Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 141-147.doi: 10.12307/2022.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Latest progress and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells on premature ovarian failure
Li Zhongkang, Zheng Jiahua, Tian Yanpeng, Huang Xianghua
- Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2020-09-18Revised:2020-09-21Accepted:2020-11-09Online:2022-01-08Published:2021-10-25 -
Contact:Huang Xianghua, MD, Chief physician, Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Li Zhongkang, Doctoral candidate, Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhongkang, Zheng Jiahua, Tian Yanpeng, Huang Xianghua. Latest progress and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells on premature ovarian failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 141-147.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
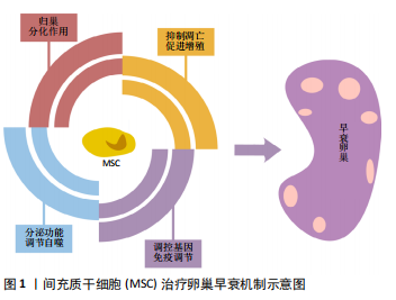
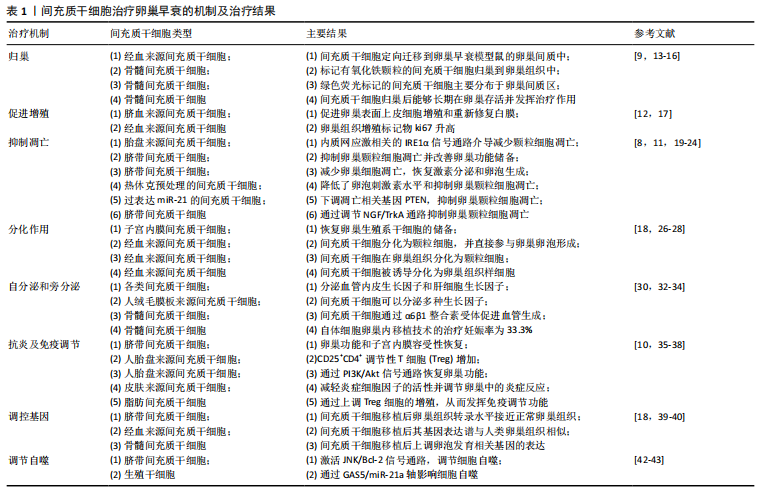
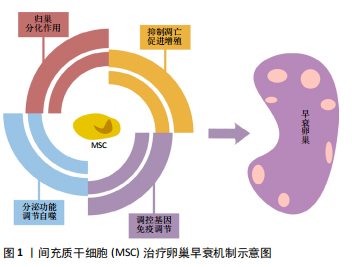
2.1.1 归巢 不同移植途径的间充质干细胞之所以会对靶器官起到治疗及恢复其功能的作用,很大程度上依赖其能够定向迁移至受损靶器官,也就是归巢作用。干细胞归巢定义为:干细胞在目标组织的脉管系统里被捕获,随后跨越血管内皮细胞迁移至目标组织的过程。当机体缺血、缺氧、损伤时,机体内或者外源性干细胞具有向损伤部位优势分布的特质。归巢效应是间充质干细胞安全有效应用于临床治疗的关键因素。WANG等[13]证实人类经血来源间充质干细胞能定向迁移到卵巢早衰模型鼠的卵巢间质中,减少颗粒细胞凋亡和减轻卵巢间质纤维化来改善卵巢微环境进而恢复卵巢功能,而不是直接分化为卵母细胞。另一项动物实验证明标记有氧化铁颗粒的间充质干细胞归巢到卵巢组织中[9],其组织学结果显示,间充质干细胞归巢于卵巢基质而不是卵泡中。该研究持这样的假设:间充质干细胞不分化为卵母细胞或颗粒细胞,但它们可能通过在卵巢卵母细胞周围的微环境中发挥重要的辅助作用来恢复卵巢功能,但需要进一步的研究来确定干细胞归巢涉及的不同机制。而另一项研究将转染了绿色荧光蛋白基因的小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞注射入早衰模型鼠卵巢中[14],在卵巢中可见绿色荧光,并且主要分布于卵巢间质区,卵泡周围也可见绿色荧光标记细胞,卵泡内未见绿色信号,同时卵巢间质纤维化减轻,这说明骨髓间充质干细胞可在小鼠损伤卵巢组织中定位存活,对卵巢组织结构及功能有修复作用。陈京京等[15]也将绿色荧光蛋白转基因小鼠的骨髓间充质干细胞经尾静脉注射至卵巢早衰模型小鼠体内,2个月后卵巢间质内可见大量绿色荧光标记的骨髓间充质干细胞,骨髓间充质干细胞归巢后能够长期在定植部位存活并发挥治疗作用。在相关临床研究中,大多数移植体内的间充质干细胞无法到达靶器官,所以试验结果不尽如人意。因此,提高间充质干细胞归巢至靶器官效率是提高其治疗效果的关键。柳颖灵等[16]认为趋化因子家族及其受体是白细胞迁移和体内重分配的重要因子,同时也是操控间充质干细胞迁移的重要因子,其中基质细胞衍生因子1(stromal cell derived factor-1,SDF-1)及其受体CXCR4(CXC chemokine receptor 4)组成的SDF-1/CXCR4轴在间充质干细胞迁移中起重要作用,过表达该趋化因子轴能够提高间充质干细胞归巢率,增加移植入体内的间充质干细胞的利用效率,从而确保其对于卵巢早衰的治疗效果。深入研究其机制进而提高间充质干细胞归巢和存活率将是其发挥治疗作用的重要保证。 2.1.2 促进增殖 增殖是生物体最为重要的生命特征。促进卵巢各类细胞尤其是卵巢颗粒细胞的增殖、激活卵泡功能同样是治疗卵巢早衰的重要途径。只有颗粒细胞数量增加、各级卵泡数量恢复,卵巢功能才能够逐步恢复。因此,促进增殖也是间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰各项研究中关注的重要治疗机制。国外一项动物研究证实脐血来源间充质干细胞通过促进卵巢表面上皮细胞增殖和重新修复白膜来直接恢复现存卵母细胞的功能进而治疗卵巢早衰,并通过抑制胱氨酸蛋白酶3,激活细胞角蛋白8/18、转化生长因子β、同源丢失性磷酸酶张力蛋白基因(phosphatase and tensin homologue,PTEN)来间接修复受损的卵巢功能[12]。LIU 等[17]向培养基添加不同的诱导因子,将多能干细胞诱导为卵巢颗粒样细胞,并将诱导成功的颗粒样细胞移植入环磷酰胺诱导的卵巢早衰模型鼠中,检测指标显示其治疗效果明显。由此可见外来颗粒细胞也能够起到治疗卵巢早衰的效果,不过其安全性和具体机制仍需要进一步探究。另一项研究利用人经血来源间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰小鼠,卵巢组织增殖标记物Ki67升高,证明其治疗机制可能为促进细胞增殖[18]。该研究同时证明人经血来源间充质干细胞也可以被诱导分化为卵巢组织样细胞,尤其是卵巢颗粒样细胞。