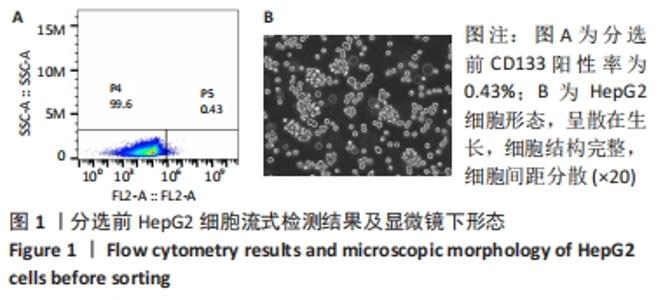
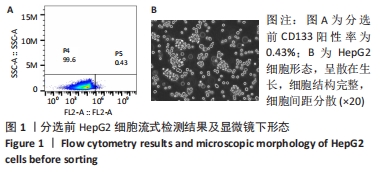
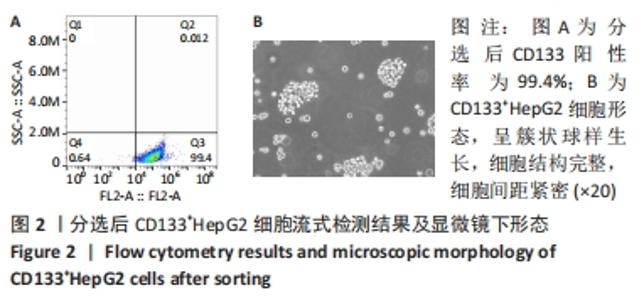
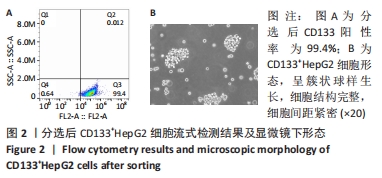
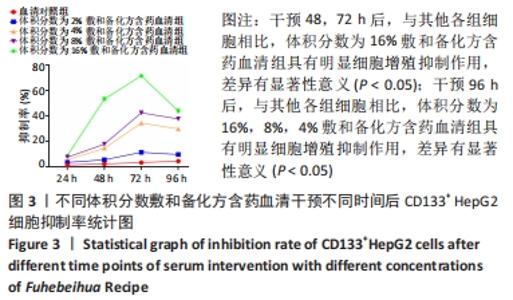
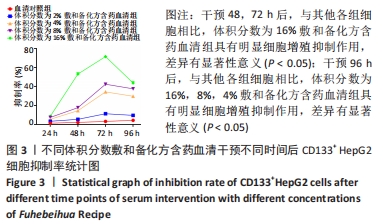
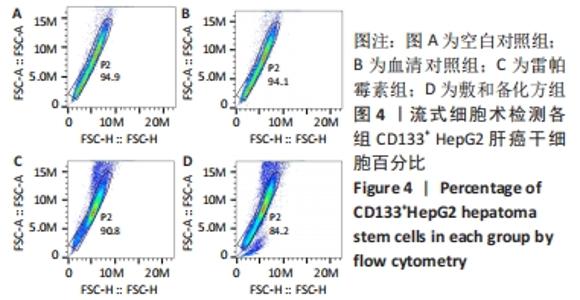
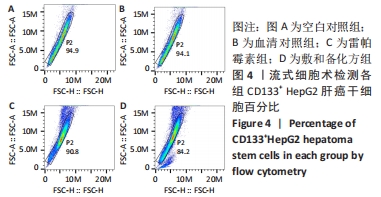
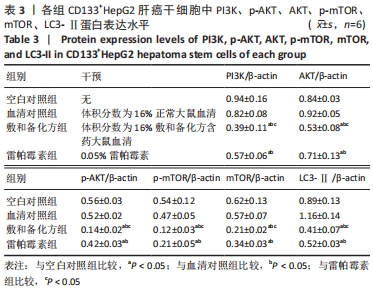
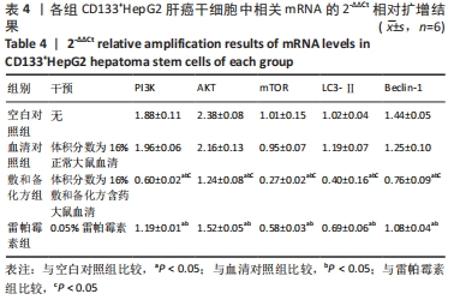
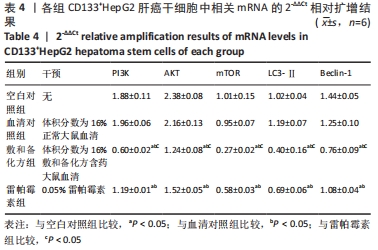
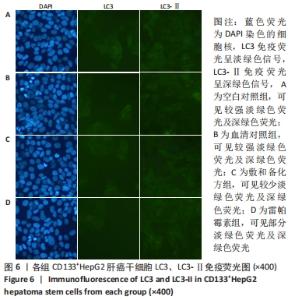
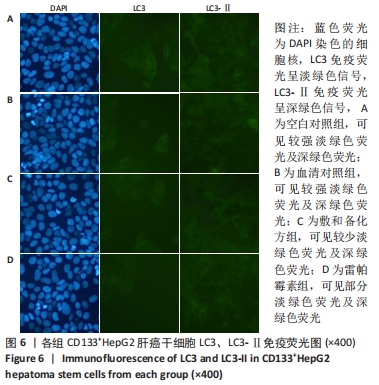
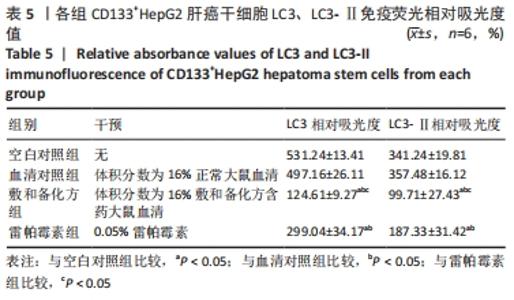
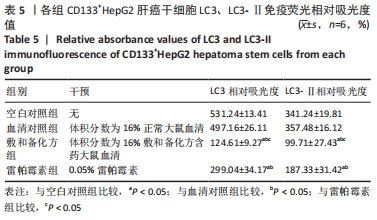
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (31): 4988-4995.doi: 10.12307/2022.992
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism underlying the effect of Fuhebeihua Recipe on the proliferation of CD133+HepG2 hepatoma stem cells and related autophagy proteins
Li Zulong1, Rong Zhen2, Sun Hua1, Jiang Ruiyuan1, Zhong Xiaoting1, Mo Chunmei2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Shenzhen Baoanchun Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment Hospital, Shenzhen 518100, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2021-08-05Accepted:2021-10-15Online:2022-11-08Published:2022-04-24 -
Contact:Mo Chunmei, Master, Chief physician, Shenzhen Baoanchun Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment Hospital, Shenzhen 518100, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Zulong, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760850 (to MCM); In-Hospital Preparation Research and Development of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2018ZJ004 (to MCM); National Science and Technology Major Special Project, No. 2018ZX10303502-001, 2018ZX10303502-002 (to MCM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zulong, Rong Zhen, Sun Hua, Jiang Ruiyuan, Zhong Xiaoting, Mo Chunmei. Mechanism underlying the effect of Fuhebeihua Recipe on the proliferation of CD133+HepG2 hepatoma stem cells and related autophagy proteins[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4988-4995.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
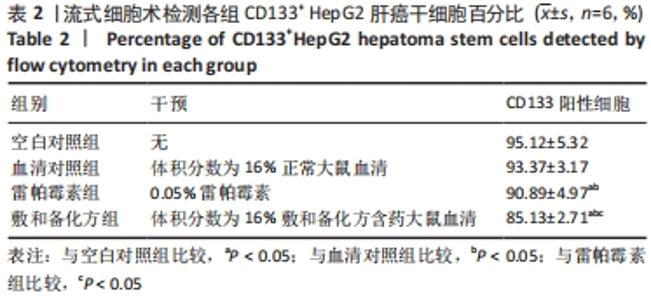
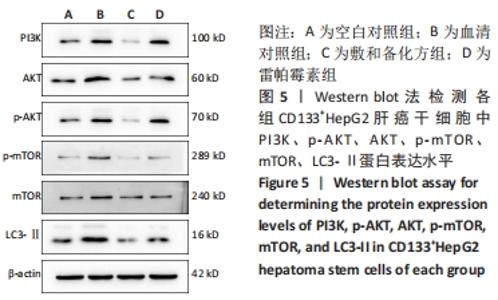
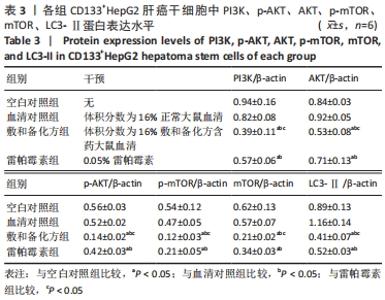
