[1] SHAH SI, PAINE JG, PEREZ C, et al. Mitochondrial fragmentation and network architecture in degenerative diseases. PLoS One. 2019;14(9): e0223014.
[2] FLIPPO KH, STRACK S. Mitochondrial dynamics in neuronal injury, development and plasticity. J Cell Sci. 2017;130(4):671-681.
[3] RODRIGUES T, FERRAZ LS. Therapeutic potential of targeting mitochondrial dynamics in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;10(182): 114282.
[4] MANCZAK M, KANDIMALLA R, FRY D, et al. Protective effects of reduced dynamin-related protein 1 against amyloid-beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage in Aizheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2016;25(23):5148-5166.
[5] FENG Y, LOGRASSO PV, DEFERT O, et al. Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitors and their therapeutic potential. J Med Chem. 2016;59(6):2269-2300.
[6] YAN Y, YU J, GAO Y, et al. Therapeutic potentials of the Rho kinase inhibitor Fasudil in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the related mechanisms. Metab Brain Dis. 2019;34(2):377-384.
[7] MARTORELL-RIERA A, SEGARRA-MONDEJAR M, REINA M, et al. Mitochondrial fragmentation in excitotoxicity requires ROCK activation. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(9):1365-9.
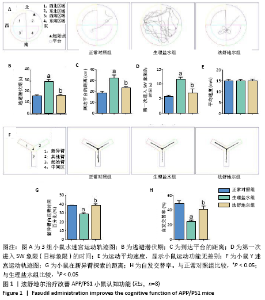
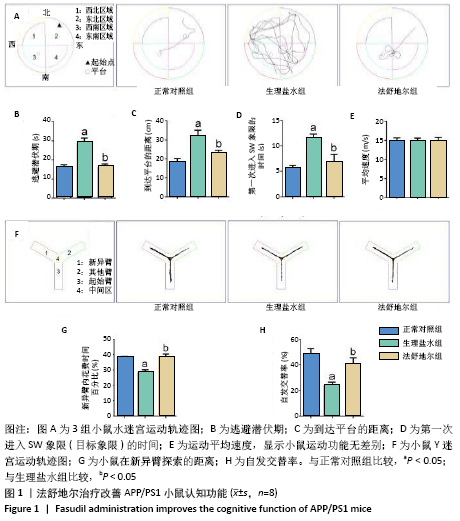
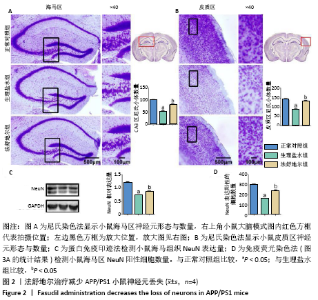
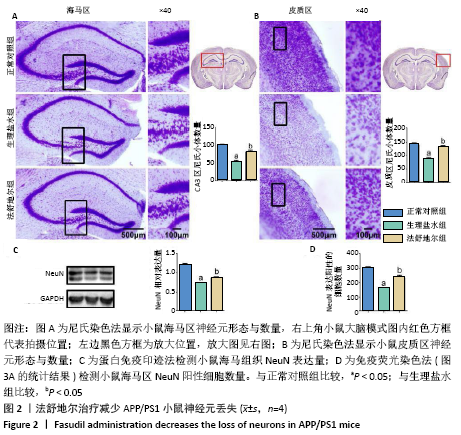
[8] 尉杰忠,闫玉清,谷青芳,等. 法舒地尔通过促进APP/PS1双转基因小鼠神经再生改善认知功能[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(7): 1153-1161.
[9] 吴昊,辛延乐,谷青芳,等. AD发病机制中ROCK对免疫炎性反应的作用[J]. 山西大同大学学报(自然科学版),2017,33(1):52-55.
[10] YU JZ, LI YH, LIU CY, et al. Multitarget Therapeutic Effect of Fasudil in APP/PS1transgenic Mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017;16:199-209.
