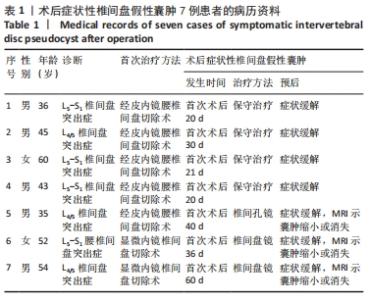
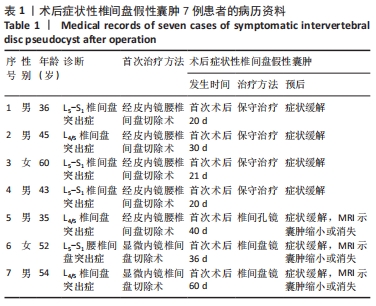
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 1403-1409.doi: 10.12307/2023.210
Previous Articles Next Articles
Early symptomatic intervertebral disc pseudocysts after discectomy detected on MRI
You Zhengqiu, Zhang Zhongzu, Wang Qunbo
- Department of Orthopedics, Yongchuan Hospital Affiliated to Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China
-
Received:2021-12-23Accepted:2022-01-30Online:2023-03-28Published:2022-07-02 -
Contact:Wang Qunbo, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Yongchuan Hospital Affiliated to Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China -
About author:You Zhengqiu, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Yongchuan Hospital Affiliated to Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
You Zhengqiu, Zhang Zhongzu, Wang Qunbo. Early symptomatic intervertebral disc pseudocysts after discectomy detected on MRI[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1403-1409.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
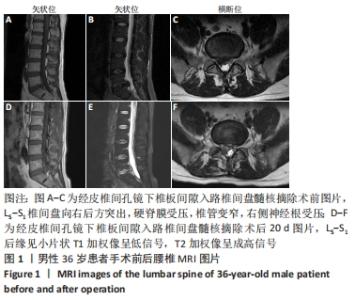
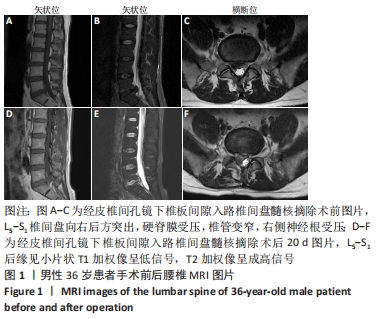
病例1:36岁男性患者,因“反复腰背部疼痛、右下肢胀痛3个月”入院。入院查体:L5/S1椎间隙及右侧椎旁肌肉压、叩痛明显,目测类比评分为6分,向右下肢放射,右下肢直腿抬高试验40°(+)、加强试验(+),右小腿后侧、足底浅感觉减退,右足跖屈肌力4级,左下肢未见明显异常。完善检查,腰椎动力位片未见明显失稳;腰椎MRI提示:L5/S1椎间盘突出(旁中央型),L5/S1右侧神经根受压,椎管变窄,见图1A-C。其余检查未见明显异常。择期在全麻下行经皮椎间孔镜下椎板间隙入路L5/S1椎间盘髓核摘除手术。术后腰腿痛症状明显缓解,术后第1天目测类比评分为1分,5 d后出院。 术后第20天,患者因抬重物后出现腰部胀痛不适,第2天疼痛明显加重,并出现右下肢大腿后侧、小腿后侧、外踝、右足外侧放射性疼痛。查体:L5/S1椎间隙和椎旁肌肉明显叩压痛,目测类比评分为6分。右下肢直腿抬高试验40°(+)、加强试验(+)。右小腿后侧、足底浅感觉减退,肌力未见明显减退。复查MRI示:L5/S1椎间盘术区软组织肿胀,L5/S1后缘异常信号灶,与椎间盘相通,见图1D-F。给予患者口服止痛药、活血化瘀药等,患者腰腿痛症状缓解不明显。给予患者保守治疗,止痛消肿、营养神经、卧床休息等对症治疗,1周后患者诉疼痛症状较前缓解,目测类比评分为4分。3个月后随访,患者诉疼痛好转,目测类比评分为2分,偶有右小腿后侧、足底处麻木不适感。 "
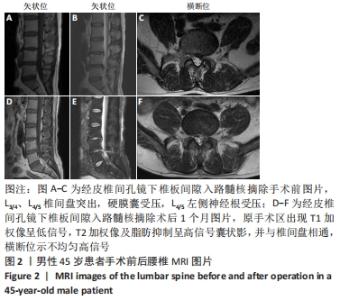
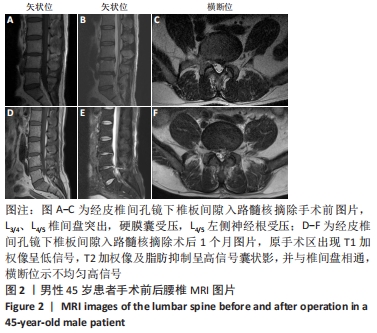