| [1] EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OF THE LIVER. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;69(1):182-236. [2] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [3] ZHANG X, MENG S, ZHANG R, et al. GP73-regulated oncolytic adenoviruses possess potent killing effect on human liver cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7(20):29346-29358. [4] LI X, HE S, MA B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):12-16. [5] DIKIC I, ELAZAR Z. Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(6):349-364. [6] GALLUZZI L, BRAVO-SAN PEDRO JM, Levine B, et al. Pharmacological modulation of autophagy: therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(7):487-511. [7] MATHEW R, WHITE E. Autophagy in tumorigenesis and energy metabolism: friend by day, foe by night. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011; 21(1):113-119. [8] XU Z, HAN X, OU D, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;104(2): 575-587. [9] XIE Y, SHI X, SHENG K, et al. PI3K/Akt signaling transduction pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2019; 19(2):783-791. [10] GUERTIN DA, SABATINI DM. The pharmacology of mTOR inhibition.Sci Signal. 2009;2(67):pe24. [11] 付彬.敷和备化方对肝癌干细胞的调控作用研究[D].南宁:广西中医药大学,2020. [12] SONG Y, JANG J, SHIN TH, et al. Sulfasalazine attenuates evading anticancer response of CD133-positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):38-42. [13] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394-424. [14] VILLANUEVA A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(15): 1450-1462. [15] RAGHAV PK, MANN Z. Cancer stem cells targets and combined therapies to prevent cancer recurrence. Life Sci. 2021;277:119465. [16] YANG ZF, NGAI P, HO DW, et al. Identification of local and circulating cancer stem cells in human liver cancer. Hepatology. 2008;47(3):919-928. [17] AGHAJANI M, MANSOORI B, MOHAMMADI A, et al. New emerging roles of CD133 in cancer stem cell: Signaling pathway and miRNA regulation. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):21642-21661. [18] TAKAMURA A, KOMATSU M, HARA T, et al. Autophagy-deficient mice develop multiple liver tumors. Genes Dev. 2011;25(8):795-800. [19] LI J, YANG B, ZHOU Q, et al. Autophagy promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion through activation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(6):1343-1351. [20] CHANG Y, YAN W, HE X, et al. miR-375 inhibits autophagy and reduces viability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells under hypoxic conditions. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(1):177-187. [21] WU DH, JIA CC, CHEN J, et al. Autophagic LC3B overexpression correlates with malignant progression and predicts a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(12):12225-12233. [22] LAZOVA R, CAMP RL, KLUMP V, et al. Punctate LC3B expression is a common feature of solid tumors and associated with proliferation, metastasis, and poor outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(2):370-379. [23] ZHOU Y, CHEN E, TANG Y, et al. miR-223 overexpression inhibits doxorubicin-induced autophagy by targeting FOXO3a and reverses chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(11):843-847. [24] ZHANG K, CHEN J, ZHOU H, et al. PU.1/microRNA-142-3p targets ATG5/ATG16L1 to inactivate autophagy and sensitize hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(3):312-318. [25] LEE YG, JEON TI. Modulation of the Autophagy-lysosomal Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Small Molecules. Molecules. 2020; 25(7):1580. [26] ISHIZAWA T, HASEGAWA K, AOKI T, et al. Neither multiple tumors nor portal hypertension are surgical contraindications for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(7):1908-1916. [27] LLOVET JM. Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2004;7(6):431-441. [28] CUCCHETTI A, PISCAGLIA F, CESCON M, et al. Cost-effectiveness of hepatic resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2013;59(2):300-307. [29] 尹常健.中医药治疗肝癌的几个理论与实践问题[J].中西医结合肝病杂志,2019,29(2):112-113,117. [30] 王磊,周荣耀.周荣耀补肾健健脾法治疗原发性肝癌经验[J].辽宁中医杂志,2014,41(2):2547-2548. |
| [1] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [2] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [3] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [4] | Cui Xing, Sun Xiaoqi, Zheng Wei, Ma Dexin. Huangqin Decoction regulates autophagy to intervene with intestinal acute graft-versus-host disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1057-1062. |
| [5] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [6] | Mo Weibin, Huang Tianchang, Zeng Zhiwei, Yan Linbo. Effects of Pueraria lobata flavonoids on expressions of beta-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in the brain of rats undergoing exhaustive exercise after long endurance exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 736-741. |
