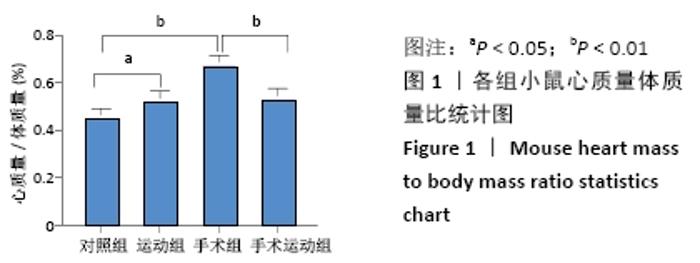
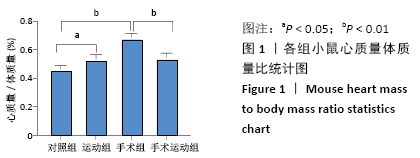
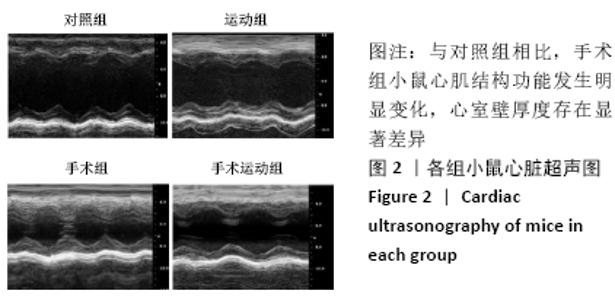
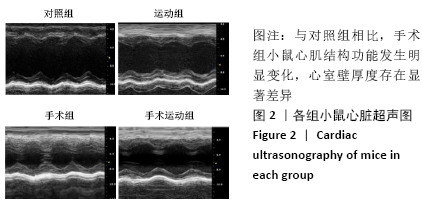
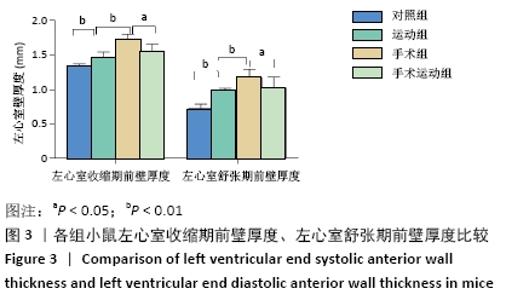
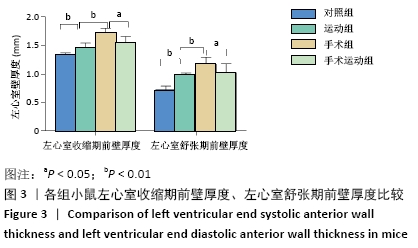
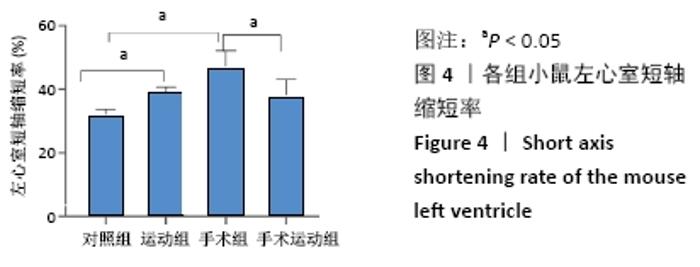
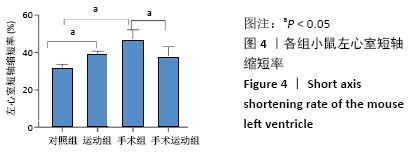
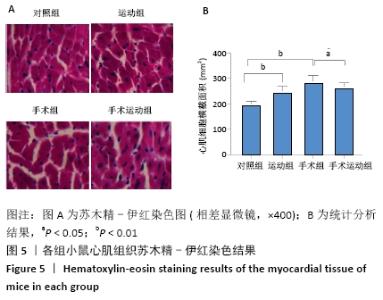
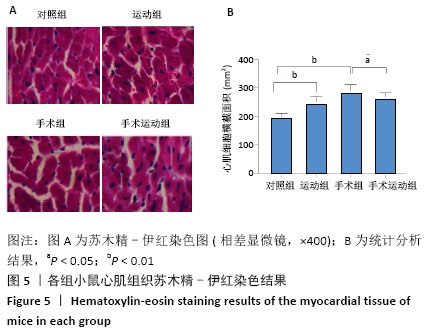
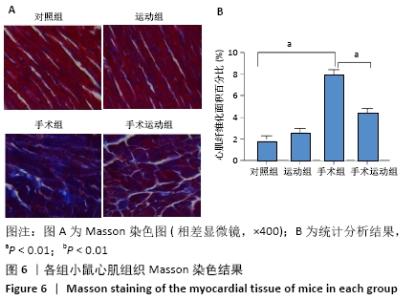
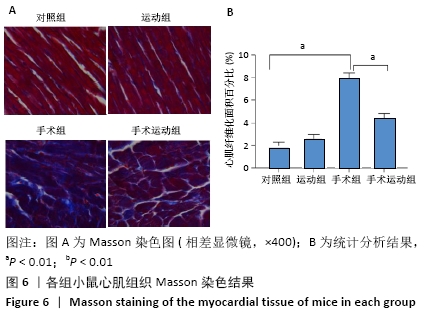
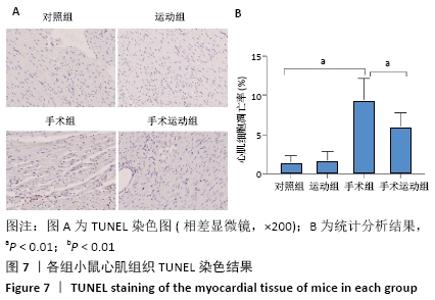
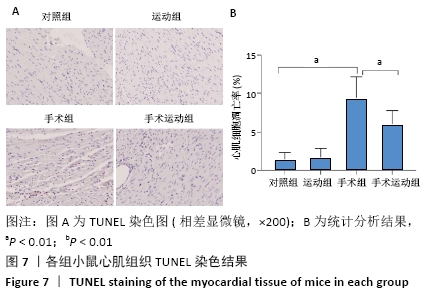
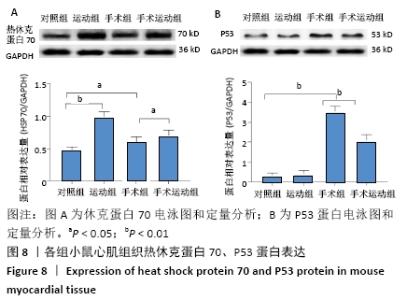
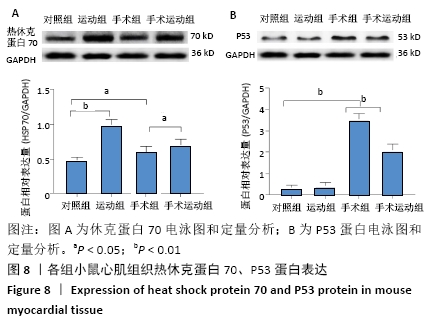
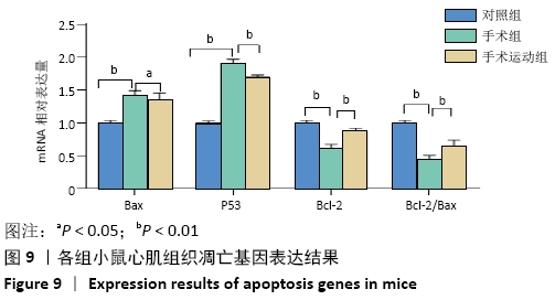
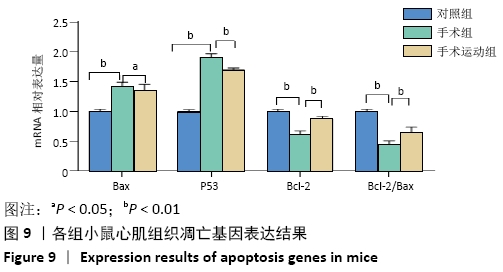
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (5): 717-723.doi: 10.12307/2022.117
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of exercise preconditioning on myocardial protection and apoptosis in a mouse model of myocardial remodeling due to early stress overload
Deng Shuang1, 2, Pu Rui2, Chen Ziyang2, Zhang Jianchao2, Yuan Lingyan2
- 1School of Health, Tianhua College, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 201815, China; 2School of Physical Education, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 200234, China
-
Received:2021-03-15Revised:2021-03-20Accepted:2021-04-15Online:2022-02-18Published:2021-11-02 -
Contact:Yuan Lingyan, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Physical Education, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 200234, China -
About author:Deng Shuang, Master, Rehabilitative therapist, School of Health, Tianhua College, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 201815, China; School of Physical Education, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 200234, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31371196 (to YLY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Deng Shuang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Zhang Jianchao, Yuan Lingyan . Effects of exercise preconditioning on myocardial protection and apoptosis in a mouse model of myocardial remodeling due to early stress overload[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 717-723.