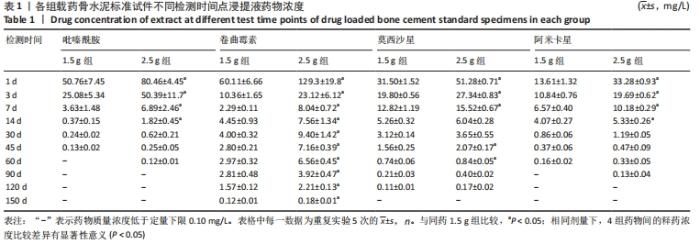
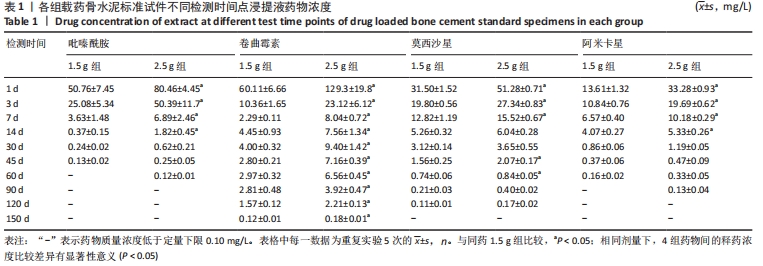
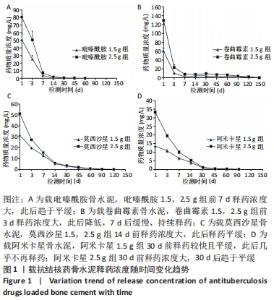
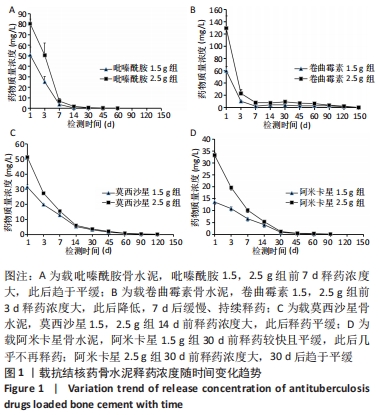
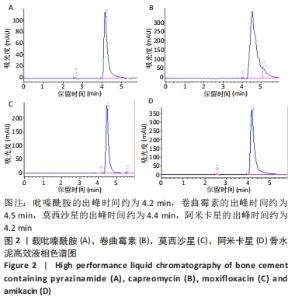
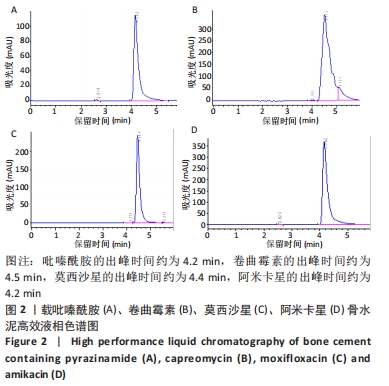
[1] 竺祖军,夏强,岳永宁,等.Xpert MTB/RIF检测技术在骨关节结核诊断中的应用价值[J].预防医学,2017,29(3):322-324.
[2] BOUSHAB BM, BASCO LK. Miliary tuberculosis and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2019;16:100-113.
[3] 戈朝晖,马荣,陈振,等.载异烟肼及利福平白蛋白纳米粒治疗兔脊柱结核的实验观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(3):253-261.
[4] 袁虎成,石仕元,马文鑫,等.载抗结核药物聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥的体外缓释性能观察[J].中国组织工程研究,2018;22(14): 2133-2139.
[5] WANG B, GAO W, HAO D. Current study of the detection and treatment targets of spinal tuberculosis. Curr Drug Targets. 2019;10(2):15-16.
[6] KHANNA K, SABHARWAL S. Spinal tuberculosis:a comprehensive review for the modern spine surgeon. Spine J. 2019;19(11):1858-1870.
[7] PENG Q, OU Y, ZHU Y, et al. Effect of surgical timing on effectiveness of thoracic spinal tuberculosis with myelopathy. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(3):273-279.
[8] SHI R, GONG M, CHI C, et al. Nano Twin-Fiber Membrane with Osteogenic and Antibacterial Dual Functions as Artificial Periosteum for Long Bone Repairing. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019;15(2):272-287.
[9] GONG M, HUANG C, HUANG Y, et al. Core-sheath micro/nano fiber membrane with antibacterial and osteogenic dual functions as biomimetic artificial periosteum for bone regeneration applications. Nanomedicine. 2019;8(17):124-136.
[10] 马文鑫,金卫东,王骞,等.载利福平、异烟肼、吡嗪酰胺、莫西沙星骨水泥物理性能及洗脱性能的体外研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(11):735-744.
[11] 袁虎成,马文鑫,王骞,等.载抗结核药骨水泥的筛选、制备及物理性能测定[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019(12):2260-2263.
[12] 国家食品药品监督管理局.《YY 0459-2003/IS0 5833.2002外科植人物-丙烯酸类树脂骨水泥》[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2003:1-16.
[13] 赵晨,王骞,施建党,等.复合三联抗结核药涂层材料(HRZ/PLGA)在大鼠体内释药特性观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(7):635-641.
[14] 朱荣,龚俊.HPLC测定盐酸莫西沙星的含量和有关物质[J].华西药学杂志,2017,32(4):398-400.
