Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 669-675.doi: 10.12307/2023.092
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of long non-coding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 involved in pelvic organ prolapse
Hu Xinming1, Qiao Yanhua1, Wang Xiaofan1, Li Linyu2, Zhao Bing1
- 1Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Academic Affairs, Zheng Zhou Feng Yang Foreign Language School, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-02Accepted:2022-04-23Online:2023-02-18Published:2022-07-23 -
Contact:Zhao Bing, MD, Associate researcher, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Hu Xinming, Master candidate, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Provincial University Science and Technology Innovation Talent Support Program, No. 18HASTIT045 (to ZB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Xinming, Qiao Yanhua, Wang Xiaofan, Li Linyu, Zhao Bing. Mechanism of long non-coding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 involved in pelvic organ prolapse[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 669-675.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
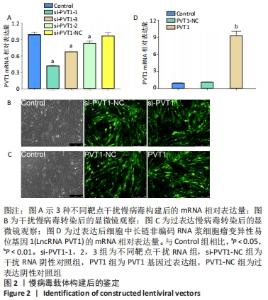
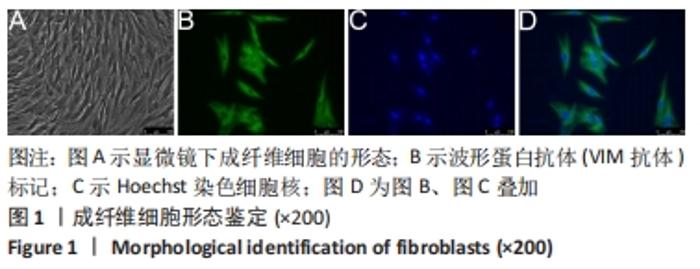
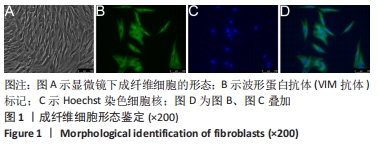
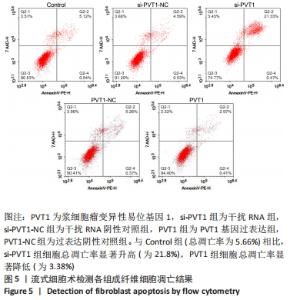
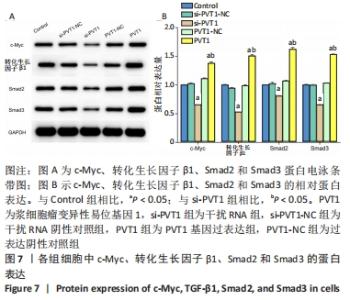
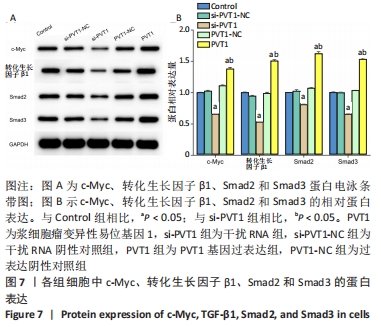
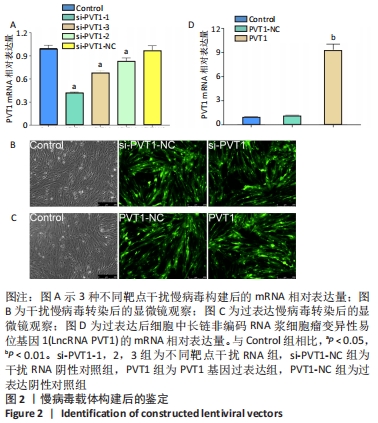
2.2 慢病毒载体构建 RT-PCR结果显示,si-PVT1-1、si-PVT1-2 和si-PVT1-3三组的相对mRNA表达量均显著小于Control组(P < 0.05);其中si-PVT1-1组和另外两组相比,其相对mRNA表达量最低,说明该病毒干扰效果最好,因此选择si-PVT1-1组的细胞用于后续实验,见图2A。 干扰或过表达慢病毒感染细胞72 h后,在荧光倒置显微镜下观察可见si-PVT1-NC组、si-PVT1组、PVT1-NC组和PVT1组的细胞内均发出不同程度的绿色荧光,其中si-PVT1组的绿色荧光要弱于si-PVT1-NC组,PVT1组要强于PVT1-NC组。Control组未进行转染,普通显微镜下可见细胞形态规则,呈长梭形,细胞排列规则,见图2B,C。 RT-PCR结果显示,PVT1组的相对mRNA表达量显著高于Control组(P < 0.01),PVT1-NC组则与Control组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图2D。实验结果提示成纤维细胞过表达或干扰都转染成功。 "
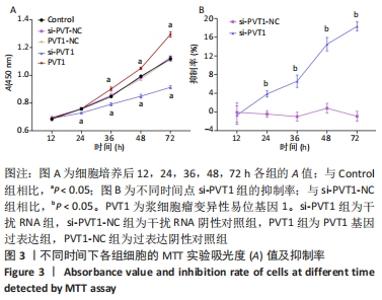
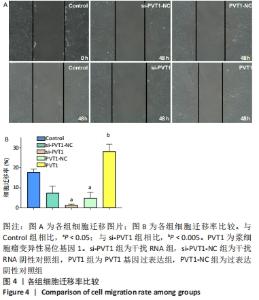
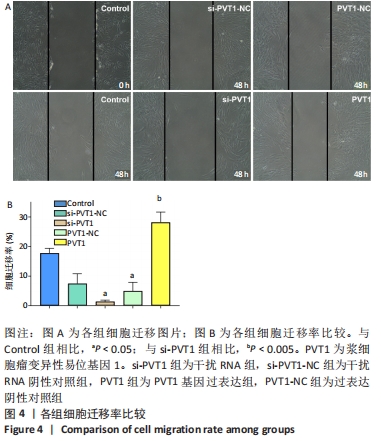
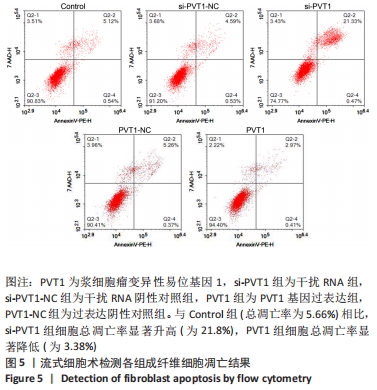
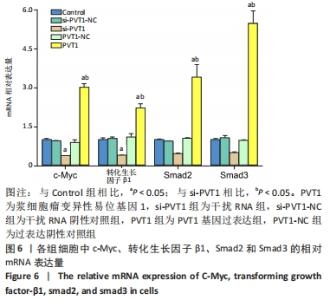
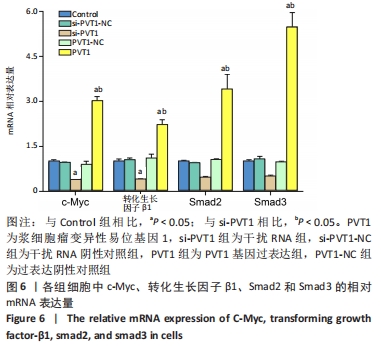
2.3 MTT实验结果 结果显示,随细胞培养时间延长,各组细胞的A值均逐渐升高,其中PVT1组的A值在12,24 h与Control组的A值均无明显差异(P > 0.05)。培养后36,48,72 h检测结果显示PVT1组的A值均显著高于Control组(P < 0.05)。而si-PVT1组的A值在培养后24,36,48,72 h 时与Control组相比明显降低(P < 0.05)。以上结果说明LncRNA PVT1过表达时可显著促进成纤维细胞的增殖,而其受到干扰时,细胞增殖则受到抑制,见图3A。将si-PVT1组和si-PVT1-NC组的相对抑制率比较,显示从培养后24,36,48及72 h 时si-PVT1组的抑制率明显高于si-PVT1-NC组,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3B,再次说明当干扰PVT1时,成纤维细胞的增殖受到抑制。"
