Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (32): 5232-5239.doi: 10.12307/2021.230
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with Duhuo Jisheng Decoction in treating rheumatoid arthritis
Li Hongzhu1, 2, Yuan Si1, 2, Zhao Jiaying1, 2, Lu Liming1, 2, Xu Nenggui1, 2
- 1Medical College of Acupuncture and Rehabilitation, 2South China Research Center for Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-09-07Revised:2020-09-08Accepted:2020-10-26Online:2021-11-18Published:2021-07-26 -
Contact:Xu Nenggui, MD, Professor, Medical College of Acupuncture and Rehabilitation, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; South China Research Center for Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Hongzhu, MD candidate, Medical College of Acupuncture and Rehabilitation, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; South China Research Center for Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Program), No. 81704168 (to ZJY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Hongzhu, Yuan Si, Zhao Jiaying, Lu Liming, Xu Nenggui. Meta-analysis of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with Duhuo Jisheng Decoction in treating rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5232-5239.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
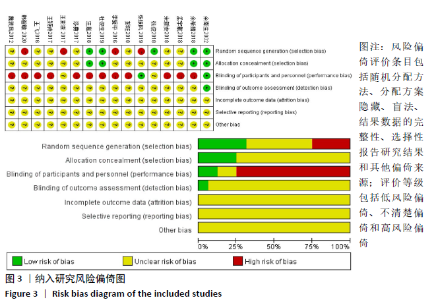
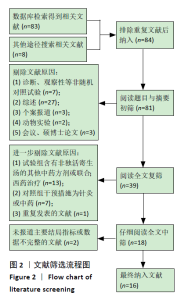
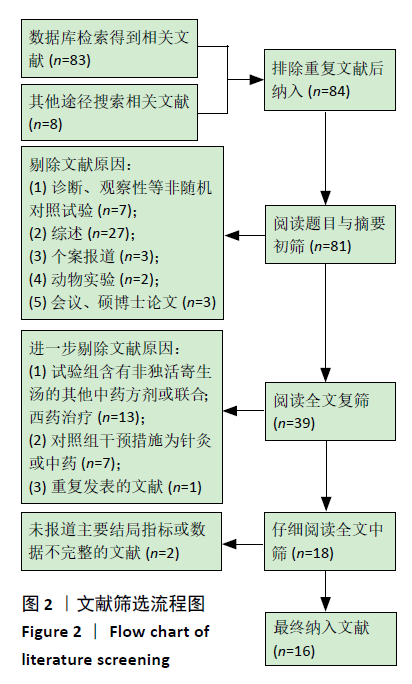
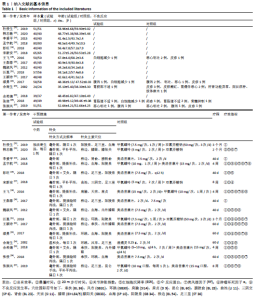
