Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 765-771.doi: 10.12307/2023.142
Previous Articles Next Articles
MicroRNA, long non-coding RNA and circular RNA mediate the mechanism of decreasing uric acid, anti-inflammation and regulating bone metabolism in gout
Shao Zichen1, Li Huanan2, Gu Bing3, Zhang Xiaoyun1, 4, Sun Weikang1, Liu Yongqian1, Gan Bin1
- 1Clinical Medical College of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China; 3School Pharmacy, Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, Nanchang 330013, Jiangxi Province, China; 4Department of Orthopedics, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-03-24Accepted:2022-05-13Online:2023-02-18Published:2022-07-23 -
Contact:Li Huanan, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral/Master’s supervisor, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Shao Zichen, Master candidate, Clinical Medical College of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81860857 and 82060871 (to LHN); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, No. 20202BAB206071 (to LHN); the Science and Technology Research Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education, No. GJJ190582 (to GB); and the Second National Medical Master Studio of Jiangxi Province, No. 2021-201 (to LHN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shao Zichen, Li Huanan, Gu Bing, Zhang Xiaoyun, Sun Weikang, Liu Yongqian, Gan Bin. MicroRNA, long non-coding RNA and circular RNA mediate the mechanism of decreasing uric acid, anti-inflammation and regulating bone metabolism in gout[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 765-771.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
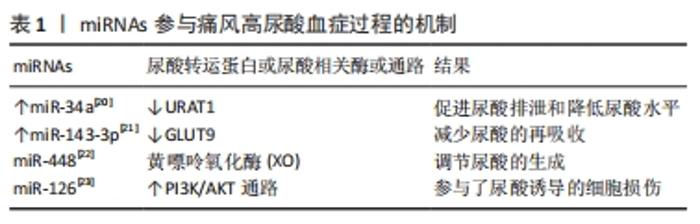
2.1 三种RNA概述 2.1.1 miRNA miRNA是一类长度约为20个核苷酸的内生高度保守性小RNA,可以微妙而复杂地调控基因表达的转录后,它们涉及各种过程,包括细胞分化、代谢和炎症等[6]。有相关研究发现,miRNAs主要通过与mRNA的3′非翻译区(3’-UTR)结合来抑制蛋白质翻译或促进mRNA降解,介导基因表达的转录后调控[7-8]。miRNAs可以在血液或体液中稳定循环,成熟的miRNA加载到RNA诱导沉默复合体中,RNA诱导沉默复合体通过识别靶向mRNA中的互补序列来指导mRNA的调控[7]。miRNA的这些特点表明它们有潜力作为临床诊断疾病的生物标志物。miRNAs对炎症性疾病、肿瘤和代谢性疾病等多种人类疾患都发挥重要作用[9-10]。 2.1.2 lncRNA lncRNAs在近年来的医学研究中备受关注,lncRNAs的典型特征是其转录长度超过200个核苷酸,且在许多生物过程中不被翻译成蛋白质。lncRNAs在许多炎症和自身免疫性疾病中对基因发挥重要调控作用,包括以RNA的形式进行转录及转录后调控[11-12]。lncRNAs在调节先天免疫、适应性免疫反应以及免疫细胞发育中也发挥重要作用[13]。lncRNA的这些特点表明它们有潜力作为许多疾病的诊断性生物标志物。大量相关研究证实,lncRNAs可能成为包括冠状动脉疾病、胃癌疾病在内的多种疾病的新的诊断标志物[14-15]。 2.1.3 circRNA circRNA具有多种生物学特性,但相关研究主要集中在其与miRNA调控机制上。富含miRNA结合位点的circRNA是miRNA的海绵吸附体,可抑制miRNA与靶基因结合,从而发挥miRNA海绵效应,上调靶基因的表达,是一类高效率的内源竞争RNA(ceRNA)[16-17]。miRNA与mRNA的联结状态可调控蛋白质翻译合成。