Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5304-5308.doi: 10.12307/2023.752
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ultrastructural features and clinical significance of autophagosome in benign meningiomas
Zhang Qi, Li Guilin, He Yanjiao
- Ultrastructural Pathology Department, Beijing Neurosurgical Institute, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100070, China
-
Received:2022-10-14Accepted:2022-12-13Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-03-30 -
Contact:Zhang Qi, MD, Assistant researcher, Ultrastructural Pathology Department, Beijing Neurosurgical Institute, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100070, China -
About author:Zhang Qi, MD, Assistant researcher, Ultrastructural Pathology Department, Beijing Neurosurgical Institute, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100070, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Qi, Li Guilin, He Yanjiao. Ultrastructural features and clinical significance of autophagosome in benign meningiomas[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5304-5308.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

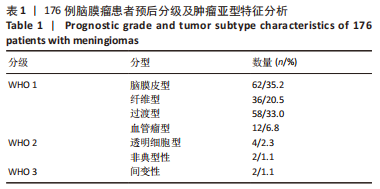
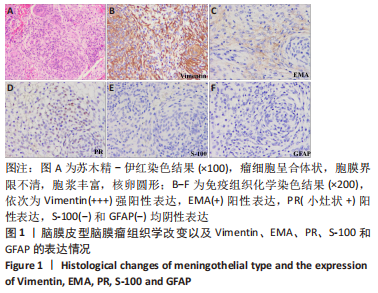
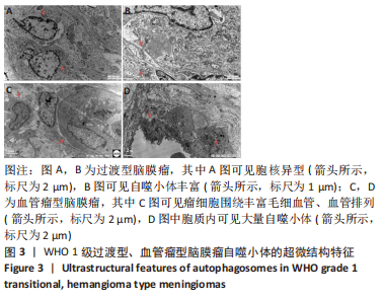
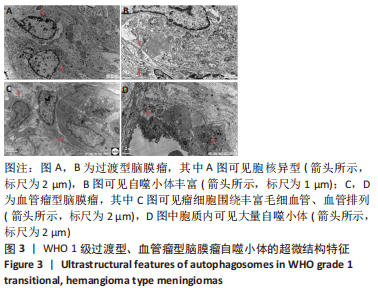
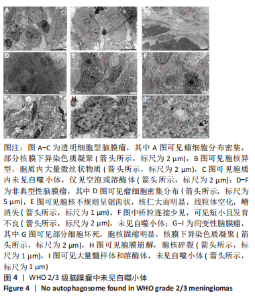
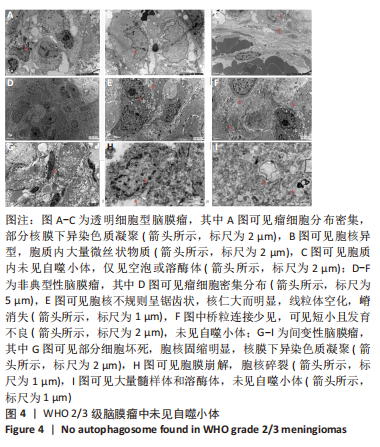
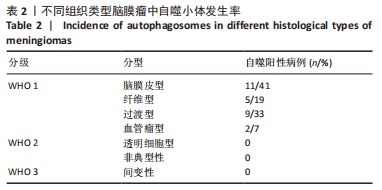
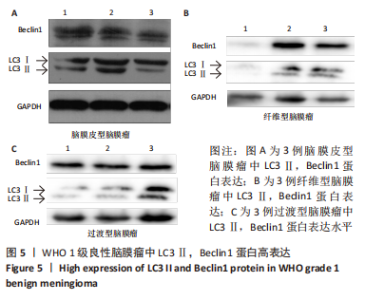
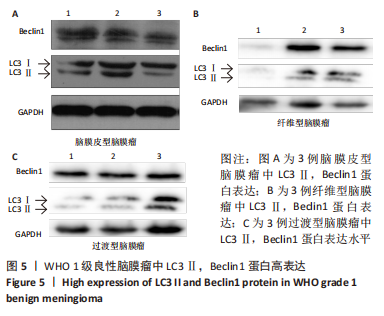
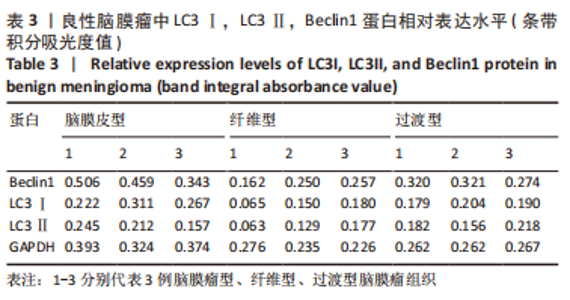
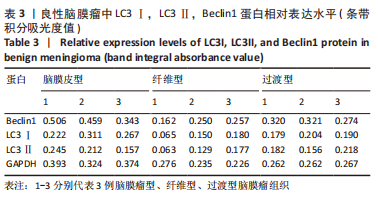
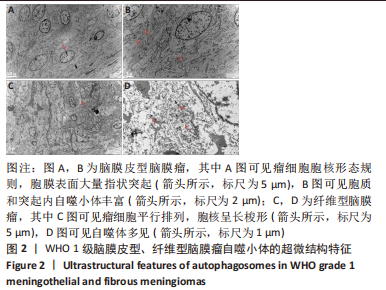
2.2 透射电镜观察结果 利用透射电子显微镜下观察不同组织类型脑膜瘤中自噬体超微结构特点,见图2-4。电镜下自噬体形态是包裹胞质组分的双层膜结构。判断病例为自噬阳性肿瘤的方法是观察3个以上自噬小体细胞视为阳性细胞,随机观察100个脑膜瘤细胞,计数细胞自噬体发生率。图2和图3分别显示WHO 1级不同组织类型脑膜瘤细胞和自噬小体的超微结构特点,图4显示WHO 2/3级脑膜瘤细胞超微结构特点。表2显示,WHO 1级良性脑膜瘤中过渡型(以脑膜皮型为主)和脑膜皮型脑膜瘤自噬体发生率较高,分别占比33%和41%,此外,纤维型占比19%,血管瘤型仅占7%,比例较低,此外,WHO 2级非典型性、透明细胞型和WHO 3级间变性均未见自噬体。"
| [1] GRITSCH S, BATCHELOR TT, GONZALEZ CASTRO LN. Diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications of the 2021 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer. 2022;128(1):47-58. [2] GONDAR R, PATET G, SCHALLER K, et al. Meningiomas and Cognitive Impairment after Treatment: A Systematic and Narrative Review. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(8): 1846. [3] CORNIOLA MV, MELING TR. Management of Recurrent Meningiomas: State of the Art and Perspectives. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(16):3995. [4] LI X, HE S, MA B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):12. [5] ANTUNES F, ERUSTES AG, COSTA AJ, et al. Autophagy and intermittent fasting: the connection for cancer therapy? Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018;73(suppl 1):e814s. [6] USMAN RM, RAZZAQ F, AKBAR A, et al. Role and mechanism of autophagy-regulating factors in tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2021;17(3):193-208. [7] FENG X, ZHANG H, MENG L, et al. Hypoxia-induced acetylation of PAK1 enhances autophagy and promotes brain tumorigenesis via phosphorylating ATG5. Autophagy. 