Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (24): 3914-3920.doi: 10.12307/2022.576
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells on aging-related ischemic stroke
Chen Na, Wang Xiaohan, Zhang Yunke
- Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-24Accepted:2021-09-15Online:2022-08-28Published:2022-01-24 -
Contact:Zhang Yunke, PhD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Post-doctoral co-supervisor, Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chen Na, Doctoral candidate, Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81974564 (to ZYK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Na, Wang Xiaohan, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells on aging-related ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3914-3920.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
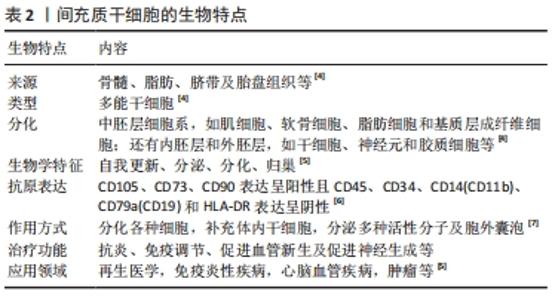
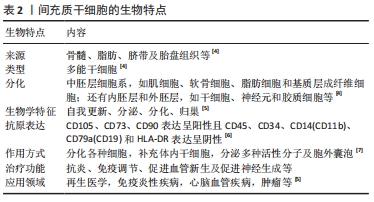
2.1 间充质干细胞的生物学特点 间充质干细胞是一种多能干细胞,具有自我更新、分化、分泌及归巢的能力,最初在骨髓中被发现,在骨髓、脂肪、脐带和胎盘组织中较为丰富而且容易提取[4-5]。间充质干细胞可以分化为中胚层细胞系,如肌细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞和基质层成纤维细胞;还有内胚层和外胚层,如干细胞、神经元和胶质细胞。间充质干细胞也可分泌神经营养因子,促进细胞生长及迁移,还具有免疫抑制作用,可以减轻机体炎症反应,在再生医学中发挥着重要的作用[4]。2006年国际细胞治疗协会定义并阐述了间充质干细胞的特征:①间充质干细胞必须在标准培养下黏附在塑料上;②间充质干细胞有抗原表达,CD105,CD73,CD90呈阳性且CD45,CD34,CD14(CD11b),CD79a(CD19)和HLA-DR呈阴性;③间充质干细胞必须在体外分化为成骨细胞、脂肪细胞和软骨细胞[6]。间充质干细胞具有较为广泛的组织分化能力、免疫原性较低及获取来源广泛等生物特点,近年来在组织工程和再生医学领域体现明显优势,是近年来研究的热点,见表2。"
分泌的囊泡根据直径大小和来源可分为凋亡小体、微泡、外泌体,分泌的神经营养因子、生长因子及抗炎分子等可以促进细胞迁移增生、信息交流、减少炎症反应等。外泌体是一种由细胞主动向外分泌的直径为30-100 nm脂质双分子层的囊泡小体。之前认为这些囊泡是细胞主动向外排泄的一种废物,随后越来越多的研究表明外泌体具有在细胞间传递信息、组织再生、免疫调节等功能[7]。间充质干细胞移植治疗疾病虽然具有较好的前景,但是也存在一些限制需要进一步研究。实验研究通过动静脉、鼻腔或局部脑组织注射移植间充质干细胞能够通过分泌物质促进血管新生、神经突触形成、抑制炎症反应,分化为神经元、周细胞及神经胶质细胞等途径,起到对神经血管单元功能修复及保护作用。 2.2 衰老与缺血性卒中的关系 "
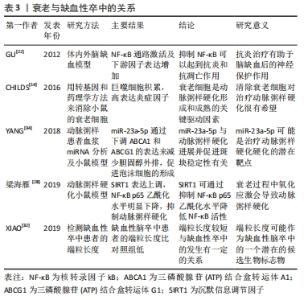
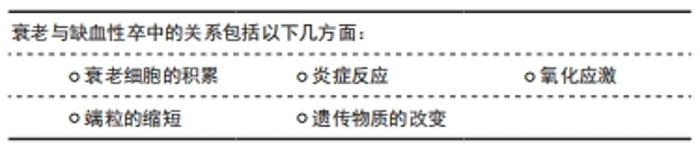
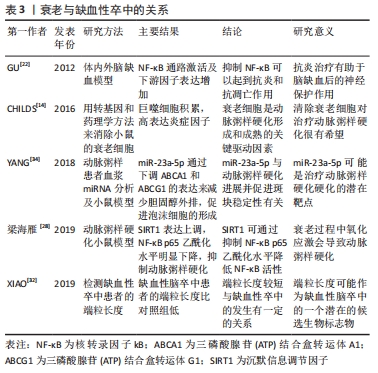
衰老是人类正常生命活动的自然规律,人类的机体在生长发育完成之后,便逐渐进入衰老的过程。衰老可分为2类:即生理性衰老及病理性衰老。生理性衰老是指随年龄的增长到成熟期以后所出现的生理性退化,也就是人体在体质方面的年龄变化,这是一切生物的普遍规律。上古圣人能“形与神俱,而尽终其天年”“精神内守”“度百岁乃去”。然而当今之人,不重视养生,不重视起居,出现病理性衰老,“半百而衰”,由于内在的或外在的原因使人体发生病理性变化,使衰老现象提前发生,这种衰老又称为早衰。缺血性脑卒中的发病与病理性早衰有一定关系。人体衰老的本质是细胞的衰老,细胞衰老是由于损伤积累诱发了细胞周期抑制通路的激活,细胞永久地退出细胞增殖周期。细胞衰老具有永久性细胞周期阻滞、DNA损伤积累、凋亡抵抗、衰老相关的炎症因子分泌以及代谢和表观遗传特征改变等特征[8]。 2.2.1 衰老细胞的积累 不可逆的细胞周期阻滞和促炎性衰老相关的分泌表型是细胞衰老的特征,这也是衰老与年龄相关疾病的重要因素。衰老细胞的积聚,激活衰老相关的分泌表型炎症因子分泌,进一步恶化细胞生存的微环境[9]。内皮细胞衰老或功能失调时,血管收缩、促凝和促炎因子被释放,引起血管通透性增加和内皮细胞迁移[10]。炎症会改变动脉壁细胞的功能,从而导致动脉粥样硬化[11]。衰老相关分泌表型是衰老和年龄相关疾病的主要因素[12]。衰老相关分泌表型主要通过核转录因子κB上调转化生长因子β表达,导致周边细胞发生周期阻滞,进而出现细胞衰老,也可以转换为白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素6,8[13]。