circRNA的这些特点表明它们有能力作为疾病的新诊断标志物。越来越多的研究表明,circRNA在包括系统性红斑狼疮、类风湿性关节炎和骨关节炎在内的多种风湿病中都有重要作用[18]。 2.2 miRNA在高尿酸血症中作用机制 作为痛风的首要危险因素,高尿酸血症是因嘌呤代谢过剩或尿酸排泄不足而造成尿酸水平增加的代谢性疾病,该疾病由尿酸转运蛋白及尿酸相关酶的异常所驱动[19]。大量的研究表明miRNAs可以调节尿酸转运蛋白、尿酸相关酶的表达及参与尿酸分泌机制,对降低尿酸水平具有积极作用,可有效抑制痛风的进展。例如,URAT1,GLUT9和ABCG2均为尿酸转运蛋白,在调控尿酸的再吸收与排泄当中发挥重要作用。一项实验研究表明,miR-34a可能通过结合URAT1的3’-UTR区靶向抑制URAT1蛋白的表达,促进尿酸排泄和降低尿酸水平[20]。RIPPERGER等[21]研究发现,上调miR-143-3p可以抑制GLUT9蛋白的表达,减少尿酸的再吸收;但miRNAs或lncRNAs与ABCG2介导的尿酸转运功能之间的关系尚不明确,有待进一步研究。黄嘌呤氧化酶(XO)是一种涉及尿酸产生的重要酶,miR-448可调控黄嘌呤氧化酶的表达,从而调节尿酸的生成[22]。另一项研究发现白藜芦醇(RSV)可以通过调节miR-126和激活PI3K/AKT信号通路来保护小鼠胰岛β(MIN6)细胞免受尿酸诱导的损伤和功能障碍,这表明miR-126参与了尿酸诱导的细胞损伤[23]。见表1。"
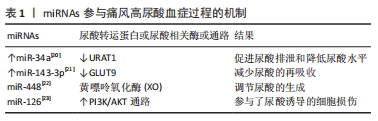

到目前为止,虽然miRNAs在高尿酸血症中的研究不够完善,但是其在尿酸转运调控当中发挥重要作用,有望成为识别高尿酸血症的生物标志物,成为降低尿酸药物治疗的新靶点。 2.3 三种RNA在免疫炎症反应中作用机制 尿酸在关节及关节周围组织持续累积形成单钠尿酸盐(MSU)晶体,以多通路、多基因、多炎症递质作为载体,打破局部微环境免疫平衡,诱发炎症反应[24]。虽然中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞被普遍认为在痛风的免疫炎症反应中作用重要[25],但最近的研究强调了miRNA、lncRNA和circRNA通过参与调控免疫炎症途径发挥治疗痛风性关节炎的作用。 2.3.1 miRNA在免疫炎症反应中作用机制 促炎细胞因子(白细胞介素1β为主)及NLRP3炎症小体可受miRNAs的调控[26]。例如,单钠尿酸盐晶体可诱导单核细胞THP-1细胞中miR-146a的表达,从而抑制促炎细胞因子(白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、单核细胞趋化蛋白1和白细胞介素8)表达。有研究表明,MiR-146a通过抑制TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路,下调白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和NLRP3炎症小体水平。另一项研究表明,miR-146a在NF-κB启动的炎症信号通路中起负反馈效应,miR-146a可靶向TRAF6和IRAK1蛋白直接下调单钠尿酸盐晶体诱导的促炎因子(白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6)的释放;敲除miR-146a使TRAK6和IRAK1蛋白表达上调,加重单钠尿酸盐晶体诱导的炎症反应;测序结果显示,虽然miR-146a 巨噬细胞中NALP3炎性小体成分mRNA水平升高,但NAPL3不包含miR-146a的直接结合位点,推断miR-146a可能间接靶向NALP3炎症小体,提高白细胞介素1β的活化[27-30]。WANG等[31]研究发现,miR-22-3p可通过与NLRP3的3’-UTR区结合,靶向抑制NLRP3炎症小体的表达,减少白细胞介素1β的释放;另外在活体实验中,miR-22-3p可抑制Sirtuin 1蛋白的表达,促进炎性因子(白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素8)的高表达。通过上调miR-449a,可直接靶向下调NLRP3炎症小体的活性,降低促炎因子(白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6)表达;另外,通过miR-449a的调节,阻断NF-κB信号通路和抑制STAT3蛋白表达,减轻痛风性关节炎炎症[32]。 JIN等[33]和YANG等[34]研究发现,miRNA-155通过下调SHIP1,增加Akt的磷酸化水平,激活Akt/NF-kB通路,加强促炎因子白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α的表达。研究表明,miR-488和miR-920通过直接靶向白细胞介素1β的3’-UTR区域,抑制促炎因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素8和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,在单钠尿酸盐晶体诱导的巨噬细胞或THP-1细胞中发挥抗炎作用[35]。一项研究发现,miR-302b是在单钠尿酸盐晶体诱导的炎症机制中重要负调控因子,miR-302b通过直接靶向抑制(或沉默)IRAK4和EphA2蛋白的表达,并靶向调控NF-κB和caspase-1信号通路,降低内源性NF-κB p65和caspase-1 p20的磷酸化水平,减弱白细胞介素1β释放[36]。一些研究人员还发现,下调miR-34a可能通过介导Sirt1/p53信号通路,靶向上调sirt1蛋白表达,进而下调p53 蛋白表达,降低白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平[37]。