Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 751-757.doi: 10.12307/2023.068
Previous Articles Next Articles
Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis
Li Long1, Li Guangdi1, 2, Shi Hao2, Deng Keqi2
- 1Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-03Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-02-18Published:2022-07-23 -
Contact:Li Guangdi, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Long, Master candidate, Physician, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Program), No. 82160432 (to LGD); Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Fund Project, No. gzwkj2021-244 (to LGD); the Basic Research Project of Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. ZK[2022]-427 (to LGD); the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Guizhou Medical University, No. 20NSP045 (to LGD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
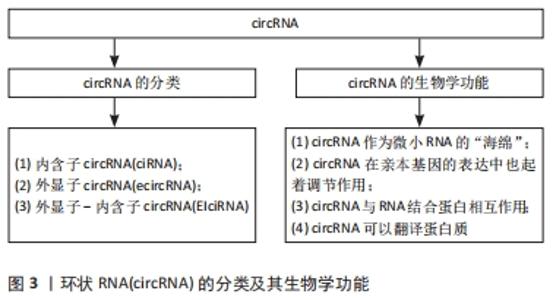
2.1 circRNA及其生物学功能 20世纪90年代,人们首次发现了circRNA,并将其视为外显子混乱的转录本[21]。circRNA起初被认为是RNA异常剪接或前体信使RNA(per-mRNA)剪接过程的无功能的副产物[22],所以当时并未被人们所关注。然而,随着近年来高通量测序技术的高速发展,证实了circRNA在真核细胞和组织中普遍存在,具有表达量大、稳定性高、序列高度保守、组织特异性强、在不同发育阶段特异性表达等特点[23]。由于circRNA缺乏5′末端帽子和 3′末端 poly(A)尾结构,其3端与5端通过紧密的共价键连接而形成闭环结构,并且对核糖核酸酶不敏感,使其区别于微小RNA、长链非编码RNA等线性RNA,具有更稳定、高度保守性以及组织特异性更强的特点[24]。circRNA主要由前体信使RNA通过套索驱动环化和内含子配对驱动环化产生[25-26],也存在RNA结合蛋白或某些反式因子驱动的环化和内含子自身环化形成[27-28]。根据外显子和内含子的基因组起源,circRNA可分为内含子circRNA(ciRNA)、外显子circRNA(ecircRNA)以及外显子-内含子circRNA(EIciRNA)[29],见图3。"
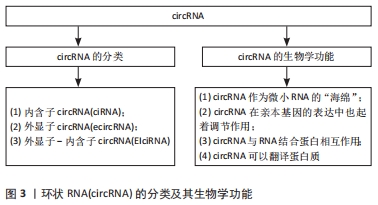
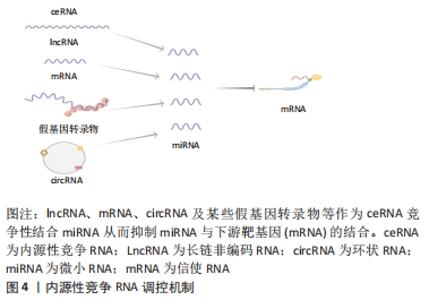
2.1.1 circRNA作为微小RNA的“海绵” 微小RNA是一类普遍存在的典型非编码RNA,其可转录后调控基因表达,主要是通过直接与信使RNA(mRNA)结合,然后影响亲本基因表达[30]。根据目前的研究发现circRNA上存在大量的微小RNA的结合位点(microRNA response element,MRE),这些结合位点起到微小RNA“海绵”的作用,circRNA通过MRE吸附微小RNA的3′端的非翻译区,使微小RNA减少其与下游靶基因的相互作用,从而进一步调控下游靶基因的表达[31]。 2.1.2 circRNA在亲本基因的表达中也起着调节作用 研究表明,一些外显子-内含子circRNA和内含子circRNA可与小核糖核蛋白U1和RNA聚合酶Ⅱ相互作用来促进亲本基因的转录。例如,Ci-ankrd52是细胞核中丰富的ciRNA,其可通过调节RNA聚合酶Ⅱ的转录活性在其亲本基因的表达水平上发挥调节作用[32],此外,一些外显子-内含子circRNA,如circ-EIF3J和circ-PAIP2,也可以调节基因表达[33]。 2.1.3 circRNA与RNA结合蛋白相互作用 RNA结合蛋白是一大类调节蛋白,可以特异性结合RNA,并与之相互作用,包括circRNA[34]。circRNA可以通过与调节信使RNA的RNA结合蛋白结合,进而改变信使RNA的剪接模式或影响信使RNA稳定性[35]。 2.1.4 circRNA可以翻译蛋白质 circRNA以前被认为是剪接错误的副产品,被认为是非功能性和不可翻译的。然而,许多的研究发现,circRNA可以被翻译,有少部分circRNA可被核糖体翻译并编码成多肽,进而行使调控功能[36]。 2.2 内源性竞争RNA调控机制 内源性竞争RNA调控机制是SALMENA等[37]于2011年首先提出的一种全新的基因表达调控模式,该机制指出,内源性竞争RNA并不是全新的RNA,而是一些RNA可以共同竞争性结合相同的微小RNA,通过调节微小RNA来调控基因的表达,这些RNA称为内源性竞争RNA。目前,发现了不同种类的内源性竞争RNA,包括lncRNA、mRNA、circRNA、某些假基因转录物等[38]。这些内源性竞争RNA上都含有微小RNA结合位点,具有相同的微小RNA结合位点的RNA转录本可以通过“海绵”作用竞争性结合微小RNA,抑制微小RNA与其靶点结合,从而调控其靶基因的表达水平,从而能够调控其所属细胞的相关增殖、凋亡和分化等,见图4。"