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] ZHANG YB, PAN XF, CHEN J, et al. Combined lifestyle factors, all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2021;75(1):92-99. [2] RESTREPO C, PATEL SK, RETHNAM V, et al. Left ventricular hypertrophy and cognitive function: a systematic review. J Hum Hypertens. 2018; 32(3):171-179. [3] SINGH MV, CICHA MZ, NUNEZ S, et al. Angiotensin II-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy are differentially mediated by TLR3- and TLR4-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019;316(5):H1027-H1038. [4] TSCHÖPE C, KHERAD B, KLEIN O, et al. Cardiac contractility modulation: mechanisms of action in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and beyond. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21(1):14-22. [5] SACO-LEDO G, VALENZUELA PL, RUIZ-HURTADO G, et al. Exercise Reduces Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Patients With Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9(24):e018487. [6] YAMAKOSHI S, NAKAMURA T, MORI N,et al. Effects of exercise training on renal interstitial fibrosis and renin-angiotensin system in rats with chronic renal failure. J Hypertens. 2021;39(1):143-152. [7] KAIDONIS X, NIU W, CHAN AY, et al. Adaptation to exercise-induced stress is not dependent on cardiomyocyte α1A-adrenergic receptors. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021 Feb 26:S0022-2828(21)00047-X. [8] CATTADORI G, SEGURINI C, PICOZZI A, et al. Exercise and heart failure: an update. ESC Heart Fail. 2018;5(2):222-232. [9] SCOTT JM, MARTIN D, PLOUTZ-SNYDER R, et al. Efficacy of Exercise and Testosterone to Mitigate Atrophic Cardiovascular Remodeling. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(9):1940-1949. [10] MCGINNIS GR, BALLMANN C, PETERS B, et al. Interleukin-6 mediates exercise preconditioning against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;308(11):H1423-1433. [11] FENG R, CAI M, WANG X, et al. Early Aerobic Exercise Combined with HydrogenRich Saline as Preconditioning Protects Myocardial Injury Induced by Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;187(3):663-676. [12] SONG YJ, ZHONG CB, WANG XB. Heat shock protein 70: A promising therapeutic target for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(2):1190-1207. [13] KRÜGER K, REICHEL T, ZEILINGER C. Role of heat shock proteins 70/90 in exercise physiology and exercise immunology and their diagnostic potential in sports. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(4):916-927. [14] CAI WF, ZHANG XW, YAN HM, et al. Intracellular or extracellular heat shock protein 70 differentially regulates cardiac remodelling in pressure overload mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;88(1):140-149. [15] TANIIKE M, YAMAGUCHI O, TSUJIMOTO I, et al. Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1/p38 signaling pathway negatively regulates physiological hypertrophy. Circulation. 2008;117(4):545-552. [16] PFLEGER J, GRESHAM K, KOCH WJ. G protein-coupled receptor kinases as therapeutic targets in the heart. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019;16(10): 612-622. [17] RAMACHANDRA CJA, CONG S, CHAN X, et al.Oxidative stress in cardiac hypertrophy: From molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic targets. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;166:297-312. [18] HE J, LUO Y, SONG J, et al. Non-coding RNAs and Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1229:231-245. [19] MATSUURA TR, LEONE TC, KELLY DP. Fueling Cardiac Hypertrophy. Circ Res. 2020;126(2):197-199. [20] MOORE MN, CLIMIE RE, OTAHAL P, et al. Exercise blood pressure and cardiac structure:A systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. J Sci Med Sport. 2021;S1440-2440(21). [21] BO B, ZHOU Y, ZHENG Q, et al. The Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Aerobic Exercise-Induced Cardiac Regeneration. Biomolecules. 2020;11(1):19.
