Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (5): 804-812.doi: 10.12307/2022.131
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis
Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang
- Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2020-10-24Revised:2020-10-29Accepted:2021-01-21Online:2022-02-18Published:2021-12-03 -
Contact:Qiu Junqiang, PhD, Professor, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Liu Yiyi, Master candidate, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Special Project of China, No. 2018YFC2000601 (to QJQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
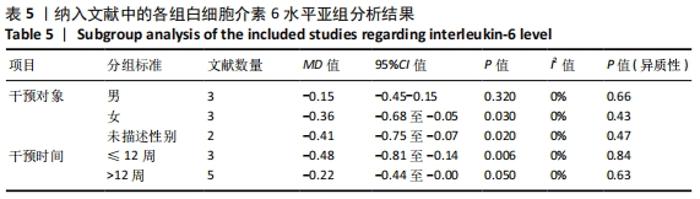
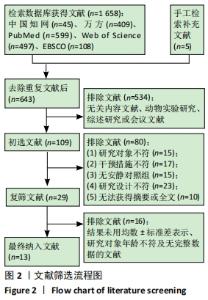
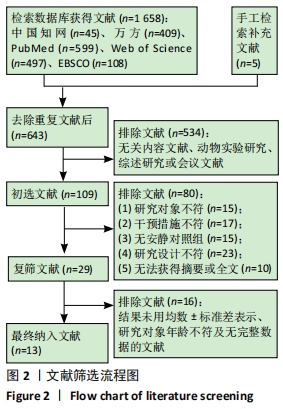
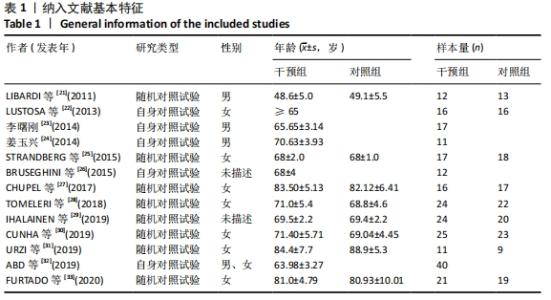
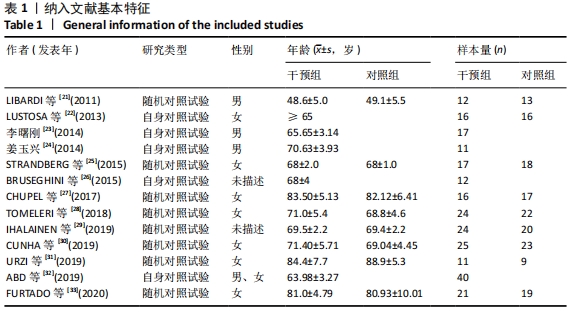
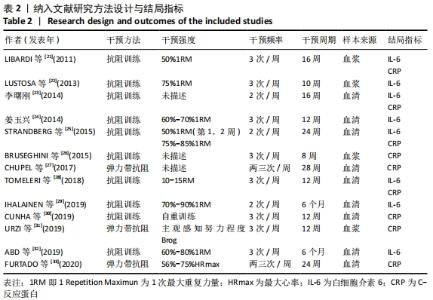
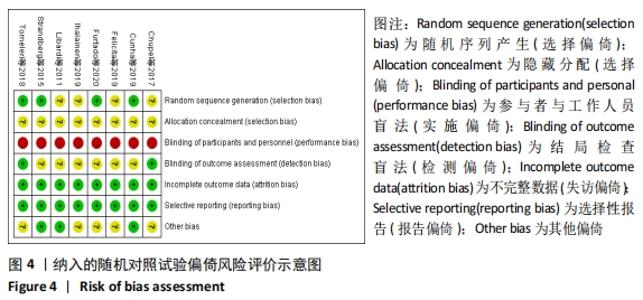
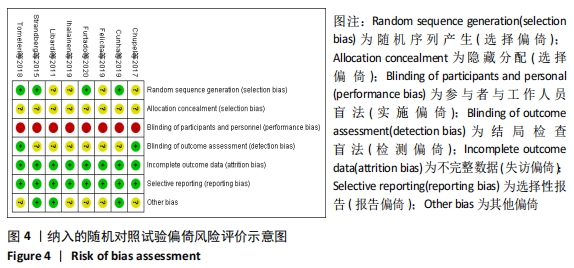
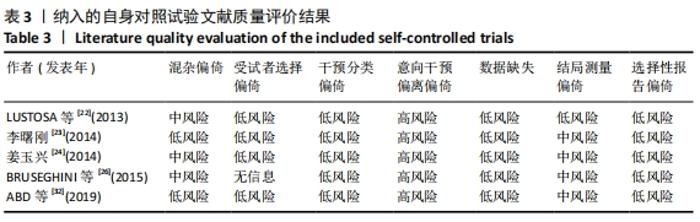
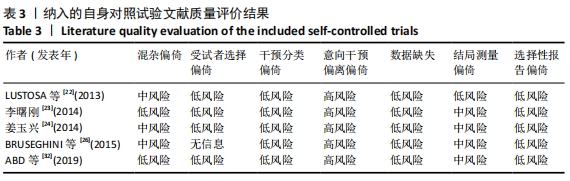
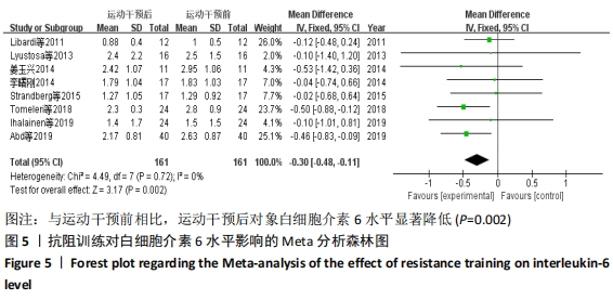
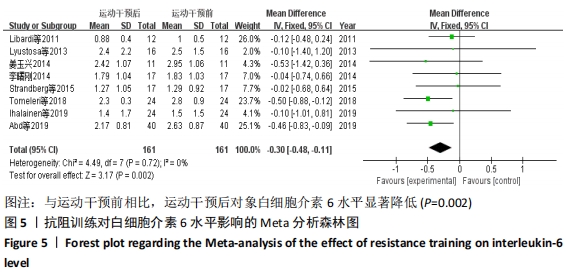
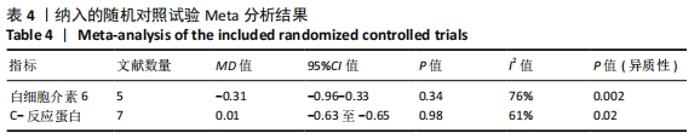
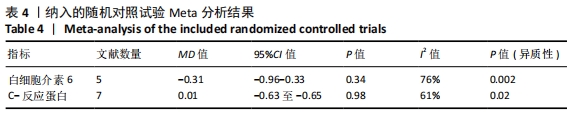
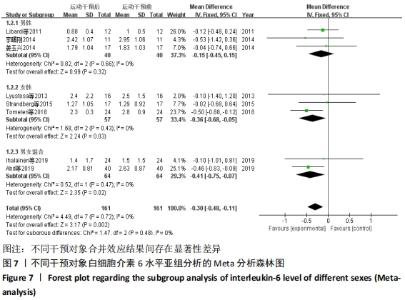
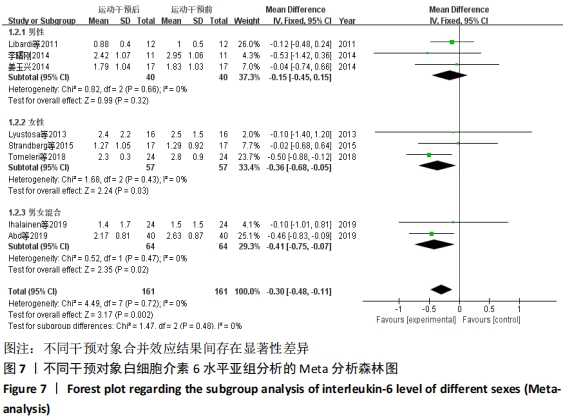
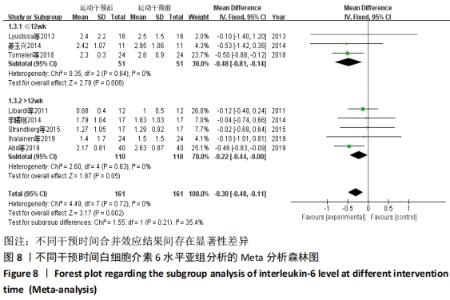
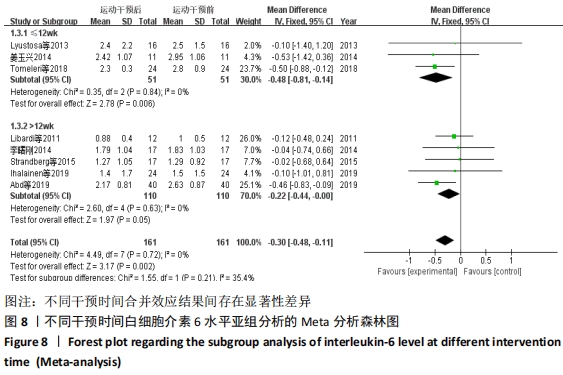
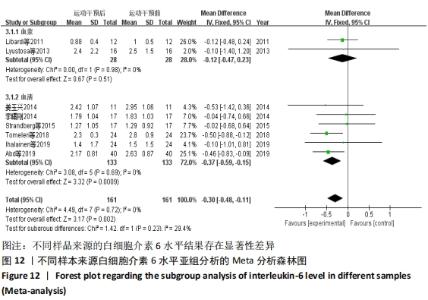
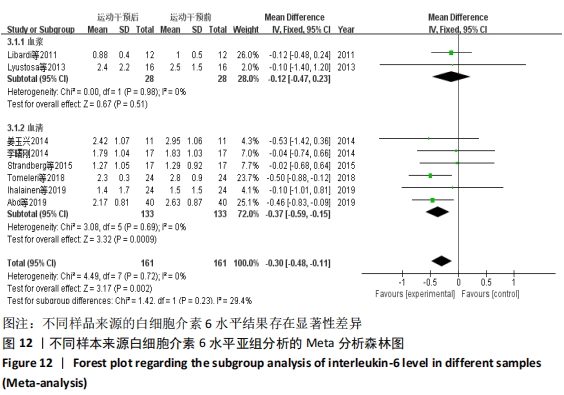
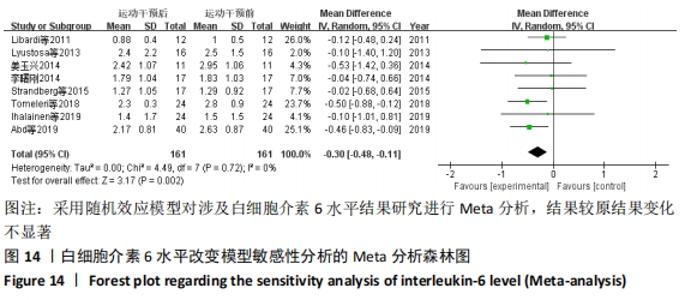
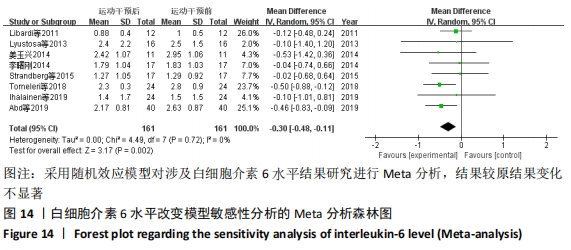
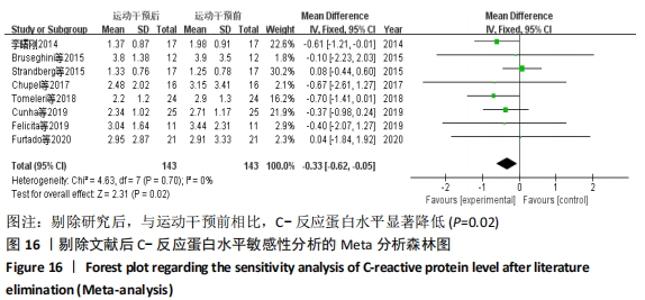
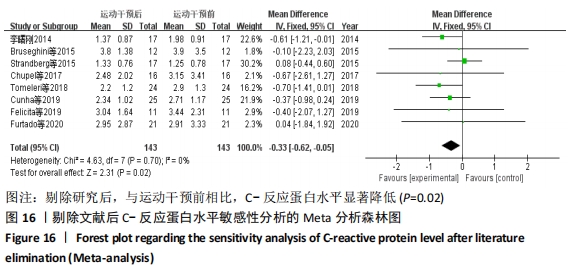
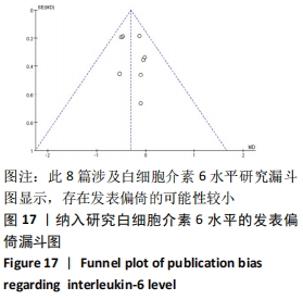
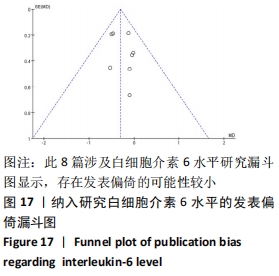
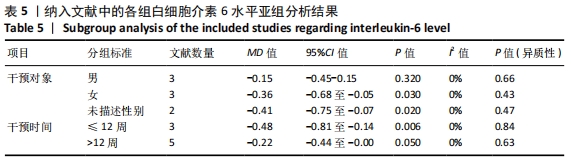