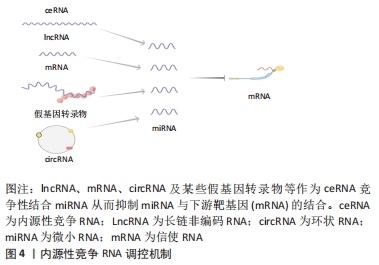
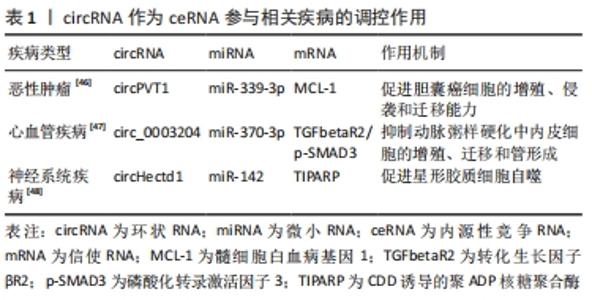
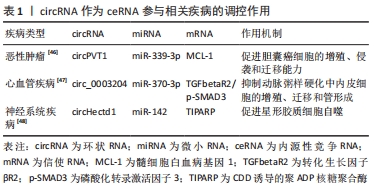
此外拥有同种微小RNA结合位点的两种RNA分子之间共享的miRNA类型越相似,他们之间的竞争关系就越强[39-40]。circRNA作为一种特殊的非编码RNA,现已成为内源性竞争RNA调控网络新的研究热点。 2.3 影响内源性竞争RNA活性的因素 最近一些研究发现,内源性竞争RNA的活性由一系列因素所决定,主要包括了微小RNA/内源性竞争RNA相对丰富度,RNA编辑,mRNA 3′端的非翻译区(3′UTR)以及RNA结合蛋白的变化[41]。MUKHERJI等[42]研究中发现当微小RNA和内源性竞争RNA的丰富度相近时,内源性竞争RNA的活性最佳。当总转录水平远远超过微小RNA水平时,内源性竞争RNA的作用显著降低,因为可用的微小RNA数量有限;相反,当微小RNA的数量远高于内源性竞争RNA的数量时,则不太可能发生相互作用,因为大多数转录物被完全抑制。 最近的研究表明,RNA编辑主要通过两种方式影响内源性竞争RNA活性。微小RNA编辑可能影响生物合成过程,从而影响RNA分子的稳定性,甚至改变其作用和靶点。此外,下游RNA分子编辑可能会消除或产生新的微小RNA结合位点[43]。研究发现,微小RNA主要作用于信使RNA的3′UTR后参与相互调节,因此信使RNA 3′UTR的改变也会影响内源性竞争RNA的活性[44]。RNA结合蛋白可以通过直接占据RNA靶点或通过改变RNA二级结构影响其对微小RNA的亲和力来影响内源性竞争RNA的相互作用[41]。此外,内源性竞争RNA的活性还取决于每个细胞中所含miRNA结合位点的数量和内源性竞争RNA的亚细胞定位[41,45]。组织疾病的发展和病理环境也会影响内源性竞争RNA的活性[41]。 2.4 circRNA作为内源性竞争RNA参与相关疾病的调控 许多研究发现,circRNA作为内源性竞争RNA参与许多疾病发病机制中的细胞信号通路,并调控相关疾病的发生发展如恶性肿瘤、心血管疾病、神经系统疾病等。WANG等[46]发现circPVT1在胆囊癌组织及细胞中的表达显著上调,过表达的circPVT1可通过“海绵”作用,作为内源性竞争RNA竞争性结合miR-339-3p来调节髓细胞白血病基因1(MCL-1)的表达,从而促进胆囊癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和迁移能力。研究报道,circ_0003204竞争性结合miR-370-3p,调控其下游靶基因转化生长因子βR2(TGFbetaR2)及磷酸化转录激活因子3(phosph-SMAD3)的表达,从而抑制暴露于氧化低密度脂蛋白(ox-LDL)的人主动脉内皮细胞(HAECs)增殖及迁移等能力[47]。 有研究发现,在短暂性大脑中动脉闭塞构造的小鼠卒中模型的脑组织及急性缺血性脑卒中患者的血浆中发现circHectd1的表达水平明显上调,并发现其可作为miR-142的内源性竞争RNA,抑制miR-142的活性,抑制其下游靶基因TCDD诱导的聚ADP核糖聚合酶(TIPARP)的表达,从而促进星形胶质细胞自噬[48]。由此可见circRNA作为内源性竞争RNA调控基因表达参与疾病的发生发展是非常普遍的,见表1。 "

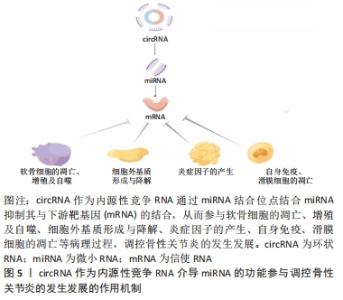
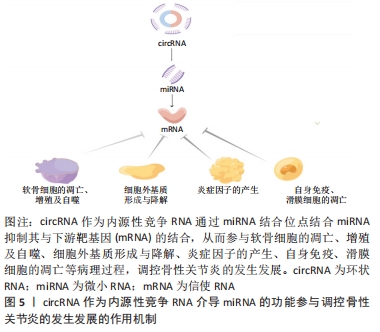
2.5.1 circRNA参与软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡与自噬 软骨细胞的凋亡、增殖和自噬在骨性关节炎的发病机制中起着关键作用。通过各种途径导致的软骨细胞凋亡,是骨性关节炎发病的重要机制。有研究报道,circCDH13(hsa_circ_0040646)有促凋亡和促代谢作用。在骨性关节炎软骨细胞和经白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α处理的人软骨细胞中检测到circCDH13表达上调,敲除circCDH13后基质金属蛋白酶13(MMP13)和软骨蛋白聚糖抗体(ADAMTS5)表达下调,并增加Ⅱ型胶原基因(COL2A1)和聚蛋白多糖(aggrecan)的表达,但所有这些效应都被circCDH13的过度表达所逆转,circCDH13可作为内源性竞争RNA竞争性结合miR-296-3p,起到“海绵”作用,减少其与下游靶基因的结合,人第10号染色体缺失的磷酸酶及张力蛋白同源的基因(PTEN)可直接被miR-296-3p靶向。PTEN对MMP13, ADAMTS5,aggrecan,和COL2A1的作用与circCDH13的作用一致,并加入miR-296-3p模拟物使其上调后这些效应则会被逆转。circCDH13的过度表达通过miR-296-3p/PTEN途径促进软骨细胞凋亡[49]。circ_0114876在骨性关节炎软骨细胞中表达上调,敲除软骨细胞中的circ_0114876可增加软骨细胞活力、抑制炎症反应以及软骨细胞凋亡,而circ_0114876可作为内源性竞争RNA靶向miR-671调节肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子2(TRAF2)的表达,从而促进软骨细胞凋亡[50]。