Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 758-764.doi: 10.12307/2023.114
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury
Li Zhichao1, Tan Guoqing2, Su Hui1, Xu Zhanwang2, Xue Haipeng1, 2
- 1Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-25Accepted:2022-05-16Online:2023-02-18Published:2022-07-23 -
Contact:Xue Haipeng, MD, Associate chief physician, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Li Zhichao, MD candidate, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82174410 (to XZW); Key Project of Shandong Natural Science Foundation, No. ZR202011050051 (to XZW); Jinan Municipal Clinical Medicine Science and Technology Innovation Program, No. 202019148 (to XHP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
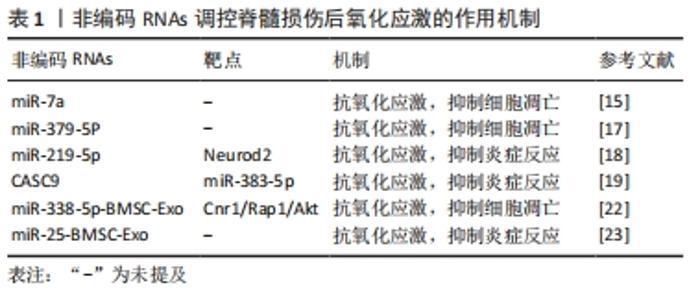
2.1 脊髓损伤后非编码RNAs的差异表达 非编码RNAs主要由微小RNAs(microRNAs,miRNAs)、长链非编码RNAs(long non-coding RNAs,lncRNAs)和环状RNAs(circular RNAs,circRNAs)组成,作为重要的调节因子,几乎参与了正常发育和各种疾病(包括脊髓损伤)中的所有细胞变化进程。miRNAs长度为20-22个核苷酸,可识别靶mRNAs的3’非翻译区域从而抑制或降解靶mRNAs[6]。lncRNAs是一类长度大于200个核苷酸的非编码RNAs,可以通过自身的核苷酸序列或折叠的二级结构与底物结合,并通过转录和转录后水平的多种机制调节基因表达[7]。circRNAs是共价闭合环状的非编码RNAs,主要作为miRNAs海绵调节基因表达[8]。研究人员发现,脊髓损伤后存在多种非编码RNAs的差异表达,例如基于微阵列分析的几项研究分别鉴定了97个miRNAs、1 676个circRNAs和772个lncRNAs在大鼠脊髓损伤后差异表达,这意味着非编码RNAs具有成为全新生物标志物和治疗靶点的潜力[9-11]。随着研究的深入,非编码RNAs参与调节脊髓损伤后氧化应激、炎症反应、细胞自噬和凋亡的重要作用机制被逐渐揭示。 2.2 非编码RNAs调控脊髓损伤后氧化应激 与脊髓损伤病理生理过程中涉及的其他因素和机制相比,氧化应激似乎发挥了更重要的作用。从机制的角度来看,氧化应激和炎症反应被认为是脊髓损伤后交联失调机制(例如细胞凋亡和自噬)的主要上游启动因素[12]。正常情况下,活性氧的产生和消除处于动态平衡,然而在脊髓损伤刺激下,活性氧过量产生和消除减弱导致受损区域活性氧代谢失衡,过量的活性氧会攻击神经组织并激活一系列级联反应[13]。因此抑制氧化途径可以显著降低脊髓损伤后的严重程度,同时也被认为是防治脊髓损伤的最合适策略之一[14]。 近年来的研究显示,非编码RNAs通过调节氧化应激在脊髓损伤的细胞和动物模型中发挥重要作用。DING等[15]发现miR-7a在脊髓损伤大鼠损伤组织中表达下调,其机制与活性氧产生和进一步激活的细胞凋亡有关,通过上调miR-7a表达可下调线粒体动力相关蛋白1和上调线粒体融合蛋白2水平以挽救线粒体活性,并增加超氧化物歧化酶1和血红素加氧酶1活性,从而有效拮抗氧化应激,抑制细胞凋亡,促进脊髓损伤大鼠的功能恢复。内皮素是目前已知的最强大的血管收缩剂,脊髓损伤后内皮素1的过量产生导致血管收缩,这与脊髓损伤后缺血和缺氧症状密切相关[16]。在脊髓损伤大鼠损伤组织中,伴随着内皮素1水平的增加,miR-379-5p表达持续下调,而在注射了miR-379-5p的大鼠中观察到内皮素1减少,同时血红素加氧酶1表达增加,并有效恢复了大鼠运动功能,表明miR-379-5p通过提高损伤脊髓对抗氧化应激能力从而改善脊髓损伤[17]。此外,两种非编码RNAs被报道同时参与脊髓损伤后的氧化应激和炎症反应。其中,miR-219-5p通过靶向并抑制神经源性分化蛋白2(neurogenicdifferentiation 2,NeuroD2)的表达以减轻氧化应激和炎症反应,促进脊髓损伤恢复[18]。LncRNA CASC9则作为miR-383-5p的内源竞争RNA,逆转了脊髓损伤大鼠和脂多糖诱导的PC12细胞中丙二醛、乳酸脱氢酶、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的高表达,在脊髓损伤后氧化应激和炎症反应中发挥保护作用[19]。 外泌体是细胞分泌的囊泡,可以介导细胞之间的物质和信息交换,作为药物或分子载体在神经损伤修复中发挥着重要作用[20-21]。作为新的研究热点,几项研究关注了miRNAs-外泌体在脊髓损伤后的作用机制。来自骨髓间充质干细胞过表达miR-338-5p的外泌体改善了神经细胞的生存环境,并在体内和体外抑制了脊髓损伤后的氧化应激和细胞凋亡,其潜在机制是miR-338-5p通过调节大麻素受体1(cannabinoid receptor 1,Cnr1)/Ras相关蛋白1(Ras-associated protein 1,Rap1)/Akt轴实现的[22]。同时,鞘内注射富含miR-25的外泌体可提高短暂缺血脊髓中超氧化物歧化酶1活性,并降低脊髓中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和丙二醛水平,通过拮抗氧化应激和炎症提供了较好的神经保护作用,展现出了作为新兴无细胞疗法治疗脊髓损伤的独特优势[23]。 了解脊髓损伤后的氧化应激机制至关重要,只有平衡好氧化与抗氧化状态,才有可能提前阻断脊髓损伤后炎症反应以及后续包括自噬、凋亡在内的一系列失调机制。因此,为氧化应激寻找新的生物标志物和治疗靶点对于防治脊髓损伤必不可少。有关脊髓损伤后非编码RNAs在氧化应激方面的作用机制研究给研究者指明了一个有潜力的前进方向。目前而言,作为非编码RNAs重要组成部分之一的circRNAs在有关氧化应激方面的研究仍然十分匮乏,但不难想象circRNAs-miRNAs轴在其中一定扮演着重要角色。见表1。 "
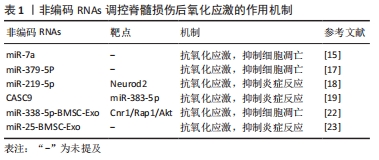
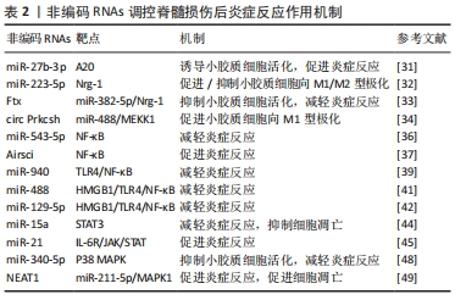