2.4.4 亚组分析结果 根据Meta分析结果显示,白细胞介素6水平无异质性(I2=0%),C-反应蛋白水平存在轻度异质性(I2=30%),考虑全部研究的具体干预对象、干预手段及干预时间等方面存在显著性差异,因此对这些方面的异质性进行进一步分析。 抗阻训练对中老年人白细胞介素6影响的亚组分析:纳入8篇涉及白细胞介素6水平的研究中受试者性别、干预时间及干预方式均存在显著性差异[21-25,28-29,32],因此根据不同性别分组与不同干预时间分组比较,其中受试者男性3篇[21,23-24],女性3篇[22,25,28],未描述性别的研究2 篇[29,32];干预时间≤12周研究3篇[22,24,28],干预时间>12周的研究5篇[21,23,25,29,32]。结果显示:各亚组无异质性(I2=0%),说明目前纳入的文献研究中,抗阻训练对中老年人白细胞介素6的影响不同性别人群与不同干预时间之间存在异质性来源的可能性较低。而根据分组后合并效应结果显示:①抗阻训练能降低女性白细胞介素6水平;②无论训练是否超过12周,均显示抗阻训练能显著降低白细胞介素6水平,提示干预对象不同对试验结果可能存在影响。分析结果见表5,图7,8。"
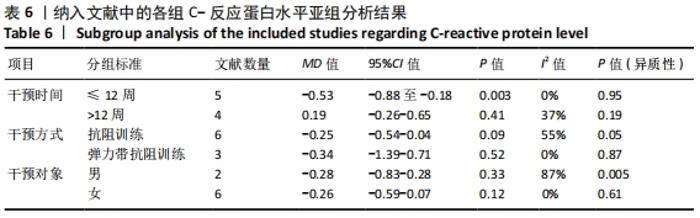
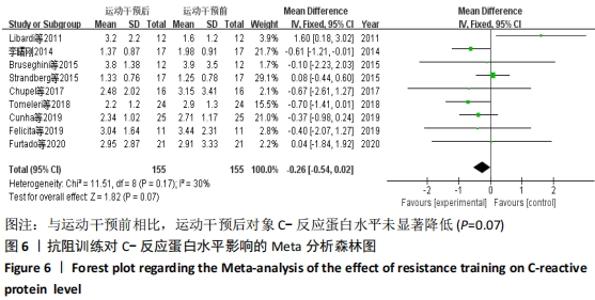
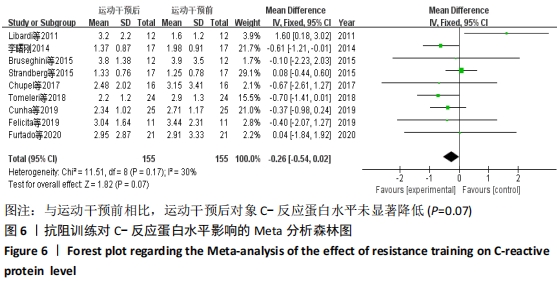
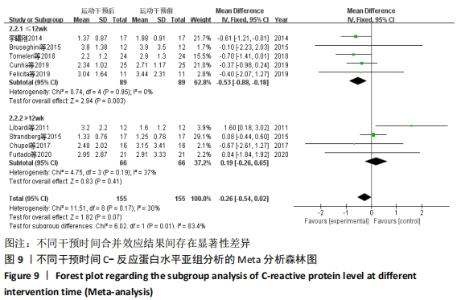
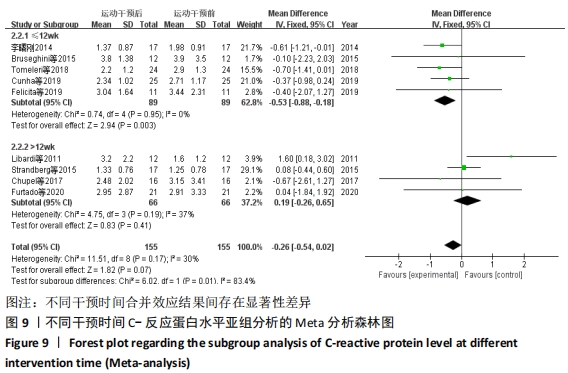
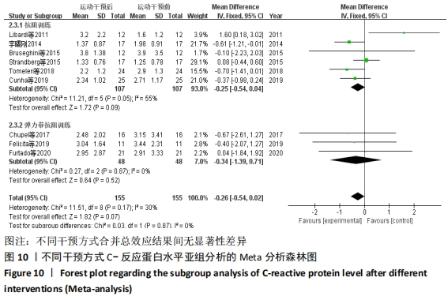
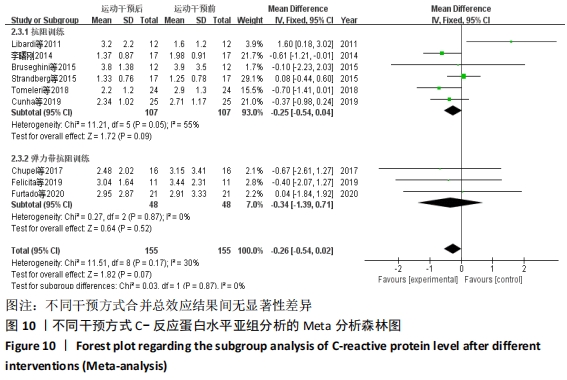
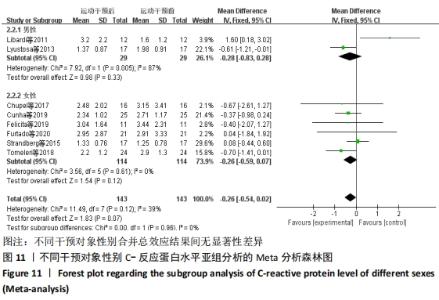
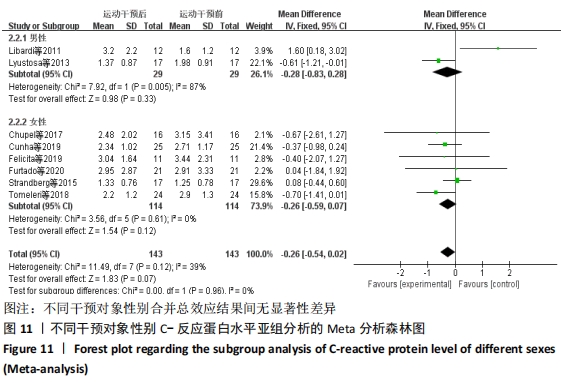
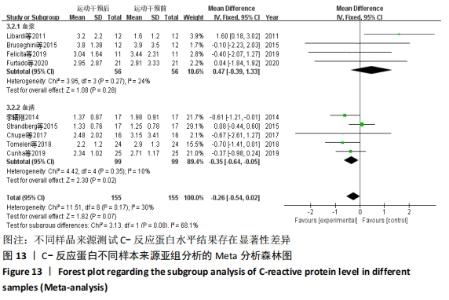
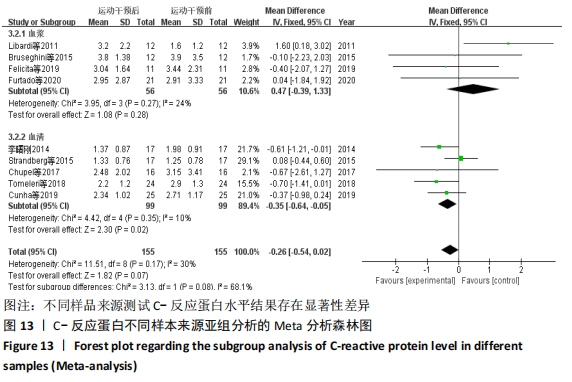
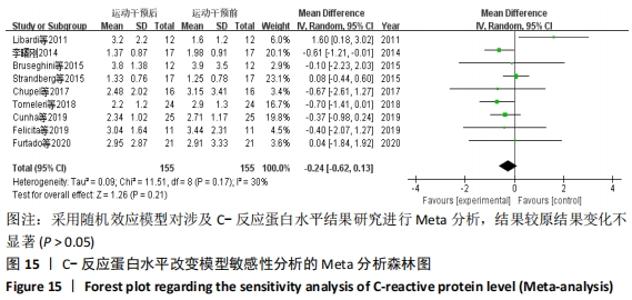
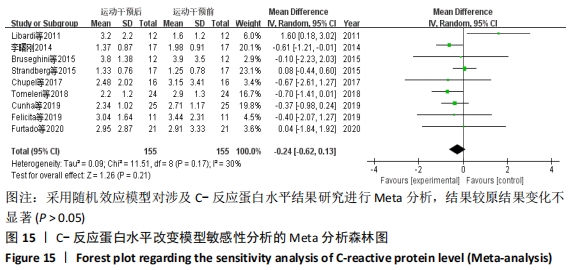
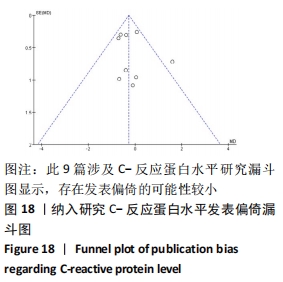
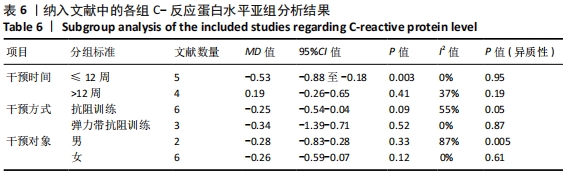
抗阻训练对中老年人C-反应蛋白的影响亚组分析:在纳入关于C-反应蛋白水平研究9篇[21,23,25-28,30-31,33],其中各研究的干预时间与干预方式存在显著性差异,因此根据不同干预时间与不同干预方式分组比较,其中干预时间≤12周的研究5篇[23,26,28,30-31],>12周的研究4篇[21,25,27,33]。采用抗阻训练干预的研究6篇[21,23,25-26,28,30],采用弹力带抗阻训练研究3篇[27,31,33]。结果显示:①干预时间分组分析结果存在轻度异质性(I2=37%);②采用不同抗阻训练方式分组分析结果存在中度异质性(I2=55%),提示在目前纳入研究中,抗阻训练对中老年人C-反应蛋白水平的影响不同干预时间与不同干预方式是异质性来源可能性较高,但由于分组后异质性产生变化,因此不能完全排除其可能性。合并效应结果显示:干预时间未超过12周的抗阻训练能降低C-反应蛋白水平(P < 0.05),提示不同干预时间对试验结果可能存在影响。分析结果见表6,图9,10。"
| [1] 孙景权,上官若男,严翊,等.心肺适能和炎症标志物的相关性及其机制的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(2):228-234. [2] SINGH T, NEWMAN AB. Inflammatory markers in population studies of aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10(3):319-329. [3] NOORDAM R, OUDT CH, BOS MM, et al. High-sensitivity c-reactive protein, low-grade systemic inflammation and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;28(8):795-802. [4] AGCA R, HESLINGA SC, HALM VP, et al. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic inflammatory joint disorders. Heart. 2016;102(10):790-795. [5] GROSICKI GJ, BARRETT BB, ENGLUND DA, et al. Circulating interleukin-6 is associated with skeletal muscle strength, quality, and functional adaptation with exercise training in mobility-limited older adults. J Fraility Aging. 2020;9(1):57-63. [6] SWERDLOW ID, HOLMES MV, KUCHENBAECKER KB, et al. The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: a mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet. 2012; 379(9822):1214-1224. [7] 刘国华,盛迪晔.渐进式抗阻训练延缓骨骼肌衰减的Meta分析[J].内江师范学院学报,2018, 33(8):107-115. [8] 郑丽,李冬咏,李金虎,等.弹力带抗阻训练在老年患者下肢肌肉力量训练中的应用效果[J].安徽医学,2019,40(2):219-222. [9] TAKENAMI E, IWAMOTO S, SHIRAISHI N, et al. Effects of low-intensity resistance training on muscular function and glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2019;10(2):331-338. [10] PAULA AMC, RICA RL, EVANGELISTA AL, et al. Effects of exercise intensity on post exercise hypotension after resistance training session in overweight hypertensive patients. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:1487-1495. [11] FORTI LN, NJEMINI R, BEYER I, et al. Strength training reduces circulating interleukin-6 but not brain-derived neurotrophic factor in community-dwelling elderly individuals. AGE. 2014;36(5):9704. [12] TOMELERI CM, SOUZA MF, BURINIR C, et al. Resistance training reduces metabolic syndrome and inflammatory markers in older women: a randomized controlled trial. J Diabetes. 