CHILDS等[14]用转基因和药理学方法来消除小鼠的衰老细胞,结果显示血管内皮下方出现衰老标记阳性的泡沫样巨噬细胞堆积,高水平表达一些炎症细胞因子,形成斑块病理性改变,表明衰老细胞是动脉粥样硬化形成和成熟的关键驱动因素。 衰老细胞还可以通过自分泌或旁分泌巩固衰老表型并促进临近细胞衰老、阻碍组织再生与重塑[15]。随着年龄增长,血管会出现不同程度的老化,毛细血管数目下降,内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞形态学异常,弹性动脉管壁增厚,可见胶原纤维增加,弹力纤维减少、断裂,基质黏多糖沉积增加等[16]。弹性动脉僵硬度增加、顺应性下降以及血管修复、新生能力降低影响正常功能。星形胶质细胞衰老相关分泌表型积累增加,分泌炎性细胞因子、趋化因子和蛋白酶等,小胶质血管炎症引起血脑屏障的通透性的异常。小胶质细胞在中枢神经系统充当巨噬细胞的角色,脑白质衰老后会释放更多的细胞因子和炎症因子,这些都有助于小胶质细胞的活化和募集。小胶质细胞的M1表型会加剧脑白质损伤,在衰老的脑组织中小胶质细胞表型以M1为主,这是衰老后脑神经血管单元损害加重的因素[17]。衰老后成体干细胞出现衰老趋势,神经干细胞的分化能力减退,在皮质、海马及浦肯野等有丝分裂后的中枢神经细胞以及周围神经元均表现出细胞衰老的特征,如衰老相关分泌表型和周期阻滞因子表达[18]。缺血缺氧环境会改变干细胞生存的微环境,加速干细胞的衰老。 由此可见,衰老细胞在脑内的堆积,激活衰老相关分泌表型分泌炎性递质,造成神经干细胞分化功能减退、胶质细胞的炎性改变、基质黏多糖沉积和血管粥样硬化等神经血管单元结构病理变化,成为脑卒中的基础因素。 2.2.2 炎症反应 衰老不仅伴随着组织的局部促炎微环境,而且还伴随着系统性炎症和疾病发生率的增加,包括年龄有关的脑血管疾病[19]。脑缺血后加剧炎症细胞的浸润,激活相关通路放大为缺血瀑布效应引起严重的并发症,使衰老后脑神经血管单元损伤“雪上加霜”。 脑卒中后中枢神经系统炎症反应的发生,激活小胶质细胞改变血脑屏障通透性,随后外周免疫细胞浸润到脑实质,分泌炎症细胞因子导致神经元的损伤和死亡[20]。小胶质细胞首先受到刺激,活化的小胶质细胞(M1)释放促炎因子干扰素α、白细胞介素1,激活反应性星形胶质细胞(A1)的核转录因子κB炎症反应,并放大这种效应。由于炎症反应的刺激,神经血管单元结构发生改变,微环境的变化刺激小胶质细胞(M2)发挥吞噬作用并分泌转化生长因子因子、白细胞介素10,同时激活反应性星形胶质细胞(A2)的改变[21]。星形胶质细胞中核转录因子κB的激活通过诱导炎症因子、兴奋性毒素等的产生和释放导致神经元变性。核转录因子κB在神经元、神经胶质细胞和脑血管内皮细胞中通常有较低量的表达。缺血时神经细胞、胶质细胞和脑血管内皮细胞中的PKCθ被激活,在T细胞中能够特异性的活化核转录因子κB级联反应,参与炎性递质(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素2、白细胞介素6)、黏附因子、炎性相关酶如基质金属酶的释放和调节。核转录因子κB调节肿瘤坏死因子诱导的黏附因子的转录[22-23]。 GU等[22]用银杏内酯干预体内外脑缺血模型,显示核转录因子κB通路激活及下游因子表达增加,表明抑制核转录因子κB可以起到抗炎和抗凋亡作用,保护神经细胞。脑缺血再灌注损伤时核转录因子κB活化,核转录因子κB是炎症反应的中枢,也是细胞内信号转导途径的中间枢纽,其活化后与DNA特定序列结合,诱导相关基因转录和表达从而激活炎症因子及细胞因子,导致缺血后炎症反应的发生[23]。核转录因子κB诱发的一系列炎性改变,加剧了衰老后脑缺血再灌注的损伤,引起脑水肿等并发症。由此可见,脑缺血后激活相关通路,加剧炎症反应,形成级联反应,脑衰老后神经血管单元的损伤“雪上加霜”。 2.2.3 氧化应激 衰老后,衰老相关分泌表型炎性因子或趋化因子引起的细胞微环境恶化,造成氧化应激增强,细胞内部的线粒体受到攻击,引起其结构破坏和功能障碍,进而影响体内各种系统疾病的发生和发展[24]。衰老的脑组织中,过度的氧化应激很可能会加剧脑白质损伤。衰老过程中线粒体功能紊乱,合成ATP的功能下降,氧自由基超载,加之衰老的细胞中抗氧自由基能力减弱,因此衰老后缺血性卒中引起的损伤更大[25]。 沉默信息调节因子1是一种NAD+依赖性蛋白脱乙酰化酶,通过调控多种组蛋白及非组蛋白p53、核转录因子κB、PPARγ等乙酰化底物参与机体器官发育、炎症反应、氧化应激、代谢和凋亡等多种信号通路[26-27]。沉默信息调节因子1与年龄相关疾病过程有关,而且随着衰老表达减少,诱发血管炎性反应。沉默信息调节因子1可通过下调炎性反应中重要的核转录因子核转录因子κB的活性来抑制促炎因子的释放从而控制动脉粥样硬化斑块形成及发展。梁海雁等[28]用沉默信息调节因子1过表达干预动脉粥样硬化小鼠模型,结果显示沉默信息调节因子1表达上调,核转录因子κB p65乙酰化水平明显下降,抑制动脉粥样硬化。在大脑中,沉默信息调节因子1主要定位于神经元细胞核中,在神经干细胞、星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞中也有表达。沉默信息调节因子1调控大脑中许多重要的生理过程,如基因组稳定性、神经发生、神经突向外生长、突出可塑性和认知功能[29]。在脑缺血发生后,沉默信息调节因子1具有维持线粒体功能稳态、介导NAD+的神经保护作用、减少氧化应激、维持血容量以及减少炎症反应的作用。 2.2.4 端粒的缩短 端粒是真核细胞染色体末端的结构,起着保护染色体、维持遗传系统稳定的作用。端粒随着细胞的分裂而缩短,当达到临界长度时细胞失去了分裂增殖能力而衰老死亡,这种缩短就是衰老的标志,因此,端粒也被称为细胞的“生命钟”。人类端粒DNA是重复TTAGGG序列,具有防止染色体融合、维持基因完整性和稳定性的作用。