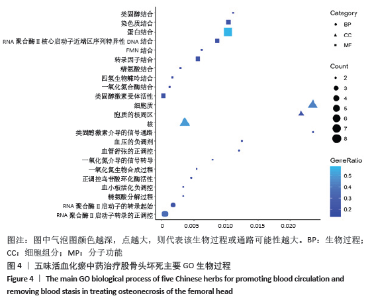
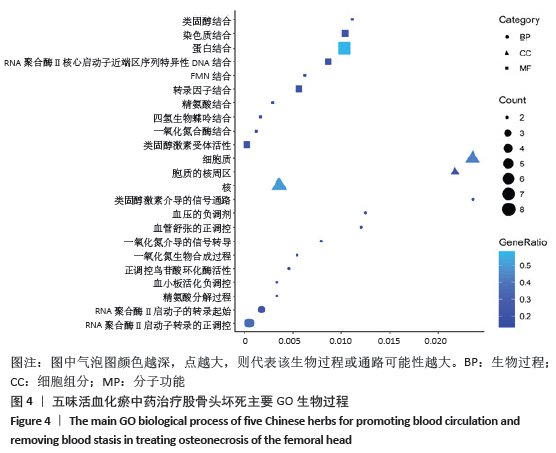
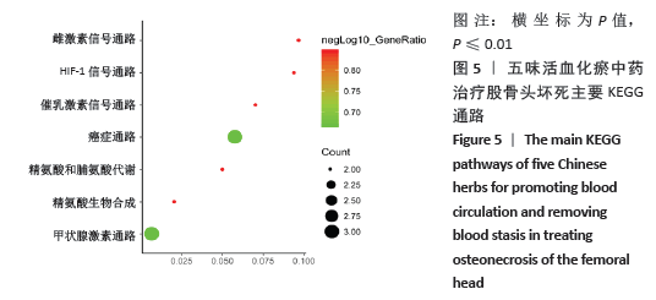
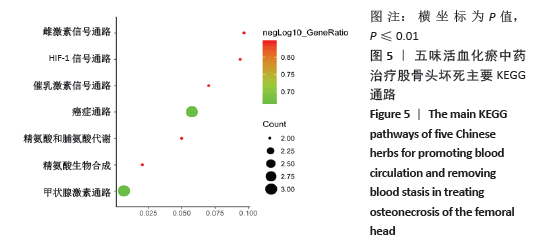
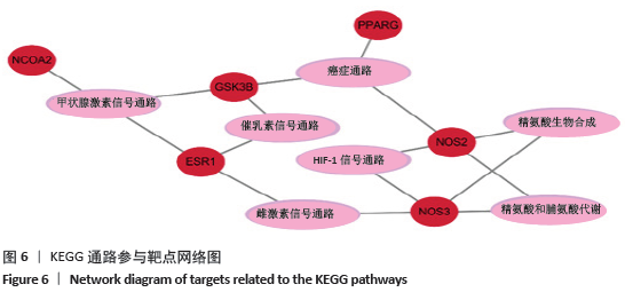
[1] WANG C, PENG J, LU S. Summary of the various treatments for osteonecrosis of the femoral head by mechanism: A review. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(3):700-706.
[2] CHEN SB, HU H, GAO YS, et al. Prevalence of Clinical Anxiety, Clinical Depression and Associated Risk Factors in Chinese Young and Middle-Aged Patients with Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Plos One. 2015;10(3):e120234.
[3] 何伟. 如何把握股骨头坏死患者的保髋治疗时机[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2016, 5(2):82-86.
[4] 何伟,陈镇秋,张庆文.补肾活血中药治疗股骨头坏死临床研究[J]. 新中医,2012, 44(4):50-51.
[5] 李慧英,王义生. 中药配合髓芯减压植骨空心螺钉支撑术治疗股骨头坏死的临床研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2011,26(8): 876-878.
