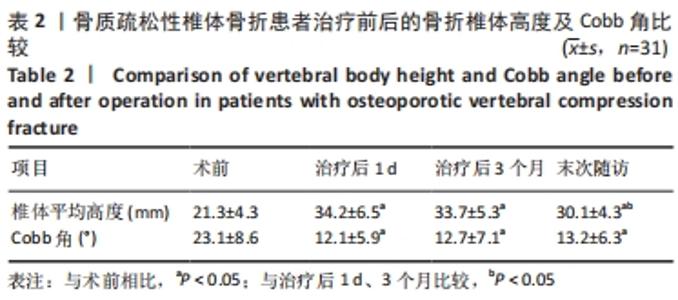
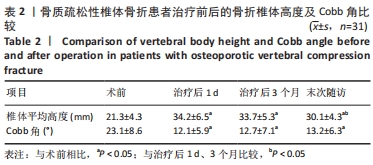
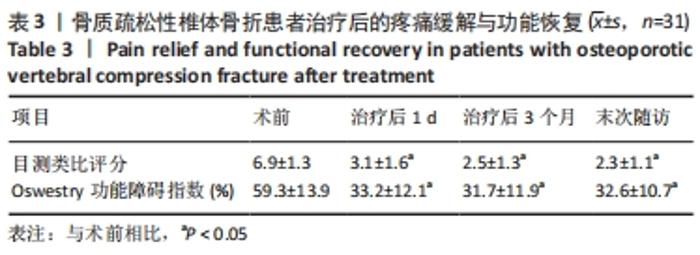
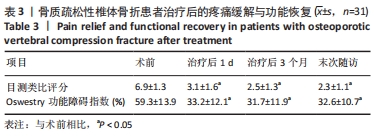
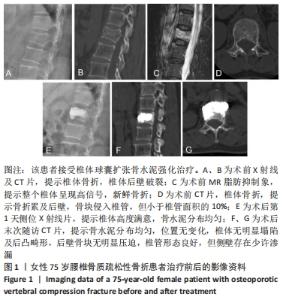
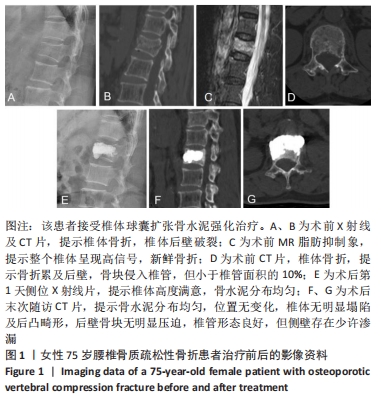
[1] 中华医学会骨科学分会骨质疏松学组.骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(1):1-10.
[2] SVENSSON HK, OLOFSSON EH, KARLSSON J, et al. A painful, never ending story: older women,s experiences of living with an osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(5):1729-1736.
[3] KURRA S, METKAR U, LIEBERMAN IH, et al. The Effect of Kyphoplasty on Mortality in Symptomatic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Review. Int J Spine Surg. 2018;12(5):543-548.
[4] NIEUWENHUIJSE M, ERKEL A, DIJKSTRA P. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: identification of risk factors. Spine J. 2011;11(9):839-848.
[5] SAXENA BP, SHAH BV, JOSHI SP. Outcome of percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in vertebral compression fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(4):458-464.
[6] 董智勇,范学辉,杨吉坤.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗后壁破裂的骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的安全性和有效性[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(4):312-315.
[7] 王旭,陈继良,刘寿坤,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性脊柱爆裂性骨折12例[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,27(10): 879-880.
[8] ZHAN Y, JIANG J, LIAO H, et al. Risk factors for cement leakage after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty: a meta-analysis of published evidence. World Neurosurg. 2017; 101:633-642.
[9] GARFIN SR, BUCKLEY RA, LEDLIE J. Balloon Kyphoplasty for Symptomatic Vertebral Body Compression Fractures Results in Rapid, Significant, and Sustained Improvements in Back Pain, Function, and Quality of Life for Elderly Patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19):2213-2220.
[10] 姜济世,干阜生,于海洋,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗后壁破裂的骨质疏松性椎体骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(3):244-246.
[11] YU W, LIANG D, JIANG X, et al. Efficacy and safety of the target puncture technique for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral clefts. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017;9(11):1113-1117.
[12] YANG W, SONG J, LIANG M, et al. Functional Outcomes and New Vertebral Fractures in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Conservative Treatment of Acute Symptomatic Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2019;131:e346-e352.
[13] ZHAO M, ZHOU J, LUO F, et al. Treatment of multsegments osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture by new design stagewise double-saccule: a case-control study. Chin J Anat Clin. 2015;20(5): 390-394.
[14] WONG E, WHYNE C, SINGH D, et al. A biomechanical assessment of kyphoplasty as a stand-alone treatment in a human cadaveric curst fracture model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(14):E808-E813.
[15] KOROVESSIS P, HADJIPAVLOU A, REPANTIS T. Minimal invasive short posterior instrumentation plus balloon kyphoplasty with calcium phosphate for burst and severe compression lumbar fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(6):658-667.
[16] 杨铁军,彭淑霞,周君琳,等.球囊二次撑开扩张后凸成形术治疗后壁不完整的椎体压缩性骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(1):24-30.
[17] 顾晓晖,杨惠林,唐天驷.后凸成形术治疗椎体后壁破裂的骨质疏松性脊柱骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(11):649-652.
[18] ZHONG B, WU C, HE S, et al. ANVCFV Score System: Assessment for Probability of New Vertebral Compression Fractures after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients with Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6):E1047-E1057.
[19] SAXENA BP, SHAH BV, JOSHI SP. Outcome of percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in vertebral compression fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(4):458-464.
[20] WENG J, WANG Z, XIAOHAI L I, et al. Optimization of partition controlled ammonia -injection grid in SCR denitrification system. Chin J Environ Eng. 2017;11 (5):2915-2919.
[21] ZENG ZL, QIAN L, JIA YW, et al. Kyphoplasty in the treatment of aged thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurological deficit. Orthop J Chin. 2011;19(20):1673-1676.
[22] 章恺,王鹏,英龙,等.体位复位与球囊扩张对椎体后凸形成术的复位效果[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015,17(3):209-212.
[23] 唐雪彬,谢林,李华,等.体位复位经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2021;24(2):159-163.
[24] HEARY RF, PARVATHREDDY NK, AGARWAL N. Biomechanical analysis of range of motion and failure characteristics of osteoporotic spinal compression fractures in human cadaver. Indian J Orthop. 2017;51(6):672-676.
|