2.3 非编码RNAs调控脊髓损伤后的炎症反应 在原发性损伤后,血脊髓屏障完整性受损,由先天性(外周:中性粒细胞、单核细胞和巨噬细胞;中枢神经系统常驻细胞:星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞)和适应性(B和T淋巴细胞)免疫应答引起炎症级联反应[24],这一炎症级联反应被认为具有神经损伤和神经保护的双重作用[25]。炎症趋化因子和细胞因子可以补充和激活中枢神经细胞和免疫细胞[26],炎性细胞也存在着不同表型,部分表型有助于脊髓损伤后的修复[27],而炎症的副作用则会诱导神经元和少突胶质细胞凋亡,导致胶质瘢痕形成[28]。 2.3.1 非编码RNAs调控小胶质细胞的炎症反应 小胶质细胞是中枢神经系统中最重要的炎症效应细胞,分为M1促炎表型和M2抗炎表型,由于它们的活化和迁移早于中枢神经系统内的大多数炎症事件,因此小胶质细胞可直接影响脊髓修复和下游炎症过程[29]。而当小胶质细胞活化时产生促炎递质如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α等,可引发神经炎症,导致神经元损伤[30]。大量证据表明,非编码RNAs调节小胶质细胞活化和极化并参与相关的炎症反应。例如,LI等[31]发现miR-27b-3p可诱导小胶质细胞活化,通过靶向抑制A20(肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白3)表达,促进白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α表达,从而导致小胶质细胞神经炎症的加重。GUAN等[32]观察到脊髓损伤后miR-223-5p水平明显升高,抑制miR-223-5p表达可显著促进M2小胶质细胞的极化,降低白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α表达并增加神经调节蛋白1(neuregulin-1,Nrg-1)表达,增加的神经调节蛋白1表达则减少了神经细胞凋亡和胶质瘢痕形成,最终改善了后肢运动功能。同样,XIANG等[33]也观察到脊髓损伤后lncRNA Ftx、Nrg-1低表达和miR-382-5p高表达,并进一步证明Ftx通过海绵化miR-382-5p,靶向Nrg-1从而改善小胶质细胞的炎症反应。此外,LI等[34]发现circ Prkcsh也可作为miR-488的内源竞争RNA来促进MEKK1表达,增加M1型小胶质细胞的极化。 2.3.2 非编码RNAs调控相关炎症信号通路 脊髓损伤后炎症反应是极其复杂的过程,炎症信号传导在其中起着重要作用,而非编码RNAs可以通过调节这些炎症信号通路如NF-κB信号通路、TLR信号通路、JAK/STAT信号通路、MAPK信号通路等参与脊髓损伤后的炎症进展。NF-κB是一种在真核细胞中广泛表达的蛋白质复合物,当它被应激和促炎因子如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1等激活时,NF-κB可以转移到细胞核内,进一步诱导促炎因子产生,这些炎症因子也可以周期性地激活NF-κB,导致炎症反应扩大[35]。最近,miR-543-5p被发现通过抑制NF-κB通路从而抑制脊髓损伤大鼠炎症反应并促进神经再生[36]。与之相反,LncRNA Airsci则通过激活NF-κB通路从而促进大鼠脊髓损伤后炎症反应[37]。Toll受体是巨噬细胞参与炎症反应的重要受体,在免疫防御中起关键作用,其中Toll受体4是Toll受体家族中与炎症反应最密切相关的成员[38]。WANG等[39]发现在脊髓损伤小鼠中miR-940表达下调,而过表达miR-940可通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路从而显著抑制炎症反应,促进脊髓损伤小鼠的运动恢复。不仅如此,高迁移率族蛋白B1(high mobility group protein B1,HMGB1)是炎症反应中常见调节剂,脊髓损伤后高迁移率族蛋白B1通过触发Toll受体4等导致NF-κB信号通路激活并诱导促炎细胞因子的产生[40]。最近的报道称miR-488、miR-129-5p均可通过抑制HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB通路从而抑制炎症反应,减轻小鼠脊髓损伤[41-42]。 信号转导与转录激活因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3)作为JAK/STAT通路家族的一员,已被证明参与神经损伤后引发星形胶质细胞活化和胶质瘢痕形成,其活化介导脊髓损伤后炎症反应[43]。WU等[44]发现小鼠脊髓损伤后miR-15a低表达,而信号转导与转录激活因子3高表达,通过上调miR-15a表达可负调控信号转导与转录激活因子3,同时使受损脊髓组织中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6表达下调,证明miR-15a通过靶向信号转导与转录激活因子3抑制脊髓损伤后的炎症反应,减轻细胞凋亡。此外,NING等[45]通过脊髓鞘内注射miR-21抑制剂实现miR-21表达下调,发现抑制miR-21可通过抑制IL-6R/JAK/STAT通路,减轻脊髓损伤后炎症反应。MAPK信号通路通过激活c-Jun氨基末端激酶、p38和细胞外信号相关激酶级联来调节与炎症、凋亡和细胞分化相关基因的表达水平[46],其促进炎症因子释放,从而导致神经炎症,并诱导细胞凋亡[47]。QIAN等[48]观察到在脊髓损伤大鼠模型中miR-340-5p表达下调,进一步实验发现过表达miR-340-5p可持续降低脂多糖诱导的小胶质细胞内肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6表达水平,而抑制miR-340-5p表达则有助于炎性细胞因子聚集,同时,P38受到了miR-340-5p负调控,最终证明miR-340-5p通过抑制P38 MAPK通路以对抗小胶质细胞炎症反应。同样,AN等[49]在脂多糖诱导的PC12细胞脊髓损伤模型中发现lncRNA NEAT1表达上调,而敲除NEAT1可增加细胞活力并抑制细胞凋亡和炎症反应,进一步研究发现NEAT1作为miR-211-5p的内源竞争RNA,促进了miR-211-5p下游基因MAPK1(ERK2)的表达,证明敲低lncRNA NEAT1可通过靶向miR-211-5p/MAPK1轴减轻脊髓损伤炎症反应,抑制细胞凋亡。 近年来,在脊髓损伤中有关非编码RNAs调节小胶质细胞炎症反应的研究明显增加,并且涉及靶点广泛,因此无法依照清单进行彻底讨论,但是通过非编码RNAs干预小胶质细胞活化,阻断诱导M1表型激活的促炎细胞因子,上调抗炎细胞因子表达,增加M2表型极化,以减轻炎症反应和促进脊髓功能恢复的治疗方法无疑极具前景。基于相关炎症信号通路的研究也日益增多,但通路之间的相互串扰使得特异性调控变得困难,脊髓损伤后激活的多条炎症相关通路之间的相对重要性也不清晰,加之脊髓损伤后非编码RNAs谱的广泛差异表达,使得研究方向的优先化和选择也十分困难。但相信这种“非编码RNAs-信号通路-炎症反应”链条关系的持续深入研究,将有利于更精确地认识脊髓损伤后的炎症反应机制。见表2。 "
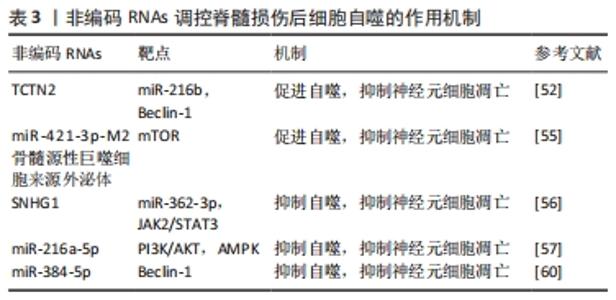
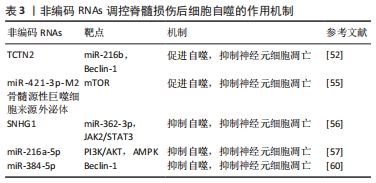
2.4 非编码RNAs调控脊髓损伤后细胞自噬 自噬是一种保守的细胞内代谢循环过程,是维持细胞稳态的重要环节。在神经元等终末分化细胞中,由于受损细胞器和蛋白不能通过有丝分裂和增殖重新分配,自噬便发挥着尤为重要的作用。先前的研究认为,脊髓损伤大鼠中自噬激活可通过抑制神经元凋亡来减少神经元损伤并促进运动功能恢复[50]。自噬相关基因Beclin-1的过表达也通过增强自噬保护脊髓神经元免受机械损伤诱导的细胞凋亡[51]。因此,自噬的激活可能在脊髓损伤中发挥保护性作用。REN等[52]在脊髓损伤大鼠模型和缺氧-葡萄糖剥夺诱导的SY-SH-5Y细胞中发现lncRNA TCTN2表达下调,而miR-216b表达上调,进一步研究发现TCTN2负向调控miR-216b,通过靶向miR-216b/Beclin-1轴促进自噬,从而改善神经元凋亡,减轻脊髓损伤。骨髓源性巨噬细胞在脊髓损伤后被招募到损伤区域,与小胶质细胞一起参与功能恢复的调节[53]。既往研究表明,源自M2小胶质细胞外泌体miRNA具有神经保护作用[54]。因此,WANG等[55]研究了M2骨髓源性巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体在脊髓损伤中的作用,发现其通过传递miR-421-3p抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)途径,提高神经元自噬水平,减少细胞凋亡,促进脊髓损伤小鼠功能恢复。 自噬的过度激活也可能造成过度自我消化,从而导致自噬性细胞死亡。