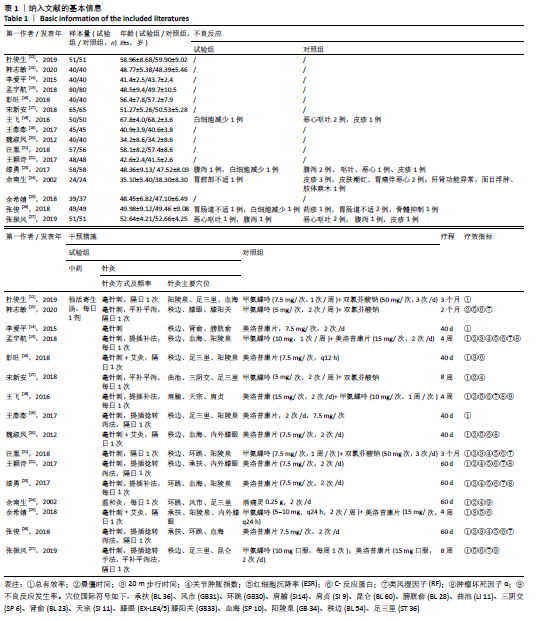
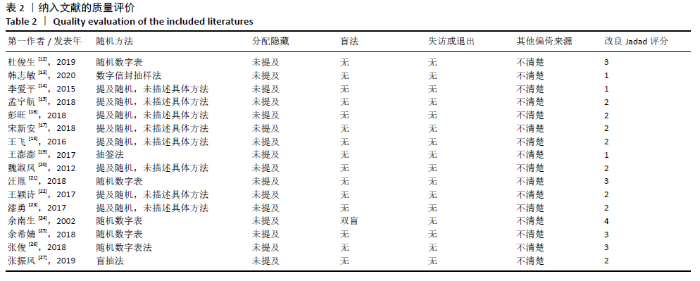
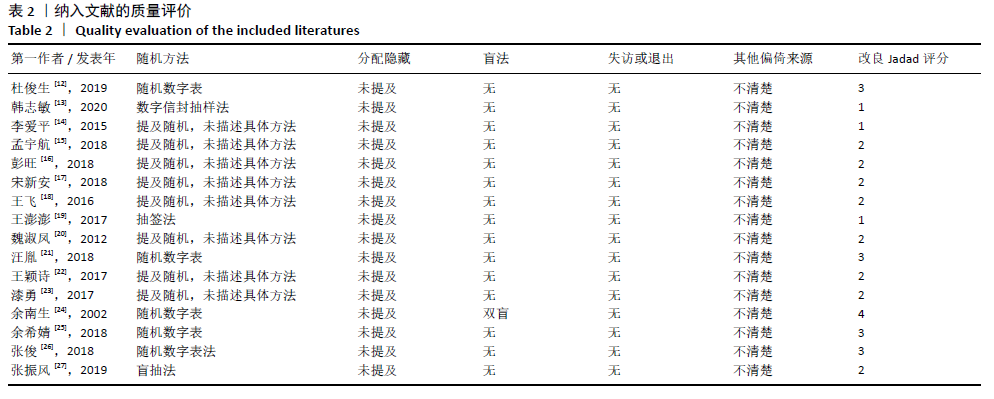
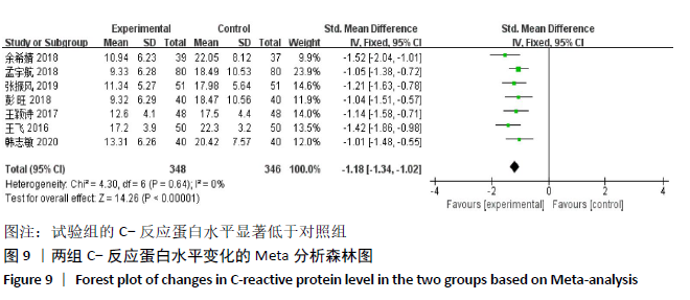
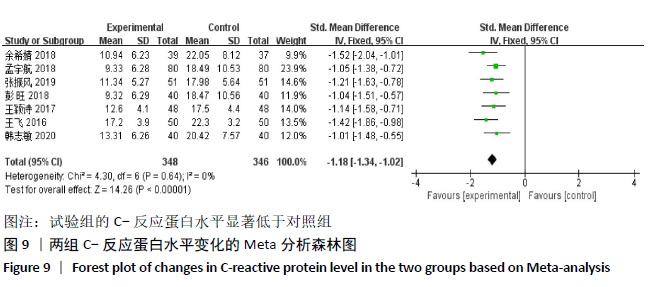
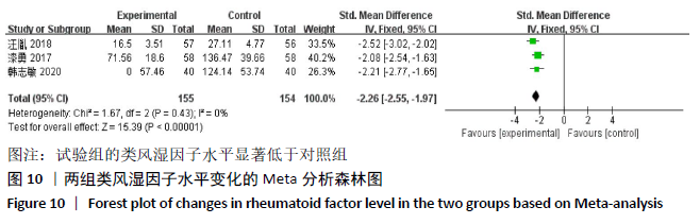
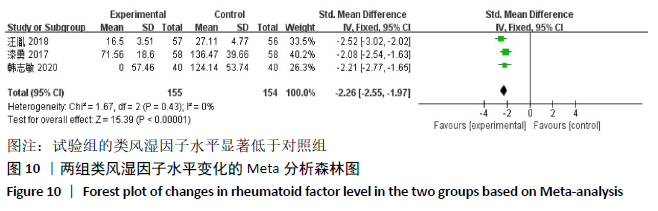
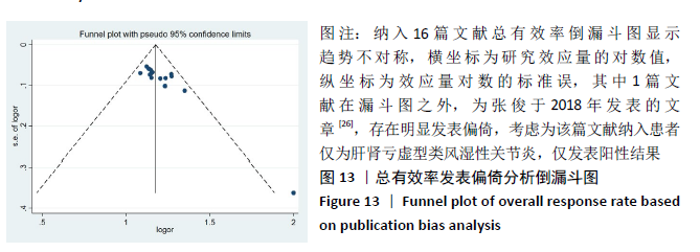
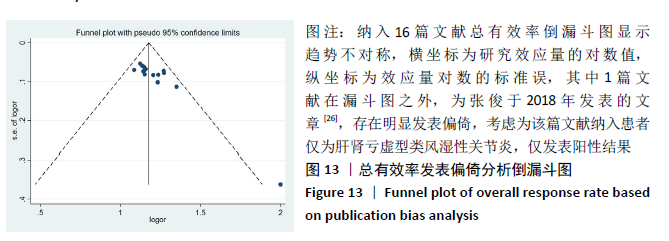
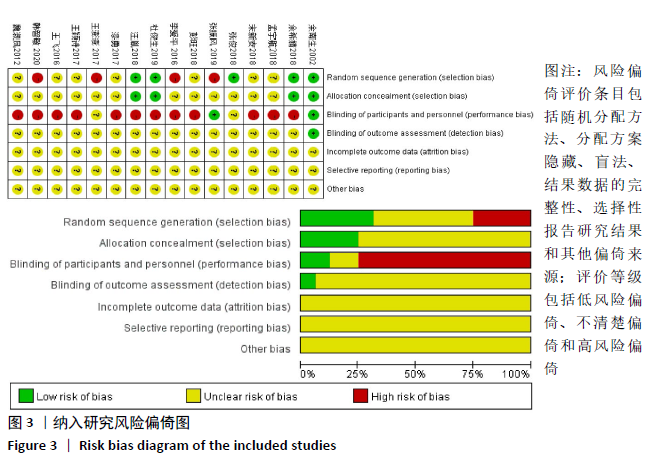
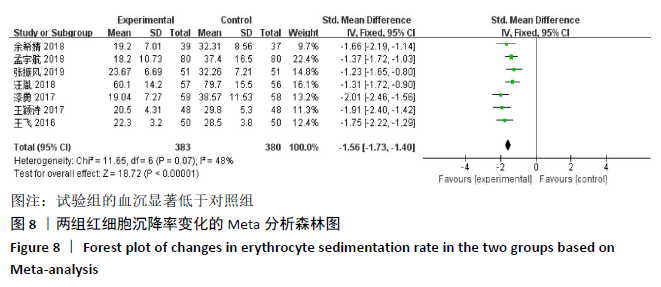
2.2 纳入文献质量评价结果 纳入文献均为中文文献;有8篇文献提及具体随机方法[12-13,19-21,24-27],剩余8篇仅提及采用随机分组[14-18,20,22-23],未描述具体随机方法;有1篇文献提及采用双盲法[24],剩余15篇未表明采用盲法;16篇文献均未提及分配隐藏方法。改良Jadad量表得分:4分文献1 篇[24],3分文献4篇[12,21,25,26],2分文献8篇[15-18,20,22-23,27],1分文献3篇[13-14,19],总体质量较低。根据线性加权Weighted Kappa系数分析显示,2位评价者评价结果的Weighted Kappa系数为0.797(P < 0.001),说明两人的评价结果一致性较强。具体偏倚风险评估结果见表2,图3。 "
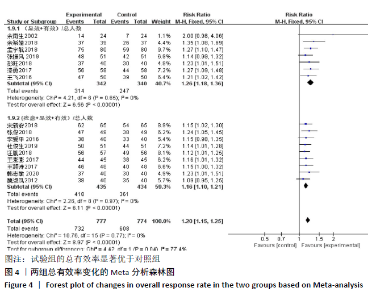
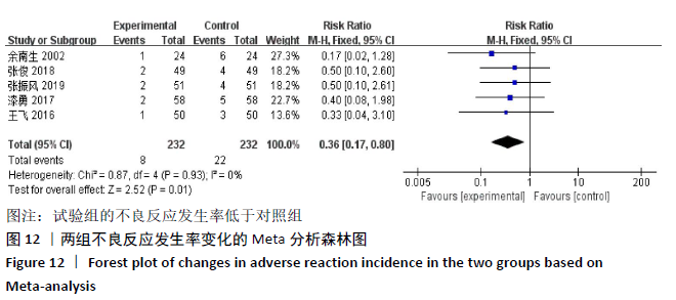
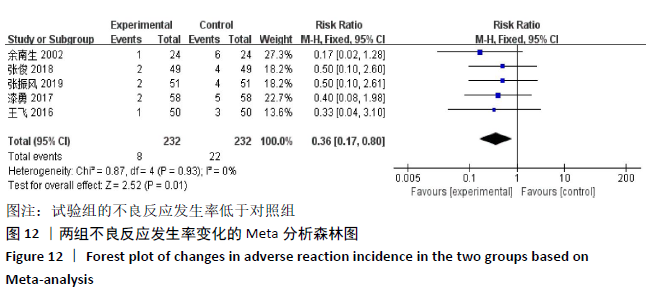
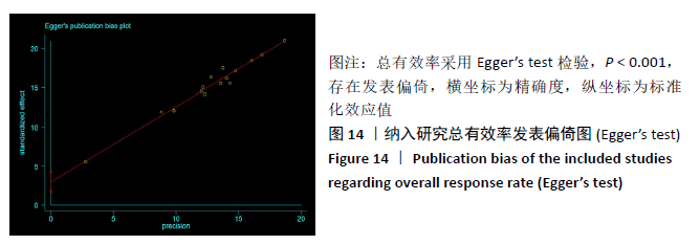
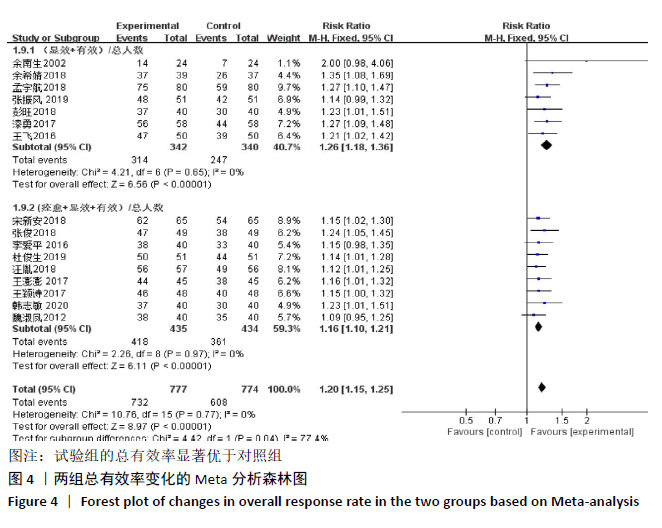
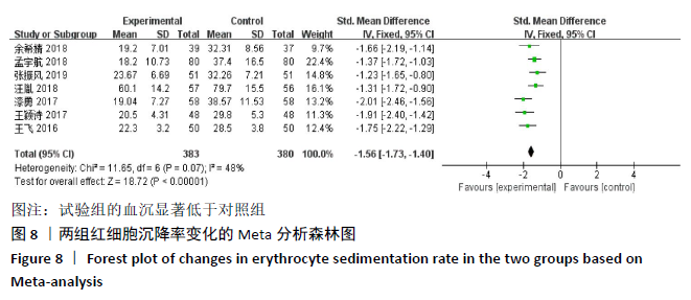
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 各组总有效率差异 有16篇文献采用总有效率为主要结局指标[12-27],异质性检验:P=0.50,I2=0%,提示各项研究之间无异质性,采用固定效应模型分析,见图4。Meta分析结果显示,试验组总有效率高于对照组(RR=1.20,95%CI:1.15-1.25,P < 0.000 01)。由于总有效率的计算方式有差异,通过亚组分析结果显示,总有效率=[(显效+有效)/总病例数]×100%的研究,Meta分析结果显示:试验组总有效率高于对照组(RR=1.26,95%CI:1.18-1.36,P < 0.000 01)。总有效率=[(痊愈+显 效+有效)/总人数]×100%的研究,Meta分析结果显示:试验组总有效率高于对照组(RR=1.16,95%CI:1.10-1.21, P < 0.000 01)。 "
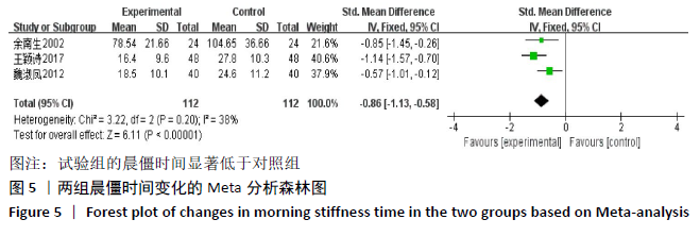