| [1] HUANG L, ZHAO Z, WEN J, et al. Cellular senescence: A pathogenic mechanism of pelvic organ prolapse (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2020; 22(3):2155-2162. [2] 朱兰, 陈娟. 《盆腔器官脱垂的中国诊治指南(2020年版)》解读[J]. 中华医学信息导报,2020,35(15):17. [3] YIN Y, HAN Y, SHI C, et al. IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse. Open Med (Wars). 2020;15(1):833-840. [4] DIEDRICH CM, ROOVERS J, SMIT TH, et al. Fully absorbable poly-4-hydroxybutyrate implants exhibit more favorable cell-matrix interactions than polypropylene. Materi Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;120:111702. [5] QUINN JJ, CHANG HY. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(1):47-62. [6] 张志磊, 赵冰, 刘灵, 等. 盆底器官脱垂疾病mRNA和lncRNA差异表达谱的综合分析[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2020,55(2):236-242. [7] PALCAU AC, CANU V, DONZELLI S, et al. CircPVT1: a pivotal circular node intersecting Long Non-Coding-PVT1 and c-MYC oncogenic signals. Molecular Cancer. 2022;21(1):33. [8] HU HH, CHEN DQ, WANG YN, et al. New insights into TGF-beta/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;292:76-83. [9] LIU N, FENG J, LU X, et al. Isorhamnetin Inhibits Liver Fibrosis by Reducing Autophagy and Inhibiting Extracellular Matrix Formation via the TGF-beta1/Smad3 and TGF-beta1/p38 MAPK Pathways. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:6175091. [10] ZHANG Q, CHANG X, WANG H, et al. TGF-beta1 mediated Smad signaling pathway and EMT in hepatic fibrosis induced by Nano NiO in vivo and in vitro. Environ Toxicol. 2020;35(4):419-429. [11] ZHANG X, FENG W, ZHANG J, et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes epithelialmesenchymal transition via the TGFbeta/Smad pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(2):1093-1102. [12] RAJU R, LINDER BJ. Evaluation and Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(12):3122-3129. [13] REN S, XIE B, WANG J, et al. Biomechanics of pelvic organ prolapse. Sci China Life Sci. 2015;58(2):218-220. [14] WEINTRAUB AY, GLINTER H, MARCUS-BRAUN N. Narrative review of the epidemiology, diagnosis and pathophysiology of pelvic organ prolapse. Int Braz J Urol. 2020;46(1):5-14. [15] EL MH, LOEUILLARD E, LEMOINNE S, et al. Culture Model of Rat Portal Myofibroblasts. Front Physiol. 2016;7:120. [16] CANALS J, NAVARRO A, VILA C, et al. Human embryonic mesenchymal lung-conditioned medium promotes differentiation to myofibroblast and loss of stemness phenotype in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. J Exp Clin Cancer Rese. 2022;41(1):37. [17] WANG D, HU Y. Long Non-coding RNA PVT1 Competitively Binds MicroRNA-424-5p to Regulate CARM1 in Radiosensitivity of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;16:130-140. [18] CHEN J, YU Y, LI H, et al. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes tumor progression by regulating the miR-143/HK2 axis in gallbladder cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):33. [19] LI Y, SUN W, PAN H, et al. LncRNA-PVT1 activates lung fibroblasts via miR-497-5p and is facilitated by FOXM1. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021; 213:112030. [20] CAO F, LI Z, DING W, et al. LncRNA PVT1 regulates atrial fibrosis via miR-128-3p-SP1-TGF-β1-Smad axis in atrial fibrillation. Mol Med. 2019; 25(1):7. [21] MARTINOTTI S, RANZATO E. Scratch Wound Healing Assay. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2109:225-229. [22] MCKINNON KM. Flow Cytometry: An Overview. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2018;120:1-5. [23] WANG J, KONG X, HU H, et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA PVT1 induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating miR-543-dependent SCUBE2 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):142. [24] ZHENG J, YU F, DONG P, et al. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 activates hepatic stellate cells through competitively binding microRNA-152. Oncotarget. 2016;7(39):62886-62897. [25] NEVZOROVA YA, CUBERO FJ, HU W, et al. Enhanced expression of c-myc in hepatocytes promotes initiation and progression of alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64(3):628-640. [26] FEGHALI CA, BOULWARE DW, FERRISS JA, et al. Expression of c-myc, c-myb, and c-sis in fibroblasts from affected and unaffected skin of patients with systemic sclerosis. Autoimmunity. 1993;16(3):167-171. [27] QIN H, TANG Y, MAO Y, et al. C-MYC induces idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis via modulation of miR-9-5p-mediated TBPL1. Cellular Signalling. 2022;93:110274. [28] ZHOU Z, NI J, LI J, et al. RIG-I aggravates interstitial fibrosis via c-Myc-mediated fibroblast activation in UUO mice. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020; 98(4):527-540. [29] ZHANG N, SUN Y. LncRNA ROR facilitates myocardial fibrosis in rats with viral myocarditis through regulating C-Myc expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(24):10982-10988. [30] JIN K, WANG S, ZHANG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 interacts with MYC and its downstream molecules to synergistically promote tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(21):4275-4289. [31] TSENG YY, MORIARITY BS, GONG W, et al. PVT1 dependence in cancer with MYC copy-number increase. Nature. 2014;512(7512):82-86. [32] GHADIRI A, SHARIFI M, MEHRZAD V, et al. Reduce proliferation of human bone marrow cells from acute myeloblastic leukemia with minimally differentiation by blocking lncRNA PVT1. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020;22(11):2103-2110. [33] SHIGEYASU K, TODEN S, OZAWA T, et al. The PVT1 lncRNA is a novel epigenetic enhancer of MYC, and a promising risk-stratification biomarker in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):155. [34] LIAN N, LI T. Growth factor pathways in hypertrophic scars: Molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:42-50. [35] 石永英, 卢俊江, 陈广原, 等. p15与c-Myc在TGF-β1诱导的大鼠心肌细胞肥大中的表达及与TGF/Smad信号通路的关系[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志,2018,26(3):245-252. [36] 刘红艳, 齐创. 萝卜硫素调控TGF-β1/Smad信号通路抑制结肠癌HT-29细胞增殖的机制研究[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报,2020,45(3):311-314. [37] HU L, LIU J, LI Z, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 activates DeltaNp63/c-Myc to promote oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2016;122(4):460-482. [38] 郝淑玲, 王卫平, 李建东, 等. 肾上腺髓质素和转化生长因子β1对肺成纤维细胞增殖及c-myc表达的影响[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2015,29(4):333-335. |