这一研究中cDNA表达谱的微阵列分析结果表明,人经血来源间充质干细胞表达谱在移植前与人卵巢组织存在明显差异,而在早衰卵巢中存活数天后,其基因表达谱与人类卵巢组织相似,这一结果有力地证明了人经血来源间充质干细胞在卵巢中被诱导分化为卵巢组织样细胞。因此,促进增殖是间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的一项重要内在机制,也是干细胞能够恢复卵巢功能的核心机制,但是其纷繁复杂的具体机制仍需要进一步深入的研究。 2.1.3 抑制凋亡 卵巢颗粒细胞位于卵母细胞透明带外侧,是卵巢的重要功能细胞,在卵泡刺激素和其他细胞因子的作用下可分泌雌激素,并通过缝隙连接与卵母细胞相连,对卵母细胞起营养和支持作用。颗粒细胞的增殖凋亡水平是反映卵巢功能的重要指标。卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡将导致体内雌激素水平下降,影响卵母细胞的正常发育。颗粒细胞凋亡和卵泡闭锁被认为是导致卵巢早衰的重要机制,因此减缓细胞凋亡和抑制卵泡闭锁是治疗卵巢早衰的重要途径。国内外多项研究证实间充质干细胞可以有效抑制颗粒细胞的凋亡,从而达到治疗卵巢早衰的效果。LI等[8]通过人胎盘来源间充质干细胞治疗自身免疫诱导型卵巢早衰小鼠模型,证明其机制与内质网应激相关的IRE1α信号通路介导降低颗粒细胞凋亡有关。另一项研究也证实脐带间充质干细胞可抑制卵巢早衰大鼠的卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡并改善卵巢功能储备[19]。SONG等[20]将脐带间充质干细胞移植入化疗药物环磷酰胺诱导的大鼠卵巢早衰模型中,除了可以减少卵巢细胞凋亡外,还可以促进卵巢早衰大鼠的激素分泌和卵泡生成,并通过荧光原位杂交技术示踪卵巢中移植的脐带间充质干细胞,结果表明其可以在卵巢组织中较长时间存活。CHEN等[21]发现1 h 42 ℃热休克预处理可显著抑制间充质干细胞凋亡并促进其增殖;将热休克处理的间充质干细胞注入大鼠卵巢后,卵巢质量增加,雌二醇水平增加,不同阶段的卵泡数量也相应增加,并降低了卵泡刺激素水平和颗粒细胞凋亡。由此他们认为热休克预处理增强了间充质干细胞的生命力,对化疗诱导的卵巢早衰的修复作用也得到了强化,进而更大程度地抑制了卵巢颗粒细胞的凋亡。YANG 等[11]证明了骨髓间充质干细胞可以通过分泌外泌体传递miR-144-5p来治疗大鼠卵巢滤泡闭锁,并可以将外泌体转移至与环磷酰胺共培养的卵巢颗粒细胞中以减少其凋亡。机制研究表明,miR-144-5p通过PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路靶向PTEN抑制卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡;当miR-144-5p被抑制时,显示相反的作用。另一项研究表明过表达miR-21的间充质干细胞体外凋亡减少、活力增加,并通过下调PTEN和程序性死亡蛋白4基因表达抑制在体外与磷酰氮芥共培养的卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡[22];同时过表达miR-21 的间充质干细胞移植到被化疗破坏的大鼠卵巢中可以更有效地抑制卵巢颗粒细胞的凋亡。ZHENG等[23]将脐带间充质干细胞移植入小鼠卵巢早衰模型后2周检测到卵巢中凋亡明星蛋白Caspase-3表达下降而神经生长因子、原肌球蛋白受体激酶A(tropomyosin receptor kinase A,TrkA)的表达增加,从而证明脐带间充质干细胞是通过调节NGF/TrkA通路抑制卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡。 干细胞移植后的存活率为10%-20%,凋亡及坏死大多发生于移植后的4 d内[24]。间充质干细胞凋亡率也是影响其疗效的关键问题,所以干细胞移植后存活率有待提高。汪庆如等[25]将构建的miR-21慢病毒表达载体转染到骨髓间充质干细胞中,降低了骨髓间充质干细胞的凋亡率,提高了其针对卵巢早衰的治疗效果。该研究认为miR-21的抗凋亡作用依赖于其对靶基因的调控,miR-21相关的靶基因包括PTEN、程序性死亡蛋白4 (PDCD4)、叉头转录因子1 (FoxO1)、 Rho亚家族蛋白B(RhoB)等。 综上,间充质干细胞通过降低卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡率恢复卵巢储备及其功能,并且间充质干细胞自身的凋亡率也会影响治疗效果,所以降低干细胞凋亡也同样重要。 2.1.4 分化作用 间充质干细胞的治疗作用主要是旁分泌作用还是分化作用一直是学界争论的焦点,但可以肯定的是分化作用是间充质干细胞发挥治疗效果的重要组成部分。正是因为间充质干细胞特有的多项分化能力,才会使间充质干细胞移植成为最具潜力的治疗受损器官的方式。一项以人类子宫内膜间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰模型鼠的研究显示,归巢于卵巢的子宫内膜间充质干细胞可以分化为颗粒细胞,但不能分化为卵泡细胞和卵母细胞[26]。最重要的是,子宫内膜间充质干细胞可以恢复卵巢生殖系干细胞的储备。另一项关于人类经血来源间充质干细胞的研究显示,人类经血来源间充质干细胞被追踪并发现其可以在早衰卵巢中分化为颗粒细胞,并且其直接参与卵巢卵泡形成、改善卵泡结构和分泌激素[27]。另一项动物研究也证实人类经血来源间充质干细胞移植后2个月在卵巢组织中分化为颗粒细胞[28]。LIU 等[18]证明人类经血来源间充质干细胞移植入卵巢早衰动物模型后可以被诱导分化为卵巢组织样细胞,尤其是卵巢颗粒样细胞。李慧等[29]总结了间充质干细胞与颗粒细胞的交互作用:间充质干细胞在体内外与颗粒细胞共培养时,可能通过影响颗粒细胞潜能、调控颗粒细胞凋亡或诱导分化为颗粒细胞来发挥各种生物学功能,从而促进卵泡的生长和发育,改善卵巢储备和功能,逆转卵巢早衰。由此推测,间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰可以通过修复颗粒细胞等来修复受损卵巢,或者直接分化为卵巢内颗粒细胞参与卵泡的形成,但具体何种作用起主要作用尚无定论,进一步深入探究间充质干细胞分化和分泌功能的关系是指导干细胞临床应用的关键步骤。 