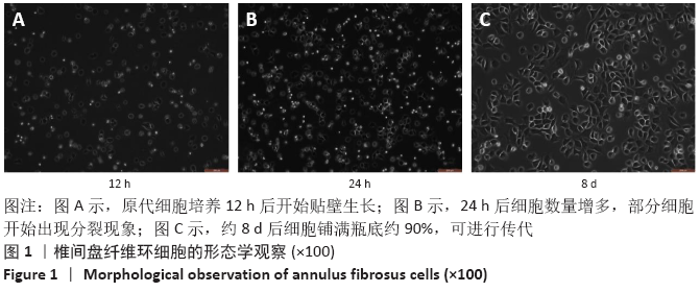
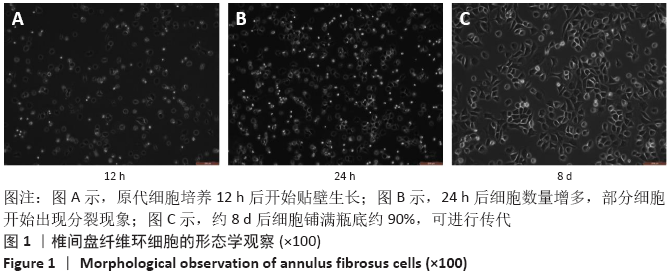
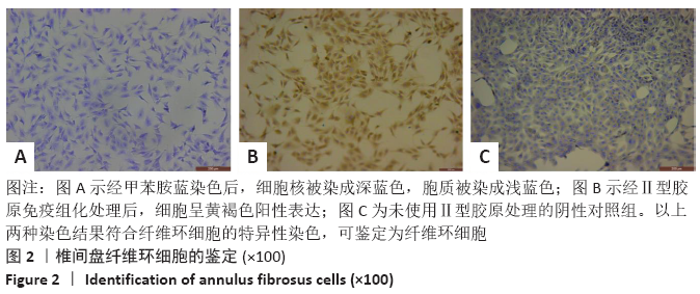
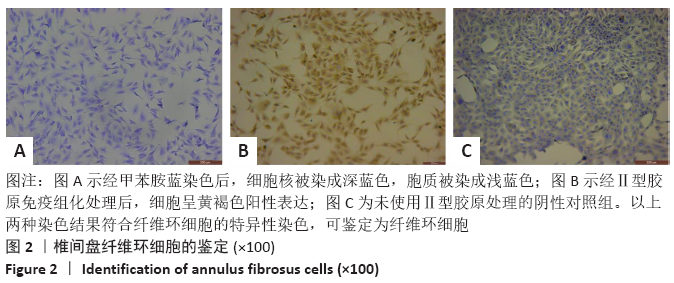
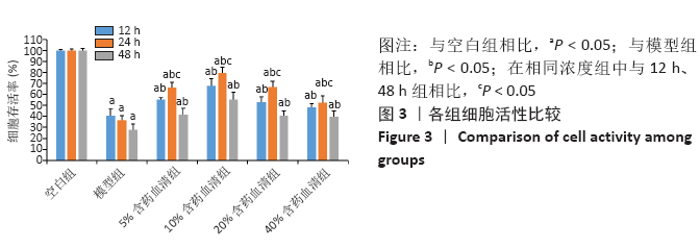
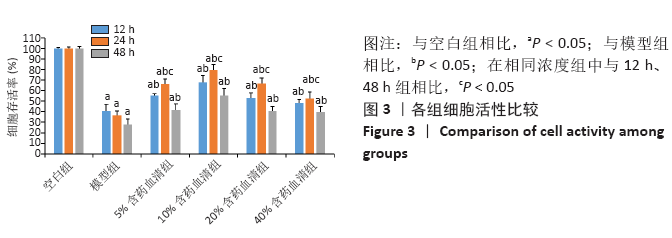
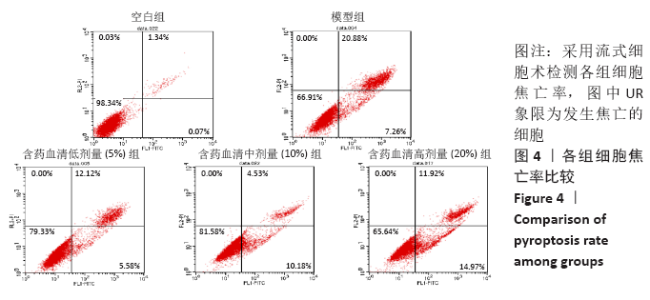
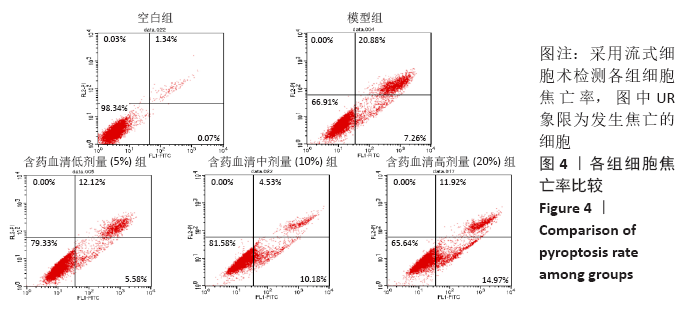
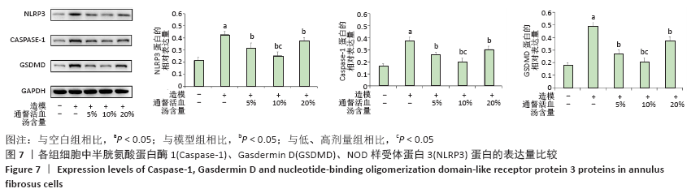
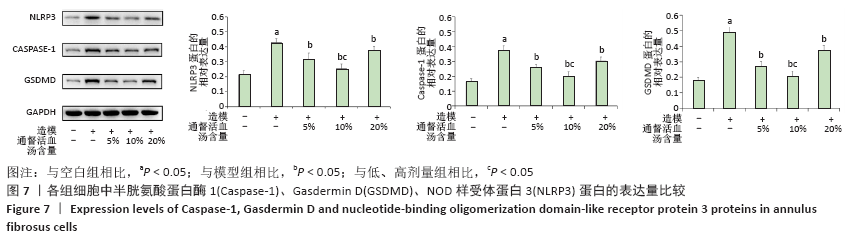
[1] 黑龙,赵建国,马莉琼,等. 腰椎间盘突出症患者突出椎间盘及相邻椎间盘退变程度的MRI分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(9): 807-812.