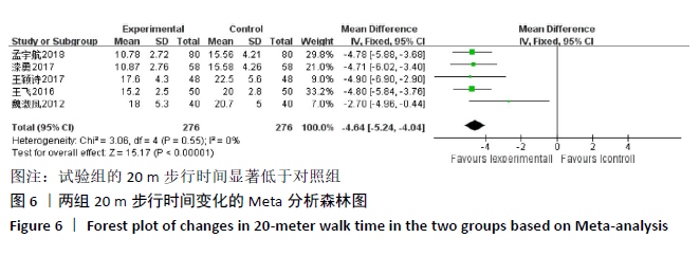
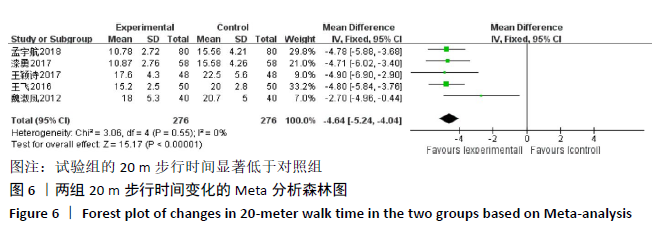
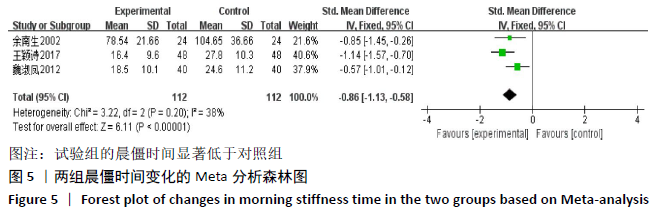
2.3.2 各组晨僵时间差异 有9篇文献报道了晨僵时间[13,15,18, 20-24,26],异质性检验:P < 0.000 01,I2=97%,提示各研究之间存在较高异质性,分析其异质性,考虑到诊断标准及患者年龄差异对数据的影响,故排除大异质性文献6篇[13,15,18,21, 23,26],针灸联合独活寄生汤对比西药组仅纳入3篇文献[20,22,24],共纳入224例患者,试验组112例,对照组112例,异质性检验:P=0.20,I2=38%,提示各研究之间无明显异质性,故应用固定效应模型合并数据。Meta分析结果显示,试验组在改善晨僵时间方面优于对照组(WMD=-0.86,95%CI:-1.13至-0.58,P < 0.000 01),见图5。 "
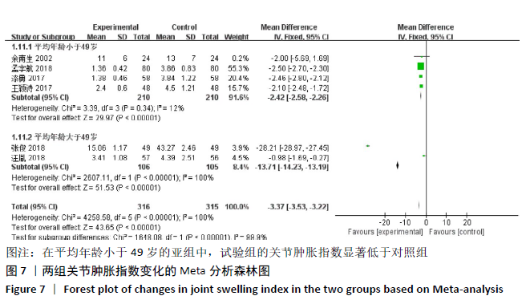
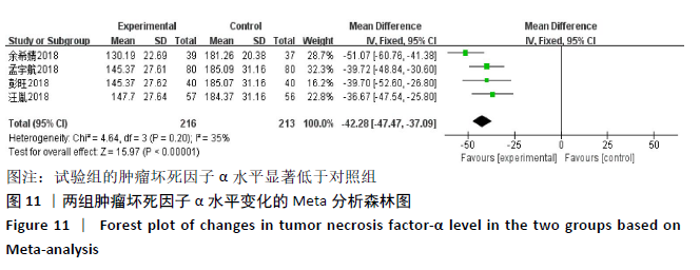
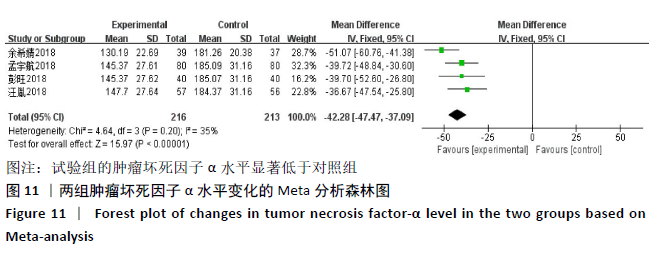
2.3.4 各组关节肿胀指数差异 有6篇文献报道了关节肿胀指数[15,21-24,26],异质性检验:P < 0.000 01,I2=100%,提示各研究之间存在较高异质性,分析其异质性,考虑到纳入患者年龄的差异,进行亚组分析,亚组为年龄小于49岁,纳入文献4篇[15,22-24],异质性检验:P=0.34,I2=12%,提示各研究之间无明显异质性,故应用固定效应模型合并数据。Meta分析结果显示,试验组在改善关节肿胀指数方面(WMD=-2.42,95%CI:-2.58至-2.26,P < 0.000 01)优于对照组,亚组年龄大于49岁,异质性检验:P < 0.000 01,I2=100%,分析其异质性,进行敏感性分析,排除大异质性文献1篇[26],考虑不同治疗方式及对照对数据分析的影响,仅1篇文献[21],故不予纳入,仅评价年龄小于49岁组,见图7。 "
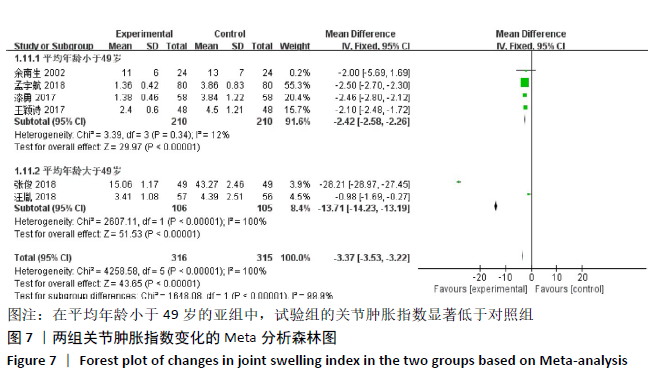
2.3.4 各组关节肿胀指数差异 有6篇文献报道了关节肿胀指数[15,21-24,26],异质性检验:P < 0.000 01,I2=100%,提示各研究之间存在较高异质性,分析其异质性,考虑到纳入患者年龄的差异,进行亚组分析,亚组为年龄小于49岁,纳入文献4篇[15,22-24],异质性检验:P=0.34,I2=12%,提示各研究之间无明显异质性,故应用固定效应模型合并数据。Meta分析结果显示,试验组在改善关节肿胀指数方面(WMD=-2.42,95%CI:-2.58至-2.26,P < 0.000 01)优于对照组,亚组年龄大于49岁,异质性检验:P < 0.000 01,I2=100%,分析其异质性,进行敏感性分析,排除大异质性文献1篇[26],考虑不同治疗方式及对照对数据分析的影响,仅1篇文献[21],故不予纳入,仅评价年龄小于49岁组,见图7。 "