LIU等[51]研究发现,hsa_circ_0134111可作为内源性竞争RNA与miR-224-5p结合,参与调节网络,通过竞争性结合miR-224-5p从而减少其对下游靶基因嗜酸粒细胞趋化蛋白1(CCL1)的促进作用,从而促进骨性关节炎患者软骨细胞的凋亡。OUYANG等[52]发现,circ_SPG11在骨性关节炎软骨和白细胞介素1β处理的软骨细胞中表达上调,敲除circ_SPG11可恢复软骨细胞的增殖,并减轻软骨细胞的凋亡和细胞外基质的降解,circ_SPG11可作为内源性竞争RNA结合miR-665,从而调控其下游靶基因人骨形态形成蛋白拮抗蛋白1(GREM1)的表达,从而促进白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞的凋亡。FU等[53]研究发现,circADAMTS6在人软骨细胞中过度表达可抑制人软骨细胞的凋亡促进软骨细胞的增殖,而miR-431-5p的过表达则可导致人软骨细胞的凋亡,circADAMTS6可作为内源性竞争RNA,竞争性结合miR-431-5p减少其在软骨细胞中的表达,通过circADAMTS6/miR-431-5p轴调节软骨细胞的增殖。ZHANG等[54]研究发现,circ_0005567调控软骨细胞自噬的作用是通过作为内源性竞争RNA竞争性结合miR-495降低其靶基因自噬相关蛋白14抗体(ATG14)的表达来实现的。因此,circ_0005567/miR-495/ATG14轴可能是调节骨性关节炎软骨细胞自噬的一个有希望的治疗靶点[54]。因此,软骨细胞凋亡、增殖和自噬机制的研究对于确定骨性关节炎软骨退变的发病机制及寻找早期治疗的潜在方法至关重要。 2.5.2 cicrRNA参与细胞外基质的形成与降解 细胞外基质主要由聚集蛋白聚糖、氨糖聚糖(GAG)、Ⅱ型胶原、纤维连接蛋白等组成,细胞外基质降解主要由基质降解酶的表达上调导致,包括基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)和去整合素和金属蛋白酶(ADAMTS)[55]。细胞外基质的降解是骨性关节炎发病机制的关键特征之一,目前circRNA作为内源性竞争RNA对细胞外基质作用的研究主要集中在促进或者抑制细胞外基质的形成。FENG等[56]的研究中发现,在白细胞介素1β处理的软骨细胞中,circ_0020093和SPRY1的表达下调,而miR-23b的表达上调。miR-23b是circ_002093作为内源性竞争RNA结合的靶点,SPRY1是miR-23b的下游靶点。有实验表明,circ_0020093通过靶向miR-23b调节SPRY1表达缓解了白细胞介素1β诱导的人软骨细胞凋亡和细胞外基质的降解[56]。WU等[57]发现,circPDE4D在骨性关节炎发生发展过程中在维持细胞外基质方面起着关键作用,其检测到circPDE4D在骨性关节炎软骨组织中表达显著下调,敲除后主要导致聚集蛋白聚糖减少以及一些基质分解代谢酶的增多,包括MMP3,MMP13,ADAMTS4和ADAMTS5等,但敲除circPDE4D后不会导致软骨细胞凋亡。其作用机制为可作为内源性竞争RNA,通过海绵作用结合miR-103a-3p,从而调节miR-103a-3p的直接靶点FGF-18的表达,从而促进细胞外基质的形成。然而,circRNA作为内源性竞争RNA也促进细胞外基质的降解,circRNF121在白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中表达上调,并且检测到上调了MMP13和ADAMTS5的表达水平,降低了聚集蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原的表达水平,表明了circRNF121的上调会诱导细胞外基质的降解,在分别转染了circRNF121和miR-665的软骨细胞中,髓样分化因子(MYD88)的表达分别上调及下调,circRNF121可作为内源性竞争RNA竞争性结合miR-665,调控其靶基因MYD88的表达,从诱导细胞外基质的降解[58]。因此,细胞外基质作为软骨细胞外重要成分对其形成与降解的机制研究十分重要。 2.5.3 circRNA参与炎症反应 骨性关节炎是一种炎症相关疾病,炎症因子的激活是骨性关节炎重要的发病机制之一,炎症因子的异常增加可导致细胞外基质的破坏和降解,并且能抑制软骨细胞的合成和修复,导致骨性关节炎患者病情加重,导致关节肿胀和疼痛等症状。重要的炎性细胞因子,包括白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α(肿瘤坏死因子α)、 白细胞介素6、白细胞介素15、白细胞介素17和白细胞介素18等。具有拮抗作用称为抗炎细胞因子,包括白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和白细胞介素13等[59]。circRNA作为内源性竞争RNA在骨性关节炎软骨细胞中起到促炎和抗炎的作用。CHEN等[60]发现,circRNA-UBE2G1及缺氧诱导因子1α在骨性关节炎组织中表达上调,并发现miR-373上含有circRNA-UBE2G1的结合点,并且miR-373可直接靶向缺氧诱导因子1α,circRNA-UBE2G1可作为内源性竞争RNA竞争性结合miR-373减少其对靶基因HIF1-α的抑制作用,circRNA-UBE2G1过表达可通过miR373/HIF-1a轴增加炎症因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的水平。