端粒复合物由富含鸟苷酸的DNA序列、端粒酶和端粒复制因子3部分构成。由于DNA的半保留复制,细胞每分裂1次端粒缩短30-200 bp,当端粒缩短到一定长度时,细胞即停止分裂进入衰老,该过程称为复制性衰老。因此,端粒长度被视为细胞生物学年龄的标记物[30]。端粒长度取决于出生时端粒长度和端粒长度缩短的速度。出生时端粒长度由遗传因素决定,端粒长度缩短由细胞分裂次数和每次细胞分裂端粒缺失引起,慢性炎症能增加细胞分裂的次数,而氧化应激可增加端粒缺失,从而引起端粒长度缩短[31]。 端粒酶能够以自身RNA结构为模板复制DNA片段延长端粒。XIAO等[32]于2019年的一项病例对照研究检测缺血性卒中患者的端粒长度,证实中国北部汉族人口中短端粒与缺血性脑卒中明显相关,端粒长度可能成为缺血性脑卒中诊断的生物标志物。短端粒与动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死密切相关,端粒长度是动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死的独立危险因素,端粒长度可影响动脉粥样斑块稳定性,同时端粒长度缩短可评估动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死的死亡风险[33]。 2.2.5 遗传物质的改变 miRNA是一种内源性的、单链的长度为18-25个核苷酸的非编码RNA,存在于线虫、果蝇、植物和包括人在内的真核生物中,与稳定载体(包括微粒子和外泌体)。YANG等[34]进行动脉粥样患者血浆miRNA分析及小鼠模型研究,结果显示miR-23a-5p通过下调ABCA1和ABCG1的表达来减少胆固醇外排,促进泡沫细胞的形成,与动脉粥样硬化形成有关。作为基因调控的负调节分子,它可以导致许多重要的人类生理和病理过程,包括分化、增殖、凋亡、迁移、体内平衡和各种疾病[35]。miRNA与衰老、脑缺血的发生密切相关,是心脑血管疾病治疗的新靶点。 在哺乳动物的胚胎发育阶段,大脑内有包括miR-34a、miR-126、miR-200b等在内大量miRNAs的表达,提示miRNAs在中枢神经系统的发育过程中以及对神经干细胞命运的调控过程中发挥了重要的作用[36]。在细胞衰老的过程中,miR-34、miR-138、miR-152和miR-493等表达上调,miR-15A、miR20A、miR-25和miR-155等表达下调。在衰老过程中,miRNA的表达上调与p53的增多有关,如miR-34家族可以从生长停滞及凋亡等方面影响p53的活性表达上调[37]。p53是调节细胞衰老的重要因子,通过不同的信号调控细胞衰老,在细胞分裂停止的衰老细胞中表达增加[38]。miR-34a是一种高度进化保守的miRNA,相关文献报道,miR-34a能够通过调节基因及蛋白的表达,参与神经细胞的增殖及分化,在神经系统疾病的发生发展过程中发挥独特的调控作用[39]。胚胎干细胞、神经干细胞等干细胞的增殖分化过程中,miR-34a能够促使胚胎干细胞、神经干细胞进一步增殖并分化为神经元等终末神经细胞。因此,遗传物质的改变与细胞衰老关系密切,也是未来基因治疗的方向。 总之,衰老的基本病理生理过程,主要与炎症反应、氧化应激、免疫反应、胆固醇变化、蛋白质稳态丧失、线粒体功能障碍、基因组损伤、表观遗传学改变、干细胞功能障碍、血管老化、衰老细胞的积累及分泌相关因子有关[3],其中衰老细胞的积累、炎症反应、氧化应激、端粒的缩短以及遗传物质的改变在缺血性卒中的发生发展中起着重要作用,见表3。"
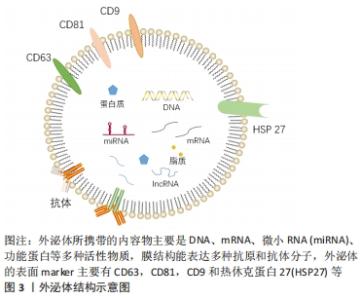
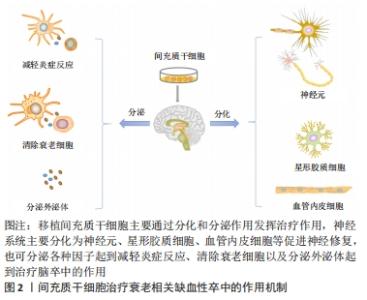
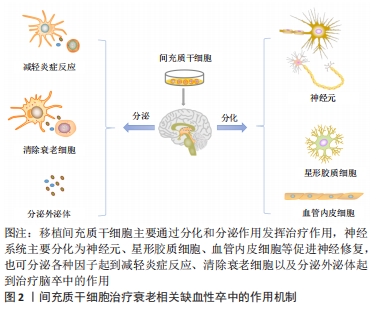
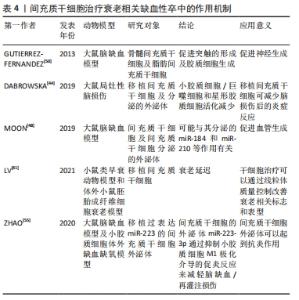
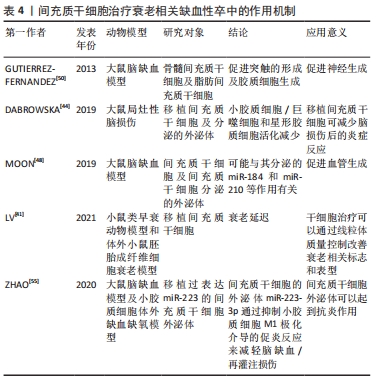
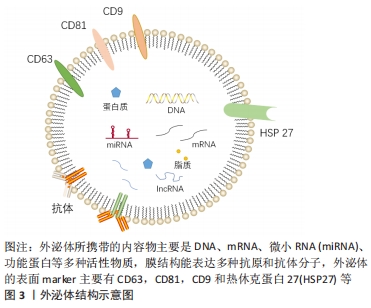
间充质干细胞移植可以通过以下几方面作用治疗衰老相关缺血性卒中,延迟衰老,减轻缺血性卒中后神经血管损伤及级联反应造成的脑损伤。 2.3.1 清除衰老细胞 清除衰老细胞可阻断炎症递质通路的损害,是保护损伤的脑神经血管单元的重要策略。衰老细胞的堆积能够引起老年性疾病的发生,给老年小鼠移植衰老细胞可以导致生存期缩短[40]。清除衰老细胞或阻断衰老相关分泌表型分泌,来阻断衰老细胞的促衰老作用,可能成为治疗老年性脑卒中的有效策略[41]。 间充质干细胞移植可以补充衰老个体的干细胞储备,促进细胞的分化,清除衰老细胞,起到“腾笼换鸟”作用,增强衰老神经血管单元的重塑。有研究通过衰老细胞和类早衰动物模型移植脂肪间充质干细胞[42],结果显示干细胞移植可以加速线粒体吞噬,清除细胞内氧化应激相关因子,改善线粒体功能,延迟衰老。 随着细胞的衰老,脑组织会出现神经元生长缓慢甚至凋亡、血管内皮结构破坏、血脑屏障通透性增加、胶质细胞减少等。间充质干细胞移植能够输入外源性干细胞,并且适当条件下能够分化为不同的细胞,及分泌营养因子刺激细胞增生及凋亡。间充质干细胞能够释放血管内皮生长因子和细胞外基质成分,刺激血管新生。干细胞移植可以分泌神经营养因子,刺激星形胶质细胞的表达,促进神经元突触的形成,也影响周细胞生理功能。周细胞是血脑屏障的组成部分,在维持神经血管单元的完整性方面起着重要的作用[43]。 2.3.2 减轻炎症反应 干细胞移植可以抑制胶质细胞的激活,抑制炎症反应保护神经元,促进抗炎因子表型的分化,以及神经营养因子的产生[44]。脑卒中后小胶质细胞首先受到刺激,活化的小胶质细胞(M1)释放促炎因子干扰素α、白细胞介素1,激活反应性星形胶质细胞(A1)的核转录因子κB炎症反应,并放大这种效应。由于炎症反应的刺激,神经血管单元结构发生改变,微环境的变化刺激星形胶质细胞(M2)发挥吞噬作用并分泌转化生长因子、白细胞介素10,同时激活反应性星形胶质细胞(A2)的改变[21]。