[1] 李凝旭,黄莺,涂艳,等.绝经后女性骨密度与雌激素水平、免疫细胞因子和骨代谢指标的相关性研究[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2017, 33(8):1201-1204.
[2] 李方方,李东阳,赵红.肥胖对骨质疏松症分子水平影响的研究进展[J].山东医药,2014,54(29):106-108.
[3] 鲍晓雪,王娜,李玉坤.肥胖与骨质疏松症关系的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2015,9(14):2749-2753.
[4] 朱婷,周里钢.肥胖和骨的相关性研究最新进展[J].医学综述, 2015,21(8): 1351-1353.
[5] 石卫红,李小林,巫国辉,等.瘦素受体(OB-RGRP)水平对脂肪细胞的影响及其作用机制研究[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(11):90-93.
[6] PETTA S, GASTALDELLI A, REBELOS E, et al. Pathophysiology of Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2082.
[7] ÇELO E, KALARI B, TOTI F. A young adult with generalized lipodystrophy and diabetes mellitus (case report). Georgian Med News. 2018(277): 27-31.
[8] 赵永琴,董进.肥胖与骨质疏松症的相关性研究现状[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2017,11(1):136-139.
[9] 曹光球,叶义全,林思祖,等.福建永定县道地药材巴戟天现状分析及其发展对策[J].中国现代中药,2007(12):38-40.
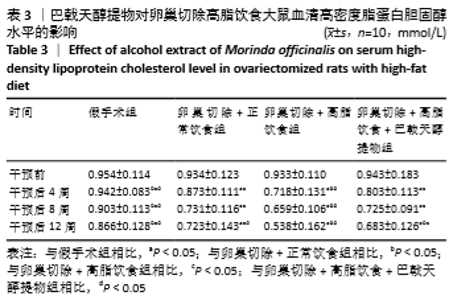
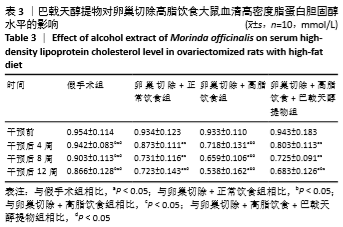
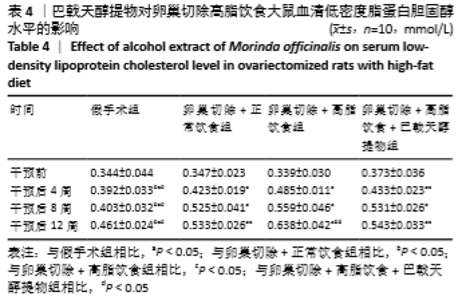
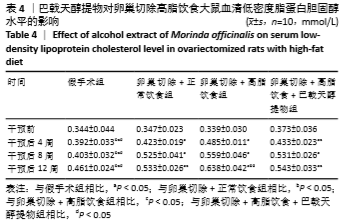
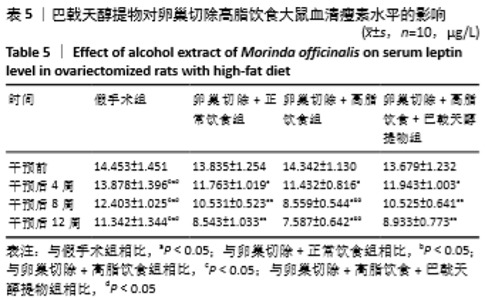
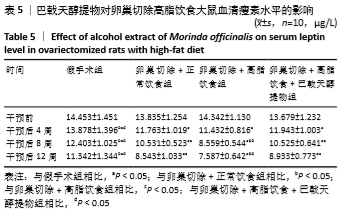
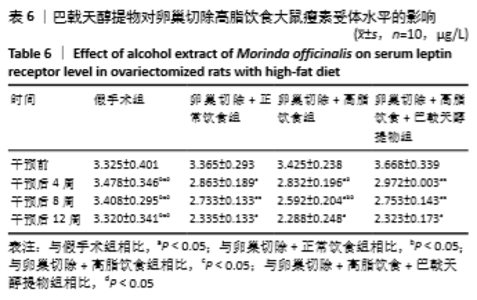
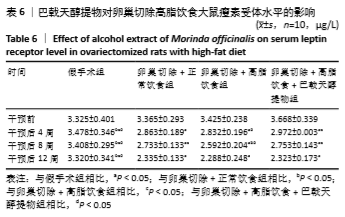
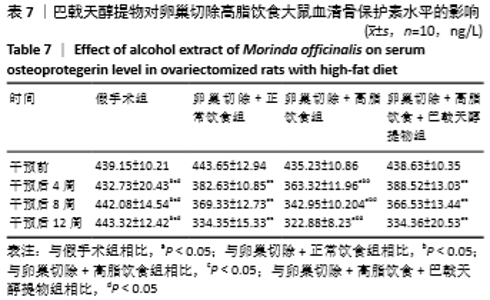
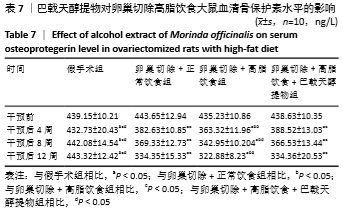
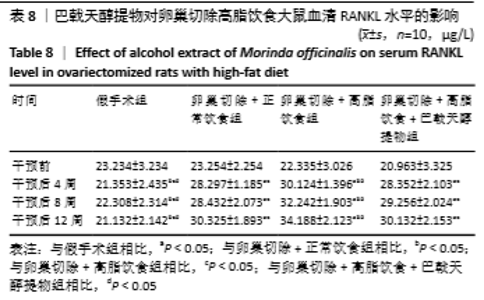
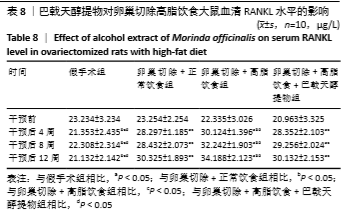
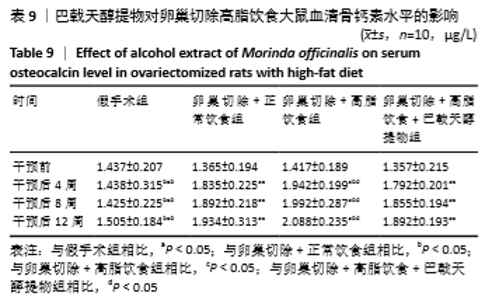
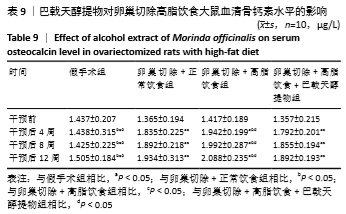
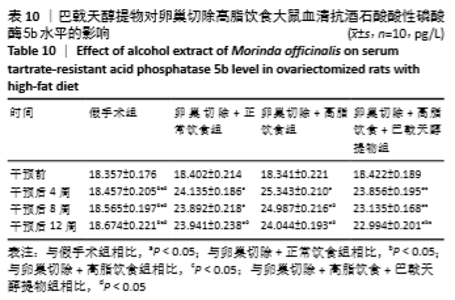
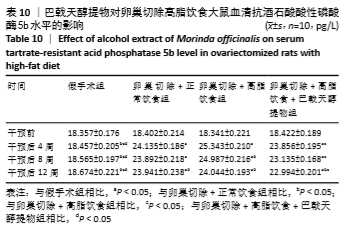
[10] 高曦,陈翔,黄朱宋,等.巴戟天醇提取物对卵巢切除大鼠在高脂饮食状态下骨质量的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(9): 1226-1230,1243.
[11] 王凤娟.巴戟天粗提物对微波辐射后下丘脑调控生精功能的影响[D].福州:福建医科大学,2013.
[12] 许兵,刘慧,金红婷,等.经典骨质疏松症模型大鼠的肾虚证研究[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(9):766-770.
[13] 王庆谚,郑洪新.补肾益气活血方对去势大鼠Wnt7b/β-catenin信号通路的调控机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(9):4249-4253.
[14] 周力学.绝经后骨质疏松症[J].新医学,2007,38(9):611-613.
