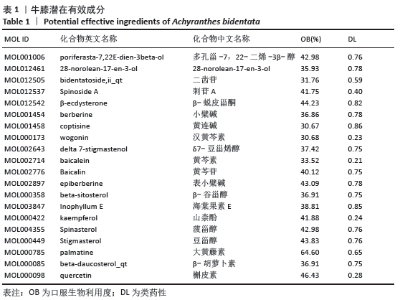
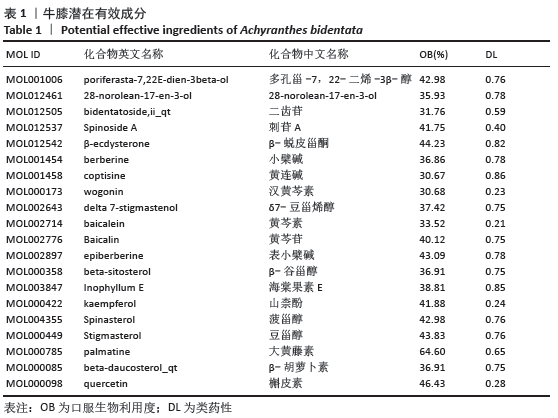
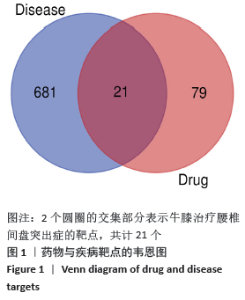
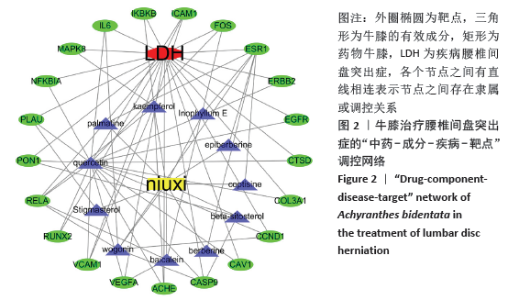
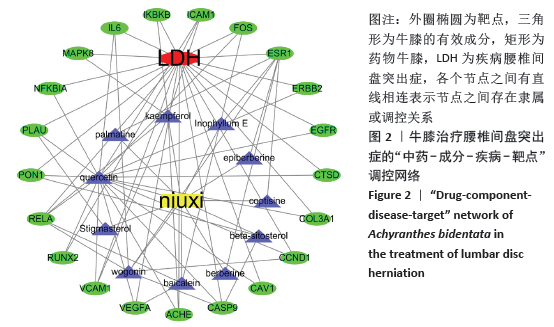
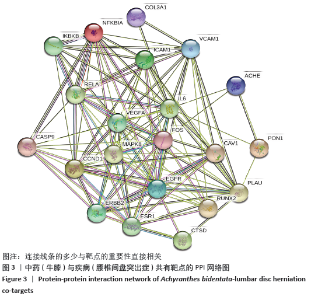
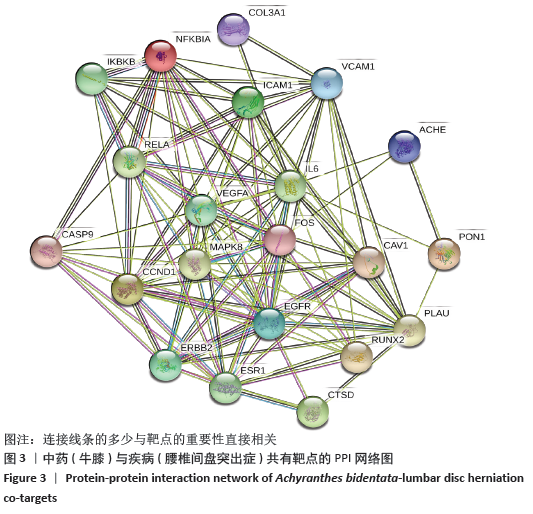
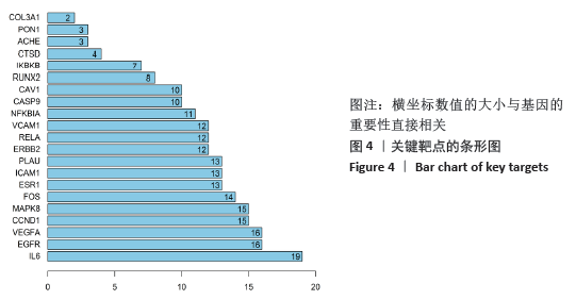
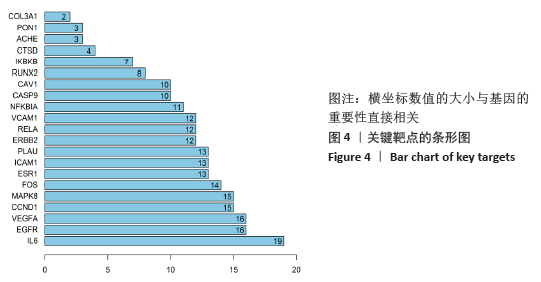
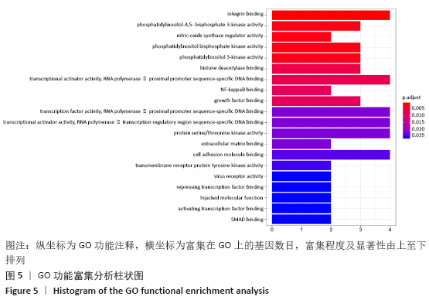
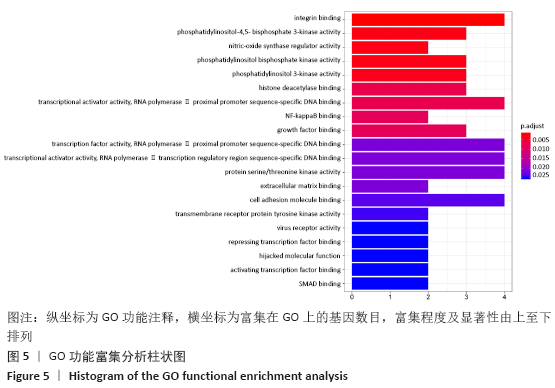
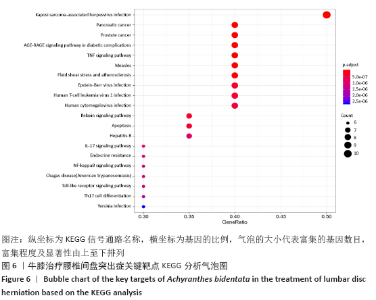
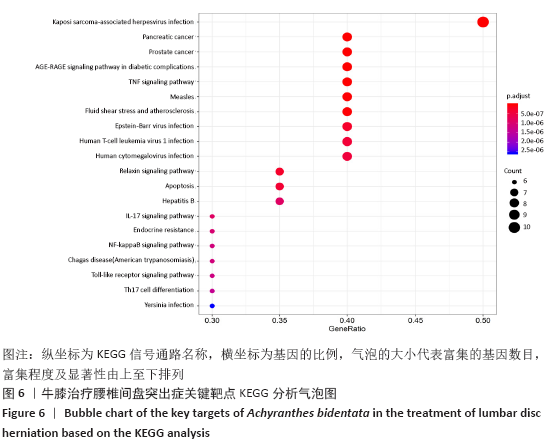
[1] 孙凯,朱立国,魏戌,等.身痛逐瘀汤治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效和安全性的系统评价和Meta分析[J].中国中药杂志, 2020,45(5):1159-1166.
[2] KREINER DS, FERNAND R, GHISELLI G, et al. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Spine J. 2014;14(1):180.
[3] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃.腰椎间盘突出症疼痛发生机制的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(7):568.