| [1] SPARKS JA. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(1):C1-C16. [2] LITTLEJOHN EA, MONRAD SU. Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Prim Care. 2018;45(2):237-255. [3] 2018中国类风湿关节炎诊疗指南[J].中华内科杂志,2018,57(4):242-251. [4] 朱丽芳,俸一然,许东云.类风湿关节炎患者生存质量的研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2018,7(4):76-80. [5] 欧敏,朱艳.针灸治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志,2018, 30(10):1934-1936. [6] 张鸿婷,杜旭,郭丹丹,等.独活寄生汤治疗类风湿关节炎药效学及作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中医药学报,2020,48(9):77-80. [7] 周铭芳,范伏元.独活寄生汤治疗类风湿关节炎的Meta分析[J].中医药临床杂志,2019,31(10):1871-1874. [8] 张星华,朱博雯,赵彬元,等.针灸治疗类风湿关节炎随机对照临床研究Meta分析[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2015,22(2):42-46. [9] 王燕,陈思思,李泽光.浅谈针药结合治疗类风湿性关节炎的临床应用及作用机制[J].针灸临床杂志,2019,35(6):92-95. [10] SILMAN AJ. The 1987 revised American Rheumatism Association criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1988; 27(5):315-324. [11] 中华医学会风湿病学分会.类风湿关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010,14(4):265-270. [12] 杜俊生.独活寄生汤加减、针灸联合治疗类风湿性关节炎的临床价值分析[J].心理月刊,2019,14(18):222. [13] 韩志敏.针刺结合独活寄生汤加减治疗类风湿性关节炎临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志,2020,6(4):431-432. [14] 李爱平.独活寄生汤加减等治疗类风湿性关节炎40例临床观察[J].现代养生, 2015(2):236. [15] 孟宇航,杨卫彬,董宝强.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿性关节炎的临床疗效分析[J].中医药信息,2018,35(1):58-62. [16] 彭旺,曾令伟.独活寄生汤方加减配合针灸疗法对肝肾亏虚患者类风湿性关节炎的疗效及其对血清TNF-α、CRP水平的影响[J].抗感染药学,2018,15(7):1285-1287. [17] 宋新安.针刺配合独活寄生汤治疗类风湿性关节炎临床观察[J]. 实用中医药杂志,2018,34(2):149-150. [18] 王飞.针刺配合独活寄生汤治疗老年类风湿性关节炎临床疗效观察[J].