[6] 李克庆. 经皮髓芯减压自体植骨结合复元活血汤治疗Ⅰ-Ⅱ期股骨头坏死[J]. 中医正骨,2005,17(9):63-64.
[7] 张永兴,徐法铭. 斯氏针髓芯减压加中药辨证治疗股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中国骨伤, 2006,19(5):301.
[8] WEI QS, HONG GJ, YUAN YJ,et al. Huo Xue Tong Luo capsule, a vasoactive herbal formula prevents progression of asymptomatic osteonecrosis of femoral head: A prospective study. J Orthop Translat. 2018;18:65-73.
[9] 李雄,袁浩.袁浩教授对股骨头坏死中医药论治的学术思想[J]. 中国中医骨伤科, 1999,7(1):61-62.
[10] 魏秋实.何伟.张庆文.等. 股骨头坏死中医证型分布规律的文献研究和系统评价[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2013, 7(3): 369-372.
[11] 韩晓蕊,洪郭驹,刘宇,等. 单侧激素性股骨头坏死患者正常侧股骨头脂肪含量及局部微循环:MR IDEAL-IQ和IVIM-DWI研究[J].放射学实践, 2017,32(12): 1291-1294.
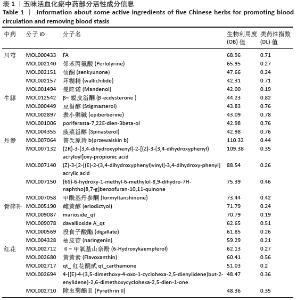
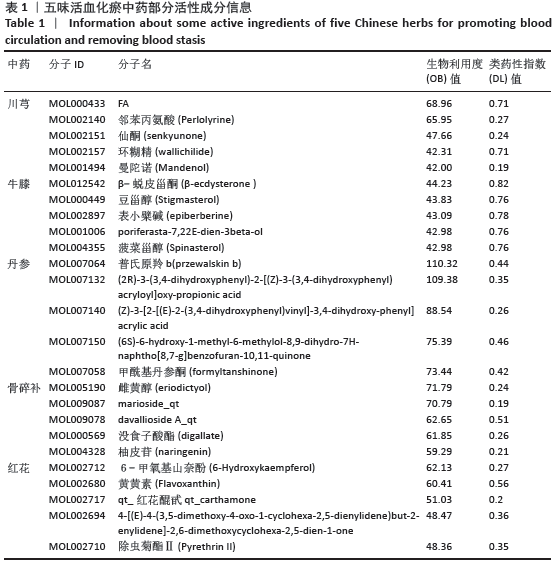
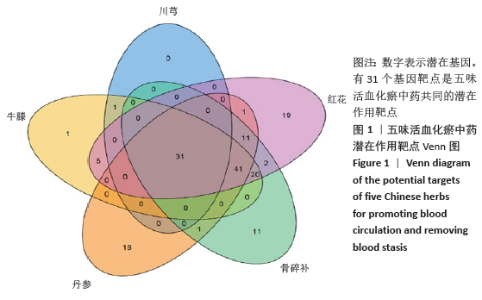
[12] 胡海,丰凡翔,雷孝勇,等.中医药治疗股骨头坏死的常用药物分析[J].中医正骨,2016,28(8):24-26.
[13] 高冲,刘璐,胡爱菊,等. 活血化瘀中药的药理作用研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2013,36(1):64-68.
[14] 黄明艳,刘超,王阶.活血化瘀中药促内皮祖细胞血管修复和新生研究进展[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2019,26(7):141-144.
[15] LI S, ZHANG B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application. Chin J Nat Med. 2013;11(2):110-120.
[16] 何伟.精确诊断前提下股骨头坏死非手术治疗实践[J]. 临床外科杂志,2017,25(8): 580-582.
[17] 魏秋实. 股骨头坏死证候学及中医药治疗适应症的规范化研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学, 2012.