有研究表明,黄芩清热除痹胶囊通过抑制miR-23a-3p,进而靶向结合PTEN mRNA的3’-UTR区域来上调PTEN蛋白,抑制白细胞介素17等炎性细胞因子诱导的NF-KB活化和多种促炎递质的表达[38]。SHAN等[39]研究发现,miR-3146直接靶向中性粒细胞中的SIRT1,并以依赖活性氧的方式启动NETs。miR-3146过表达导致SIRT1的mRNA和蛋白水平下调、活性氧和NETs的形成,诱导促炎因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素8的表达。另外miR-223可通过抑制p65的磷酸化和核转位,降低Cul1a/b、Traf6和Tab1蛋白的表达,负向调控NF-κB的激活[40]。研究显示,在THP-1细胞中miR-221-5p可能通过直接靶向白细胞介素1β蛋白,抑制炎症因子(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素8和白细胞介素1β)的释放[41]。miR-23a~27a~24-2 簇是由 miR-23a、miR-24-2和miR-27a组成的 miNRA 簇,有研究表明,miR-23a~27a~24-2 簇可能通过共同靶向sPRY2 蛋白来抑制MAPK信号通路的激活,下调炎症相关因子的表达,抑制痛风性关节炎介导的炎症反应[42],但其负向调节机制还有待进一步证实。虽然miRNA-142-3p与NETs相互作用的机制尚未明确,但NETs可以携带miRNA-142-3p并将其转移到巨噬细胞,然后通过下调蛋白激酶C的表达来降低肿瘤坏死因子α的水平[43]。在一些相关实验研究中,miR-203a、miR-3085、miR-19b-2-5p可通过调控MAPK或FoxO信号通路介导炎症反应。miR-17和miR-18a可通过激活巨噬细胞,促进白细胞介素1β等炎性因子的分泌[32-42]。 目前研究表明,miR-223-3p在巨噬细胞中能够通过NLRP3 3’-UTR内的保守结合位点靶向抑制NLRP3炎症小体活性,阻断白细胞介素 1通路,下调白细胞介素 1β、肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎因子,缩小炎症级联反应[31,44]。FOXO3是一种与血清尿酸水平相关的转录因子,miR-30c-5p可通过FOXO3靶向抑制NLRP3,致其发生凋亡,抑制炎症反应。一些研究人员发现,miR-17-5p可通过结合并降低TXNIP的mRNA来抑制NLRP3炎症小体表 达[45]。另一项研究表明,miR-92a可以通过靶向氧化应激过程中内皮稳态的关键分子,包括Sirtuin 1、KLF2和KLF4,间接激活NLRP3炎症小体;测序结果显示,ANRIL被发现是尿素肾病(UAN)中miR-122-5p的靶点[10],并通过上调BRCC3蛋白的表达,激活NLRP3炎症小体。MENG等[45]研究发现,MALAT1在THP-1细胞中通过上调miR-876-5p的表达而下调NLRP3表达,直接抑制炎症反应或进一步通过抑制单钠尿酸盐晶体诱导的TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB通路的激活来间接抑制炎症反应。但尚未见相关研究证实在痛风性关节炎中,miR-21可与NLRP3的3’-UTR区相结合,预测miR-21可能通过靶向作用Smad7、Spry1蛋白间接促进NLRP3炎性小体活化及白细胞介素1β释放[46]。miR-7、miR-133b可能通过靶向作用NLRP3的3’-UTR区,直接调控NLRP3的表达,参与多种炎性疾病发生,但其在痛风性疾病中的机制尚不明确。见表2。 "
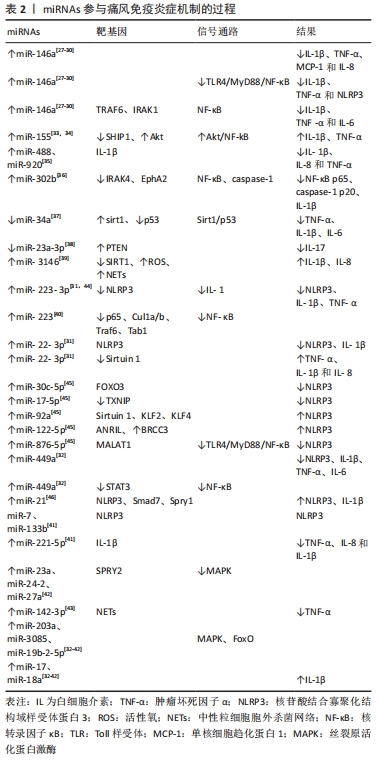
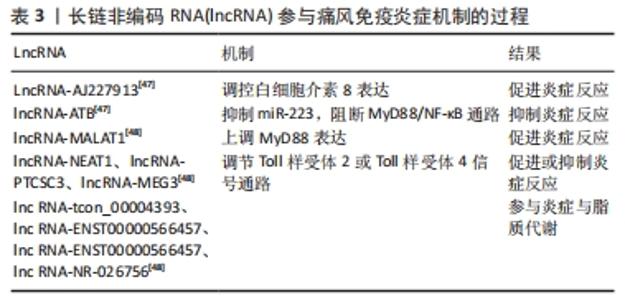
虽然已有大量的研究表明miRNAs在各种疾病中调节TLR2/TLR4及趋化因子表达中的作用,但尚未有研究评估其在痛风中调控作用。miRNAs主要通过介导NF-κB等信号通路调控NLRP3炎症小体及白细胞介素1β等炎症因子的表达,在治疗痛风的免疫炎症途径中发挥重要作用。 2.3.2 lncRNA在免疫炎症反应中作用机制 lncRNA调控相关基因介导不同通路参与痛风的免疫炎症过程。例如,相关研究表明,LncRNA-AJ227913可能调控痛风性关节炎患者白细胞介素8的表达,并触发炎症反应。一项研究结果显示,lncRNA-ATB可通过抑制miR-223,阻断MyD88/NF-κB通路,减轻炎症反应,但miR-223与lncRNA-ATB作用机制尚不明确[47]。另外lncRNA MALAT1可上调MyD88蛋白表达,促进炎症反应。NEAT1、PTCSC3、MEG3均为lncRNA,参与TLR2或TLR4信号通路的正负反馈调节,促进或抑制痛风炎症反应的发生。一项研究表明,4种差异表达的lncRNAs可能参与了痛风的炎症及脂质代谢;lnc RNA-tcon_00004393和lnc RNA-ENST00000566457可作为针对痛风发作的潜在靶点;lnc RNA-ENST00000566457和lnc RNA-NR-026756可能具有诊断和治疗痛风的潜力,有望成为诊断痛风性关节炎的生物标志物[48]。见表3。 "
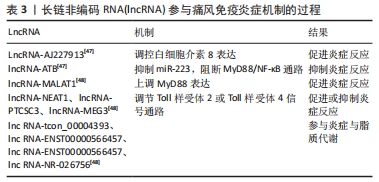
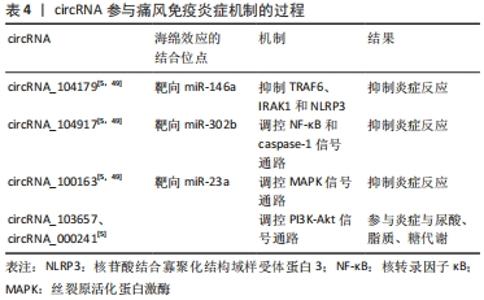
