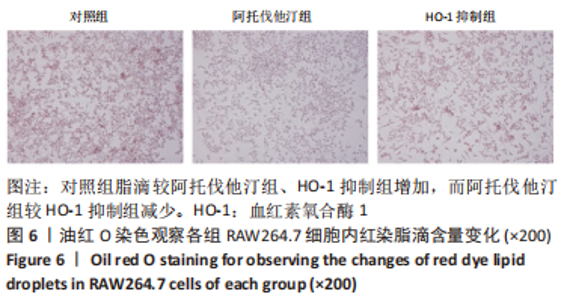
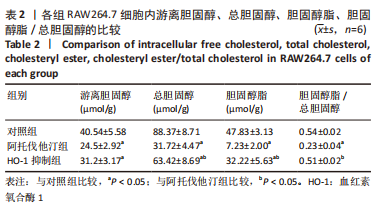
[1] ORSÓ E, GRANDL M, SCHMITZ G. Oxidized LDL-induced endolysosomal phospholipidosis and enzymatically modified LDL-induced foam cell formation determine specific lipid species modulation in human macrophages. Chem Phys Lipids. 2011;164(6):479-487.
[2] YAN Y, SONG D, WU J, et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs Link Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein With the Inflammatory Response of Macrophages in Atherogenesis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:24.
[3] LEE CH, KIM YJ, JANG JH, et al. Modulating macrophage polarization with divalent cations in nanostructured titanium implant surfaces. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(8):085101.
[4] NEOG MK, SULTANA F, RASOOL M. Targeting RAW 264.7 macrophages (M1 type) with Withaferin-A decorated mannosylated liposomes induces repolarization via downregulation of NF-κB and controlled elevation of STAT-3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:64-73.
[5] LIN P, JI HH, LI YJ, et al. Macrophage Plasticity and Atherosclerosis Therapy. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:679797.
[6] ZHANG B, MA Y, XIANG C. SIRT2 decreases atherosclerotic plaque formation in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice by modulating macrophage polarization. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 97:1238-1242.
[7] WANG Y, WANG Q, XU D. New insights into macrophage subsets in atherosclerosis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022;100(9):1239-1251.
[8] MANSOURI A, REINER Ž, RUSCICA M, et al. Antioxidant Effects of Statins by Modulating Nrf2 and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Different Diseases. J Clin Med. 2022;11(5):1313.
[9] KISHIMOTO Y, KONDO K, MOMIYAMA Y. The Protective Role of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Atherosclerotic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15): 3628.
[10] YACHIE A. Heme Oxygenase-1 Deficiency and Oxidative Stress: A Review of 9 Independent Human Cases and Animal Models. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1514.
[11] DURANTE W. Protective role of heme oxygenase-1 against inflammation in atherosclerosis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011;16(6):2372-2388.
[12] CHISTIAKOV DA, BOBRYSHEV YV, OREKHOV AN. Macrophage-mediated cholesterol handling in atherosclerosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20(1):17-28.
[13] ZHANG Y, SHI X, HAN J, et al. Convallatoxin Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization to Attenuate Atherosclerosis Through PPARγ-Integrin αvβ5 Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:803-812.
[14] MATSUO M. ABCA1 and ABCG1 as potential therapeutic targets for the prevention of atherosclerosis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022;148(2):197-203.
[15] WESTERTERP M, MURPHY AJ, WANG M, et al. Deficiency of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in macrophages increases inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis in mice. Circ Res. 2013; 112(11):1456-1465.
[16] CHEN X, ZHAO Y, GUO Z, et al. Transcriptional regulation of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 expression by a novel signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(11):8917-8923.
[17] 王玉香,燕燕,李永芳,等.沉默MAP4K4通过调控PPARγ/ABCA1通路缓解ox-LDL诱导的血管内皮细胞损伤[J].中国动脉硬化杂志, 2021,29(1):54-59.
[18] LI X, LUO H, YE Y, et al. β‑glucan, a dectin‑1 ligand, promotes macrophage M1 polarization via NF‑κB/autophagy pathway. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(1):271-282.
[19] ZHANG X, QIN Y, WAN X, et al. Rosuvastatin exerts anti-atherosclerotic effects by improving macrophage-related foam cell formation and polarization conversion via mediating autophagic activities. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):62.
[20] OUIMET M, FRANKLIN V, MAK E, et al. Autophagy regulates cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells via lysosomal acid lipase. Cell Metab. 2011;13(6):655-667.
[21] KHAMINETS A, BEHL C, DIKIC I. Ubiquitin-Dependent And Independent Signals In Selective Autophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26(1):6-16.
[22] KUMAR AV, MILLS J, LAPIERRE LR. Selective Autophagy Receptor p62/SQSTM1, a Pivotal Player in Stress and Aging. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:793328.
|