2.1.5 自分泌和旁分泌 自分泌和旁分泌作用同样被认为是间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的重要机制。已经证实由间充质干细胞分泌的生长因子,例如血管内皮生长因子和肝细胞生长因子,在恢复卵巢功能中起重要作用[30],其可能的机制是生长因子减少了颗粒细胞凋亡并恢复了卵泡发育。据一项动物研究报道,血管内皮生长因子及其受体是抑制颗粒细胞凋亡和促进卵泡发育的关键信号通路[31]。另一项动物研究推测人绒毛膜板来源间充质干细胞恢复卵巢早衰卵巢功能可能是由于干细胞可以分泌多种生长因子,而不仅仅是因为单个生长因子增多[32]。 促进血管生成:血管生成对于早衰卵巢功能恢复也很关键,因为它将为受损卵巢提供营养。前文描述的间充质干细胞分泌的细胞因子,如血管内皮生长因子和循环生长因子2,尤其是血管生成素,将会促进干细胞定植组织的血管新生。据报道,骨髓间充质干细胞通过α6β1整合素受体促进血管生成[33]。 诱导自身干细胞:一项创新的临床研究对多名卵巢反应不良的妇女(<40岁)进行了自体细胞卵巢内移植[34]。首先,通过皮下给予粒细胞集落刺激因子将干细胞从骨髓动员到外周血;然后,通过血液分离术分离骨髓间充质干细胞,并通过动脉导管将其注入一条卵巢动脉,治疗后卵巢储备生物标志窦卵泡计数和抗苗勒管激素的改善率高达81.3%,并与循环生长因子2和血小板反应蛋白1的存在呈正相关。该研究使5例患者怀孕,3例活产。该项自体细胞卵巢内移植技术的治疗妊娠率为33.3%,这表明无需采取有创的细胞收集、选择、培养程序,通过直接向卵巢基质中输注即可恢复生育能力。在未输注卵巢中的窦卵泡计数也有所改善,这表明干细胞动员期间循环中的骨髓间充质干细胞对卵巢功能的恢复也存在积极作用。这项研究向大家展示了一个新思路:激活自身干细胞,定向植入受损器官达到治疗目的,但该途径的安全性和具体操作过程仍需要进一步探究。 综上,间充质干细胞通过分泌作用减少颗粒细胞凋亡、促进颗粒细胞增殖、促进血管生成和诱导自身干细胞恢复卵泡发育等机制恢复卵巢功能。 2.1.6 抗炎及免疫调节 临床大多数卵巢早衰的确切病因尚不清楚,为特发性早衰,据估计自身免疫机制缺陷导致4%-30%的中年女性患病。自身免疫性卵巢疾病在免疫病理学上主要由卵巢炎、卵巢萎缩和血清抗卵巢抗原自身抗体等组成。自身免疫机制引起的卵巢功能异常可能与透明带(ZP)抗原有关。一项研究通过注射透明带3多肽片段(pZP3)对小鼠产生自身免疫损伤[10],建立了小鼠卵巢早衰动物模型,并验证脐带间充质干细胞治疗能促进卵巢早衰小鼠卵巢功能和子宫内膜容受性恢复,主要依赖Th1/Th2细胞因子平衡和子宫内膜自然杀伤细胞表达的调节。另一项研究采用了相同的造模方法,证实了人胎盘来源间充质干细胞移植可恢复免疫诱导小鼠卵巢早衰的卵巢功能[35],且卵巢功能的恢复与γ-干扰素和转化生长因子β细胞因子介导的CD25+CD4+调节性T细胞(Tregs)增加和炎症调节有关。YIN等[36]证实人胎盘来源间充质干细胞通过PI3K/Akt信号通路改变Th17/Tc17和Th17/Treg细胞的比例来恢复卵巢早衰小鼠卵巢功能。另一项关于皮肤来源间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的动物研究证实其通过减轻炎症细胞因子的活性调节卵巢中的炎症反应[37],研究显示干细胞移植还上调了受化疗破坏的小鼠卵巢的卵母细胞特异性转录因子,包括Nobox,Nanos3和Lhx8。宋开静等[38]指出卵巢早衰患者外周血Treg细胞数量明显减少,认为寻求促进Treg细胞增殖的有效方法可能是间充质干细胞成功治疗卵巢早衰的关键。在此项研究中,研究者将异体脂肪间充质干细胞与卵巢早衰患者的外周血单个核细胞共培养,结果证实脂肪间充质干细胞可以通过上调Treg细胞的增殖,从而发挥免疫调节功能。 综上,间充质干细胞对于自身免疫缺陷引起的卵巢早衰也有明显的治疗效果,其机制大多涉及调节免疫系统。 2.1.7 调控基因 干细胞迁移到达靶器官后,除了定向分化外,还会调节组织的DNA和RNA表达,发挥表观遗传功能,促使损伤组织的自我修复。WANG等[39]通过对比脐带间充质干细胞移植前后卵巢早衰小鼠卵巢组织RNA表达,证明移植后组织转录水平比卵巢早衰组更接近野生型;该研究也比较了野生型和卵巢早衰组之间的基因表达,发现许多通路受到影响,包括转录调控、G蛋白偶联受体蛋白信号传导途径、MAPK途径和胰岛素途径;脐带间充质干细胞治疗组表达更多的蛋白质参与DNA修饰表观遗传途径、转录途径、蛋白质修饰途径和细胞信号转导,可见干细胞通过调节卵巢组织的DNA、RNA、蛋白和相关通路,进而恢复卵巢储备和功能。不仅干细胞可以诱导靶器官的基因表达改变,靶器官也会调节归巢的干细胞基因水平,从而使其发挥治疗作用。另一项动物研究中cDNA表达谱的微阵列分析结果表明,人类经血来源间充质干细胞表达谱在移植前与人卵巢组织存在明显差异,而移植后其基因表达谱与人类卵巢组织相似[18]。彭静等[40] 证实骨髓间充质干细胞移植后卵巢组织中卵泡发育相关基因Nano3、Nobox和Lhx8 的mRNA水平明显高于对照组,提示骨髓间充质干细胞移植可能通过上调卵泡发育相关基因的表达,促进卵巢早衰小鼠卵泡发育和卵巢组织结构恢复。 总结以上研究,可以发现间充质干细胞通过影响靶器官表观遗传达到治疗目的,同时干细胞自身也会被卵巢组织诱导分化为颗粒细胞从而恢复卵巢储备功能,其中涉及的深层分子机制仍需要进一步深入研究。 2.1.8 调节自噬 自噬是一种细胞自我降解的过程,细胞通过自噬作用清除受损或多余的蛋白质、细胞器以及外来的病菌,以维持细胞功能。在生理状态下,自噬能够维持细胞稳态,在短期压力下,它可以促进细胞生存和分裂能力。有研究证明自噬参与保存幼鼠原始卵泡池,并且参与卵泡发育过程中劣势卵泡的淘汰[41]。YIN等[42]证明脐带间充质干细胞中表达的血红素加氧酶1基因可以通过激活JNK/Bcl-2信号通路调节细胞自噬和上调CD8+CD28-T细胞循环来恢复卵巢早衰小鼠的卵巢功能。一项关于生殖细胞的研究首次利用苯并硼唑类化合物ZCL-082诱导小鼠生殖干细胞发生自噬[43],该研究认为GAS5/miR-21a轴影响细胞自噬,可能是临床卵巢早衰的潜在治疗靶标。因此,间充质干细胞对于自噬的调节也是其治疗卵巢早衰的机制之一。 研究者从多个方面探究了间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的内在机制,见图1。