虽然lncRNAs的研究是一个热点话题,但相比于miRNAs的报道,涉及痛风相关的lncRNA的文章较少。lncRNAs在痛风中的研究有部分结果是基于生物信息学的预测,缺乏相关体内外实验验证。lncRNA主要通过介导MyD88/NF-κB/TLRs信号通路在痛风免疫炎症中发挥重要作用。充分探索这些lncRNAs在痛风免疫炎症中的作用,将为痛风的发病机制提供新认识。 2.3.3 circRNA在免疫炎症反应中作用机制 circRNA主要通过靶向发挥miRNA的海绵吸附效应,介导多种通路调控与基因表达,参与痛风免疫炎症机制的调节。例如,通过生物信息学分析,预测痛风中circRNA_104179、circRNA_104917、circRNA_100163可能通过影响其对应的miRNA,介导多个蛋白及信号通路调控痛风的免疫炎症反应,在痛风的发生发展中起着重要作用。circRNA_104179靶向miR-146a,通过抑制TRAF6、IRAK1和NLRP3的炎性小体功能来降低白细胞介素1β的产生。circRNA_104917靶向miR-302b,通过调控NF-κB和caspase-1信号通路,降低内源性NF-κB p65和caspase-1 p20的磷酸化水平,减弱白细胞介素1β分泌。circRNA_100163靶向miR-23a,介导MAPK信号通路来抑制炎症反应[5,49]。但这些circRNA能否真的靶向预测的miRNA的结合位点,尚不明确。一项微阵列技术研究表明,hsa_circRNA_103657和hsa_circRNA_000241可能通过影响PI3K-Akt信号通路参与痛风的发病过程,而PI3K-Akt信号通路失衡可影响尿酸代谢或炎症;同时两种circRNA均参与了痛风患者脂质或糖代谢的调节,通过ROC曲线分析可筛选出hsa_circRNA_103657很可能作为一种潜在的生物标志物来诊断痛风[5]。见表4。 "
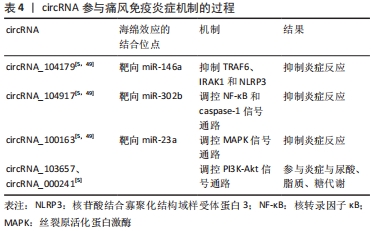

目前,对痛风相关的非编码RNA的研究大多针对miRNA,对circRNA进行总结的文章很少。circRNAs在痛风中的研究有部分结果是基于生物信息学的预测,缺乏相关体内外实验验证。circRNA主要通过靶向发挥miRNA的海绵吸附效应,调控miRNA与mRNA的结合,介导NF-κB/MAPK/ PI3K-Akt 通路调控与痛风相关基因表达,参与痛风免疫炎症反应的调节。 2.4 lncRNA在痛风性骨侵蚀中作用机制 在骨重塑过程中,吸收骨基质的破骨细胞与合成骨基质的成骨细胞互相调控,维持骨稳态。慢性痛风中的骨侵蚀是由单钠尿酸盐晶体的沉积引起的,炎性细胞因子和多个信号级联介导破骨细胞形成,而炎症关节中破骨细胞的积聚将导致骨代谢失衡[50]。因此,慢性痛风与关节及骨的损伤、畸形和残疾密切相关。 最近的研究强调了lncRNA通过参与调控破骨细胞活化发挥延缓痛风性骨侵蚀进程的作用。单钠尿酸盐晶体是引起炎症反应和痛风性骨侵蚀的关键调节剂。LEE等[51]研究表明,在单钠尿酸盐晶体诱导的破骨细胞活化中,9对lncRNA/mRNA与炎症和免疫基因的相关性最高,包含lncRNA Jak3/Jak3、lncRNA-Six4/Six4、lncRNAApobec3/Apobec3、lncRNA-Trim30/Trim30a、lncRNA-Six1/Six1、lncRNA-Trim59/Trim59、 lncRNA-Tmem173/Tmem173 、lncRNAKrt16/Krt16和lncRNA-MAEA/MAEA,其中LncRNA-Jak3显著上调;在单核巨噬细胞中,LncRNA-Jak3敲低可负调节Jak3,CTSK,NFATc1和其他蛋白的表达,对单钠尿酸盐晶体诱导的骨吸收活性具有抑制作用,可见LncRNA-Jak3作为促破骨细胞因子在破骨细胞形成中的关键调节功能。目前LncRNA Jak3是唯一被发现可调节痛风骨侵蚀中破骨细胞分化的LncRNA[50];单钠尿酸盐晶体诱导的LncRNA-Jak3可能通过Jak3/Nfatc1/Ctsk信号通路促进破骨细胞的活化,其可能作为痛风性骨侵蚀潜在的治疗靶点。 在痛风的长期治疗中,临床通常结合降尿酸治疗和低剂量秋水仙碱。多项研究表明,破骨细胞过度激活在痛风性骨侵蚀中起关键作用[52],因此lncRNA介导多种信号通路来降低破骨细胞活性是一个针对痛风性骨侵蚀的新治疗策略。 2.5 非编码RNA在痛风中的治疗 相关研究证明,苯溴马隆通过增加miR-34a和miR-146a的表达水平来降低尿酸水平。临床上,高尿酸血症患者可使用尿酸抑制剂(如别嘌呤醇和非布索坦)或尿酸排泄药物(如丙磺舒和苯溴马隆)治疗[4]。大量研究发现,秋水仙碱和依托咪昔均可上调miR-146a以达到治疗急性痛风性关节炎的目的。临床上,痛风发作期可用非类固醇类抗炎药(NSAIDs)、秋水仙碱(COLC)及白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂缓解炎症反应和疼痛[4],但存在较多不良反应和禁忌证。因此需注意监测疾病进展,遵医嘱定期复诊。目前,LncRNA Jak3是唯一被发现可调节痛风骨侵蚀中破骨细胞分化的LncRNA[50]。临床上,基本上没有治疗痛风石(tophi)和骨侵蚀的有效药物。患者体内的痛风石只能通过手术去除[4]。预测今后可能通过介导LncRNA Jak3的相关机制来延缓痛风性骨侵蚀进程,防止疾病进一步加重。尽管有许多非编码RNA治疗痛风的基础研究,但在从机制研究向临床应用过渡的过程中,仍有许多问题需要克服,如药物吸收率、安全性和有效性。 "

