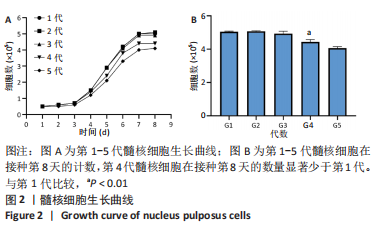
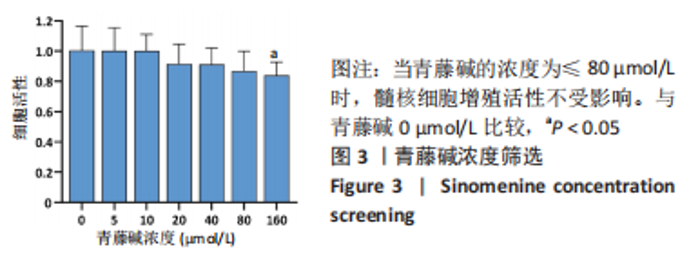
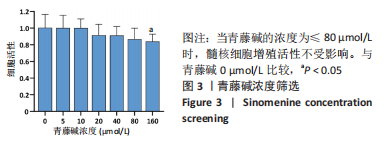
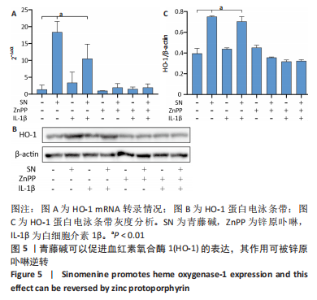
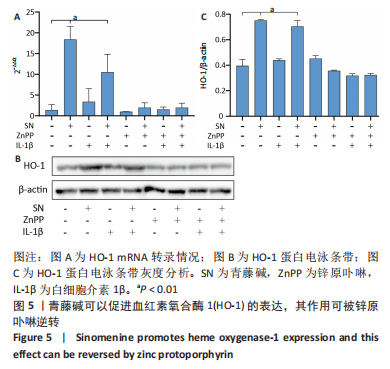
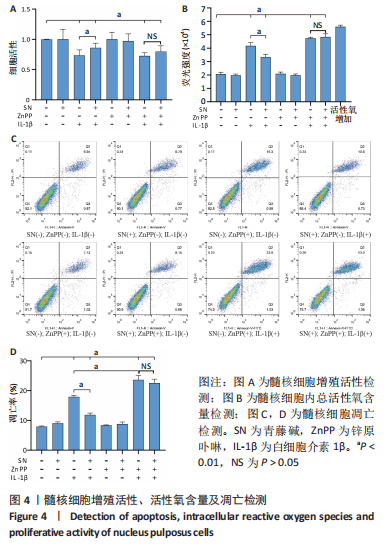
2.4 髓核细胞增殖活性、活性氧含量及凋亡检测 采用CCK-8试剂盒检测各组髓核细胞增殖活性发现,IL-1β可以显著降低髓核细胞增殖活性(P < 0.01);采用青藤碱预处理后,虽然与对照组相比髓核细胞增殖活性仍然降低(P < 0.01),但较单纯采用IL-1β处理(IL-1β组)显著增加(P < 0.01);当采用锌原卟啉干预HO-1的表达后,青藤碱的细胞保护作用可被逆转(图4A)。 采用荧光探针DCFH-DA标记法检测各组髓核细胞内总活性氧含量发现,IL-1β可以显著增加髓核细胞中活性氧的蓄积(P < 0.01);采用青藤碱预处理后,虽然与对照组相比髓核细胞中活性氧含量仍然显著增加(P < 0.01),但较单纯采用IL-1β处理(IL-1β组)显著降低(P < 0.01);当采用锌原卟啉干预HO-1的表达后,青藤碱不能减轻IL-1β诱导的活性氧含量增加(P > 0.05)(图4B)。 这种变化趋同样发现在髓核细胞的凋亡检测结果中(图4C,D),令人意外的是,采用锌原卟啉预处理后,会进一步增加IL-1β诱导的髓核细胞凋亡(P < 0.01)。"
| [1] CHEN BL, GUO JB, ZHANG HW, et al. Surgical versus non-operative treatment for lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(2):146-160. [2] JUNGEN MJ, Ter MEULEN BC, van OSCH T, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers in patients with sciatica: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):156. [3] DENES K, ARANYI Z, CSILLIK A, et al. Serum biomarkers in acute low back pain and sciatica. Orv Hetil. 2020;161(13):483-490. [4] ZHAO L, MANCHIKANTI L, KAYE AD, et al. Treatment of Discogenic Low Back Pain: Current Treatment Strategies and Future Options-a Literature Review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(11):86. [5] LIU HY, KANG HL, SONG C, et al. Urolithin A Inhibits the Catabolic Effect of TNFalpha on Nucleus Pulposus Cell and Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in vivo. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1043. [6] LI P, HOU G, ZHANG RJ, et al. High-magnitude compression accelerates the premature senescence of nucleus pulposus cells via the p38 MAPK-ROS pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):209. [7] HIDER SL, KONSTANTINOU K, HAY EM, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers do not distinguish between patients with sciatica and referred leg pain within a primary care population: results from a nested study within the ATLAS cohort. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):202. [8] WANG YJ, CHE MX, XIN JG, et al. The role of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110660. [9] ZHAO KC, AN R, XIANG Q, et al. Acid-sensing ion channels regulate nucleus pulposus cell inflammation and pyroptosis via the NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021; 4(1):e12941. [10] XU QL, XING HY, WU JQ, et al. miRNA-141 Induced Pyroptosis in Intervertebral Disk Degeneration by Targeting ROS Generation and Activating TXNIP/NLRP3 Signaling in Nucleus Pulpous Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:871. [11] LI ZW, WANG JM, MA YM. Montelukast attenuates interleukin IL-1beta-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in chondrocytes by inhibiting CYSLTR1 (Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptor 1) and activating KLF2 (Kruppel Like Factor 2). Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):8476-8484. [12] ZHU WR, TANG H, LI JC, et al. Ellagic acid attenuates interleukin-1beta-induced oxidative stress and exerts protective effects on chondrocytes through the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)/ Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):9233-9247. [13] JIANG W, FAN WM, GAO TL, et al. Analgesic Mechanism of Sinomenine against Chronic Pain. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:1876862. [14] IINO T, SAKO T. Inhibition and resumption of processing of the staphylokinase in some Escherichia coli prlA suppressor mutants. J Biol Chem. 1988;263(35):19077-19082. [15] FAN H, SHU Q, GUAN XL, et al. Sinomenine Protects PC12 Neuronal Cells against H2O2-induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress via a ROS-dependent Up-regulation of Endogenous Antioxidant System. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017;37(8):1387-1398. [16] LIU WW, ZHANG YJ, ZHU WN, et al. Sinomenine Inhibits the Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating the Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines and Monocyte/Macrophage Subsets. Front Immunol. 2018; 9:2228. [17] ZENG MY, TONG QY. Anti-inflammation Effects of Sinomenine on Macrophages through Suppressing Activated TLR4/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Curr Med Sci. 2020;40(1):130-137. [18] FAN H, SHU Q, GUAN XL, et al. Sinomenine Protects PC12 Neuronal Cells against H2O2-induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress via a ROS-dependent Up-regulation of Endogenous Antioxidant System. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017;37(8):1387-1398. [19] PENG Y, OU H, YANG MS, et al. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages by sinomenine through regulating heme oxygenase-1 expression and autophagy. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018;43(9):964-970. [20] KIM YK, KANG DM, LEE I, et al. Differences in the Incidence of Symptomatic Cervical and Lumbar Disc Herniation According to Age, Sex and National Health Insurance Eligibility: A Pilot Study on the Disease’s Association with Work. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(10):2094. [21] BAI XL, DING WY, YANG SD, et al. Higenamine inhibits IL-1beta-induced inflammation in human nucleus pulposus cells. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(6): BSR20190857. [22] ZHOU YF, CHEN ZQ, YANG X, et al. Morin attenuates pyroptosis of nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of the TXNIP/NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1beta signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;559:106-112. [23] MA ZX, TANG P, DONG W, et al. SIRT1 alleviates IL-1beta induced nucleus pulposus cells pyroptosis via mitophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;107:108671. [24] FORRESTER SJ, KIKUCHI DS, HERNANDES MS, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ Res. 2018;122(6): 877-902. [25] DAI YQ, ZHANG J, XIANG J, et al. Calcitriol inhibits ROS-NLRP3-IL-1beta signaling axis via activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling in hyperosmotic stress stimulated human corneal epithelial cells. Redox Biol. 2019;21:101093. [26] WU XX, ZHANG HQ, QI W, et al. Nicotine promotes atherosclerosis via ROS-NLRP3-mediated endothelial cell pyroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):171. [27] KANG L, HU J, WENG YX, et al. Sirtuin 6 prevents matrix degradation through inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Cell Res. 2017;352(2):322-332. [28] LI Z, WANG X, PAN H, et al. Resistin promotes CCL4 expression through toll-like receptor-4 and activation of the p38-MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways: implications for intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(2):341-350. [29] LUO X, HUAN L, LIN F, et al. Ulinastatin Ameliorates IL-1beta-Induced Cell Dysfunction in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells via Nrf2/NF-kappaB Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:5558687. [30] ZHANG CX, WANG T, MA JF, et al. Protective effect of CDDO-ethyl amide against high-glucose-induced oxidative injury via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Spine J. 2017;17(7):1017-1025. [31] EARLY JO, MENON D, WYSE CA, et al. Circadian clock protein BMAL1 regulates IL-1beta in macrophages via NRF2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018,115(36):E8460-E8468. [32] YUAN ML, ZHAO B, JIA HP, et al. Sinomenine ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy by activating Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):12778-12788. [33] GAO ZX, LIN YC, ZHANG P, et al. Sinomenine ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy in vitro and in vivo. