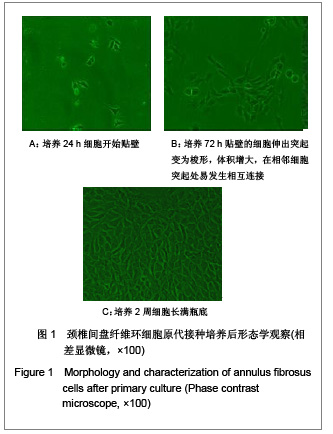
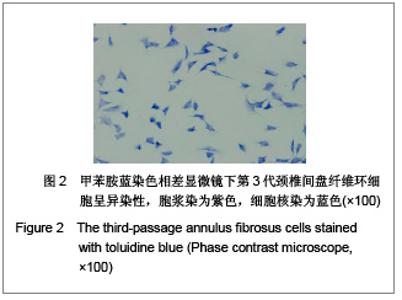
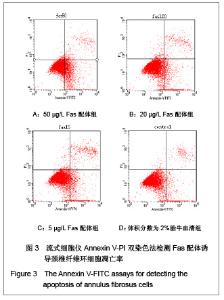
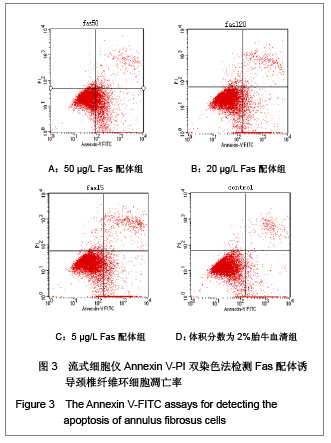
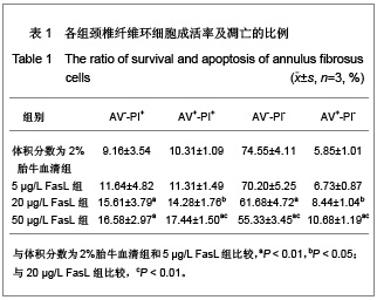
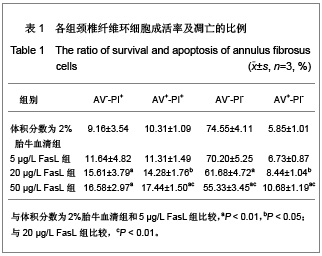
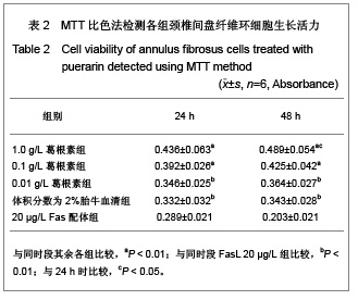
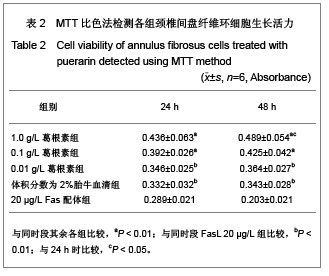
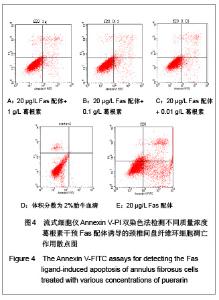
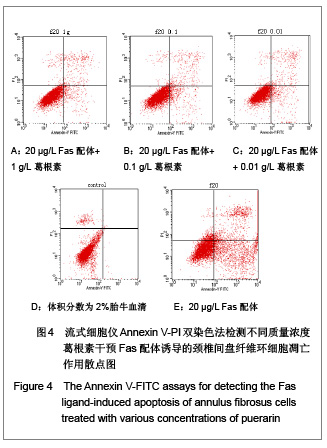
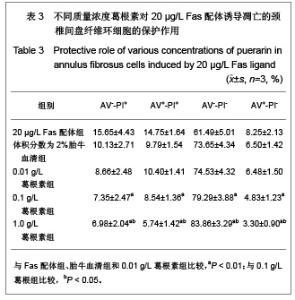
| [1] Wang SZ,Chen SJ,Song HM. Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun yu Shijian. 2005;11(11):956. 王诗忠,陈水金,宋红梅.颈椎间歇性拔伸手法治疗青年颈椎病的疗效分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2005,11(11):956.[2] Adams MA, Roughley PJ.What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2151-2161.[3] Zhao CQ, Jiang LS, Dai LY.Programmed cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration.Apoptosis. 2006;11(12): 2079-2088.[4] Park JB, Kim KW, Han CW,et al. Expression of Fas receptor on disc cells in herniated lumbar disc tissue.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(2):142-146.[5] Park JB, Chang H, Kim KW.Expression of Fas ligand and apoptosis of disc cells in herniated lumbar disc tissue.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(6):618-621.[6] Rannou F, Lee TS, Zhou RH,et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration: the role of the mitochondrial pathway in annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis induced by overload.Am J Pathol. 2004;164(3):915-924.[7] Cui LY, Liu SL, Ding Y,et al. IL-1beta sensitizes rat intervertebral disc cells to Fas ligand mediated apoptosis in vitro.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28(10):1671-1676.[8] Hadjipavlou AG, Tzermiadianos MN, Bogduk N,et al. The pathophysiology of disc degeneration: a critical review.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(10):1261-1270.[9] Wang YJ,Shi Q,Li JS,et al. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi. 2003;18(7):403-406. 王拥军,施杞,李家顺,等.椎间盘细胞信号传导及益气化瘀方调控机理的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2003,18(7):403-406.