2017; 10(4):328-337. [13] EL-KADER SMA, AL-SHREEF FM. Inflammatory cytokines and immune system modulation by aerobic versus resisted exercise training for elderly. Afr Health Sci. 2018;18(1):120-131. [14] BEAVERS KM, HSU FC, ISOM S, et al. Long-term physical activity and inflammatory biomarkers in older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(12):2189-2196. [15] KARABULUT M, SHERK VD, BEMBEN DA, et al. Inflammation marker, damage marker and anabolic hormone responses to resistance training with vascular restriction in older males. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2013;33(5):393-399. [16] MONTEIRO-JUNIOR RS, MACIEL-PINHEIRO PT, PORTUGAL EDM, et al. Effect of exercise on inflammatory profile of older persons: systematic review and meta-analyses. J Phys Act Health. 2018;15(1):64-71. [17] YOUSEFABAD HA, NIYAZI A, ALAEE S, et al. Anti-Inflammatory effects of exercise on metabolic syndrome patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol Res Nurs. 2020. doi: 10.1177/1099800420958068. [18] 谷鸿秋,王杨,李卫. Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具在随机对照试验Meta分析中的应用[J].中国循环杂志,2014,29(2):147-148. [19] JONATHAN AC, MIGUEL AH, BARNABY CR, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016;355:i4919. [20] 吴旸,李倩,包大鹏.加压力量训练对下肢骨骼肌影响的Meta分析[J].中国体育科技,2019, 55(3):20-26. [21] LIBARDI CA, SOUZA GV, GÁSPARI AF, et al. Effects of concurrent training on interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and C-reactive protein in middle-aged men. J Sports Sci. 2011; 29(14):1573-1581. [22] LUSTOSA LP, MÁXIMO PEREIRA, LEANI S, et al. Impact of an exercise program on muscular and functional performance and plasma levels of interleukin 6 and soluble receptor tumor necrosis factor in prefrail community-dwelling older women: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2013;94(4):660-666. [23] 李曙刚,周园.