星形胶质细胞中核转录因子κB的激活通过诱导炎症因子、兴奋性毒素等的产生和释放导致神经元变性。干细胞移植可以抑制胶质细胞的激活,抑制炎症反应保护神经元,促进抗炎因子表型的分化,以及神经营养因子的产生[44]。 缺血性脑卒中后也会释放另一种趋化因子MCP-1,它能够诱导单核细胞浸润,激活促炎细胞因子,引起组织损伤。DABROWSKA 等[45]通过大鼠局灶性脑损伤模型移植人骨髓间充质干细胞及其分泌的外泌体,结果显示脑损伤局部MCP-1表达增加,而移植人骨髓间充质干细胞及外泌体组MCP-1表达下降,这与小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞和星形胶质细胞活化减少有关。YOO等[46]研究也证实了此观点,缺血性脑卒中动物模型中注射间充质干细胞分泌转化生长因子β1降低了MCP-1的产生,减轻了免疫细胞浸润脑缺血区。间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死模型小鼠有助于降低炎症因子释放,促进脑内高迁移率族蛋白1释放,减轻神经损伤[47]。总之,移植间充质干细胞可以调节免疫反应,产生的抗炎因子可以抑制促炎因子的表达,抑制炎症细胞向脑缺血区迁移。 2.3.3 促进血管新生 脑卒中后血管新生可以增加脑血流量,有助于神经功能的恢复,而且血管新生影响着神经生成。间充质干细胞能够释放血管内皮生长因子和细胞外基质成分,刺激血管新生。RYU等[48]通过移植脂肪间充质干细胞薄片到局部脑表面,干预14 d后观察干细胞移植后脑组织血管新生和神经生成明显增加,神经功能改善,而且部分移植细胞分化为周细胞,保护受损的神经血管单元,结果表明干细胞移植可以改善脑卒中后引起的神经功能受损,促进血管新生及神经生成,促进神经血管单元修复。MOON等[49]研究表明以合适的剂量静脉注射间充质干细胞及间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体能够促进神经生成及血管新生,有助于卒中后恢复,可能与其分泌的miR-184和miR-210等作用有关。SHEIKH等[50]通过移植人间充质干细胞系(B10)于大鼠MCAO模型,第3天发现脑梗死区内皮生长因子缺氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子表达及mRNA均增加,缺氧诱导因子1α在星形胶质细胞和巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞中表达,血管内皮生长因子在巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞中表达,结果表明B10细胞通过调节缺氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子的表达而促进MCAO模型大鼠的脑血管生成。间充质干细胞移植通过实验证明能够促进脑卒中后的血管新生,促进神经功能改善。 2.3.4 促进神经生成 干细胞移植可以分泌神经营养因子,刺激星形胶质细胞的表达,促进神经元突触的形成,也影响周细胞生理功能。周细胞是血脑屏障的组成部分,在维持神经血管单元的完整性方面起着重要的作用[43]。GUTIERREZ-FERNANDEZ等[51]通过移植骨髓间充质干细胞及脂肪间充质干细胞治疗局灶性中动脉阻断脑缺血模型大鼠,结果发现间充质干细胞移植能够促进神经突触的形成及胶质细胞生成。XIE等[52]通过脑立体定位的方式移植人源骨髓间充质干细胞治疗MCAO大鼠模型,结果发现移植人骨髓间充质干细胞可以诱发神经细胞的生成及增强神经元的功能。脑源性神经营养因子在促进神经突触和轴突形成方面发挥着关键作用。骨髓间充质干细胞移植或联合当归素可以促进血管内皮生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子的表达,可能与激活AKT/mTOR信号通路有关[53]。CHAU等[54]通过鼻腔给予骨髓间充质干细胞治疗诱导大鼠小脑局灶性缺血,采用RT-PCR和免疫荧光分析骨髓间充质干细胞可分泌基质细胞衍生因子1α、CXCR4、血管内皮生长因子和FAK再生因子,骨髓间充质干细胞鼻腔移植脑梗死区域共标记荧光检测NeuN/BrdU和Glut-1/BrdU表达增加,促进神经生成及功能康复。缺血后脑损伤造成的神经功能损伤是导致患者残疾的重要原因,干细胞移植给治疗带来了希望。 2.3.5 分泌外泌体 间充质干细胞可以释放具有细胞功能的外泌体,通过外泌体的作用可以促进脑卒中后神经损伤修复,减轻炎症反应等,起到治疗作用。外泌体选择性地包含内容物,并通过精密的分选机制和独特的摆渡方式将这些内容物移送至靶细胞。外泌体所携带的内容物主要是mRNA、微小RNA (miRNA)、miDNA片段、功能蛋白、转录因子等多种具有生物活性的物质,而其本身的膜结构还能表达多种抗原、抗体分子,外泌体的表面marker主要有CD63,CD81,CD9,HSP27及TSG101等,从而产生生物学效应,见图3。"