研究发现,circ_0001103在骨性关节炎组织和白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中表达下调,并可作为内源性竞争RNA竞争性结合miR-375,SIRT1是miR-375的直接靶点,通过使在白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中circ_0001103过表达可以抑制miR-375表达下调并增加沉默调节蛋白1(SIRT1)的表达,减弱了白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞的炎症反应,因此,circ_0001103可调控miR-373/SIRT1轴减弱骨性关节炎软骨细胞的炎症反应[61]。对骨性关节炎中炎症因子的激活机制进行研究,有望为骨性关节炎寻找早期治疗靶点。 2.5.4 circRNA的其他调控作用 目前一些研究也发现,circRNA可通过参与滑膜细胞凋亡、自身免疫等病理过程影响骨性关节炎的进展。LIU等[62]研究发现骨性关节炎滑膜细胞中circCTNNA1表达降低与滑膜细胞凋亡相关,circCTNNA1可作为内源性竞争RNA竞争性结合miR-29a在脂多糖诱导的滑膜细胞发挥作用,实验表明,在脂多糖诱导的滑膜细胞中circCTNNA1表达下调而miR-29a表达上调,通过细胞凋亡分析circCTNNA1和miR-29a在滑膜细胞凋亡的作用,发现circCTNNA1抑制了miR-29a在骨性关节炎中的过度表达及其对骨性关节炎衍生滑膜细胞凋亡的促进作用。ZHANG等[63]研究发现,滑膜巨噬细胞极化对骨性关节炎的发展起着至关重要的作用,发现在骨性关节炎患者滑膜组织中hsa_circ_0005567表达水平下调。近年来,研究发现circRNA可参与滑膜细胞凋亡、自身免疫等病理过程,进一步了解骨性关节炎的发病机制,并对其早期诊断、治疗提供了可能的分子靶点。"

| [1] Barbour KE, Helmick CG, Boring M, et al. Vital signs: prevalence of doctor-diagnosed arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation - United States, 2013-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66(9):246-253. [2] Pereira D, Ramos E, Branco J. Osteoarthritis. Acta Med Port. 2015; 28(1):99-106. [3] Phillips RE. Review of hip and knee osteoarthritis. JAMA. 2021; 325(24):2504-2505. [4] Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707. [5] Vinatier C, Merceron C, Guicheux J. Osteoarthritis: from pathogenic mechanisms and recent clinical developments to novel prospective therapeutic options. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21(12):1932-1937. [6] Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387. [7] Pigeolet M, Jayaram A, Park KB, et al. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond. Lancet. 2021;397(10279):1059-1060. [8] Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759. [9] Zhou X, Jiang L, Fan G, et al. Role of the ciRS-7/miR-7 axis in the regulation of proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation of chondrocytes induced by IL-1β. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:233-240. [10] Carr AJ, Robertsson O, Graves S, et al. Knee replacement. Lancet. 2012;379(9823):1331-1340.. [11] Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495(7441): 333-338. [12] Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(5):453-461. [13] Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384-388. [14] Chen CY, Sarnow P. Initiation of protein synthesis by the eukaryotic translational apparatus on circular RNAs. Science. 