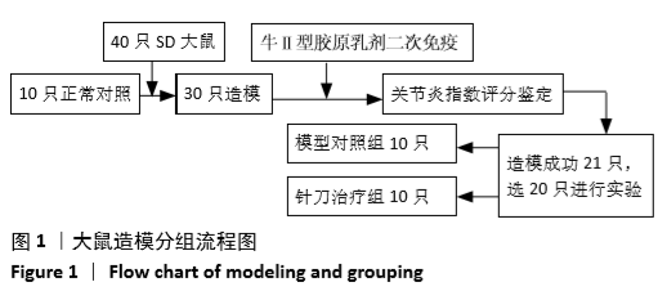
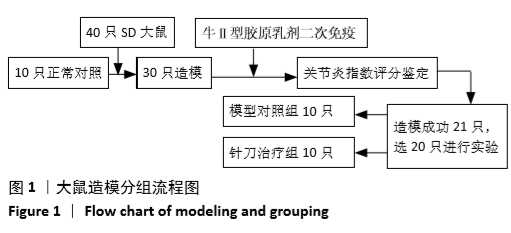
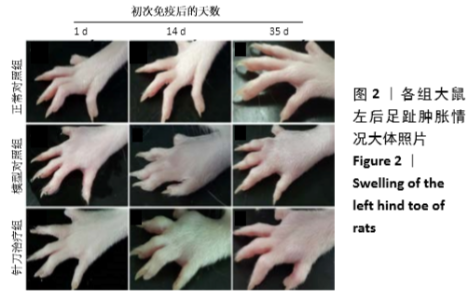
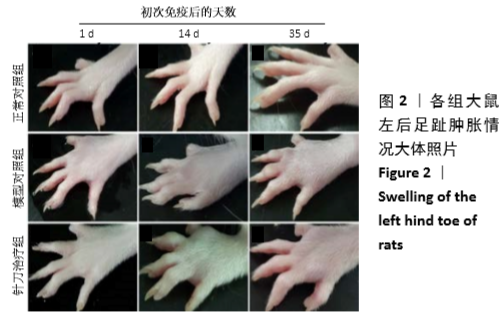
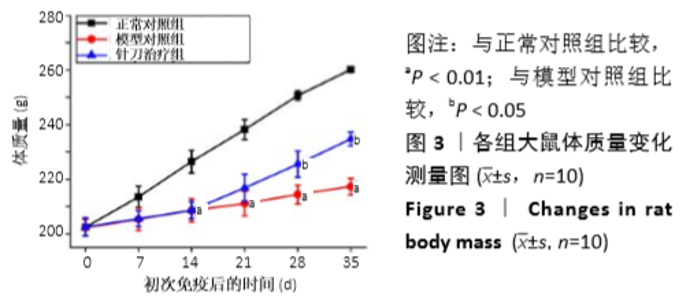
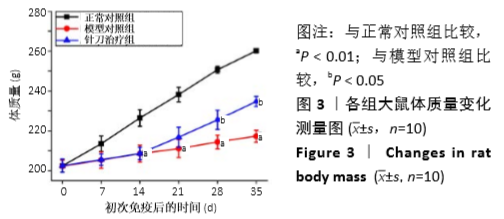
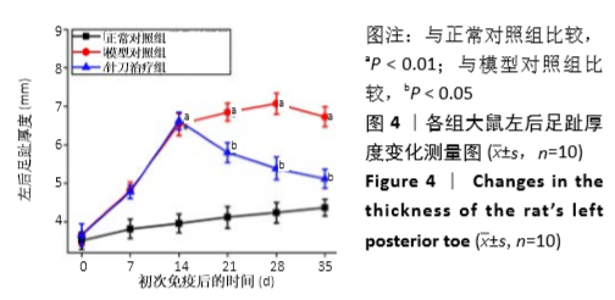
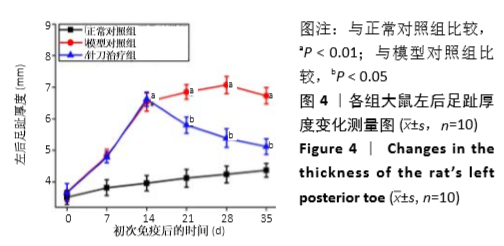
[1] 茹晋丽,李小峰,胡学芳,等.血管内皮生长因子在类风湿关节炎的表达[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2003,7(11):699-701.
[2] 姜功道,万碧江,黄伟,等.针刀松解术对类风湿关节炎肘关节僵硬患者关节液IL-6、IL-10.TNF-ɑ的影响[J].世界针灸杂志(英文版),2018,28(2):21-26.
[3] 万碧江,黄伟,任婕,等.针刀松解术对类风湿关节炎肘关节僵硬患者血清氧自由基代谢水平的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2018,34(1): 47-50.
[4] 万碧江,黄伟,张荒生,等.针刀整体松解术配合微波治疗类风湿肘关节僵硬的临床观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2018,33(12): 1429-1433.