| [1] DALBETH N, GOSLING AL, GAFFO A, et al. Gout. Lancet. 2021;397 (10287):1843-1855. [2] 张超凤,刘晓莉,李雪娟,等.痛风急性发作一线药物治疗方案的系统评价及药物经济学分析[J].中国新药杂志,2021,30(16):1530-1536. [3] DEHLIN M, JACOBSSON L, RODDY E. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(7):380-390. [4] XU YT, LENG YR, LIU MM, et al. MicroRNA and long noncoding RNA involvement in gout and prospects for treatment. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;87:106842. [5] DAI F, ZHANG QB, TANG YP, et al. Expression Profile and Potential Function of Circular RNAs in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Male Patients With Primary Gout. Front Genet. 2021;12:728091. [6] HA M, KIM VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(8):509-524. [7] NI WJ, LENG XM. miRNA-Dependent Activation of mRNA Translation. Microrna. 2016;5(2):83-86. [8] CORREIA DE SOUSA M, GJORGJIEVA M, DOLICKA D, et al. Deciphering miRNAs’ Action through miRNA Editing. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6249. [9] VISHNOI A, RANI S. MiRNA Biogenesis and Regulation of Diseases: An Overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1509:1-10. [10] WANG Y, XU D, WANG B, et al. Could MicroRNAs be Regulators of Gout Pathogenesis? Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(6):2085-2092. [11] FERRÈ F, COLANTONI A, HELMER-CITTERICH M. Revealing protein-lncRNA interaction. Brief Bioinform. 2016;17(1):106-116. [12] STATELLO L, GUO CJ, CHEN LL, et al. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2):96-118. [13] ATIANAND MK, CAFFREY DR, FITZGERALD KA. Immunobiology of Long Noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017;35:177-198. [14] SCHMITZ SU, GROTE P, HERRMANN BG. Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(13):2491-2509. [15] LI X, PAN Y, LI W, et al. The Role of Noncoding RNAs in Gout. Endocrinology. 2020;161(11):bqaa165. [16] KRISTENSEN LS, ANDERSEN MS, STAGSTED LVW, et al. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019; 20(11):675-691. [17] PANDA AC. Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1087:67-79. [18] GUO G, WANG H, YE L, et al. Hsa_circ_0000479 as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:2281. [19] ICHIDA K, MATSUO H, TAKADA T, et al. Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia. Nat Commun. 2012; 3:764. [20] SUN WF, ZHU MM, LI J, et al. Effects of Xie-Zhuo-Chu-Bi-Fang on miR-34a and URAT1 and their relationship in hyperuricemic mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;161:163-169. [21] RIPPERGER A, BENNDORF RA. The C421A (Q141K) polymorphism enhances the 3’-untranslated region (3’-UTR)-dependent regulation of ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016; 104:139-147. [22] JOSHI G, SHARMA M, KALRA S, et al. Design, synthesis, biological