抗阻训练对老年人肌肉含量与血清炎症因子水平的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014,34(23):6659-6661. [24] 姜玉兴,王戌楼,李伟,等.力量训练对老年男性增龄性肌萎缩及慢性炎症的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2014,20(7):645-650. [25] STRANDBERG E, EDHOLM P, PONSOT E, et al. Influence of combined resistance training and healthy diet on muscle mass in healthy elderly women : a randomized controlled trial. J Appl Physiol. 2015;119(8):918-925. [26] BRUSEGHINI P, CALABRIA E, TAM E, et al. Effects of eight weeks of aerobic interval training and of isoinertial resistance training on risk factors of cardiometabolic diseases and exercise capacity in healthy elderly subjects. Oncotarget. 2015;6(19):16998-17015. [27] Chupel MU, Direito F, Furtado GE, et al. Strength training decreases inflammation and increases cognition and physical fitness in older women with cognitive impairment. Front Physiol. 2017;8:377. [28] TOMELERI CM, RIBEIRO AS, CAVAGLIERI CR, et al. Correlations between resistance training-induced changes on phase angle and biochemical markers in older women. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28(10):2173-2182. [29] IHALAINEN JK, INGLIS A, MAKINEN T, et al. Strength training improves metabolic health markers in olderindividual regardless of training frequency. Front Physiol. 2019;(10):32. [30] CUNHA PM, RIBEIRO AS, NUNES JP, et al. Resistance training performed with single-set is sufficient to reduce cardiovascular risk factors in untrained older women: the randomized clinical trial: active aging longitudinal study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2019;81:171-175. [31] URZI F, MARUSIC U, LIčEN S, et al. Effects of elastic resistance training on functional performance and myokines in older women-a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;20(7):830-834. [32] ABD