[5] 方勇.针刀方案结合中药内服外敷法治疗类风湿关节炎顽固性肿痛的临床研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2016,34(3):724-727.
[6] 王凤杰,樊莎莎,陈显兵,等.Lunasin对实验性类风湿关节炎大鼠滑膜成纤维细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J].免疫学杂志,2016,32(2): 114-118.
[7] 高薇,冯欣,任立冰,等.类风湿关节炎大鼠滑膜组织中凋亡因子Bcl-xl和Bcl-2及Bax的表达及意义[J].中国全科医学,2012,15(24): 2776-2779.
[8] GU WZ, BRANDWEIN SR. Inhibition of type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats by triptolide.Int J Immunopharmacol.1998;20(8):389-400.
[9] 王琦.Dkk1在CIA大鼠骨质侵蚀中的作用及药物干预影响[D].南京:东南大学,2012.
[10] 黄英,陈哲,王玉,等.中药对类风湿关节炎成纤维滑膜细胞的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2017,35(8):2095-2097.
[11] 宋小莉,苏娟,刘重阳,等.类风湿关节炎滑膜组织中脯氨酸羟化酶及希佩尔林道肿瘤抑制蛋白的表达及意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(23):3623-3629.
[12] 肖长虹,顾为望,张嘉宁,等.南蛇藤醇提物对类风湿关节炎滑膜增生和软骨侵蚀及降解的抑制作用[J].南方医科大学学报,2007,27(7):945-950.
[13] 朱艳媚,祁岗,杨春燕,等.藏药十八味党参丸抑制CIA大鼠滑膜组织炎性因子表达和细胞凋亡诱导[J]. 中国高原医学与生物学杂志,2017,38(4):273-279.
[14] 党鹏,田杰祥,王钢,等.中医药对类风湿关节炎滑膜炎的作用机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(14):3590-3593.
[15] HA YJ, CHOI YS, HAN DW, et al. PIM-1 kinase is a novel regulator of proinflammatory cytokine-mediated responses in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Rheumatology (Oxford,Engl.). 2018;58(1): 154-164.
[16] 贾晓益,魏伟,郑咏秋,等.白芍总苷对胶原性关节炎滑膜组织中Bcl-2、Bax表达的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2006,41(2):143-146.
[17] 赵欣欣,赵丽娟,肖卫国,等.C-myc反义寡脱氧核苷酸抑制类风湿滑膜细胞增生诱导滑膜细胞凋亡[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2004,8(2): 67-72+129.
[18] GUO F, YANG F, ZHU YH. Scutellaein from Scutellaria barbata indu- ces apoptosis of human colon cancer HCT116 cells through the ROS-mediated mitochondria -dependent pathway.Nat Prod Res. 2018,19: 1-4.
[19] MALEMUD CJ. The role of the JAK/STAT signal pathway in rheuma- toid arthritis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis.2018;10(5/6): 117-127.
[20] MAHONEY JA, ROSEN A.Apoptosis and autoimmunit.Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17(6):583-588.
[21] 任玉伟, 宿华威. Bcl-2基因家族研究进展[J].大连医科大学学报, 2015, 37 (2) :202.
[22] AOUACHERIA A, BAGHDIGUIAN S, LAMB HM, et al. Connecting mitochondrial dynamics and life-or-death events via Bcl-2 family proteins. Neurochem Int.2017;109:141-161.
[23] LEE SY, KWOK SK, SON HJ, et al. IL-17-mediated Bcl-2 expression regulates survival of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis through STAT3 activation. Arthritis Res Ther.2013;15(1):R31.
[24] DAHMARDEH N, SHABANI M, BASIRI M, et al. Functional antagonism of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 prevents harmaline-induced ultrastructural alterations and Caspase-3 mediated apoptosis. Malays J Med Sci.2019;26(4):28-38.
[25] 江爱娟,王浩,李道卫,等.益气活血通络方对糖尿病大鼠坐骨神经细胞凋亡及相关蛋白表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2016,31(8): 3009-3012.
[26] 王娅妮,赵鹏飞,谈文峰,等.沉默脂联素受体1对脂多糖诱导的类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞MH7A增殖凋亡的影响[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2017,37(9):1109-1113+1153.
[27] 林昌松,陈秀敏,刘清平,等.昆母汤对类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞bax、bcl-2的影响[J].中药新药与临床药理,2014,25(6):656-659.
[28] 张义,郭长青.浅析针刀疗法与中医学的关系[J].江苏中医药,2010, 42(5):3-5.
[29] 胡佳伟,刘维,张博.针刀治疗类风湿关节炎临床研究进展[J].天津中医药,2019,36(6):617-621.
[30] 吴绪平.针刀医学[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社.2016.
[31] 王立新,代修勇,郭力军,等.针刀中药康复综合治疗膝关节外伤性滑膜炎疗效观察[J].针灸临床杂志,2010,26(10):16.
[32] 方剑乔,马桂芝,梁宜.电针足三里、三阴交穴治疗大鼠胶原性关节炎及其部分血液流变学机制[J].浙江中医药大学学报, 2008, 32(5):652-655.
|