[15] 蔡则成,马荣,马赫,等.载异烟肼、利福平纳米羟基磷灰石-硫酸钙-壳聚糖人工骨在兔脊柱结核模型中的释药研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(2):141-146.
[16] 袁虎成,石仕元,马文鑫,等.载抗结核药物聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥:联合载药方案及抗结核效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(34):5540-5546.
[17] BUCHHOLZ HW, ENGELBRECHT H. Depot effects of various antibiotics mixed with Palacos resins. Chirurg. 1970;41(11):511-515.
[18] 刘文静,张晓东,杨晓旭,等.抗生素骨水泥型假体旷置治疗髋关节置换术后假体周围感染的效果分析[J].中国医学工程,2021, 29(10):73-75.
[19] INCEOGLU S, BOTIMER G, MASKIEWICZ VK. Novel microcomposite implant for the controlled delivery of antibiotics in the treatment of osteomyelitis following total joint replacement. J Orthop Res. 2021; 39(2):365-375.
[20] TOUZOPOULOS P, ARVANITIDIS K, FILIDOU E, et al. Is serum gentamicin concentration modified with autologous cell saved blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty using tranexamic acid? a randomised control trial. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;107(3):102794.
[21] SILJANDER MP, SOBH AH, BAKER KC, et al. Multi-drug resistant oprganisms in the setting of periprosthetic joint infection-diagnosis, prevention,and treatment. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(1):185-194.
[22] DIEFENBECK M, MIICKLEY T, HOFMANN GO. Prophylaxis and treatment of implantrelated infections by local application of antbioties. Injury. 2006;37(2):95-104.
[23] CAMPOCCIA D, MONTANARO L, SPEZIALE P, et al. Antibiotie-loaded bio-malerials and the risks for the spread of antibiotic resistance following their prophylactic and therapeutic clinical use. Biomaterials. 2010;31(25):6363-6377.
[24] PERSSON C, BALEANI M, GUANDALINI L, et al. Mechanical effects of the use of vancomycin and meropenem in acrylic bone cements. Acta Orthop. 2006;77(4):617-621.
[25] DUNNE N, HILL J, MCAFEE P, et al. In vitro study of the efficacy of acrylic bone cements loadedwith supplementary amounts of gentamicin:effect on mechanical antibiotic release,andbiofilm formation. Acta Orthop. 2007;78(6):774-785.
[26] JUTTE PC, RUTGERS SR, VAN ALTENA R, et al.Penetration of isoniazid,rifampicin and pyrazinamide in tuberculous pleural effusion and psoas abscess. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2004;8(11):1368-1372.
[27] 彭学成,张博,杨静,等.超高效液相色谱柱发展现状[J].齐鲁石油化工,2020,48(3):260-264.
[28] SANCHEZ AC, FRIEDLANDER G, FEKETE S. Pushing the performance limits of reversed-phase ultra high performance liquid chromatography with 1.3 μm core shell particles. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1311:90-97.
[29] OMAMOGHO JO, GLENNON JD. Comparison between the efficiencies of sub-2 μm C18 particles packed in narrow bore columns. Anal Chem. 2011;83(5):1547-1556.
[30] 岳学锋,吴龙云,焦文勇,等.抗结核药缓释涂层在兔脊柱结核模型体内的释药性能及组织分布研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021, 31(6):549-555.
[31] 陆宇,王彬,郑梅琴,等.应用 Alamar Blue 和 MTT 测定抗结核药物最低抑菌浓度的研究[J].中国防痨杂志,2007,29(6):499-501.
[32] SINGH R, DWIVEDI SP, GAHARWAR US, et al. Recent updates on drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Appl Microbiol. 2020; 128(6):1547-1567.
[33] KHAN MT, MALIK SI, ALI S, et al. Pyrazinnzmide resistance and mutations in pncA among isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa,Pakistan. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19(1):116-118.
[34] LI K, YANG Z, GU J, et al. Characterization of pncA Mutation and Prediction of PZA Resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Clinical Isolates From Chongqing. China Front Microbiol. 2020;11:594171.
[35] EI PW, MON AS, HTWE MM, et al. Pyrazinamide resistance and pncA mutations in drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates from Myanmar. Tuberculosis(Edinb). 2020;125:102013.
[36] NALUYANGE R, MBOOWA, KOMAKECH K, et al. Hihg prevalence of phenotypic pryazinamide resistance and its association with pncA gene mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Uganda. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0232543.
[37] WU X, LU W, SHAO Y, et al. PncA gene mutations in reporting pyrazinamide resistance among the MDR-TB suspects. Infect Genet Evol. 2019;72:147-150.
[38] 高阳逸,樊亚蕾,张梦浩,等.痰热清注射液联合阿米卡星对铜绿假单胞菌耐药菌株体外抗菌作用研究[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,2019(1): 122-126.
[39] 余涌杰,赖震,费骏,等.负载抗结核药物骨水泥生物力学实验研究[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2021,31(2):121-124.
[40] GINEBRA MP, TRAYKOVA T, PLANELL JA. Calcium phosphate cements as bone drug delivery systems:a review. J Control Release. 2006;113(2): 102-110.
[41] MIAO YF, SUN JQ. Research Progress of Self-Microemulsion Drug Delivery Syste. Int J Educ Economic. 2022;5(2):110-115.
|