病例2:45岁男性患者,因“腰痛伴左下肢疼痛1年,加重3 d以上”入院。体格检查:腰椎棘突及椎旁肌肉压叩痛明显,伴左下肢大腿后侧、小腿外侧、外踝放射痛,目测类比评分为8分,左下肢直腿抬高试验40°(+),加强试验(+),左下肢小腿外侧、外踝、足背浅感觉减退。左下肢胫前肌、背伸肌肌力4级,其余肌力未见明显异常。双侧病理征未引出。术前检查:腰椎平片及动力位片未见明显异常,MRI示:L3/4、L4/5椎间盘后缘后方突出,硬膜囊受压,椎管狭窄,L4/5左侧神经根受压,见图2A-C。诊断:腰椎间盘突出症(L3/4、L4/5);腰椎椎管狭窄。择期行经皮椎间孔镜下椎板间隙入路L4/5髓核摘除手术。术后患者腰背部及左下肢疼痛症状明显缓解。 术后1个月患者就诊诉劳累后出现腰背部、左下肢大腿后侧及小腿外侧放射性疼痛,程度较轻,卧床休息可缓解。复查MRI提示:L4/5椎间盘术后改变,术区及腰背部皮下软组织肿胀,见图2D-F。因患者症状较轻且卧床休息后可缓解,暂给予患者保守治疗,连续3 d静脉输注七叶皂和甘露醇后症状缓解明显。之后口服非类固醇抗炎止痛药1周,目测类比评分为2分,之后1.5,3,6个月随访,患者未诉腰痛等不适。 "
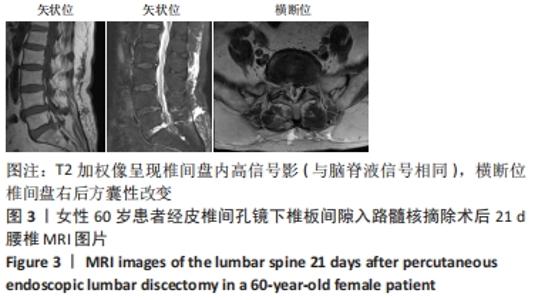
病例3:60岁女性患者,因“反复右下肢胀痛10余年,加重4 d”入院,既往无其他病史。体格检查:L5/S1及右侧椎旁肌肉明显叩压痛,向右下肢放射,目测类比评分为7分。右下肢直腿抬高试验50°(+)、加强试验(+),双下肢浅感觉、肌力未见明显异常。术前腰椎动力位提示L4椎体失稳,CT提示L5-S1椎间盘突出,无明显钙化。MRI示:L4椎体不稳定,L5/S1椎间盘突出,L5/S1椎间盘后缘纤维环裂隙。其余检查无特殊。择期在全麻下行经皮椎间孔镜下椎板间隙入路L5/S1髓核摘除手术。术后右下肢疼痛症状缓解,目测类比评分为1分。 术后第21天,患者诉晨起时右侧腰骶部、右侧臀区胀痛不适,自行服用“塞来昔布胶囊”后疼痛缓解,体格检查:L5/S1及右侧椎旁肌肉明显叩压痛,向右侧臀区放射,目测类比评分为6分。右下肢直腿抬高试验50°(+)、加强试验(+)。其余检查无异常。复查MRI示:L5/S1椎间盘内异常信号,多系术后改变,L5-S1椎间盘右后方T2加权像呈现囊性高信号密度影,见图3。给予患者卧床、消炎止痛对症治疗后,症状缓解明显,目测类比评分为3分。3个月后随访患者诉右侧臀区间断疼痛,疼痛尚可忍受,未行进一步处理。6个月后随访,患者臀区疼痛较前无明显差异,可耐受,未行处理。 "

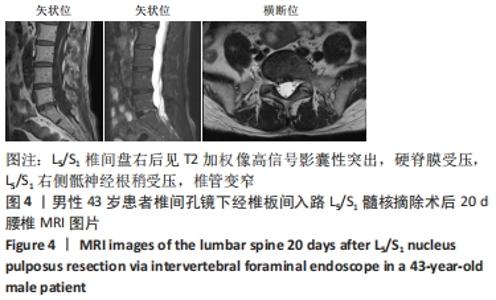
病例4:43岁男性患者,因“腰痛3年余,右下肢疼痛半年,加重7 d以上”入院。入院后查体:右下肢直腿抬高试验40°(+)、加强试验(+),双下肢肌张力未见明显异常,右小腿后侧浅感觉减退,其余部位感觉未见明显异常,右足跖屈肌力4级,其余肌力正常。术前腰椎MRI检查提示:L5/S1椎间盘突出,右侧神经根受压。无手术禁忌证,择期行椎间孔镜下经椎板间入路L5/S1髓核摘除手术。术后患者腰腿痛症状明显缓解,目测类比评分为1分。术后第4天,佩戴护腰出院。 术后10 d,患者诉偶有腰背部胀痛不适,无双下肢疼痛麻木症状,卧床休息后可好转。术后第20天,因腰背部胀痛不适次数较前增多,患者遂就诊。查体:L5/S1椎间隙及右侧椎旁肌肉压、叩痛明显,目测类比评分为4分,向右下肢放射痛,右下肢直腿抬高试验60°(-),双下肢肌力、浅感觉未见明显异常。复查MRI示:L5/S1椎间盘后缘右椎间孔见一囊性突出,与椎间盘相通,伴L5/S1右侧骶神经根受压,见图4。嘱患者佩戴护腰、口服止痛消肿等药物、卧床休息。2周后随访,腰背部胀痛症状好转,目测类比评分为2分。6个月后随访,患者未述腰腿痛等症状。 "

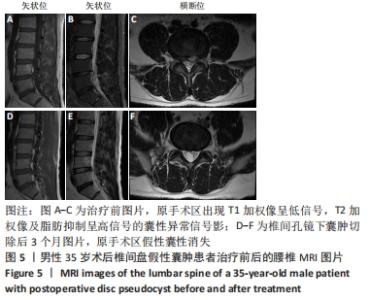
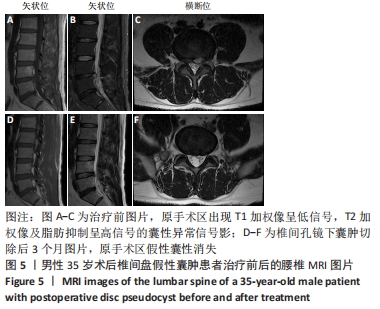
病例5:35岁男性患者,因“腰痛伴左下肢疼痛半年,加重10余天”入院。体格检查:L4-5椎棘突及椎旁肌肉压叩痛明显,伴左下肢小腿外侧,足背,足拇趾放射痛,目测类比评分为8分,左下肢直腿抬高试验30°(+),加强试验(+),左下肢小腿外侧、后侧、外踝、足背浅感觉减退。左下肢胫前肌、踇背伸肌力4级,其余肌力未见明显异常。双侧病理征未引出。术前检查:腰椎平片及动力位片未见明显异常。MRI检查提示:L4/5椎间盘突出,左侧神经根受压,硬膜囊受压。诊断为L4-L5椎间盘突出症。择期在全麻下经皮椎间孔镜下椎板间隙入路L4/5髓核摘除手术。术后患者疼痛症状明显缓解,目测类比评分为1分,麻木症状有所改善。1周后好转出院。 术后40 d,患者无明显诱因出现左下肢小腿外侧,足背,足拇趾胀痛不适。查体:左下肢小腿外侧,足背,足拇趾放射痛,目测类比评分为6分。左下肢直腿抬高试验50°(+),加强试验(+),左下肢小腿外侧、后侧、外踝、足背浅感觉减退。肌力未见明显异常。复查MRI示:L4/5椎间盘切除术后,L4/5椎间盘左后方见大小约1.0 cm×1.3 cm囊性异常信号影,T1加权像呈低信号,T2加权像及脂肪抑制呈高信号,并与椎间盘相通,邻近左侧椎间孔狭窄,见图5A-C。与患者及其家属沟通后,同意行椎间孔镜下囊肿切除手术,术中见肉芽组织增生,术后患者疼痛明显缓解,目测类比评分为2分,之后好转出院。出院后3个月复查MRI,假性囊肿消失,见图5D-F。术后6,9,12个月随访,患者未诉腰腿痛等不适。 "