[2] 马金超, 伍骥, 郑超, 等. 腰椎椎间盘退变的临床及实验室评价方法研究进展[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2016,14(1): 53-57.
[3] CARLA C, ANA JS, PAULO P,et al. The Inflammatory Response in the Regression of Lumb-ar Disc Herniation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1): 251.
[4] IVAN CG, TATIANA CG, GIANCARLO MP, et al. Inflammation in the Intervertebral Disc Her-niation. Neurocirugia(Astur). 2020;10(20): S1130-1473.
[5] SHI JJ, GAO WQ, SHAO F, et al. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(4): 245-254.
[6] 邢栋, 王焕焕, 吕勃. 细胞程序性坏死与细胞焦亡[J]. 生理科学进展, 2020,51(2):113-116.
[7] 鄢来军, 颜浪辉, 林庆宾, 等. 通督活血汤对大鼠脊髓损伤后内质网应激信号表达的影响[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(5):1-4+9.
[8] 蒋顺琬, 陈大宇, 麦庆春. 通督活血汤治疗腰椎手术失败综合征临床研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2018,36(7):1640-1642.
[9] 黄导,丑钢,谢添,等. 通督活血汤配合经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗腰椎骨折[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2018,24(1):92-94.
[10] ZHAO LR, XING RL, WANG PM, et al. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate LP-S/ATP-induced pyropt-osis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Reports. 2018;17(4):5463-5469.
[11] 纪雪霞, 郭远波, 邱倩琪, 等. 丙泊酚抑制内毒素血症中巨噬细胞发生焦亡的分子机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2020,40(4):525-530.
[12] 金新蒙, 杨铁毅, 王雷. 纤维环退变机制及生物学治疗的研究综述[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(2):156-160.
[13] PURMESSUR D, WALTER BA, ROUGHLEY PJ, et al. A role for TNFa in intervertebral disc degeneration: a non-recoverable catabolic shift. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;433(1):151-156.
[14] V VO N, HARTMAN RA, YURUBE T, et al. Expression and regulation of metalloproteinas-es and their inhibitors in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Spine. 2013;13(3):331-341.
[15] WEILER C, SCHIETZSCH M, KIRCHNER T, et al. Age-related changes in human cervical, th-oracal and lumbar intervertebral disc exhibit a strong intra-individual correlation. Eur Spine. 2012;21(6):S810-818.
[16] VERGROESEN PP, KINGMA I, EMANUEL KS, et al. Mechanics and Biology in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: A Vicious Circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(7):1057-1070.
[17] SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by Inflammatory Caspases Deter-mines Pyroptotic Cell Death. Nature. 2015;526(7575): 660-665.
[18] MIAO EA, RAJAN JV, ADEREM A. Caspase-1-induced pyroptotic cell death. Immunol Rev. 2011;243(1):206-214.
[19] JORGENSEN I, MIAO EA. Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol Rev. 2015;265(1):130-142.
[20] ZU Y, MU Y, LI Q, et al. Icariin Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting NLRP3-mediat-ed Pyroptosis. Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):307.
[21] 杨留志,杨娜.通督活血汤联合针刺治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[J]. 哈尔滨医药,2017,37(5):472-473.
[22] 梁平,周绍稳.通督活血汤治疗退行性腰椎管狭窄症112例[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2014,22(8):55-56.
[23] 王婷,戴冀斌.盘龙七片联合通督活血汤治疗风湿痹阻型腰椎管狭窄症临床观察[J]. 中国药业,2019,28(2):64-66.
[24] 颜浪辉,鄢来军,林庆宾,等. 通督活血汤对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后炎症反应影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2020 ,22(4):51-54.
[25] 吴昊,董秋梅.通督活血汤抗炎镇痛作用的实验研究[J]. 中医研究, 2016,29(1):63-65.
[26] 丁兵.通督活血汤治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学,2016.
[27] SHI J, GAO W, SHAO F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(4):245-254.
[28] WANG K, SUN Q, ZHONG X, et al. Structural Mechanism for GSDMD Targeting by Au-toprocessed Caspases in Pyroptosis. Cell . 2020;180(5): 941-955.
|