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9):5956-5966. [34] HOU XF, SHEN YC, SUN ML, et al. Effect of regulating macrophage polarization phenotype on intervertebral disc degeneration. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022;10(11):e714. |
| [1] | Zhou Shuliang, Xu Liang, Qian Xuefeng, Zeng Jincai, Zhu Lifan. Correlation between the expression of miRNA-142-3p, mixed lineage kinase 3 and interleukin-1beta in nucleus pulposus and the degree of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 165-171. |
| [2] | Ran Lei, Han Haihui, Xu Bo, Wang Jianye, Shen Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Molecular docking analysis of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Cibotium barometz and Epimedium for rheumatoid arthritis: animal experiment validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 208-215. |
| [3] | Zuo Jun, Ma Shaolin. Mechanism of beta-sitosterol on hypertrophic scar fibroblasts: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 216-223. |
| [4] | Chen Simin, Hu Yingjun, Yan Wenrui, Ji Le, Shao Mengli, Sun Ze, Zheng Hongxing, Qi Shanshan. Establishment and evaluation of a streptozotocin-induced diabetic encephalopathy rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 237-241. |
| [5] | Ai Fangfang, Xiao Hongyan, Wang Fang, Zhu Yongzhao, Ma Lijun. Reversal effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide in combination with oxaliplatin on drug resistance of colon cancer stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 74-79. |
| [6] | Cheng Haotian, Zhao Xiaofeng, Lu Xiangdong, Zhao Yibo, Fan Zhifeng, Qi Detai, Wang Xiaonan, Zhou Runtian, Jin Xinjie, Zhao Bin. Single-cell RNA sequencing and the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 93-99. |
| [7] | Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Liu Tao, Li Yan, He Yuanxu, He Bo, Wang Weiwei, Wei Xiaotao. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in the prevention and treatment of flap necrosis by regulating “autophagy” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 153-158. |
| [8] | Zheng Rongjiong, Deng Zerun, Han Dan, Sun Lihua. Mechanism underlying rat hepatocyte apoptosis regulated by exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 44-49. |
| [9] | Sun Jing, Liao Jian, Sun Jiangling, Cheng Ping, Feng Hongchao. Recombinant human growth hormone promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 56-61. |
| [10] | Deng Rui, Huang Keming, Luo Jian, Chen Gong, Feng Jian, Huang Weiyi, Wei Gang. Effect of heme oxygenase-1-mediated atorvastatin on macrophage polarization and cholesterol accumulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 62-67. |
| [11] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-6. |
| [12] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [13] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [14] | You Zhengqiu, Zhang Zhongzu, Wang Qunbo. Early symptomatic intervertebral disc pseudocysts after discectomy detected on MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1403-1409. |
| [15] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||