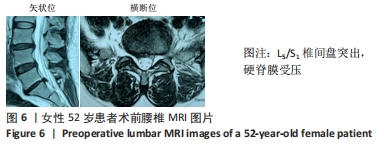
病例6:52岁女性患者,因“腰痛伴右下肢放射痛半年,加重5 d”入院。查体:L5/S1棘突及椎旁肌肉压、叩痛,伴右臀部、大腿后外侧、小腿后侧放射痛,目测类比评分为7分,腰椎屈伸、旋转部分受限,以屈曲为主;右下肢直腿抬高试验50°(+)、加强试验(+);右足跖屈肌肌力约Ⅳ级,余下肢肌力V级,双下肢浅感觉未见明显减退。在另外一家医院完善腰椎MRI,提示:L3/4、L4/5椎间盘纤维环撕裂,L5/S1椎间盘突出,见图6。腰椎X射线片无明显异常,腰椎CT示L5/S1椎间盘突出。择期在全麻下行后路椎间盘镜下行L5/S1椎间盘髓核摘除手术,神经根松解手术。术后患者症状明显缓解,腰腿疼痛目测类比评分降至1分。之后护腰保护,出院随访。 "
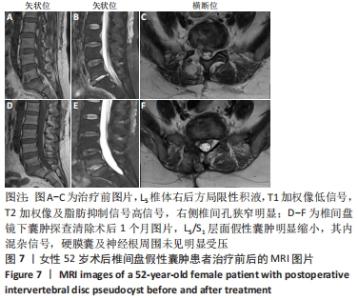
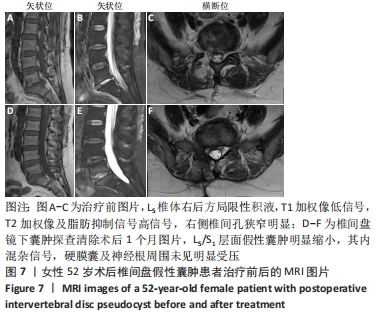
术后36 d,患者无明显诱因再次出现腰痛伴右下肢放射痛。查体:腰椎屈伸、旋转部分受限;L5/S1棘突及椎旁肌肉压、叩痛,伴右臀部、大腿后外侧、小腿后侧放射痛,目测类比评分为8分,右下肢直腿抬高试验40°(+)、加强试验(+);双下肢肌力Ⅴ级,双下肢浅感觉未见明显减退。实验室检查:血常规、C-反应蛋白、红细胞沉降率及降钙素原未见异常。复查MRI示:L5/S1椎间盘髓核摘除术后,L5/S1后缘后纵韧带前方囊性灶大小约1.0 cm×1.7 cm,椎管受压明显,见图7A-C。诊断为术后症状性椎间盘假性囊肿,因患者腰腿疼症状明显,在全麻下行椎间盘镜下囊肿探查清除手术,术中镜下见淡红色肉芽组织增生,切除囊性肿物,神经根减压充分。囊液为清亮液体,未见明显突出或游离髄核样组织,取囊壁进行病理检查,术后组织病理学(提示L5-S1局灶肉芽组织增生伴大量炎性细胞浸润,见图8。术后腰部及右下肢放射痛症状明显缓解,随访1个月,患者未诉腰腿痛不适,复查腰椎MRI示原假性囊肿明显缩小,硬膜囊及神经根周围无明显受压,见图7D-F。随访3个月,患者未再出现腰腿痛等不适。 "
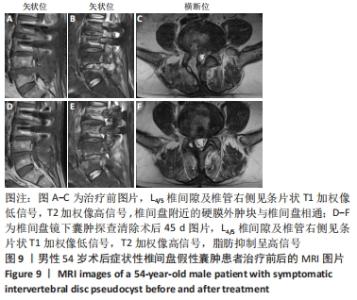
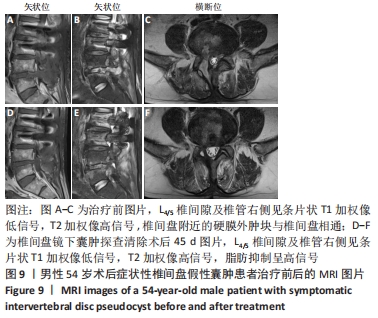
病例7:54岁男性患者,因“反复腰腿痛6年以上,加重10余天”入院。入院查体:L4/5椎棘突及椎盘肌肉压叩痛明显,右下肢放射痛,沿右大腿外侧、右小腿外侧放射至右足背,腰椎屈伸、旋转部分受限,以屈曲为著;右下肢直腿抬高试验40°(+),加强试验(+),右大腿外侧、右小腿外侧、右足背浅感觉减退,右侧股四头肌4级,右胫前肌力3+级,右足拇趾背伸肌力3+级,右跖屈肌力4级,左下肢肌力未见明显减退。入院完善腰椎MRI示:L2/3、L3/4、L4/5椎间盘膨出,L3椎体后缘低信号,游离髓核?其余检查无明显异常。结合患者症状和体征,择期在全身麻醉下行后路L2/3椎管减压、髓核摘除、L2/3椎间植骨融合内固定+后路椎间盘镜下L4/5椎间盘髓核摘除,神经根松解手术。术后患者腰腿痛症状明显减轻,病情平稳后出院。 术后1个月左右,患者诉右侧腰骶部及臀区间歇性胀痛,久站、久坐和久行后加重,卧床休息后可缓解。之后疼痛间断发作,术后约2个月,患者右侧腰骶部及臀区间歇性胀痛加重,伴右髋部活动受限,卧床休息后症状缓解不明显。查体:L4/5椎间隙、L5/S1椎间隙及右侧椎旁肌肉压叩痛明显;目测类比评分为7分,腰椎屈伸、旋转部分受限;右下肢直腿抬高试验45°(+)、加强试验(+);右臀部、大腿后外侧、小腿外侧、外踝浅感觉减退;右侧髂腰肌肌力2+级,股四头肌肌力3+级,右足背伸及足拇趾背伸肌力4级,跖屈肌肌力3+级;左下肢肌力、浅感觉未见明显异常。复查腰椎MRI示:腰椎术后改变,L4/5椎间隙及椎管右侧条状异常信号,术后包裹性积液,见图9A-C。实验室检查:血常规、C-反应蛋白、红细胞沉降率及降钙素原未见异常。回顾文献,考虑上述临床特征及影像学表现,诊断为术后症状性椎间盘假性囊肿,之后行椎间盘镜下囊肿探查清除手术,术中L4/5手术区域发现包裹性囊性积液,张力明显,尽可能地切除囊肿壁并送病理检查,术后组织病理学示致密纤维结缔组织,囊壁内未见内衬上皮细胞及新生血管,未见椎间盘及含铁血红素巨噬细胞成分,见图10。术后患者的腰骶部及臀区疼痛得到缓解,给予常规药物治疗,手术24 h后,患者起床,在腰支撑带的保护下行走。手术1周后,患者病情明显改善出院。在2个月的随访期间,患者未诉腰腿痛等不适。术后45 d复查MRI示:腰椎术后改变,L4/5椎间隙及椎管右侧条状异常信号,范围较前明显缩小,见图9D-F。硬膜囊及神经根周围无致压物。 "