| [7] | Li Jiajun, Xia Tian, Liu Jiamin, Chen Feng, Chen Haote, Zhuo Yinghong, Wu Weifeng. Molecular mechanism by which icariin regulates osteogenic signaling pathways in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [8] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [9] | Li Weiming, Xu Qingwen, Li Yijun, Sun Yanbo, Cui Jin, Xu Pengyuan . Deep seawater promotes wound healing in diabetic mice by activating PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 724-729. |
| [10] | Qian Xiaofen, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Wang Hao, Zhou Shulong, Pan Haida. Screening key genes in synovium of osteoarthritis by a combination of differentially expressed genes and weighted co-expression network analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5342-5349. |
| [11] | Li Yi, Yang Yanjun, Peng Songyun, Cheng Zhigang, Zhong Kai, Yin Tianping, Tang Lianghua. Effect of Miao medicine Jiuxian Luohan Jiegu Decoction on osteogenic differentiation and fracture healing in tibial fracture rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5350-5356. |
| [12] | Yu Yunbao, Chen Lin, Wu Xiya, Yan Lerong, Miao Zhang, Man Yang, Jing Renyi, Lei Zhen, Chu Zhiqiang, Zhang Hongwei. Vascular endothelial growth factor-Notch signaling pathways in endothelial precursor cells in promoting the transformation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4946-4953. |
| [13] | Wang Xue, Liu Yang, Xu Jianfeng, Long Qianfa, Wang Tong, Zhong Jun. Neuroprotective effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on hippocampal neurons in mice with intracerebral hemorrhage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4928-4934. |
| [14] | Wei Hewei, Zheng Weipeng, Liu Zhijun, Zhao Guoyuan, Fang Weihua, Chen Sheng, Liao Zhihao, Wan Lei. Expression of autophagy in rotator cuff tendon stem cells induced by oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4954-4961. |
| [15] | Li Xiheng, Li Xinyue, Mao Tianjiao, Yang Wanqi, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Cannabidiol promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4867-4872. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||