[11] ALDANA BI. Microglia-Specific Metabolic Changes in Neurodegeneration. J Mol Biol. 2019;431(9):1830-1842.
[12] PUROHIT PK, SAINI N. Mitochondrial microRNA (MitomiRs) in cancer and complex mitochondrial diseases: current status and future perspectives. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(4):1405-1421.
[13] OBULESU M, LAKSHMI MJ. Apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: an understanding of the physiology, pathology and therapeutic avenues. Neurochem Res. 2014;39(12):2301-2312.
[14] KOCH JC, TATENHORST L, ROSER AE, et al. ROCK inhibition in models of neurodegeneration and its potential for clinical translation. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;189(6):1-21.
[15] 周荣,尉杰忠,马存根,等. ROCK抑制剂对AD的神经保护作用研究进展[J].山西大同大学学报(自然科学版),2017,33(1):49-51.
[16] LI XC, HU Y, WANG ZH, et al. Human wild-type full-length tau accumulation disrupts mitochondrial dynamics and the functions via increasing mitofusins. Sci Rep. 2016;5(21):24756.
[17] 杨瀚宇,王璐,臧彩霞,等.线粒体动力学调控的分子机制及其与β淀粉样蛋白的关系[J].中国新药杂志,2017,26(19):2285-2290.
[18] GAO S, HU J. Mitochondrial Fusion: The Machineries In and Out. Trends Cell Biol. 2021;31(1):62-74.
[19] GUPTA A, BECKER T. Mechanisms and pathways of mitochondrial outer membrane protein biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2020;1862(1):148323.
[20] FRANK S, GAUME B, BERGMANN-LEITNER ES, et al. The Role of Dynamin-related protein 1, a mediator of mitochondrial fission, in apoptosis. Dev Cell. 2001;1(4):515-525.
[21] WU P, LI Y, ZHU S, et al. Mdivi-1 alleviates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats, possibly via inhibition of Drp1-activated mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(5):1449-1458.
[22] CHAE U, MIN JS, LEE H, et al. Chrysophanol suppresses pro-inflammatory response in microglia via regulation of Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2017;39(5): 268-275.
[23] WANG W, YIN J, MA X, et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial fragmentation protects against Alzheimer’s disease in rodent model. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(21):4118-4131.
[24] MANCZAK M, CALKINS MJ, REDDY PH. Impaired mitochondrial dynamics and abnormal interaction of amyloid beta with mitochondrial protein Drp1 in neurons from patients with Alzheimer’s disease: implications for neuronal damage. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20(13): 2495-2509.
[25] JIANG S, NANDY P, WANG W, et al. Mfn2 ablation causes an oxidative stress response and eventual neuronal death in the hippocampus and cortex. Mol Neurodegener. 2018;13(1):5.
[26] YAN J, LIU XH, HAN MZ, et al. Blockage of GSK3β-mediated Drp1 phosphorylation provides neroprotection in neuonal and mouse models of Aizheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(1):211-227.
[27] BAEK SH, PARK SJ, JEONG JI, et al. Inhibition of Drp1 Ameliorates Synaptic Depression, Aβ Depression, and Cognitive Impairment in an Aizheimer’s disease Model. J Neurosci. 2017;37(20):5099-5110.
[28] KANDIMALLA R, MANCZAK M, YIN X, et al. Hippocampal phosphorylated tau induced cognitive decline, dendritic spine loss and mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(1):30-40.
[29] MANCZAK M, REDDY PH. Abnormal interaction between the mitochondrial fission protein Drp1 and hyperphosphorylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease neurons: implications for mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal damage. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(11): 2538-2547.
[30] KANDIMALLA R, MANCZAK M, FRY D, et al. Reduced dynamin-related protein 1 protects against phosphorylated Tau-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2016;25(22):4881-4897.
[31] 高晨皓,孙争宇,张杰文.线粒体动力学失衡与阿尔茨海默病发病机制的相关性研究进展[J].中华神经医学杂志,2019,56(4):337-343. |