evaluation of 3,5-diaryl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole carbaldehydes as non-purine xanthine oxidase inhibitors: Tracing the anticancer mechanism via xanthine oxidase inhibition. Bioorg Chem. 2021;107:104620. [23] BOHATÁ J, HORVÁTHOVÁ V, PAVLÍKOVÁ M, et al. Circulating microRNA alternations in primary hyperuricemia and gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):186. [24] NARANG RK, DALBETH N. Pathophysiology of Gout. Semin Nephrol. 2020;40(6):550-563. [25] WANG B, CHEN S, QIAN H, et al. Role of T cells in the pathogenesis and treatment of gout. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;88:106877. [26] HANEKLAUS M, O’NEILL LA, COLL RC. Modulatory mechanisms controlling the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammation: recent developments. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013;25(1):40-45. [27] ZHANG QB, QING YF, YIN CC, et al. Mice with miR-146a deficiency develop severe gouty arthritis via dysregulation of TRAF 6, IRAK 1 and NALP3 inflammasome. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):45. [28] CHEN X, GAO Q, ZHOU L, et al. MiR-146a alleviates inflammation of acute gouty arthritis rats through TLR4/MyD88 signal transduction pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(21):9230-9237. [29] DALBETH N, POOL B, SHAW OM, et al. Role of miR-146a in regulation of the acute inflammatory response to monosodium urate crystals. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(4):786-790. [30] 徐阳洋,青玉凤,张全波,等.微小RNA-146a在原发性痛风性关节炎患者的变化及其临床意义[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2016,20(12): 796-800. [31] WANG X, CHI J, DONG B, et al. MiR-223-3p and miR-22-3p inhibit monosodium urate-induced gouty inflammation by targeting NLRP3. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021;24(4):599-607. [32] WANG Y. Tripterine ameliorates monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis by altering macrophage polarization via the miR-449a/NLRP3 axis. Inflamm Res. 2021;70(3):323-341. [33] JIN HM, KIM TJ, CHOI JH, et al. MicroRNA-155 as a proinflammatory regulator via SHIP-1 down-regulation in acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R88. [34] YANG Q, ZHANG Q, QING Y, et al. miR-155 is dispensable in monosodium urate-induced gouty inflammation in mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):144. [35] ZHOU W, WANG Y, WU R, et al. MicroRNA-488 and -920 regulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines in acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):203. [36] MA T, LIU X, CEN Z, et al. MicroRNA-302b negatively regulates IL-1β production in response to MSU crystals by targeting IRAK4 and EphA2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):34. [37] 杨彬,黄俊卿,孟庆良,等.