2021;17(3):723-742. [8] WHITE E. The role for autophagy in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(1):42-46. [9] ZAMAME RAMIREZ JA, ROMAGNOLI GG, KANENO R. Inhibiting autophagy to prevent drug resistance and improve anti-tumor therapy. Life Sci. 2021;265:118745. [10] LIU W, MENG Y, ZONG C, et al. Autophagy and Tumorigenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1207:275-299. [11] WANG Y, DU J, WU X, et al. Crosstalk between autophagy and microbiota in cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):163. [12] PARK S, CHA YJ, SUH SH, et al. Risk group-adapted adjuvant radiotherapy for WHO grade I and II skull base meningioma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019;145(5): 1351-1360. [13] MAGGIO I, FRANCESCHI E, TOSONI A, et al. Meningioma: not always a benign tumor. A review of advances in the treatment of meningiomas. CNS Oncol. 2021; 10(2):CNS72. [14] HORBINSKI C, BERGER T, PACKER RJ, et al. Clinical implications of the 2021 edition of the WHO classification of central nervous system tumours. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022;18(9):515-529. [15] PREUSSER M, BRASTIANOS PK, MAWRIN C. Advances in meningioma genetics: novel therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018;14(2):106-115. [16] KLIONSKY DJ, PETRONI G, AMARAVADI RK, et al. Autophagy in major human diseases. EMBO J. 2021;40(19):e108863. [17] CHEN X, YU C, KANG R, et al. Cellular degradation systems in ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(4):1135-1148. [18] LI W, HE P, HUANG Y, et al. Selective autophagy of intracellular organelles: recent research advances. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):222-256. [19] CAO W, LI J, YANG K, et al. An overview of autophagy: Mechanism, regulation and research progress. Bull Cancer. 2021;108(3):304-322. [20] ONORATI AV, DYCZYNSKI M, OJHA R, et al. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Cancer. 2018;124(16):3307-3318. [21] YANG K, NIU L, BAI Y, et al. Glioblastoma: Targeting the autophagy in tumorigenesis. Brain Res Bull. 2019;153:334-340. [22] YAMAZAKI T, BRAVO-SAN PEDRO JM, GALLUZZI L, et al. Autophagy in the cancer-immunity dialogue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;169:40-50. [23] XU Z, HAN X, OU D, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;104(2):575-587. [24] SMITH AG, MACLEOD KF. Autophagy, cancer stem cells and drug resistance. J Pathol. 2019;247(5):708-718. [25] COCCO S, LEONE A, PIEZZO M, et al. Targeting Autophagy in Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 22;21(21):7836. [26] 曲宝清,米蕊芳,杜江,等. 脑胶质瘤超微结构及组织形态观察39例[J].