ESM, AL-SHREEF FM, AL-JIFFRI OH. Impact of aerobic exercise versus resisted exercise on endothelial activation markers and inflammatory cytokines among elderly. Afr Health Sci. 2019;9(4): 2874-2880. [33] FURTADO G, CHUPEL MU, MINUZZI L, et al. The mediating effect of different exercise programs on the immune profile of frail older women with cognitive impairment. Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26: 1-10. [34] JOHNSON ML, IRVING BA, LANZA IR, et al. Differential effect of endurance training on mitochondrial protein damage, degradation, and acetylation in the context of aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015;70(11):1386-1393. [35] FEDEWA MV, HATHAWAY ED, WARD-RITACCO CL. Effect of exercise training on C reactive protein: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and non-randomised controlled trials. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(8):bjsports-2016- 095999. [36] AMORIM MGS, OLIVEIRA MD, SOARES DS, et al. Efects of exergaming on cardiovascular risk factors and adipokine levels in women. J Physiol Sci. 2018; 68(5):671-678. [37] UNAMUNO X, GÓMEZ-AMBROSI J, RODRÍGUEZ A, et al. Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48(9):e12997. [38] XIA Z, CHOLEWA J, ZHAO Y, et al. Targeting inflammation and downstream protein metabolism in sarcopenia: a brief up-dated description of concurrent exercise and leucine-based multimodal intervention. Front Physiol. 2017;8:434. [39] ELHAKEEM A, MURRAY ET, COOPER R, et al. Leisure-time physical activity across adulthood and biomarkers of cardiovascular disease at age 60e64: a prospective cohort study. Atherosclerosis. 2018;269:279-287. [40] IRENA S, GABRIELA RO, LORI BB. Does one size fit all? The role of body mass index and waist circumference in systemic inflammation in midlife by race and gender. Ethn Health. 