| [1] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [2] | Shao Zichen, Li Huanan, Gu Bing, Zhang Xiaoyun, Sun Weikang, Liu Yongqian, Gan Bin. MicroRNA, long non-coding RNA and circular RNA mediate the mechanism of decreasing uric acid, anti-inflammation and regulating bone metabolism in gout [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 765-771. |
| [3] | Huang Bin, Zheng Jinxu, Zhang Jun. Progress of non-coding RNAs in stem cell abnormality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 130-137. |
| [4] | Li Qin, Mao Shuangfa, Li Min, Cheng Jiyan. Protective effect and mechanism of dendrobium on fibroblasts damaged by ultraviolet B [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1228-1233. |
| [5] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [6] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [7] | Liu Pei, Zhang Guanying, Yu Quanfeng, Li Zeyu, Han Guangye, Wu Chunlei. Basic fibroblast growth factor combined with poly(lactic acid)/collagen scaffold for urethral defect in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5468-5474. |
| [8] | Kang Teng, Lan Fengjun, Qin Hao, Liu Gang. Long non-coding RNA and osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5242-5247. |
| [9] | Wang Dandan, Yu Yabin, Liu Shiqi, Yan Yulou, Zhang Jianhuai. Role of long non-coding RNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 in the differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4847-4851. |
| [10] | Wang Rui, Yu Fei, Liu Taibin, Hou Xiuli, Liu Zhendong, Huo Jing, Song Jianbo. Recombinant human interferon alpha-2b inhibits the proliferation and migration of scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4611-4615. |
| [11] | Zhang Ansheng, Zhang Haiou, Ni Longxing. Regulating the expression of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome-related molecules in dental pulp fibroblasts under inflammation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4107-4112. |
| [12] | Zhang Gaofei, Wang Di, Li Jiamei, Lou Hanxiao, Zeng Yueqin, Liu Wenjun. Mesenchymal stem cells promote wound healing by regulating the autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4058-4063. |
| [13] | Zhong Ruiying, Wang Fuke, Yang Guiran, Wang Guoliang, Hou Jianfei, Liao Xinyu. Co-culture of fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells affects proliferation and osteogenesis of adipose stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3833-3839. |
| [14] | Chen Sheng, Yang Yan, Ding Liang, Ye Chuanjin, Zhang Lei, Xia Shu, Li Huiling, Huang Xiaofeng. Establishment and identification of an immortalized oral cancer-related fibroblast line [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3808-3813. |
| [15] | Zhou Fanqi, Li Baoying, Wang Kaitao, Tan Quanquan, Yun Chenxia, Leng Jing. Isolation and identification of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from tree shrews and establishment of TLR8 pathway related molecular detection methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3721-3727. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||