新中医,2016,48(6):97-99. [19] 王澎澎.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿性关节炎的临床疗效[J].中国保健营养,2017,27(35):109. [20] 魏淑凤,李秀兰,梁利娜,等.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿性关节炎40例临床观察[J].中医药导报,2012,18(9): 67-69. [21] 汪胤.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿关节炎的临床疗效及对炎症因子的影响[J].江西医药,2018,53(4):325-328. [22] 王颖诗.独活寄生汤加减联合针灸治疗类风湿性关节炎48例[J].中医外治杂志, 2017,26(2):18-19. [23] 漆勇,漆良,夏会敏,等.独活寄生汤联合针灸治疗肝肾亏虚型类风湿关节炎效果观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2017, 26(7):742-744. [24] 余南生,詹可顺.独活寄生汤加艾灸治疗类风湿性关节炎疗效观察及免疫学指标分析[J].安徽医药,2002,6(4):18-20. [25] 余希婧,华水生.独活寄生汤方加减与针灸疗法对类风湿关节炎患者的疗效及其对血清CRP、ESR和氧化应激指标水平的影响[J].抗感染药学,2018,15(10): 1784-1786. [26] 张俊.针灸联合独活寄生汤治疗肝肾亏虚型类风湿关节炎49例疗效观察[J].云南中医中药杂志,2018,39(1):64-66. [27] 张振风.针药结合治疗类风湿性关节炎疗效观察[J].湖北中医杂志,2019,41(3): 53-55. [28] SEOANE-MATO D, SANCHEZ-PIEDRA C, SILVA-FERNANDEZ L, et al. Prevalence of rheumatic diseases in adult population in Spain (EPISER 2016 study): aims and methodology. Reumatol Clin. 2019;15(2): 90-96. [29] WEINBLATT ME. Methotrexate: who would have predicted its importance in rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):103. [30] CUTOLO M. Glucocorticoids and chronotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. 2016;2(1):e203. [31] GILANI ST, KHAN DA, KHAN FA, et al. Adverse effects of low dose methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012;22(2):101-104. [32] 袁娟,胡玲,宋小鸽,等.