2017;22(2):169-183. [41] 王光旭.弹力带抗阻训练对老年人肌力、行走能力和生活质量影响的实验研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2018. [42] 王鹏,江海洋,赵超,等.不同标本类型C反应蛋白检测结果的一致性分析[J].东南国防医药,2019,21(3):254-257. [43] 刘少峰,陈昇,黄思源,等.太极拳联合抗阻训练对55-60岁女性骨密度的疗效分析[J].安阳师范学院学报,2019(5):82-86. [44] Brunelli DT, Chacon-Mikahil MPT, Gspari AF, et al. Combined training reduces subclinical inflammation in obese middle-age men. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(10):2207-2215. |
| [1] | Tan Xinfang, Guo Yanxing, Qin Xiaofei, Zhang Binqing, Zhao Dongliang, Pan Kunkun, Li Yuzhuo, Chen Haoyu. Effect of uniaxial fatigue exercise on patellofemoral cartilage injury in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [3] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [4] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [5] | Wu Min, Zhang Yeting, Wang Lu, Wang Junwei, Jin Yu, Shan Jixin, Bai Bingyi, Yuan Qiongjia. Effect of concurrent training sequences on body composition and hormone response: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Gu Zhengqiu, Xu Fei, Wei Jia, Zou Yongdi, Wang Xiaolu, Li Yongming. Exploratory study on talk test as a measure of intensity in blood flow restriction training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1154-1159. |
| [7] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng . Effects of aerobic and resistance exercises on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nuclear factor-kappa B and inflammatory cytokines in skeletal muscle of type II diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 669-675. |
| [8] | Deng Shuang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Zhang Jianchao, Yuan Lingyan . Effects of exercise preconditioning on myocardial protection and apoptosis in a mouse model of myocardial remodeling due to early stress overload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 717-723. |