秦艽醇提物对痛风性关节炎大鼠氧化应激损伤及miR-34a/sirt1轴的影响研究[J].中药药理与临床,2019, 35(5):64-69. [38] 孙广瀚,刘健,万磊,等. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊含药血清对痛风性关节炎CD4+T细胞与心肌细胞共培养后miR-23a-3p/PTEN表达的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报,2021,44(8):735-743. [39] SHAN L, YANG D, FENG F, et al. miR-3146 induces neutrophil extracellular traps to aggravate gout flare. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(11): e24032. [40] YANG QB, LI LQ, ZHANG QB, et al. microRNA-223 Deficiency Exacerbates Acute Inflammatory Response to Monosodium Urate Crystals by Targeting NLRP3. J Inflamm Res. 20211;14:1845-1858. [41] LI G, ZHANG H, MA H, et al. MiR-221-5p is involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses in acute gouty arthritis by targeting IL-1β. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021;24(3):335-340. [42] 李玲琴,王东生,青玉凤,等. 微小RNA-23a~27a~24-2簇在原发性痛风性关节炎患者的表达及其临床意义[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2015,19(2):76-80. [43] LU Y, FANG L, XU X, et al. MicroRNA-142-3p facilitates inflammatory response by targeting ZEB2 and activating NF-κB signaling in gouty arthritis. Cell Cycle. 2022:1-15. [44] TIAN J, ZHOU D, XIANG L, et al. MiR-223-3p inhibits inflammation and pyroptosis in monosodium urate-induced rats and fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting NLRP3. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021;204(3):396-410. [45] MENG Q, MENG W, BIAN H, et al. Total glucosides of paeony protects THP-1 macrophages against monosodium urate-induced inflammation via MALAT1/miR-876-5p/NLRP3 signaling cascade in gouty arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138:111413. [46] 陈刚,李梦兰,彭春梅,等. 微RNA-21在原发性痛风患者中的变化及意义[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2019,23(3):165-169. [47] 杨颜瑜,熊琴,谭敏,等.长链非编码RNA调节痛风炎症信号通路的研究进展[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2019,18(6):473-477. [48] QING YF, ZHENG JX, TANG YP, et al. LncRNAs Landscape in the patients of primary gout by microarray analysis. PLoS One. 2021;16(2): e0232918. [49] 戴菲,郑建雄,唐乙萍,等.