ZHOU等[56]在脂多糖诱导的PC12细胞中发现lncRNA SNHG1上调和miR-362-3p下调,细胞活力减弱而凋亡和自噬增加,进一步研究发现SNHG1作为miR-362-3p的内源竞争RNA激活JAK2/STAT3通路,而下调SNHG1可通过抑制自噬来抑制细胞凋亡,进而增强脂多糖诱导的PC12细胞活性。YI等[57]发现人参皂苷Rg1能够显著增加300 μmol/L浓度下H2O2诱导的PC12细胞活性,并通过靶向miR-216a-5p,激活PI3k/Akt和AMPK信号通路,抑制自噬减少细胞凋亡,对细胞损伤起到保护作用。除了过度自噬导致的自噬性细胞死亡之外,自噬通量阻断也是脊髓损伤后自噬损害机制之一。自噬通量是指从自噬起始至自噬溶酶体降解的动态过程,而自噬通量阻断可能因为有毒蛋白聚集物和缺陷细胞器的积累从而导致细胞损伤和死亡[58]。先前的研究发现,自噬通量在不同类型脊髓损伤中进展不同,轻中度损伤后自噬通量激活,重度损伤后自噬通量阻断[59]。ZHOU等[60]研究miR-384-5p在脊髓损伤中的作用,发现miR-384-5p直接靶向Beclin-1抑制自噬,同时通过降低GRP78表达抑制内质网应激,促进脊髓损伤大鼠的恢复,并认为自噬小体降解不足可能是脊髓损伤大鼠神经元中自噬小体积累的原因,miR-384-5p在脊髓损伤中的保护作用可能与通过抑制自噬的激活来减轻自噬通量阻断有关。 很多研究认为,自噬与凋亡的相互作用是决定细胞命运的关键。然而目前为止,自噬在脊髓损伤中的作用仍不明确,自噬通量在不同类型脊髓损伤中进展也不同,自噬水平的动态监测也没有统一标准,很多基于静态自噬水平监测的实验也并不能够合理地解释这一动态过程在脊髓损伤中的具体作用,在不同刺激下触发的不同自噬相关信号通路也不同程度影响了自噬在脊髓损伤中的进程,这些差异性表达使得自噬在脊髓损伤中呈现出了有益和有害的双重作用。但毫无疑问,自噬在脊髓损伤中具有重要作用,借助非编码RNAs对自噬进行精细化调控,确定理想化的自噬水平,保持自噬通量通畅,在脊髓损伤的治疗中具有极大积极意义。见表3。 "
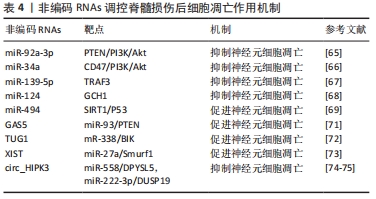
2.5 非编码RNAs调控脊髓损伤后细胞凋亡 细胞凋亡作为最常见的细胞程序性死亡形式,是一个高度保守的生物学过程,包括杀死或消除过时、有害或有缺陷的细胞,这一过程在正常情况下对维持细胞内稳态十分重要[61]。而在组织损伤后,细胞凋亡因为兴奋性毒性物质、自由基和炎症递质的刺激被激活[62]。脊髓损伤后的继发性损伤被认为是由于细胞凋亡被激活后的持续破坏所致,损伤脊髓神经元和少突胶质细胞大范围凋亡导致了长期的神经功能缺损[63]。近年来,部分研究探讨了非编码RNAs作为内源性调节因子调控凋亡参与脊髓损伤进程的作用机制。 在涉及细胞凋亡的途径中,PI3K/Akt信号通路被认为发挥重要作用[64]。最近发现2种miRNAs,即miR-92a-3p和miR-34a,可分别通过靶向磷酸酶张力蛋白同源物(phosphatase and tensin homolog,PTEN)和整合素相关蛋白(CD47)激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,从而抑制脊髓组织的细胞凋亡,促进脊髓损伤后功能恢复[65-66]。同时,其他研究关注了脊髓损伤后miR-139-5p、miR-124、miR-494的表达失调,以及它们与神经元凋亡的关联。靶向肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3(tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3,TRAF3)的miR-139-5p在脊髓损伤大鼠模型中低表达,促进其表达可有效减轻细胞凋亡[67]。miR-124被证明可显著降低脂多糖诱导的脊髓神经元凋亡,其机制与抑制三磷酸鸟苷环化水解酶1(GTP cyclohydrolase 1,GCH1)表达有关[68]。与之相反,靶向SIRT1的miR-494可通过p53信号通路在体内和体外诱导脊髓损伤后细胞凋亡,并下调Caspase-3和Caspase-9表达[69],而Caspase-3凋亡通路的上游和下游成分在先前已被证明在脊髓损伤后激活,并在细胞凋亡过程中发挥重要作用[70]。 几项研究还关注了lncRNAs和circRNAs在脊髓损伤后细胞凋亡过程中的作用。CAO等[71]发现在脊髓损伤小鼠和缺氧细胞模型中,敲低lncRNA GAS5可通过miR-93/PTEN轴发挥抗炎和抑制神经元凋亡的作用。与之相似,lncRNA TUG1的敲低也可通过miR-338/BCL-2相互作用杀伤因子(Bel-2 interacting killer,BIK)轴阻止神经元凋亡,从而减轻急性脊髓损伤[72]。lncRNA XIST的敲低可通过miR-27a/Smad泛素化调节因子1(Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 1,Smurf1)轴减轻脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞的凋亡和炎症损伤[73]。两项研究提供了circ_HIPK3参与脊髓损伤后细胞凋亡的证据。在ZHAO等[74]研究中发现circ_HIPK3的表达在脊髓损伤大鼠模型以及CoCl2诱导的AGE1.HN和PC12细胞中逐渐下调,抑制或过表达circ_HIPK3可以分别提高或降低AGE1.HN和PC12细胞凋亡,并且circ_HIPK3被鉴定为miR-558的内源竞争RNA,可上调抗二氢嘧啶酶相关蛋白5(dihydropyrimidinase like 5,DPYSL5)表达,证明circ_HIPK3通过miR-558/DPYSL5轴减轻脊髓损伤后神经元凋亡。与上述机制类似,Liu等[75]证明了circ_HIPK3同样可通过miR-222-3p/双特异性磷酸酶19(dual specificity phosphatases 19,DUSP19)轴作为脊髓损伤进展中的抑制剂,从而减轻神经元凋亡。 脊髓损伤后细胞凋亡的增加促进了组织损伤,因此寻找抑制细胞凋亡的方法可能对进一步治疗具有重要临床意义。目前脊髓损伤后凋亡相关非编码RNAs的研究已经初具成果,确立了很多有潜力的治疗策略,但开展相应的临床转化却存在困难。部分研究也需要谨慎对待,因为它们并未对相关非编码RNAs靶点和凋亡之间的作用机制做出明确解释,也没有提供这些非编码RNAs和凋亡之间联系的实质性证据;并且脊髓损伤后导致神经元、星形胶质细胞、少突胶质细胞和小胶质细胞凋亡的详细机制也尚未完全阐明。但是,靶向非编码RNAs抑制细胞凋亡作为治疗脊髓损伤的重要切入点,值得进一步深入研究。见表4。 "
| [1] JIANG B, SUN D, SUN H, et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and External Causes of Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury in China: A Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Survey. Front Neurol. 2022;12:784647. [2] WU X, YAN Y, ZHANG Q. Neuroinflammation and Modulation Role of Natural Products After Spinal Cord Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:5713-5737. [3] GUO XD, HE XG, YANG FG, et al. Research progress on the regulatory role of microRNAs in spinal cord injury. Regen Med. 2021;16(5):465-476. [4] RAMER LM, RAMER MS, BRADBURY EJ. Restoring function after spinal cord injury: towards clinical translation of experimental strategies. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(12):1241-1256. [5] LI P, JIA Y, TANG W, et al. Roles of Non-coding RNAs in Central Nervous System Axon Regeneration. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:630633. [6] LI Z, SUN Y, HE M, et al. Differentially-expressed mRNAs, microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration identified by RNA-sequencing. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):1026-1039. [7] YANG Y, YUJIAO W, FANG W, et al. The roles of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):40. [8] XU D, MA X, SUN C, et al. Circular RNAs in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: An Updated Review. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;8:781424. [9] LIU NK, WANG XF, LU QB, et al. Altered microRNA expression following traumatic spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2009;219(2):424-429. [10] QIN C, LIU CB, YANG DG, et al. Circular RNA Expression Alteration and Bioinformatics Analysis in Rats After Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;11:497. [11] ZHOU H, SHI Z, KANG Y, et al. Investigation of candidate long noncoding RNAs and messenger RNAs in the immediate phase of spinal cord injury based on gene expression profiles. Gene. 2018;661:119-125. [12] FAKHRI S, ABBASZADEH F, MORADI SZ, et al. Effects of Polyphenols on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Interconnected Pathways during Spinal Cord Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:8100195. [13] 刘雅普,苏圆圆,刘祺,等.三羟乙基芦丁对大鼠颈脊髓损伤的抗氧化应激作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(36):5868-5874. [14] FATIMA G, SHARMA VP, DAS SK, et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidative parameters in patients with spinal cord injury: implications in the pathogenesis of disease. Spinal Cord. 2015;53(1):3-6. [15] DING LZ, XU J, YUAN C, et al. MiR-7a ameliorates spinal cord injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(1):11-17. [16] PETERS CM, ROGERS SD, POMONIS JD, et al. Endothelin receptor expression in the normal and injured spinal cord: potential involvement in injury-induced ischemia and gliosis. Exp Neurol. 2003;180(1):1-13. [17] A JC, LI ZY, LONG QF, et al. MiR-379-5p improved locomotor function recovery after spinal cord injury in rats by reducing endothelin 1 and inhibiting astrocytes expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(22): 9738-9745. [18] ZHU Y, XU Q, SHA WP, et al. MiR-219-5p promotes spinal cord injury recovery by inhibiting NEUROD2-regulated inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(1):37-43. [19] GUAN C, WANG Y. LncRNA CASC9 attenuates lactate dehydrogenase-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation in spinal cord injury via sponging miR-383-5p. Inflammation. 2021;44(3):923-933. [20] 胡伟,谢兴奇,屠冠军.骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体改善脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的完整性[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(7):992-998. [21] HUANG JH, XU Y, YIN XM, et al. Exosomes Derived from miR-126-modified MSCs Promote Angiogenesis and Neurogenesis and Attenuate Apoptosis after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Neuroscience. 2020;424:133-145. [22] ZHANG A, BAI Z, YI W, et al. Overexpression of miR-338-5p in exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells provides neuroprotective effects by the Cnr1/Rap1/Akt pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2021;761:136124. [23] ZHAO L, JIANG X, SHI J, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing microRNA-25 protect spinal cords against transient ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;157(2):508-517. [24] ULNDREAJ A, CHIO JC, AHUJA CS, et al. Modulating the immune response in spinal cord injury. Expert Rev Neurother. 