艾灸对类风湿性关节炎大鼠关节滑膜组织Toll样受体4-骨髓样分化因子88-核转录因子-κB信号通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2015, 40(3):199-204. [33] 李佳,李静,唐宏图,等.电针对类风湿性关节炎大鼠膝关节滑膜组织肿瘤坏死因子-α转换酶/核转录因子-κB信号通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2016,41(3):215-219. [34] 张传英,胡玲,蔡荣林,等.艾灸对类风湿性关节炎大鼠踝关节滑膜组织Toll样受体4/核因子-κB信号通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2018,43(11):687-691. [35] 高晓鹏,鲁贵生.独活寄生汤含药血清对佐剂性关节炎大鼠滑膜成纤维细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J].新中医,2018,50(4):1-5. [36] 农贤刚,程卫萍,曾麟杰,等.艾灸加独活寄生汤对中老年膝关节炎患者hs-CRP、IL-1β和TNF-α的影响[J]. 针灸推拿医学(英文版), 2017,15(4):277-280. [37] HAZLEWOOD GS, BARNABE C, TOMLINSON G, et al. Methotrexate monotherapy and methotrexate combination therapy with traditional and biologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis: abridged Cochrane systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2016;353:i1777. [38] 周铭芳,范伏元.独活寄生汤治疗类风湿关节炎的Meta分析[J].中医药临床杂志,2019,31(10):1871-1874. [39] 王海瑜,宋陈惠,刘小平,等.针灸联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的Meta分析[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(6):1399-1403. [40] 张星华,朱博雯,赵彬元,等.针灸治疗类风湿关节炎随机对照临床研究Meta分析[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2015,22(2): 42-46. |
| [1] | Zheng Hongrui, Zhang Wenjie, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Shen Yajun, Fan Lei. Femoral neck system combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1390-1395. |
| [2] | Du Xueting, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Yanjun, Wang Mei, Chen Wubiao, Huang Wenhua. Application of compressed sensing technology in two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1396-1402. |