[4] 郭召. miRNA-502在椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡中的表达及干预机制[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2019.
[5] WONG JJ, COTG J, SUTTON DA, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the noninvasive management of low back pain:a systematic review by the ontario protocol for traffic injury management (OPTIMa) collaboration. Eur J Pain. 2017;21(2):201-216.
[6] 李朝辉.基于数据挖掘的治疗腰椎间盘突出症的用药规律探讨[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2017.
[7] 熊婷,何堃,孙梦盛,等.基于网络药理学的牛膝防治阿尔茨海默病的物质基础与作用机制研究[J].中草药,2019,50(1): 142-149.
[8] 杨杰科,王嘉伟,周科望,等.独活寄生汤结合推拿对腰椎间盘突出疗效及TXB_2、TNF-α、IL-1β变化研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(2):44-46.
[9] 邓效禹,邓治英.加味身痛逐瘀汤配合牵引、针灸治疗腰椎间盘突出症效果及对血液流变学、疼痛指数和血清炎症因子水平的影响[J].四川中医,2018,36(6):148-151.
[10] 周银芝,夏淑芳,段晓梅,等.高脂日粮对肥胖易感和肥胖抵抗小鼠骨性能的影响以及槲皮素的干预作用[J].食品与生物技术学报,2019,38(7):100-107.
[11] 司海超,司小萌,刘展.槲皮素减轻坐骨神经慢性缩窄性损伤大鼠的神经病理性疼痛及其相关机制[J].第三军医大学学报,2017,39(1):54-59.