中国临床医生杂志,2019,47(5):63-65. [27] KOUSTAS E, SARANTIS P, THEOHARIS S, et al. Autophagy-related Proteins as a Prognostic Factor of Patients With Colorectal Cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2019; 42(10):767-776. [28] ROY BC, AHMED I, RAMALINGAM S, et al. Co-localization of autophagy-related protein p62 with cancer stem cell marker dclk1 may hamper dclk1’s elimination during colon cancer development and progression. Oncotarget. 2019;10(24):2340-2354. [29] TOTON E, LISIAK N, SAWICKA P, et al. Beclin-1 and its role as a target for anticancer therapy. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;65(4):459-467. [30] HAMURCU Z, DELIBAŞI N, GEÇENE S, et al. Targeting LC3 and Beclin-1 autophagy genes suppresses proliferation, survival, migration and invasion by inhibition of Cyclin-D1 and uPAR/Integrin β1/ Src signaling in triple negative breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018;144(3):415-430. [31] HU Y, LI X, XUE W, et al. TP53INP2-related basal autophagy is involved in the growth and malignant progression in human liposarcoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;88:562-568. [32] YING H, QU D, LIU C, et al. Chemoresistance is associated with Beclin-1 and PTEN expression in epithelial ovarian cancers. Oncol Lett. 2015;9(4):1759-1763. [33] WANG L, WANG J, XIONG H, et al. Co-targeting hexokinase 2-mediated Warburg effect and ULK1-dependent autophagy suppresses tumor growth of PTEN- and TP53-deficiency-driven castration-resistant prostate cancer. EBioMedicine. 2016; 7:50-61. [34] ABDELZAHER E, EL-GENDI SM, YEHYA A, et al. Recurrence of benign meningiomas: predictive value of proliferative index, BCL2, p53, hormonal receptors and HER2 expression. Br J Neurosurg. 2011;25(6):707-713. [35] DOMINGUES PH, SOUSA P, OTERO Á, et al. Proposal for a new risk stratification classification for meningioma based on patient age, WHO tumor grade, size, localization, and karyotype. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16(5):735-747. [36] FOLKERTS H, HILGENDORF S, VELLENGA E, et al. The multifaceted role of autophagy in cancer and the microenvironment. Med Res Rev. 2019;39(2):517-560. |
| [1] | Tao Bonan, Wang Yonglan, Jiang Lu, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Wan Xing, Huang Debin, Yuan Lin. Rougan Jiangmei Formula medicated serum inhibits activation and autophagy of human hepatic stellate cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5334-5341. |
| [2] | Wang Xing, Ageru, Jiregelegen, Zhang Chi, Zhao Lei, Zhang Yuanyuan, Bu Jiaqi, Keerqin, Zhao Xueting, Yang yuanhuizi, Wang Chaoqun, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Shi Jun, Li Zhijun. Aging morphological characteristics of uncinate process of cervical vertebra and its clinical significance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3580-3586. |
| [3] | Ma Hailong, Zhao Zhenqun, Liu Wanlin, Sun Jun. Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 is involved in the occurrence and development of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head in a rabbit model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5167-5172. |