| [1] SIFAT AE, VAIDYA B, ABBRUSCATO T J. Blood-brain barrier protection as a therapeutic strategy for acute ischemic stroke. AAPS J. 2017;19(4):957-972. [2] LIU D, XU L, ZHANG X, et al. Snapshot:Implications for mTOR in Aging-related Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Aging Dis. 2019;10(1):116-133. [3] UNGVARI Z, TARANTINI S, DONATO AJ, et al. Mechanisms of vascular aging. Circ Res. 2018;123(7):849-867. [4] SHERMAN LS, ROMAGANO MP, WILLIAMS SF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapies in brain disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;95:111-119. [5] SONG N, SCHOLTEMEIJER M, SHAH K. Mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2020;41(9):653-664. [6] DOEPPNER TR, BAHR M, GIEBEL B, et al. Immunological and non-immunological effects of stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles on the ischaemic brain. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2018;11:1277010894. [7] JAFARI D, SHAJARI S, JAFARI R, et al. Designer exosomes: a new platform for biotechnology therapeutics. BioDrugs. 2020;34(5):567-586. [8] KIRKLAND JL, TCHKONIA T. Cellular senescence: a translational perspective. EBioMedicine. 2017;21:21-28. [9] ACOSTA J C, BANITO A, WUESTEFELD T, et al. A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(8):978-990. [10] LI X, DAI Y, SHEN T, et al. Induced migration of endothelial cells into 3D scaffolds by chemoattractants secreted by pro-inflammatory macrophages in situ. Regen Biomater. 2017;4(3):139-148. [11] LIBBY P, BURING JE, BADIMON L, et al. Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019; 5(1):56. [12] OGRODNIK M, EVANS SA, FIELDER E, et al. Whole-body senescent cell clearance alleviates age-related brain inflammation and cognitive impairment in mice. Aging Cell. 2021:e13296. [13] CHILDS BG, GLUSCEVIC M, BAKER DJ, et al. Senescent cells:an emerging target for diseases of ageing. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(10):718-735. [14] CHILDS BG, BAKER DJ, WIJSHAKE T, et al. Senescent intimal foam cells are deleterious at all stages of atherosclerosis. Science. 2016;354(6311):472-477. [15] MUNOZ-ESPIN D, SERRANO M. Cellular senescence: from physiology to pathology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(7):482-496. [16] 姜平,黎健.血管衰老及其机制[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2014,41(3): 295-304. [17] MANIEGA SM, VALDES HM, CLAYDEN JD, et al. White matter hyperintensities and normal-appearing white matter integrity in the aging brain. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(2):909-918. [18] 陈祥宁,刘洋,纪俊峰. 清除衰老细胞在衰老与老龄化相关疾病中的研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2019,46(12):1150-1161. [19] LI PH, ZHANG R, CHENG LQ, et al. Metabolic regulation of immune cells in proinflammatory microenvironments and diseases during ageing. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;64:101165. [20] GONZALEZ H, ELGUETA D, MONTOYA A, et al. Neuroimmune regulation of microglial activity involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroimmunol. 2014;274(1-2):1-13. [21] LIU LR, LIU JC, BAO JS, et al. Interaction of Microglia and Astrocytes in the Neurovascular Unit. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1024. [22] GU JH, GE JB, LI M, et al. Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation is associated with anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of Ginkgolide B in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012;47(4):652-660. [23] MA M, UEKAWA K, HASEGAWA Y, et al. Pretreatment with rosuvastatin protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Brain Res. 2013;1519:87-94. [24] 赵滔.赭曲霉毒素A诱导HEK293T细胞氧化应激及自噬研究[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2017. [25] WU P, ZHOU Y M, ZENG F, et al. Regional brain structural abnormality in ischemic stroke patients: a voxel-based morphometry study. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(9):1424-1430. [26] RAZI S, COGGER VC, KENNERSON M, et al. SIRT1 polymorphisms and serum-induced SIRT1 protein expression in aging and frailty: the CHAMP study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72(7):870-876. [27] HAN Y, LUO H, WANG H, et al. SIRT1 induces resistance to apoptosis in human granulosa cells by activating the ERK pathway and inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling with anti-inflammatory functions. Apoptosis. 2017;22(10):1260-1272. [28] 梁海雁,王世喜.过表达SIRT1对动脉粥样硬化小鼠炎症反应的治疗效果[J].解剖学研究,2019,41(6):513-517. [29] UTANI K, FU H, JANG SM, et al. Phosphorylated SIRT1 associates with replication origins to prevent excess replication initiation and preserve genomic stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(13):7807-7824. [30] FUSTER JJ, ANDRES V. Telomere biology and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2006;99(11):1167-1180. [31] SAMANI N J, VAN DER HARST P. Biological ageing and cardiovascular disease. Heart. 2008;94(5):537-539. [32] XIAO J, YUAN Q, ZHANG S, et al. The telomere length of peripheral blood cells is associated with the risk of ischemic stroke in Han population of northern China. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(7):e14593. [33] 李丹青.外周血白细胞端粒长度与大动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死及颈动脉粥样硬化斑块稳定性的相关研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2017. [34] YANG S, YE ZM, CHEN S, et al. MicroRNA-23a-5p promotes atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability by repressing ATP-binding cassette transporter A1/G1 in macrophages. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;123:139-149. [35] 张真,廖清池,柳书可,等.微小RNA与血管内皮细胞的衰老关系研究进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2018,20(12):1327-1329. [36] 王瑞彤,闫昕,陈辉,等.miR-155在胶质瘤干细胞样细胞的表达及临床意义[J].临床神经外科杂志,2019,16(4):277-281. [37] 宓林,于晓峰,邹健.miRNA对衰老调控的相关研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014,34(17):5024-5027. [38] 郑桂纯,赵姝灿,黄丽贞,等.不同来源间充质干细胞条件培养基对内源性衰老细胞作用的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(21):3357-3363. [39] 张勃昕,吉爱红,曹正垚,等.miR-34a对人颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].口腔生物医学,2019,10(1):1-5. [40] 苏路路,管博文,樊飞跃,等.衰老细胞清除剂研究进展[J].中国药理学通报, 2019,35(10):1333-1337. [41] XU M, PIRTSKHALAVA T, FARR JN, et al. Senolytics improve physical function and increase lifespan in old age. Nat Med. 2018;24(8):1246-1256. [42] LV M, ZHANG S, JIANG B, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells regulate metabolic homeostasis and delay aging by promoting mitophagy. FASEB J. 2021;35(7): e21709. [43] GERANMAYEH MH, RAHBARGHAZI R, FARHOUDI M. Targeting pericytes for neurovascular regeneration. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):26. [44] AMANTEA D, MICIELI G, TASSORELLI C, et al. Rational modulation of the innate immune system for neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:147. [45] DABROWSKA S, ANDRZEJEWSKA A, STRZEMECKI D, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate neuroinflammation evoked by focal brain injury in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):216. [46] YOO SW, CHANG DY, LEE HS, et al. Immune following suppression mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the ischemic brain is mediated by TGF-beta. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;58:249-257. [47] 张桂芳,杨孟丽,常玉霞,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植在小鼠脑梗死中的作用机制及对大脑HMGB1水平的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(2):387-391. [48] RYU B, SEKINE H, HOMMA J, et al. Allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheet that produces neurological improvement with angiogenesis and neurogenesis in a rat stroke model. J Neurosurg. 2019;132(2):442-455. [49] MOON GJ, SUNG JH, KIM DH, et al. Application of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for stroke:biodistribution and microRNA study. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(5):509-521. [50] SHEIKH AM, YANO S, MITAKI S, et al. A Mesenchymal stem cell line (B10) increases angiogenesis in a rat MCAO model. Exp Neurol. 