[12] WONG SK, CHIN KY, IMA-NIRWANA S. The Osteoprotective Effects Of Kaempferol:The Evidence From In Vivo And In Vitro Studies.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:3497-3514.
[13] 吉晓丽.黄芩的化学成分与药理作用研究进展[J].中医临床研究,2017,9(9): 128-129.
[14] 杨波,龙慧,王郑钢,等.黄芩素通过促进miR-29a-3p抑制MAP2K6改善骨性关节炎模型大鼠软骨细胞退化[J].中药药理与临床,2019,35(6):32-37.
[15] 刘威良,姬昱,黄艾祥.β-谷甾醇的研究及开发进展[J].农产品加工,2019(1): 77-79+82.
[16] 曾莉萍,徐贤柱,饶华,等.杜仲叶β-谷甾醇对成骨细胞和卵巢颗粒细胞的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2012,23(5):1051-1053.
[17] 马洪亮.腰痹通胶囊治疗腰椎间盘突出症疼痛的效果及对IL-6、IL-8因子的影响[J].空军医学杂志,2018,34(3):199-201+205.
[18] WEBER KT, ALIPUI DO, SISON CP, et al. Serum levels of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 vary based on diagnoses in individuals with lumbar intervertebral disc disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):3-8.
[19] DAGISTAN Y, CUKUR S, DAGISTAN E, et al. Importance of IL-6, MMP-1, IGF-1, and BAX Levels in lumbar herniated disks and posterior longitudinal ligament in patients with sciatic pain.World Neurosurg. 2015; 84(6):1739-1746.
[20] MARTIN LJ, SMITH SB, KHOUTORSKY A, et al. Epiregulin and EGFR interactions are involved in pain processing. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3353-3366.
[21] 黄杰聪,闻博,叶君健.TGF-α及EGFR在退变椎间盘髓核组织中的表达及与血管浸润的关系[J].中国冶金工业医学杂志, 2014,31(6):684-685.
[22] 曹凯,安洪,蒋电明.血管内皮生长因子及其对成骨的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005(06):427-429.
[23] 王庆来,周江涛,赵依娜.丝裂原活化蛋白激酶在退变兔腰椎间盘纤维环中基因表达的相关性研究[J].福建中医药,2013, 44(1):56-57.
[24] WU YM, VOIGT M, RAYHILL S, et al. Suprahepatic venacavaplasty (cavaplasty) with retrohepatic cava extension in liver transplantation: experience with first 115 cases. Transplantation. 2001;72(8): 1389-1394.
[25] 李小川,付勤,贾长青,等.一氧化氮合酶抑制剂对延缓腰椎间盘退变的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(4):479-481.
[26] 陈江,肖辉灯,孙旗,等.人椎间盘髓核细胞增殖活性与益肾活血通络方的干预调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8): 1200-1206.
[27] 关海森,刘全喜,卫星.鼠神经生长因子治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后神经功能恢复效果观察[J].中国现代药物应用,2017, 11(21):118-119.
[28] NG HH, SHEN M, SAMUEL CS, et al. Relaxin and extracellular matrix remodeling: Mechanisms and signaling pathways. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019;487:59-65.
[29] 丁惠娟,程智刚.PI3K/Akt介导TRPV1表达上调参与CCI大鼠神经病理性疼痛[J].中国医师杂志,2018,20(9):1392-1394.
[30] 李殿奇. PDGF-BB调节成、破骨细胞的作用机制及促进骨愈合的实验研究[D]. 武汉:武汉大学,2016.
[31] 林向全,郑忠,李超雄,等.细胞因子在椎间盘退变中的研究进展[J].湖南中医杂志,2016,32(12):185-188.
[32] ONDA A, YABUKI S, KIKUCHI S. Effects of neutralizing antibodies to tumor necrosis fact or-alpha on nucleus pulposus-induced abnormal nociresponses in rat dorsal horn neurons. Spine.2003;28(10):967-972.
[33] 李经坤. IL-17A在退变椎间盘炎症反应及股骨头坏死软骨退变中的作用及机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2016.
[34] 杨金丰,马三辉.聚集蛋白代谢通路基因多态性与腰椎间盘突出严重程度的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(31): 4939-4944.
[35] 吴伟平,江建明,瞿东滨,等. HIF-1α、MMP-2在退变腰椎间盘髓核中的表达及相关意义[J].南方医科大学学报,2010, 30(5):1152-1155.
[36] 盛云露,马丹,王思婷,等.不同年龄组男性人群甲状腺功能与骨密度及骨微结构的相关性[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2017,37(12):1577-1582. |