[1] LIMANDJAJA GC, NIESSEN FB, SCHEPER RJ, et al. Hypertrophic scars and keloids: Overview of the evidence and practical guide for differentiating between these abnormal scars. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30:146-161.
[2] TAPKING C, PRASAI A, BRANSKI LK. Are hypertrophic scars and keloids the same? Br J Dermatol. 2019;182(4):832-833.
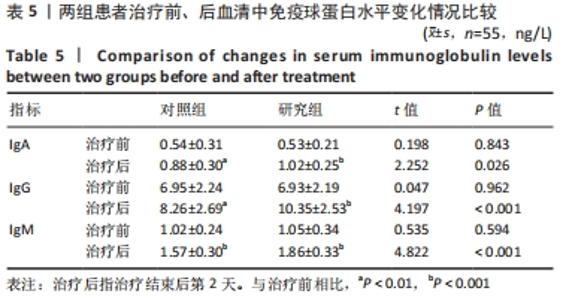
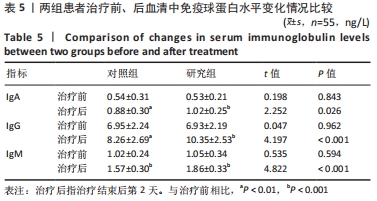
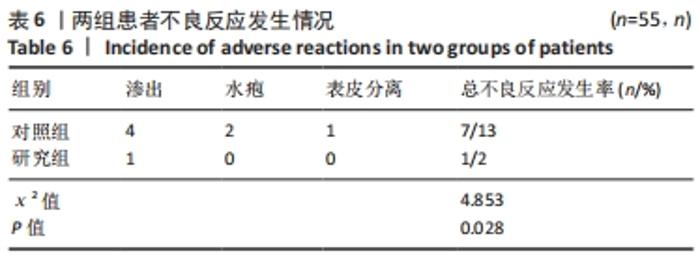
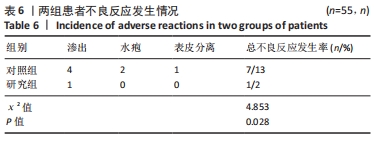
[3] 姚翠英,陈芳.炎症和纤维标志物在痤疮增生性瘢痕形成中的表达[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(6):450-456.
[4] 杨丽, 李娜, 程静, 等. 脉冲染料激光用于烧伤后增生性瘢痕的最佳治疗间隔的前瞻性随机对照临床研究[J]. 中华烧伤杂志,2020, 37(1):57-63.
[5] 雷颖, 彭诗绮, 陈红阳, 等. 点阵激光联合脉冲染料激光加多点微量注射曲安奈德对兔耳增生性瘢痕的影响[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2020,36(10):1128-1138.
[6] 尹光文, 刘聪, 王小云,等. 氨基酮戊酸-光动力疗法对尖锐湿疣组织中血管内皮生长因子和增殖细胞核抗原表达的影响[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志,2020,53(1):48-50.
[7] LAN J, DU H, LI Y, et al. Dextran-based acitretin nanoparticle ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(7):S1.
[8] KIM SG, KIM EY, KIM YJ, et al. The Efficacy and safety of abla-tive fractional resurfacing using a 2, 940-Nm Er: YAG laser for traumatic scars in the early posttraumatic period. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39(3): 232-237.
[8] ELREFAIE AM, SALEM RM, FAHEEM MH. High-resolution ultrasound for keloids and hypertrophic scar assessment. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;35: 379-385.
[9] MIGITA H, RIKIMARU H, RIKIMARU-NISHI Y, et al. Analysis of Scars and Keloids by Focused Ion Beam/Scanning Electron Microscopy: Distinguishing Between Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids. Ann Plastic Surg. 2020;84(4):379-384.
[10] KHAN FA, DRUCKER NA, LARSON S, et al. Pediatric earlobe keloids: Outcomes and patterns of recurrence – Science Direct. J Pediatr Surg. 2020;55(3):461-464.
[11] WANG X, GU C, SHANG F, et al. Inhibitory Effect of the LY2109761 on the Development of Human Keloid Fibroblasts. Analyt Cell Pathol (Amsterdam). 2021;2021:8883427.
[12] 程梦星, 邱丽华. 光动力治疗在宫颈疾病中的应用[J]. 现代妇产科进展,2020,29(5):79-81.
[13] 谢春晖, 高欣欣, 孟祥龙, 等. 早期应用序贯激光治疗烧伤患儿增生性瘢痕的效果分析[J]. 中华烧伤杂志,2021,37(4):327-332.
[14] 黄振, 陈烨, 王朋, 等. 二氧化碳点阵激光联合自体脂肪注射治疗烧伤后增生性瘢痕效果的前瞻性平行对照临床研究[J]. 中华烧伤杂志,2020,37(1):49-56.
[15] PETTERSSON CM, BROSTRÖM H, HUMBLOT P, et al. Topical treatment of equine sarcoids with imiquimod 5% cream or Sanguinaria canadensis and zinc chloride - an open prospective study. Vet Dermatol. 2020;31: 471.
[16] 青玉,巴图德力根,韩志强,等. 咪喹莫特诱导小鼠银屑病样动物模型的建立与评价[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2019,35(1):73-75.
[17] KORPPI M, TERSJRVI J, LAUHKONEN E, et al. Toll‐like receptor 4 polymorphisms were associated with low serum pro‐inflammatory cytokines in BCG osteitis survivors. Acta Paediatrica. 2020;109(7): 1417-1422.
[18] SHAHID H, SHAHZAD M, SHABBIR A, et al. Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Curcumin for the Treatment of Allergic Asthma: Effects on Expression Levels of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines and Aquaporins. Inflammation. 2019;42(6):2037-2047.
[19] FAN Y, YANG L, WEI Q, et al. Toll-like receptor 10 (TLR10) exhibits suppressive effects on inflammation of prostate epithelial cells. Asian J Androl. 2019;21(4):393-399.
[20] LIM E, JEON JY. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia presenting as pelvic inflammatory disease in a phenotypic male: A case report. Medicine. 2020;99(2):e18387.
[21] 李燕姿,武咪,平宝华,等. 抑制吲哚胺2,3双加氧酶活性可增强Toll样受体7激动剂咪喹莫特在胃癌中的抗肿瘤作用[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2020,41(5):696-700,723.
[22] 林康,苏海燕,虞庆,等. 苏拉明通过抑制纤维增生和炎症反应减轻小鼠的瘢痕增生[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(11):2070-2077.
[23] 张思敏,亓发芝. 巨噬细胞极化在增生性瘢痕和瘢痕疙瘩中的作用[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(5):639-642.
[24] 苏秦, 高进, 付俊鲜,等. 血流动力学指标和IL-6在脓毒症肾损伤患儿中的表达及其与免疫指标的相关性[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2020, 36(10):1235-1239.
[25] ANGELOPOULOU A, ALEXANDRIS N, KONSTANTINOU E, et al. Imiquimod-A toll like receptor 7 agonist - Is an ideal option for management of COVID 19. Environmental Res. 2020;188:109858.
[26] SCIULLO PD, MENAY F, COCOZZA F, et al. Systemic administration of imiquimod as an adjuvant improves immunogenicity of a tumor-lysate vaccine inducing the rejection of a highly aggressive T-cell lymphoma. Clin Immunol. 2019;203:154-161.
|