| [3] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [4] | Bi Gengchao, Zhang Yanlong, Li Qiuyue, Hu Longwei, Zhang Yu. Knee joint mechanics and activation characteristics of surrounding muscles during deep jumps at different heights and distances [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1211-1218. |
| [5] | Yuan Hucheng, Ding Yongguo, Ma Xuehua, Ma Wenxin, Sun Jianmin, Wang Zili, Jin Weidong. Sustained releasing of pyrazinamide, capreomycin, moxifloxacin and amikacin loaded bone cement in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1017-1022. |
| [6] | Xiong Bohan, Yu Yang, Lu Xiaojun, Wang Xu, Yang Tengyun, Zhang Yaozhang, Liao Xinyu, Zhou Xiaoxiang, He Lu, Li Yanlin. Research progress in promoting tendon to bone healing during anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 779-786. |
| [7] | Liang Xiao, Zhao Panchao, Li Jiahui, Ji Zhongqiu, Jiang Guiping. Gait and biomechanical characteristics of lower limbs in multi-task walking of 4-6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 505-512. |
| [8] | Li Yaping, Liu Hong, Gao Zhen, Chen Xiaolin, Huang Wujie, Jiang Zheng. Three-dimensional motion analysis of lower limb biomechanical performance in Tai Chi practitioners accompanied by knee joint pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 520-526. |