| [1] YOUNG PM, FENTON DS, CZERVIONKE LF. Postoperative annular pseudocyst: report of two cases with an unusual complication after microdiscectomy, and successful treatment by percutaneous aspiration and steroid injection. Spine J. 2009;9:e9-e15. [2] AYDIN S, ABUZAYED B, YILDIRIM H, et al. Discal cysts of the lumbar spine: report of five cases and review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2010;19:1621-1626. [3] KANG SH, PARK SW. Symptomatic postdiscectomy pseudocyst after endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Korean Neurosug Noc. 2001;49(1):31-36. [4] SHIBOI R, OSHIMA Y, KANEKO T, et al. Different operative findings of cases predicted to be symptomatic discal pseudocysts after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. J Spine Surg. 2017;3(2):233-237. [5] CHUNG D, CHO DC, SUNG JK, et al. Retrospective report of symptomatic postoperative discal pseudocyst after lumbar discectomy. Acta Neurochir. 2012;154(4):715-722. [6] 邱小明.椎间孔镜术后并发症状性椎间盘假性囊肿二例报告及相关文献复习[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(17):1114-1120. [7] CHIBA K, TOYAMA Y, MATSUMOTO M, et al. Intraspinal cyst communicating with the intervertebral disc in the lumbar spine: discal cyst. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26:2112-2118. [8] KONO K, NAKAMURA H, INOUE Y, et al. Intraspinal extradural cysts communicating with adjacent herniated disks: imaging characteristics and possible pathogenesis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20:1373-1377. [9] 吴环宇,张明彦,刘向阳,等.经皮内窥镜下腰椎间盘切除术后并发假性囊肿3例报道[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(5):475-480. [10] XU W, WU D,CHEN C, et al. Symptomatic Postoperative Discal Pseudocyst After Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy: Case Report and Literature Review. Orthop Surg. 2020;13(1):347-352. [11] JHA SC, TONOGAI I, HIGASHINO K, et al. Postoperative discalcyst: An unusual complication after microendoscopic discectomy in teenagers. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2016;9(1): 89-92. [12] LI J, LIANG S, XIE W, et al. Symptomatic postoperative discal pseudocyst following percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine. 2021;100(3):e24026. [13] PRASAD GL, MENON GR. Post-discectomy annular pseudocyst: A rare cause of failed back syndrome. NeurolIndia. 2017;65(3):650-652. [14] 王国军,余将明,韩庭良,等.经皮椎间孔镜治疗椎间盘切除术后症状性椎间盘假性囊肿1例[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(9):862-864. [15] 高琨,董视师,胡美琴.椎间孔镜Beis技术治疗椎间盘术后假性囊肿1例[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(1):8. |
| [1] | Lü Qianyi, Chen Xinyi, Zheng Huie, He Haolong, Li Qilong, Chen Chutao, Tian Haomei. Stress and displacement of normal lumbar vertebra and posterior structure with different elbow pressing methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1346-1350. |
| [2] | Ma Chao, Wang Fei, Liu Xiaomin, Wang Ziyun, Xu Kui, Yang Wendong, Feng Wei. Quantification of the objective index of lumbar disc herniation with body surface topography map: three-dimensional angulation of the elastically fixed turning point of the lower back curve [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 924-928. |
| [3] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [4] | Wang Yiming, Yang Fengdong, Mao Wenbin, Jia Xin, Wei Shuxin, Wei Xinting. Comparison of clinical application of skull repair materials of three-dimensional digital shaping polyether ether ketone and titanium mesh [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5492-5497. |
| [5] | Xue Huawei, Zhu Min, Li Yuqian. Interleukin-27 is associated with the pathogenesis of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3750-3755. |
| [6] | Yang Yang, Liu Jiajia, Xue Jianhua, Liu Yunfei, Yao Yu. Correlation between interleukin 23/helper T17 cell axis and lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2190-2195. |