[10] Yang J. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi. 2004;31(7):559. 杨军.颈椎病常用内服中药选配规律[J].辽宁中医杂志,2004, 31(7): 559. [11] Zhao GC,Li CR. Sichuan Shengli Kexue Zazhi. 2009;31(1): 24-25. 赵桂昌,李才锐.葛根素注射液对颈椎病的临床观察[J].四川生理科学杂志, 2009,31(1):24-25.[12] Song YJ. Yunnan Zhongyi Zhongyao Zazhi. 2001;22(3): 20-21. 宋云娟.葛根素治疗颈椎病的临床观察[J].云南中医中药杂志, 2001,22(3):20-21.[13] Qu SH. Xinjiang Zhongyiyao. 2005;23(5):28-29. 曲少华.葛根素配合针灸电脑中频治疗颈椎病31例[J].新疆中医药,2005,23(5):28-29.[14] Yang SH. Hebei Zhongyi. 2006;28(10):746. 杨绍华.葛根素合中药熏蒸治疗颈椎病临床观察[J].河北中医, 2006,28(10):746.[15] Jiang DH,Zhang AH. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi. 2004;10(10):759-761. 姜东辉,张爱华.葛根素配合手法治疗颈椎病62例临床疗效观察[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2004,10(10):759-761.[16] Zou QB. Zhongguo Xiandai Yaowu Yingyong. 2010;4(12): 382-384. 邹清波.葛根素对心血管系统的药用价值[J].中国现代药物应用, 2010,4(12):382-384.[17] Zhou Q,Wang YJ,Shi Q. Jizhu Waike Zazhi. 2003;1(4): 226-229. 周泉,王拥军,施杞.椎间盘纤维环细胞的培养[J].脊柱外科杂志, 2003,1(4):226-229.[18] Cui LY, Liu SL, Ding Y,et al. IL-1beta sensitizes rat intervertebral disc cells to Fas ligand mediated apoptosis in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28(10):1671-1676.[19] Wang WT,Hao ML,Wang FY,et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2006;22(8):1575-1580. 王万铁,郝卯林,王方岩,等.葛根素对肺缺血-再灌注损伤时Fas/FasL表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2006,22(8): 1575-1580.[20] Wen J,Chen SL,Xu HX. Xiandai Zhongyao Yanjiu yu Shijian. 2006;20(1):61-64. 温葭,陈士林,徐宏喜.葛根素对细胞凋亡影响的研究[J].现代中药研究与实践,2006,20(1):61-64.[21] Han JQ,Li GC,Zhou XL,et al. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xinnao Xueguanbing Zazhi. 2008;6(10):1179-1181. 韩江全,李官成,周晓兰,等.葛根素对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注后神经细胞凋亡及Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达的影响[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2008,6(10):1179-1181.[22] Xiao X,Mei GL,Hu WD,et al. Jiaotong Yixue. 2008;22(5): 472-473. 肖旭,梅广林,胡卫东,等.葛根素对大鼠肝缺血再灌注后Caspase-3和Bcl-2表达的影响[J].交通医学,2008,22(5): 472-473. |