[22] XU T, TANG H, ZHANG B, et al. Exercise preconditioning attenuates pressure overload-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(1):530-540. |
| [1] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [2] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [3] | Li Anan, Jiang Tao, Zhan Min, Cai Yuning, Song Min, Li Congcong, Lin Wenzheng, Zhang Jiayuan, Liu Wengang. Pharmacological mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 197-204. |
| [4] | Wei Wenyue, Wang Yuyin, Guo Minfang, Zhang Jing, Gu Qingfang, Song Lijuan, Chai Zhi, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Fasudil inhibits neuronal apoptosis via regulating mitochondrial dynamics in APP/PS1 mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 232-238. |
| [5] | Huang Mei, Wang Feiqing, Liang Huiling, Yang Xu, Zhao Jianing, Wang Kun, Liu Yanqing, Zhou Yuan, Wang Jishi, Li Yanju, Liu Yang. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium on the proliferation of multiple myeloma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3024-3029. |
| [6] | Zhu Yaping, Li Xiang, Chen Zhiwen, Liu Ying, Zhao Wenzhuo, Ma Ketao, Gu Qiang. Calcium-sensitive receptors influence pulmonary vascular remodeling in neonatal mice with persistent pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2708-2712. |
| [7] | You Kun, Liu Yuanxin. Protective effect of exercise preconditioning on lung injury induced by hypobaric hypoxia in rats based on the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element signal pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2702-2707. |
| [8] | Xu Xuezhen, Song Lixian, Li Aiqun, Yang Jian, Li Xiaokun, Wang Zhanqing, Shi Qingpeng. Bone morphogenetic protein 7 inhibits apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2726-2731. |
| [9] | Zhu Zheng, Fu Changxi, Ma Wenchao, Ma Gang, Peng peng. Regulatory mechanism of aerobic exercise on cardiac remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2231-2237. |
| [10] | Sun Haitao, Huang Yonghui, Gong Aihua, Cao Xingbing, Li Zhen. Protective effect of lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned astrocyte extracellular vesicles on neurons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 1985-1992. |
| [11] | Yu Dong, Liu Kan, Shi Zongting, Yang Xiaoxia, Liu Hengping, Zhang Qingfeng. Pathological changes of the cervical intervertebral discs and rules of migration and apoptosis in endplate chondrocytes in a rabbit model of dynamic disequilibrium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1675-1679. |
| [12] | Xing Hongchang, Cao Jianping, Zhu Jing, Yao Kun. Mechanism by which enalapril alleviates myocardial injury in a rat model of limb ischemia-reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1747-1751. |
| [13] | Jiang Shengyuan, Deng Bowen, Xu Lin, Liu Gang, He Feng, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Mu Xiaohong. Role and mechanism of tetramethylpyrazine in spinal cord injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1799-1804. |
| [14] | Cai Shengsheng, Mei Heng, Zhang Xuequan, Deng Jin, Cao Jun, He Bin. Prepared HPe6DF composite nanoparticles enhance the effect of photodynamic therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1566-1573. |
| [15] | Li Zhongkang, Zheng Jiahua, Tian Yanpeng, Huang Xianghua. Latest progress and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells on premature ovarian failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 141-147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||