[15] 朱晶,傅晓华,张岭,等.选择性雌激素受体调节剂对小鼠肥胖及脂代谢的作用[J].浙江医学,2018,40(12):1295-1298.
[16] 景彦林,杨修昭,白振军,等.高脂饮食诱导肥胖对雌性生育大鼠卵巢功能的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(8):106-110.
[17] 王雅媛,梁凤霞.热量控制对肥胖大鼠白色脂肪中瘦素及糖脂代谢的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(7):3247-3250.
[18] 曾春艳,梁秀文,邱珺,等.肥胖对骨质疏松调节机制的研究进展[J].呼伦贝尔学院学报,2016,24(4):78-81.
[19] 赵鹏,李树锋.瘦素对绝经后骨质疏松病人骨髓间质干细胞定向分化后增殖的影响及相关机制研究[J].安徽医药,2017,21(6): 1049-1054.
[20] 韩龙,万仕炜,王睿,等.脂肪因子与绝经后骨质疏松症关系研究进展[J].生命的化学,2018,38(4):524-528.
[21] VALLE M, GASCÓN F, MARTOS R, et al. Relationship between high plasma leptin concentrations and metabolic syndrome in obese pre-pubertal children. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27(1): 13-18.
[22] 李兰兰,任建功.瘦素、脂联素与代谢综合征的相关性研究进展[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2019,27(8):632-634.
[23] 王春花,王敏,刘鸿丽,等.瘦素与代谢综合征相关性的研究进展[J].当代医药论丛,2019,17(13):35-37.
[24] SUN X, WEI B, PENG Z, et al. Protective effects of Dipsacus asper polysaccharide on osteoporosis in vivo by regulating RANKL/RANK/ OPG/VEGF and PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019; 129:579-587.
[25] 唐小玲,毛绍蓉.更年期雌激素、孕酮、睾酮与肥胖的关系[J].标记免疫分析与临床,2010,17(2):132-133,121.
[26] 张明发,沈雅琴.女贞子及其活性成分抗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].药物评价研究,2014,37(6):566-571.
[27] 李晓曦,陈宇恒,唐秀凤,等.基于雌激素作用的淫羊藿女贞子配伍对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的影响研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2019(9):1-6,10.
[28] ZHANG Y, LAI WP, LEUNG PC, et al. Improvement of Ca balance by Fructus Ligustri Lucidi extract in aged female rats. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19(2):235-242.
[29] 潘奇,陈黔,钱黎.绝经后骨质疏松症患者血清TRACP-5b、Hcy、BAP水平变化及诊断效能[J].山东医药,2017,57(35):58-60.
[30] 王俊玲,黄思敏,梁启瑶,等.雌激素的来源及其在骨代谢中的作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):729-732.
[31] 孔德策,杨铁毅,邵进.绝经后骨质疏松骨代谢标志物研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(1):36-41.
[32] 易伟莲,廖德权,林柏云,等.绝经后骨质疏松症患者性激素、细胞因子及骨代谢指标的变化及关系[J].检验医学,2012,27(4):296-298. |