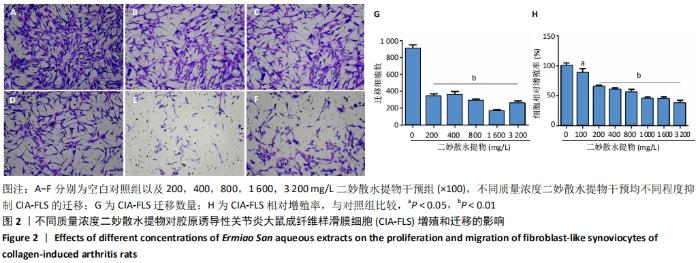
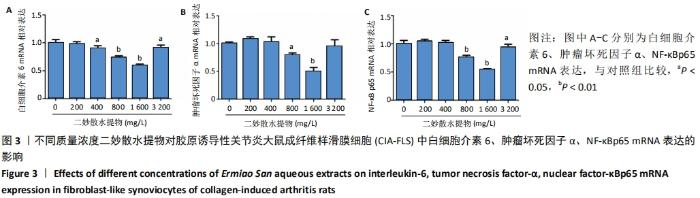
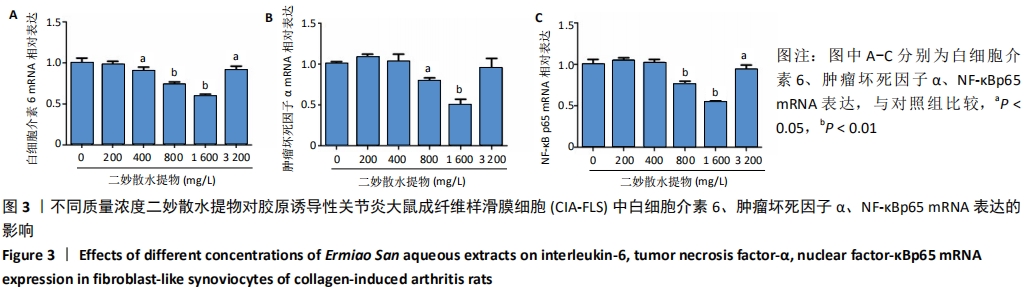
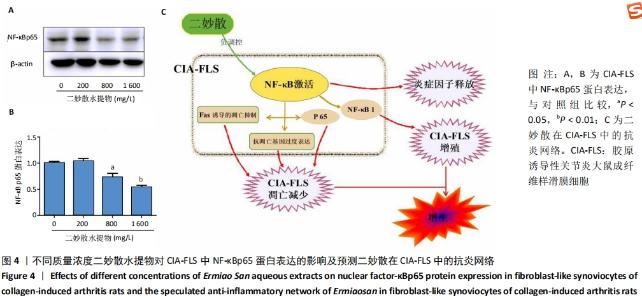
[1] VAAMONDE-GARCIA C, MALAISE O, CHARLIER E, et al. 15-Deoxy-Δ-12, 14-prostaglandin J2 acts cooperatively with prednisolone to reduce TGF-β-induced pro-fibrotic pathways in human osteoarthritis fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:66-78.
[2] FALCONER J, MURPHY AN, YOUNG SP, et al. Review: Synovial Cell Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(7):984-999.
[3] WANG S, WANG S, LI H, et al. Inhibition of the TGF-β/Smads signaling pathway attenuates pulmonary fibrosis and induces anti-proliferative effect on synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(5):1835-1845.
[4] CHAWLA M, ROY P, BASAK S. Role of the NF-κB system in context-specific tuning of the inflammatory gene response. Curr Opin Immunol. 2020;68:21-27.
[5] BROEREN MGA, WATERBORG CEJ, WIEGERTJES R, et al. A three-dimensional model to study human synovial pathology. ALTEX. 2019; 36(1):18-28.
[6] BAE S, JUNG Y, CHOI YM, et al. Effects of er-miao-san extracts on TNF-alpha-induced MMP-1 expression in human dermal fibroblasts. Biol Res. 2015;48(1):8.
[7] LAM FF, KO IW, NG ES, et al. Analgesic and anti-arthritic effects of Lingzhi and San Miao San supplementation in a rat model of arthritis induced by Freund’s complete adjuvant. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;120(1):44-50.
[8] NEGATBAKHSH SL, FARHADI E, TAHMASEBI MN, et al. NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis with focus on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Auto Immun Highlights. 2020; 11(1): 11-20.
[9] BRONDELLO JM, DJOUAD F, JORGENSEN C. Where to Stand with Stromal Cells and Chronic Synovitis in Rheumatoid Arthritis? Cells. 2019;8(10):1257.
[10] ABBASI M, MOUSAVI MJ, JAMALZEHI S, et al. Strategies toward rheumatoid arthritis therapy; the old and the new. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(7):10018-10031.
[11] CHEN Z, BOZEC A, RAMMING A, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019; 15(1):9-17.
[12] LONG M, PARK SG, STRICKLAND I, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB modulates regulatory T cell development by directly regulating expression of Foxp3 transcription factor. Immunity. 2009;31(6):921-931.
[13] ZHANG X, FENG H, DU J, et al. Aspirin promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation by blocking G0/G1 into S phase in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via downregulation of JAK/STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(6):3135-3148.
[14] BAI L, BAI Y, YANG Y, et al. Baicalin alleviates collagen‑induced arthritis and suppresses TLR2/MYD88/NF‑κB p65 signaling in rats and HFLS‑RAs. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(4):2833-2841.
[15] FURST DE. The risk of infections with biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;39(5):327-346.
[16] WANG L, DONG H, SONG G, et al. TXNDC5 synergizes with HSC70 to exacerbate the inflammatory phenotype of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis through NF-κB signaling. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018;15(7):685-696.
[17] ZHANG LM, ZHOU JJ, LUO CL. CYLD suppression enhances the pro-inflammatory effects and hyperproliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by enhancing NF-κB activation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):219.
[18] ZHANG W, ZHANG Q, XUAN Z, et al. The Protective Effect of Different Polar Solvent Extracts of Er Miao San on Rats with Adjuvant Arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:5305278.
[19] DAI X, DING M, ZHANG W, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Different Elution Fractions of Er-Miao-San on Acute Inflammation Induced by Carrageenan in Rat Paw Tissue. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:7958-7965.
[20] SANMARTÍ R, RUIZ-ESQUIDE V, BASTIDA C, et al. Tocilizumab in the treatment of adult rheumatoid arthritis. Immunotherapy. 2018;10(6): 447-464.
[21] 考希良,董嘉琪. 二妙散不同配伍对大鼠佐剂性关节炎的抗炎效应[J].中医药学报,2013,41(3):107-109.
[22] DAI X, YANG D, BAO J, et al. Er Miao San, a traditional Chinese herbal formula, attenuates complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats by regulating Th17/Treg cells. Pharm Biol. 2020;58(1):157-164.
[23] LI Z, HAO H, GAO Y, et al. Expression and localization analyses of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and α7nAchR in different tissues of rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Histochem. 2019;121(6):742-749.
[24] BOROVIKOVA LV, IVANOVA S, ZHANG M, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature. 2000;405(6785):458-462.
[25] LI Z, LIU J, HAO HQ, et al. Chinese Herbal Formula Ermiao Powder () Regulates Cholinergic Anti-inflammatory Pathway in Rats with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Chin J Integr Med. 2020;26(12):905-912.
|