| [9] | Wei Bo, Yao Qingqiang, Tang Cheng, Li Xuxiang, Xu Yan, Wang Liming. Advantage of medial pivot prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty via medial subvastus approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 552-557. |
| [10] | Li Shihao, Li Qi, Li Zhen, Zhang Yuanyuan, Liu Miaomiao, Ouyang Yi, Xu Weiguo. Plantar pressure and gait analysis in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 626-631. |
| [11] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [12] | Guo Feng, Zhang Zhifeng, Sun Zhiwen, Lyu Xin, Piao Junjie, Wang Di, Niu Shuang, Chen Xiaowei, Zhang Yibo. Preoperative planning-based navigation system-assisted total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4324-4331. |
| [13] | Shang Zijian, Guo Lin, Wang Zhi, Meng Xianghong, Chen Fei, Zhang Xuejun. Effect of sigmoid notch of distal radius on the stability of distal radioulnar joint based on CT images [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4357-4361. |
| [14] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Effect of distal tibial tuberosity-high tibial osteotomy on patellofemoral joint degeneration and patellar height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4367-4372. |
| [15] | Li Panpan, Qing Haomiao, Ren Sixie, Zhang Yuanyuan. Correlation of medial and lateral posterior tibial slope and their differences with anterior cruciate ligament injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4379-4384. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||