| [9] | Mo Weibin, Huang Tianchang, Zeng Zhiwei, Yan Linbo. Effects of Pueraria lobata flavonoids on expressions of beta-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in the brain of rats undergoing exhaustive exercise after long endurance exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 736-741. |
| [10] | Wei Xing, Liu Shufang, Mao Ning. Roles and values of blood flow restriction training in the rehabilitation of knee joint diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 774-779. |
| [11] | Tang Jiping, Zhang Yeting. Exercise regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanism and role [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 798-803. |
| [12] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [13] | Wei Zhoudan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan, Guo Dong, Hao Min. Platelet-rich fibrin as a material for alveolar ridge preservation significantly reduces the resorption of alveolar bone height and width after tooth extraction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 643-648. |
| [14] | Ou Liang, Kong Dezhong, Xu Daoqing, Ni Jing, Fu Xingqian, Huang Weichen. Comparative clinical efficacy of polymethyl methacrylate and self-solidifying calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 649-656. |
| [15] | Yang Ruijia, Jiang Lingkai, Dong Zhengquan, Wang Yunfei, Ma Zhou, Cong Linlin, Guo Yanjing, Gao Yangyang, Li Pengcui. Open reduction and internal fixation versus circular external fixation for tibial plateau fractures: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 480-486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||