2019;311:182-193. [51] GUTIERREZ-FERNANDEZ M, RODRIGUEZ-FRUTOS B, RAMOS-CEJUDO J, et al. Effects of intravenous administration of allogenic bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells on functional recovery and brain repair markers in experimental ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(1):11. [52] XIE P, DENG M, SUN QG, et al. Therapeutic effect of transplantation of human bone marrowderived mesenchymal stem cells on neuron regeneration in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3065-3074. [53] ZHANG Q, ZHAO Y, XU Y, et al. Sodium ferulate and n-butylidenephthalate combined with bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) improve the therapeutic effects of angiogenesis and neurogenesis after rat focal cerebral ischemia. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):223. [54] CHAU MJ, DEVEAU TC, GU X, et al. Delayed and repeated intranasal delivery of bone marrow stromal cells increases regeneration and functional recovery after ischemic stroke in mice. BMC Neurosci. 2018;19(1):20. [55] 罗刘军,祝美珍,陈兰,等.基于“肾-脑髓-干细胞”轴探讨缺血性卒中及神经再生[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(3):104-107. [56] ZHAO Y, GAN Y, XU G, et al. Exosomes from MSCs overexpressing microRNA-223-3p attenuate cerebral ischemia through inhibiting microglial M1 polarization mediated inflammation. Life Sci. 2020,260:118403. [57] ZHENG B, von SEE MP, YU E, et al. Quantitative magnetic particle imaging monitors the transplantation, biodistribution, and clearance of stem cells in vivo. theranostics. 2016;6(3):291-301. [58] 钱楠楠,张潜,杨睿,等.间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤:细胞治疗及联合新药和生物材料[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13):2114-2120. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [4] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [5] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [6] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [7] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [8] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [9] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [10] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [11] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [12] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [13] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [14] | Tang Jiping, Zhang Yeting. Exercise regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanism and role [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 798-803. |
| [15] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||