2016;16(10):1127-1129. [25] PANG QM, CHEN SY, FU SP, et al. Regulatory Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Secondary Inflammation in Spinal Cord Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2022; 15:573-593. [26] PATERNITI I, MAZZON E, EMANUELA E, et al. Modulation of inflammatory response after spinal cord trauma with deferoxamine, an iron chelator. Free Radic Res. 2010;44(6):694-709. [27] LUKACOVA N, KISUCKA A, KISS BIMBOVA K, et al. Glial-Neuronal Interactions in Pathogenesis and Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(24):13577. [28] 李建平,何留民,吴武田.脊髓损伤的病理改变及修复策略[J/OL].中国科学:生命科学:1-12[2022-04-30].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5840.Q.20211207.0857.002.html [29] ZHOU X, HE X, REN Y. Function of microglia and macrophages in secondary damage after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(20):1787-1795. [30] FAN H, TANG HB, SHAN LQ, et al. Quercetin prevents necroptosis of oligodendrocytes by inhibiting macrophages/microglia polarization to M1 phenotype after spinal cord injury in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2019; 16(1):206. [31] LI L, QI C, LIU Y, et al. MicroRNA miR-27b-3p regulate microglial inflammation response and cell apoptosis by inhibiting A20 (TNF-α-induced protein 3). Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):9902-9913. [32] GUAN YZ, SUN C, WANG HL, et al. MiR-223-5p inhibitor suppresses microglia inflammation and promotes Nrg-1 in rats of spinal cord injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(22):9746-9753. [33] XIANG W, JIANG L, ZHOU Y, et al. The lncRNA Ftx/miR-382-5p/Nrg1 axis improves the inflammation response of microglia and spinal cord injury repair. Neurochem Int. 2021;143:104929. [34] LI X, KANG J, LV H, et al. CircPrkcsh, a circular RNA, contributes to the polarization of microglia towards the M1 phenotype induced by spinal cord injury and acts via the JNK/p38 MAPK pathway. FASEB J. 2021;35(12): e22014. [35] HUANG SJ, ZHOU LY, REN F, et al. Inhibition of Spinal Interleukin-33 Attenuates Peripheral Inflammation and Hyperalgesia in Experimental Arthritis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(4):2246-2257. [36] ZHAO CL, CUI HA, ZHANG XR. MiR-543-5p inhibits inflammation and promotes nerve regeneration through inactivation of the NF-κB in rats after spinal cord injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(3 Suppl):39-46. [37] ZHANG T, LI K, ZHANG ZL, et al. LncRNA Airsci increases the inflammatory response after spinal cord injury in rats through the nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(4):772-777. [38] ZHANG P, LI LQ, ZHANG D, et al. Over-expressed miR-27a-3p inhibits inflammatory response to spinal cord injury by decreasing TLR4. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(17):5416-5423. [39] WANG B, SHEN PF, QU YX, et al. miR-940 promotes spinal cord injury recovery by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway-mediated inflammation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(8):3190-3197. [40] GHOLAMINEJHAD M, JAMEIE SB, ABDI M, et al. All-Trans Retinoic Acid-Preconditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Motor Function and Alleviate Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibition of HMGB1/NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway Through Autophagy Activation. J Mol Neurosci. 