痛风患者外周血单个核细胞环状RNA的表达谱分析[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2021,25(1):26-31,c1-3,c1-4. [50] SCHLESINGER N, THIELE RG. The pathogenesis of bone erosions in gouty arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(11):1907-1912. [51] LEE CP, HUANG YN, NITHIYANANTHAM S, et al. LncRNA-Jak3:Jak3 coexpressed pattern regulates monosodium urate crystal-induced osteoclast differentiation through Nfatc1/Ctsk expression. Environ Toxicol. 2019;34(2):179-187. [52] DALBETH N, SMITH T, NICOLSON B, et al. Enhanced osteoclastogenesis in patients with tophaceous gout: urate crystals promote osteoclast development through interactions with stromal cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(6):1854-1865. [53] EULER M, HOFFMANN MH. The double-edged role of neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019;47(6): 1921-1930. |
| [1] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [2] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [3] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [4] | Lu Huixiu, Cao Haiyu, Lou Dan, Li Jianying, Liu Hongyuan, Sun Jing. Imiquimod combined with photodynamic therapy for hypertrophic scars: immune response and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 690-694. |
| [5] | Liu Hongwen, Li Jiao, Xu Wenhao, Nie Hua, Liu Shaojiang, Xu Jie, Yin Li. Differential expression profiles of microRNAs in muscle tissue of denervated skeletal muscle atrophy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 732-737. |
| [6] | Hu Xinming, Qiao Yanhua, Wang Xiaofan, Li Linyu, Zhao Bing. Mechanism of long non-coding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 involved in pelvic organ prolapse [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 669-675. |
| [7] | Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299. |
| [8] | Zhang Yujuan, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Tian Feng, Fu Yuan, Wang Chunfang. miR-31 promotes the proliferation and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 66-71. |
| [9] | Huang Bin, Zheng Jinxu, Zhang Jun. Progress of non-coding RNAs in stem cell abnormality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 130-137. |
| [10] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [11] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [12] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [13] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [14] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [15] | Luo Shiren, Xie Yan, Zhang Li, Yin Na. miRNA screening for targeted regulation of bone growth by semen ziziphi spinosae extract [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5658-5664. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||