[18] 魏秋实,杨帆,陈哓俊,等. 激素性与酒精性股骨头坏死患者骨标本坏死区域病理与显微结构特点分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(7):866-872.
[19] GUO C, HOU GQ, LI XD, et al. Quercetin triggers apoptosis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced osteoclasts and inhibits bone resorption in RAW264.7 cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(1):123-136.
[20] WANG XC, ZHAO NJ, GUO C, et al. Quercetin reversed lipopolysaccharide-induced inhibition of osteoblast differentiation through the mitogenactivated protein kinase pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(6):3320-3326.
[21] LEE HW, SUH JH, KIM HN, et al. Berberine Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation by Runx2 Activation With p38 MAPK. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(8):1227-1237.
[22] TAO K, XIAO D, WENG J, et al. Berberine promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Toxicol Lett. 2016;240(1): 68-80.
[23] 李琼静,罗琪.小檗碱通过激活PI3K/AKT通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的体外迁移[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(29): 4620-4624.
[24] LEE JW, IWAHASHI A, HASEGAWA S,et al. Coptisine inhibits RANKL-induced NF-κB phosphorylation in osteoclast precursors and suppresses function through the regulation of RANKL and OPG gene expression in osteoblastic cells. J Nat Med. 2012;66(1):8-16.
[25] 宋伟.丹参新酮抗血小板作用及对血栓形成的影响[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学, 2018.
[26] 肖倩,陈雄燕,欧阳清,等. 槲皮素对血小板凋亡的影响及其机制[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2019,27(5):1612-1616.
[27] KONDOH S, INOUE K, IGARASHI K, et al. Estrogen receptor alpha in osteocytes regulates trabecular bone formation in female mice. Bone. 2014;60:68-77.
[28] 张萌萌. 雌激素与雌激素受体骨代谢调节作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(5): 704-708.
[29] BALESTRIERI A, MADEO B, ROCHIRA V, et al. Bilateral osteonecrosis of the femoral head in an adult man affected by congenital estrogen deficiency. J Endocrinol Invest. 2003;26(8):762-764.
[30] SHARMA D, LARRIERA AI, PALACIO-MANCHENO PE,et al. The effects of estrogen deficiency on cortical bone microporosity and mineralization. Bone. 2018;110:1-10.
[31] 宋淑珍,吴建平,高良霜,等. 过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ信号通路调控脂质代谢的研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020,32(4):1473-1483.
[32] 周龙涛,韦标方,任金钊,等. 酒精性股骨头坏死发病机制的研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2015,4(4):67-71.
[33] 韩雨薇,张媛媛,赖秀英,等. 中药对一氧化氮合酶/一氧化氮系统调节作用的研究进展[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2017, 48(1):8-15.
[34] REID IR. Short-term and long-term effects of osteoporosis therapies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015;11(7):418-428.
[35] DAVIS PJ, DAVIS FB, MOUSA SA, et al. Membrane Receptor for Thyroid Hormone: Physiologic and Pharmacologic Implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;51(1): 99-115.
[36] 王苹苹,孔繁平,陈学群,等. 低氧细胞应激的HIF-1信号通路[J]. 浙江大学学报(医学版),2011,40(5):559-566.
[37] 陆蕴松,高忠礼,刘光耀. 低氧诱导因子-1对血管内皮生长因子的调控[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2009,29(7):905-907.
[38] YOSHIDA T, ZHANG H, IWASE T, et al. Digoxin inhibits retinal ischemia-induced HIF-1alpha expression and ocular neovascularization. FASEB J. 2010;24(6):1759-1767.
[39] SANO M, MINAMINO T, TOKO H, et al. p53-induced inhibition of Hif-1 causes cardiac dysfunction during pressure overload. Nature. 2007;446(7134):444-448.
[40] SHIBLI-RAHHAL A, SCHLECHTE J.The effects of hyperprolactinemia on bone and fat. Pituitary. 2009;12(2):96-104. |