2022; 72(5):947-962. [41] NIU F, PAN S. MicroRNA-488 inhibits neural inflammation and apoptosis in spinal cord injury through restraint on the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Neuroreport. 2021;32(12):1017-1026. [42] WAN G, AN Y, TAO J, et al. MicroRNA-129-5p alleviates spinal cord injury in mice via suppressing the apoptosis and inflammatory response through HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(3):BSR20193315. [43] SHAO W, ZHANG C, LI K, et al. Wogonin inhibits inflammation and apoptosis through STAT3 signal pathway to promote the recovery of spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2022;1782:147843. [44] WU WD, WANG LH, WEI NX, et al. MicroRNA-15a inhibits inflammatory response and apoptosis after spinal cord injury via targeting STAT3. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(21):9189-9198. [45] NING SL, ZHU H, SHAO J, et al. MiR-21 inhibitor improves locomotor function recovery by inhibiting IL-6R/JAK-STAT pathway-mediated inflammation after spinal cord injury in model of rat. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(2):433-440. [46] SUN Y, LIU WZ, LIU T, et al. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015;35(6):600-604. [47] HUANG Y, LI S, CHEN H, et al. Butorphanol reduces the neuronal inflammatory response and apoptosis via inhibition of p38/JNK/ATF2/p53 signaling. Exp Ther Med. 2022;23(3):229. [48] QIAN Z, CHANG J, JIANG F, et al. Excess administration of miR-340-5p ameliorates spinal cord injury-induced neuroinflammation and apoptosis by modulating the P38-MAPK signaling pathway. Brain Behav Immun. 2020; 87:531-542. [49] AN Q, ZHOU Z, XIE Y, et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 relieves the inflammatory response of spinal cord injury through targeting miR-211-5p/MAPK1 axis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):2702-2712. [50] TANG P, HOU H, ZHANG L, et al. Autophagy reduces neuronal damage and promotes locomotor recovery via inhibition of apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;49(1):276-287. [51] WANG ZY, LIN JH, MUHARRAM A, et al. Beclin-1-mediated autophagy protects spinal cord neurons against mechanical injury-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2014;19(6):933-945. [52] REN XD, WAN CX, NIU YL. Overexpression of lncRNA TCTN2 protects neurons from apoptosis by enhancing cell autophagy in spinal cord injury. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9(7):1223-1231. [53] ZOU Y, ZHANG J, XU J, et al. SIRT6 inhibition delays peripheral nerve recovery by suppressing migration, phagocytosis and M2-polarization of macrophages. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):210. [54] SONG Y, LI Z, HE T, et al. M2 microglia-derived exosomes protect the mouse brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury via exosomal miR-124. Theranostics. 2019;9(10):2910-2923. [55] WANG J, RONG Y, JI C, et al. MicroRNA-421-3p-abundant small extracellular vesicles derived from M2 bone marrow-derived macrophages attenuate apoptosis and promote motor function recovery via inhibition of mTOR in spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):72. [56] ZHOU J, LI Z, ZHAO Q, et al. Knockdown of SNHG1 alleviates autophagy and apoptosis by regulating miR-362-3p/Jak2/stat3 pathway in LPS-injured PC12 cells. Neurochem Res. 2021;46(4):945-956. [57] YI G, LIU L, LV C, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 defenses PC-12 cells against hydrogen peroxide-caused damage via up-regulation of miR-216a-5p. Life Sci. 2019;236:116948. [58] BOVÉ J, MARTÍNEZ-VICENTE M, VILA M. Fighting neurodegeneration with rapamycin: mechanistic insights. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12(8):437-452. [59] LIPINSKI MM, WU J, FADEN AI, et al. Function and Mechanisms of Autophagy in Brain and Spinal Cord Trauma. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015; 23(6):565-577. [60] ZHOU Z, HU B, LYU Q, et al. miR-384-5p promotes spinal cord injury recovery in rats through suppressing of autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neurosci Lett. 2020;727:134937. [61] ZHANG Z, BAI L, HOU L, et al. Trends in targeting Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic proteins for cancer treatment. Eur J Med Chem. 2022;232:114184. [62] LIAO MF, LU KT, HSU JL, et al. The Role of Autophagy and Apoptosis in Neuropathic Pain Formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2685. [63] SHI Z, YUAN S, SHI L, et al. Programmed cell death in spinal cord injury pathogenesis and therapy. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(3):e12992. [64] WANG M, ZHANG J, GONG N. Role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver ischemia reperfusion injury: a narrative review. Ann Palliat Med. 2022; 11(2):806-817. [65] HE S, WANG Z, LI Y, et al. MicroRNA-92a-3p enhances functional recovery and suppresses apoptosis after spinal cord injury via targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(5):BSR20192743. [66] QI L, JIANG-HUA M, GE-LIANG H, et al. MiR-34a Inhibits Spinal Cord Injury and Blocks Spinal Cord Neuron Apoptosis by Activating Phatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT Pathway Through Targeting CD47. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2019;16(4):373-381. [67] ZHANG Z, SHEN L, YAN Y. MiR-139-5p alleviates neural cell apoptosis induced by spinal cord injury through targeting TRAF3. Acta Biochim Pol. 2020;67(3):359-365. [68] YUAN S, WANG YX, GONG PH, et al. MiR-124 inhibits spinal neuronal apoptosis through binding to GCH1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(11):4564-4574. [69] YU X, ZHANG S, ZHAO D, et al. SIRT1 inhibits apoptosis in in vivo and in vitro models of spinal cord injury via microRNA-494. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(4): 1758-1768. [70] HUANG C, ZHANG W, CHU F, et al. Patchouli Alcohol Improves the Integrity of the Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Through the Akt/CHOP/Caspase-3 Pathway Following Spinal Cord Injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:693533. [71] CAO Y, JIANG C, LIN H, et al. Silencing of Long Noncoding RNA Growth Arrest-Specific 5 Alleviates Neuronal Cell Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses Through Sponging microRNA-93 to Repress PTEN Expression in Spinal Cord Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:646788. [72] WU H, LI Y, WANG X, et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 knockdown prevents neurons from death to alleviate acute spinal cord injury via the microRNA-338/BIK axis[J]. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):5566-5582. [73] ZHAO Q, LU F, SU Q, et al. Knockdown of long noncoding RNA XIST mitigates the apoptosis and inflammatory injury of microglia cells after spinal cord injury through miR-27a/Smurf1 axis. Neurosci Lett. 2020;715:134649. [74] ZHAO J, QI X, BAI J, et al. A circRNA derived from linear HIPK3 relieves the neuronal cell apoptosis in spinal cord injury via ceRNA pattern. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;528(2):359-367. [75] LIU Y, AO S, ZHANG H, et al. Circ_HIPK3 alleviates CoCl2-induced apoptotic injury in neuronal cells by depending on the regulation of the miR-222-3p/DUSP19 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;553:126-133. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [3] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [4] | Wu Yujie, Wan Xiaofang, Wei Mianxing, Peng Shiyuan, Xu Xiaomei. Correlation between autophagy and the Hippo-YAP protein pathway in periodental ligament cells on the pressure side of a mouse model of orthodontic tooth movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 683-689. |
| [5] | Zhao Siqi, Du Juan, Qu Haifeng, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Effects of enriched environment combined with melatonin on learning and memory function and brain neuron apoptosis in SAMP8 mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 701-706. |
| [6] | Zhang Qing, Gao Chunlan, Yu Feifei, Zhang Zhenghao, Ma Fang, Gao Yuan, Li Guizhong, Jiang Yideng, Ma Shengchao. Ephrin A receptor 2 DNA methylation increases in pancreatic beta cell apoptosis induced by homocysteine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 714-719. |
| [7] | Tao Xin, Xu Yi, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Hippo signaling pathway in the regulation of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 619-625. |
| [8] | Zhang Lichen, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Inorganic ion bionic periosteum regulates immune microenvironment to promote bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| [9] | Wang Huanhuan, Wang Qing, Tang Peng, Zhang Rui, Min Hongwei. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave on the proliferation and autophagy of chondrocytes from osteoarthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 252-257. |
| [10] | Wu Shuangshuang, Zhang Ying, Kou Xianjuan. Treadmill exercise improves cognitive dysfunction in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 208-215. |
| [11] | Shui Xiaoping, Li Chunying, Li Mingjuan, Li Shunchang, Sun Junzhi, Su Quansheng. Effects of aerobic and resistance exercise on antioxidant stress index and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the hippocampus of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 264-269. |
| [12] | Liu Gang, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Xu Lin, Fan Xiao, Tao Jingwei, Zhang Houjun, He Feng, Zhao Yi, Mu Xiaohong. Tetramethylpyrazine improves hemorheological indexes in rats with complete spinal cord transection: a dynamic observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 282-286. |
| [13] | Ou Hangjun, Zhao Guangjian, Pan Yujia, Gong Caiwei, Zhao Quanwei, Liu Danan. Construction of a lentiviral vector overexpressing fibronectin type III domain containing 5 to inhibit apoptosis of endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 216-222. |
| [14] | Zhu Zhenghuan, Zou Hongjun, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Cellular microenvironment in nerve repair after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 114-120. |
| [15] | Shi Xu, Li Ruiyu, Zhang Bing, Chen Qi, Zuo Hua. Effect of inflammatory reaction mediated by microglia polarization in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 121-129. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||