当然,仍有一些机制需要进一步探究,相信随着这一热点问题的深入研究,间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰这一新型疗法最终会应用于临床,为患者带来希望。 2.2 细胞外囊泡 近年来,随着再生医学中干细胞领域的发展,间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的有效性已经被大量研究证实。但是,同种异体间充质干细胞移植期间可能存在免疫排斥的风险。另外,自体间充质干细胞移植前取材面临着侵入性手术的问题,同时间充质干细胞还面临移植后存活率较低的问题。因此,进一步研究间充质干细胞分泌的胞外囊泡,如外泌体和微囊泡,是解决这些问题的突破口。胞外囊泡是细胞间通讯的重要介质,是干细胞治疗各类疾病的另一项重要机制,故详细综述以全面概括其治疗卵巢早衰的内在机制。外泌体和微囊泡构造不同但功能类似,二者都是细胞分泌的携带小分子蛋白质、miRNA、lncRNA和细胞因子的囊泡,主要参与细胞间通讯并调节受体细胞的功能。一项关于间充质干细胞分泌的微囊泡研究显示[44]:微囊泡可以促进共培养的颗粒细胞的增殖,其可以通过激活PI3K/AKT通路恢复化疗诱导的小鼠早衰卵巢的功能并抑制颗粒细胞的凋亡。YANG 等[11]证明了骨髓间充质干细胞可以通过分泌外泌体传递miR-144-5p来治疗大鼠卵巢滤泡闭锁,并可以将外泌体转移至与环磷酰胺共培养的卵巢颗粒细胞中以减少其凋亡。另一项研究证实miR-23a和miR-27a在卵巢早衰患者的血浆中高度表达,并证明间充质干细胞中的miR-23a 和miR-27a靶向颗粒细胞SMAD5基因[45],通过FasL-Fas途径调节人颗粒细胞的凋亡。DING等[46]证实人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过传递miR-17-5P抑制SIRT7表达进而减少活性氧的积累,恢复了卵巢早衰小鼠的卵巢表型和功能。另一项研究证明人羊膜间充质干细胞来源外泌体可改善卵巢早衰患者的颗粒细胞增殖,抑制细胞凋亡[47],探究其内在机制为:外泌体携带的miR-320靶向SIRT4从而抑制细胞氧化应激的发生。由此可见,外泌体及微囊泡通过自身携带的物质可以起到与移植间充质干细胞同样甚至更佳的治疗效果,针对细胞外囊泡的研究将会是未来干细胞治疗领域研究的重点。 2.3 女性生殖干细胞 以往传统观念认为哺乳动物的卵母细胞不能在出生后或成年后更新,暗示哺乳动物卵巢中没有生殖干细胞。但是近年来一些关于小鼠、大鼠和人类的最新研究提供了卵巢中雌性生殖干细胞存在的有力证据。因此,刺激卵巢内生殖干细胞的原位增殖来恢复卵巢功能将是自体干细胞原位治疗的新方式。一项开创性的研究显示在出生后的小鼠卵巢中观察到原始卵泡的更新,这也就表明卵巢中存在生殖干细胞[48]。有研究者开发了一种从新生小鼠卵巢中分离雌性生殖干细胞的快速有效方法,并证明雌性生殖干细胞移植入小鼠体内后分化为卵母细胞[49]。一篇关于卵巢干细胞的综述认为卵巢干细胞是否存在是有一定争议的,但目前主流观点支持卵巢干细胞存在理论[50],基本上已经否定了卵母细胞数量固定学说。在人类卵巢皮质中确实检测到有丝分裂活性的卵巢干细胞,并且实验工作也证明了这些细胞能够分化产生卵母细胞。因此,利用女性生殖系统存在的干细胞,寻找激活并促进其增殖的新方法也许是未来治疗卵巢早衰的新思路。 2.4 组织工程 间充质干细胞移植治疗会受到靶组织中细胞沉降不足的限制,此外,由于炎症、凋亡、缺血性损伤等多种因素相互作用,移植入体内的间充质干细胞难以长期保留在靶器官中。因此,将组织工程材料复合间充质干细胞是弥补这些不足的重要措施。一项关于组织工程的研究显示[51]:胶原蛋白支架复合脐带间充质干细胞移植后通过促进卵巢早衰模型小鼠的颗粒细胞增殖、卵巢血管生成和卵泡发育从而改善卵巢功能;使用胶原蛋白支架可以增加干细胞的存活时间,限制干细胞向外转移,同时支持细胞的附着和增殖;胶原蛋白支架上的脐带间充质干细胞仍具有生物活性,具有长期的治疗作用;干细胞与胶原蛋白支架相互作用可以构造3D微环境,保持干细胞存活率和高表达血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子β1、肝细胞生长因子和成纤维细胞生长因子2,从而促进颗粒细胞形成和增殖。因此,利用组织工程材料复合间充质干细胞的诸多优势来提高治疗卵巢早衰的效果将是该领域研究的前沿方向。"
| [1] TORREALDAY S, KODAMAN P, PAL L. Premature Ovarian Insufficiency - an update on recent advances in understanding and management. F1000Res. 2017;6:2069. [2] 吴洁,陈蓉.早发性卵巢功能不全的激素补充治疗专家共识[J].中华妇产科杂志,2016,51(12):881-886. [3] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411): 143-147. [4] JIANG Y, JAHAGIRDAR BN, REINHARDT RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002; 418(6893):41-49. [5] KRAMPERA M, PASINI A, PIZZOLO G, et al. Regenerative and immunomodulatory potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6(4):435-441. [6] ULLAH I, SUBBARAO RB, RHO GJ. Human mesenchymal stem cells - current trends and future prospective. Biosci Rep. 2015;35(2):e00191. [7] ZAHER W, HARKNESS L, JAFARI A, et al. An update of human mesenchymal stem cell biology and their clinical uses. Arch Toxicol. 2014;88(5):1069-1082. [8] LI H, ZHAO W, WANG L, et al. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit apoptosis of granulosa cells induced by IRE1α pathway in autoimmune POF mice. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(8):899-909. [9] GABR H, RATEB MA, EL SISSY MH, et al. The effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on chemotherapy induced ovarian failure in albino rats. Microsc Res Tech. 2016;79(10):938-947. [10] LU X, CUI J, CUI L, et al. The effects of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on endometrial receptivity are associated with Th1/Th2 balance change and uNK cell expression of uterine in autoimmune premature ovarian failure mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):214. [11] YANG M, LIN L, SHA C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-144-5p improves rat ovarian function after chemotherapy-induced ovarian failure by targeting PTEN. Lab Invest. 2020;100(3):342-352. [12] ELFAYOMY AK, ALMASRY SM, EL-TARHOUNY SA, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-mesenchymal stem cells transplantation renovates the ovarian surface epithelium in a rat model of premature ovarian failure: Possible direct and indirect effects. Tissue Cell. 2016;48(4):370-382. [13] WANG Z, WANG Y, YANG T, et al. Study of the reparative effects of menstrual-derived stem cells on premature ovarian failure in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):11. [14] 王琰,杨瑛,刘兵,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对VCD所致卵巢损伤的修复研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2011,11(10):1844-1846,1850. [15] 陈京京,殷慧群,汪存利,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植在卵巢早衰小鼠卵巢及生育功能重建中的作用[J].安徽医科大学学报,2017, 52(11):1611-1615. [16] 柳颖灵,刘炜,纪亚忠. SDF-1/CXCR4轴在间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰中的研究进展[J].实用临床医学,2015,16(7): 100-103,107. [17] LIU T, LI Q, WANG S, et al. Transplantation of ovarian granulosa‑like cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells for the treatment of murine premature ovarian failure. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(6): 5053-5058. [18] LIU T, HUANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Transplantation of human menstrual blood stem cells to treat premature ovarian failure in mouse model. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(13):1548-1557. [19] 杜静,刘文慧,王婷,等.人脐带间充质干细胞对卵巢早衰大鼠卵巢超微结构和功能的影响[J].现代妇产科进展,2018,27(2):127-130. [20] SONG D, ZHONG Y, QIAN C, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Therapy in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Premature Ovarian Failure Rat Model. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2517514. [21] CHEN X, WANG Q, LI X, et al. Heat shock pretreatment of mesenchymal stem cells for inhibiting the apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells enhanced the repair effect on chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):240. [22] FU X, HE Y, WANG X, et al. Overexpression of miR-21 in stem cells improves ovarian structure and function in rats with chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage by targeting PDCD4 and PTEN to inhibit granulosa cell apoptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):187. [23] ZHENG Q, FU X, JIANG J, et al. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Prevents Chemotherapy-Induced Ovarian Failure via the NGF/TrkA Pathway in Rats. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:6539294. [24] ZHANG M, METHOT D, POPPA V, et al. Cardiomyocyte grafting for cardiac repair: graft cell death and anti-death strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33(5):907-921. [25] 汪庆如,陈小莹,李欣然,等.过表达miR-21的骨髓间充质干细胞对化疗性卵巢早衰的修复作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2019,44(3): 203-209. [26] LAI D, WANG F, YAO X, et al. Human endometrial mesenchymal stem cells restore ovarian function through improving the renewal of germline stem cells in a mouse model of premature ovarian failure. J Transl Med. 2015;13:155. [27] MANSHADI MD, NAVID S, HOSHINO Y, et al. The effects of human menstrual blood stem cells-derived granulosa cells on ovarian follicle formation in a rat model of premature ovarian failure. Microsc Res Tech. 2019;82(6):635-642. [28] NOORY P, NAVID S, ZANGANEH BM, et al. Human Menstrual Blood Stem Cell-Derived Granulosa Cells Participate in Ovarian Follicle Formation in a Rat Model of Premature Ovarian Failure In Vivo. Cell Reprogram. 2019;21(5):249-259. [29] 李慧,陈曦,昌晓红.脐带间充质干细胞与卵巢早衰中颗粒细胞交互作用的研究进展[J].中国医药生物技术, 2019,14(3):263-265. [30] FU X, HE Y, XIE C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves ovarian function and structure in rats with chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage. Cytotherapy. 2008;10(4): 353-363. [31] YAO X, GUO Y, WANG Q, et al. The Paracrine Effect of Transplanted Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells on Ovarian Function Improvement in a Mouse Model of Chemotherapy-Induced Primary Ovarian Insufficiency. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:4148923. [32] LI J, YU Q, HUANG H, et al. Human chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation restores ovarian function in a chemotherapy-induced mouse model of premature ovarian failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):81. [33] CARRION B, KONG YP, KAIGLER D, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis via their α6β1 integrin receptor. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(19):2964-2976. [34] HERRAIZ S, ROMEU M, BUIGUES A, et al. Autologous stem cell ovarian transplantation to increase reproductive potential in patients who are poor responders. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(3):496-505. [35] YIN N, ZHAO W, LUO Q, et al. Restoring Ovarian Function With Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Autoimmune-Induced Premature Ovarian Failure Mice Mediated by Treg Cells and Associated Cytokines. Reprod Sci. 2018;25(7):1073-1082. [36] YIN N, WANG Y, LU X, et al. hPMSC transplantation restoring ovarian function in premature ovarian failure mice is associated with change of Th17/Tc17 and Th17/Treg cell ratios through the PI3K/Akt signal pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):37. [37] LAI D, WANG F, DONG Z, et al. Skin-derived mesenchymal stem cells help restore function to ovaries in a premature ovarian failure mouse model. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e98749. [38] 宋开静,何援利,蔡慧华,等.异体脂肪间充质干细胞对卵巢早衰患者外周血调节性T细胞的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2018,43(4): 294-298. [39] WANG S, YU L, SUN M, et al. The therapeutic potential of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in mice premature ovarian failure. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:690491. [40] 彭静,肖娜,程腊梅.骨髓来源间充质干细胞对卵巢早衰小鼠的修复作用[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2018,43(1):7-13. [41] HUŁAS-STASIAK M, GAWRON A. Follicular atresia in the prepubertal spiny mouse (Acomys cahirinus) ovary. Apoptosis. 2011;16(10):967-975. [42] YIN N, WU C, QIU J, et al. Protective properties of heme oxygenase-1 expressed in umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells help restore the ovarian function of premature ovarian failure mice through activating the JNK/Bcl-2 signal pathway-regulated autophagy and upregulating the circulating of CD8+CD28- T cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):49. [43] LI B, HU X, YANG Y, et al. GAS5/miR-21 Axis as a Potential Target to Rescue ZCL-082-Induced Autophagy of Female Germline Stem Cells In Vitro. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:436-447. [44] LIU M, QIU Y, XUE Z, et al. Small extracellular vesicles derived from embryonic stem cells restore ovarian function of premature ovarian failure through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):3. [45] NIE M, YU S, PENG S, et al. miR-23a and miR-27a promote human granulosa cell apoptosis by targeting SMAD5. Biol Reprod. 2015; 93(4):98. [46] DING C, ZHU L, SHEN H, et al. Exosomal miRNA-17-5p derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improves ovarian function in premature ovarian insufficiency by regulating SIRT7. Stem Cells. 2020;38(9):1137-1148. [47] DING C, QIAN C, HOU S, et al. Exosomal miRNA-320a Is Released from hAMSCs and Regulates SIRT4 to Prevent Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in POI. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:37-50. [48] JOHNSON J, CANNING J, KANEKO T, et al. Germline stem cells and follicular renewal in the postnatal mammalian ovary. Nature. 2004; 428(6979):145-150. [49] LIU J, SHANG D, XIAO Y, et al. Isolation and characterization of string-forming female germline stem cells from ovaries of neonatal mice. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(39):16003-16013. [50] SILVESTRIS E, D’ORONZO S, CAFFORIO P, et al. In Vitro Generation of Oocytes from Ovarian Stem Cells (OSCs): In Search of Major Evidence. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6225. [51] YANG Y, LEI L, WANG S, et al. Transplantation of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells on a collagen scaffold improves ovarian function in a premature ovarian failure model of mice. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019;55(4):302-311. [52] TAUCHMANOVÀ L, SELLERI C, DE ROSA G, et al. Estrogen-progestin therapy in women after stem cell transplant: our experience and literature review. Menopause. 2007;14(2):320-330. [53] 李慧,张琛,崔恒,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的研究进展[J].中国妇产科临床杂志,2017,18(5): 478-480. [54] DING C, LI H, WANG Y, et al. Different therapeutic effects of cells derived from human amniotic membrane on premature ovarian aging depend on distinct cellular biological characteristics. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):173. [55] 叶小凤,何援利,付霞霏,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗顺铂致卵巢的化疗性损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(10):1597-1602. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1316-1322. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1323-1329. |
| [3] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1330-1335. |
| [4] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1183-1190. |
| [5] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1191-1197. |
| [6] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1068-1074. |
| [7] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1128-1132. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1133-1140. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1141-1150. |
| [10] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1151-1155. |
| [11] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1156-1162. |
| [12] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1163-1169. |
| [13] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1170-1176. |
| [14] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1177-1182. |
| [15] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1086-1092. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||