| [4] | Li Zulong, Rong Zhen, Sun Hua, Jiang Ruiyuan, Zhong Xiaoting, Mo Chunmei. Mechanism underlying the effect of Fuhebeihua Recipe on the proliferation of CD133+HepG2 hepatoma stem cells and related autophagy proteins [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4988-4995. |
| [5] | Dong Liping, Luo Jia, Li Guangyi, Yuan Heng. Effect of aging on the ultrastructure of common iliac artery in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4123-4126. |
| [6] | Jiang Jie, Zhao Baixiao, Chen Libin, Wen Li, Zhang Shanshan, Ma Jie, Zhao Hua. Effect of moxibustion pretreatment on autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome expression in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3615-3619. |
| [7] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [8] | Huang Yunmei, Feng Fangfang, Chen Wenlie, Lu Xiaodong, Lin Ruhui, Li Zuanfang, Huang Meiya, Tan Chunjiang, Li Xihai, Li Xiaodong. Anti-inflammatory and anti-swelling effects of Tougu Xiaotong Capsule in rat models of early osteoarthritis with synovial edema [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2697-2702. |
| [9] | Wang Guoyu, Cheng Zhijian, Yang Baohui, Li Haopeng, He Xijing. Olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation promotes the ultrastructure repair at the lesion site of rat models of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 699-703. |
| [10] | Luo Xiaofei, Wei Xuan, Wang Jinliang, Wang Shaohua, Li Zhe, Bai Yu. Ultrastructural changes of tibial subchondral bone in patients with knee osteoarthritis: CT evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(15): 2399-2404. |
| [11] | Mo Binyu, Wei Tao, Li Jihui, Feng Haiyan, Chen Meiqiu, Wei Yumei. Changes of auditory function and mechanisms in tinnitus rats treated by Wuling Capsule [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5645-5651. |
| [12] | Pu Daojing, Zheng Fu, Xu Xianshun, Ding Wenjuan, Chen Yan, Zou Zhaoyin. Effects of sulforaphane on mitophagy-related proteins in nanobacteria-induced renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5503-5507. |
| [13] | Lin Xiaomin1, Pan Weibin1, Wu Yuqiong1, Fan Xiao2. Effects of Buyang Huanwu decoction on the expression of collagen type I and IV after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4986-4991. |
| [14] | Li Xue, Wang Ming-guo, Yang Shuai, Gao Jie, Fan Yuan-yuan, Song Yan. Ultrastructural changes of reconstructed mandibular condylar cartilage under continuous mandibular advancement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(29): 4634-4639. |
| [15] | Yang Yong, Lin Hui, Wen Zhao-ke, Huang Ai-lan, Wen Hong, Huang Guo-yong, Hu Yan-yan. Myocardial ultrastructure and hemodynamic changes of donor heart preserved in normothemic beating status [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(5): 851-858. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||