| [7] | Yin Xunlu, Jin Zhefeng, Zhu Liguo, Feng Minshan, Yu Jie, Wei Xu, Zhan Jiawen, Gao Chunyu, Yin He, Liang Long, Han Tao, Sun Kai, Xie Rui . Effect and mechanism of mechanical factors on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1816-1821. |
| [8] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [9] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [10] | Gu Honglin, Zheng Xiaoqing, Liang Changxiang, Zeng Shixing, Zhan Shiqiang, Chang Yunbing. Long-term survival rate and reoperation of Wallis interspinous dynamic stabilization system for treatment of lumbar degenerative disc disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(30): 4863-4869. |
| [11] | Xie Zhifeng, Liu Qing, Liu Bing, Zhang Tao, Li Kun, Zhang Chunqiu, Sun Yanfang. Biomechanical characteristics of the lumbar disc after fatigue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 339-343. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, He Bingkun, Wu Zhuotan, Wu Sixian, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng. An exploration on the mechanism of Shaoyao Gancao Decoction in treating early pain of lumbar disc herniation based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3194-3201. |
| [13] | Hou Yulong, Wang Jingshi, Wang Xukai. Potential mechanism of Achyranthes bidentata in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2734-2739. |
| [14] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Zhou Xiaohong, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Tongdu Huoxue Decoction-medicated serum inhibits pyroptosis in annulus fibrosus cells of the intervertebral disc [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2148-2153. |
| [15] | Qian Yuzhang, Wang Nan, Dong Yuqi, Xie Lin, Kang Ran. Factors for the recurrence of lumbar disc herniation after percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5886-5896. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||