1995;268(5209):415-417. [15] Granados-Riveron JT, Aquino-Jarquin G. The complexity of the translation ability of circRNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016; 1859(10):1245-1251. [16] Liu C, Ge HM, Liu BH, et al. Targeting pericyte-endothelial cell crosstalk by circular RNA-cPWWP2A inhibition aggravates diabetes-induced microvascular dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019; 116(15):7455-7464. [17] Aufiero S, Reckman YJ, Pinto YM, et al. Circular RNAs open a new chapter in cardiovascular biology. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019;16(8):503-514. [18] Chen L, Nan A, Zhang N et al. Circular RNA 100146 functions as an oncogene through direct binding to miR-361-3p and miR-615-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):13. [19] Liu Q, Zhang X, Hu X, et al. Circular RNA Related to the Chondrocyte ECM Regulates MMP13 Expression by Functioning as a MiR-136 ‘Sponge’ in Human Cartilage Degradation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22572. [20] Zhou ZB, Du D, Huang GX, et al. Circular RNA Atp9b, a competing endogenous RNA, regulates the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting miR-138-5p. Gene. 2018;646:203-209. [21] Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19(2):141-157. [22] Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, et al. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30733. [23] Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H, et al. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014; 15(7):409. [24] Shen T, Han M, Wei G, et al. An intriguing RNA species-perspectives of circularized RNA. Protein Cell. 2015;6(12):871-880. [25] Li X, Yang L, Chen LL. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 2018;71(3):428-442. [26] Wilusz JE. A 360° view of circular RNAs: from biogenesis to functions. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018;9(4):e1478. [27] Qu S, Yang X, Li X, et al. Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett. 2015;365(2):141-148. [28] Ehrlich GD. Circular RNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for osteoarthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2019;23(10):701-702. [29] Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(3):256-264. [30] Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215-233. [31] Li BF, Zhang Y, Xiao J, et al. Hsa_circ_0045714 regulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix synthesis by promoting the expression of miR-193b target gene IGF1R. Hum Cell. 2017;30(4):311-318. [32] Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, et al. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2013;51(6):792-806. [33] Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(3):256-264. [34] Zang J, Lu D, Xu A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: an important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(1):87-97. [35] Du WW, Zhang C, Yang W, et al. Identifying and Characterizing circRNA-Protein Interaction. Theranostics. 2017;7(17):4183-4191. [36] Wang Y, Wang Z. Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA. 2015;21(2):172-179. [37] Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, et al. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. 2011;146(3):353-358. [38] Guo LL, Song CH, Wang P, et al. Competing endogenous RNA networks and gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(41):11680-11687. [39] Gong Z, Yang Q, Zeng Z, et al. An integrative transcriptomic analysis reveals p53 regulated miRNA, mRNA, and lncRNA networks in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(3):3683-3695. [40] Yu J, Liu Y, Gong Z, et al. Overexpression long non-coding RNA LINC00673 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes invasion and metastasis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(10):16621-16632. [41] Cheng DL, Xiang YY, Ji LJ, et al. Competing endogenous RNA interplay in cancer: mechanism, methodology, and perspectives. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(2):479-488. [42] Mukherji S, Ebert MS, Zheng GX, et al. MicroRNAs can generate thresholds in target gene expression. Nat Genet. 2011;43(9):854-859. [43] Maas S. Posttranscriptional recoding by RNA editing. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2012;86:193-224. [44] Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature. 2014;505(7483):344-352. [45] Ala U, Karreth FA, Bosia C, et al. Integrated transcriptional and competitive endogenous RNA networks are cross-regulated in permissive molecular environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110(18):7154-7159. [46] Wang S, Su TT, Tong H, et al. CircPVT1 promotes gallbladder cancer growth by sponging miR-339-3p and regulates MCL-1 expression. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):191. [47] Zhang S, Song G, Yuan J, et al. Circular RNA circ_0003204 inhibits proliferation, migration and tube formation of endothelial cell in atherosclerosis via miR-370-3p/TGFβR2/phosph-SMAD3 axis. J Biomed Sci. 2020;27(1):11. [48] Han B, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Novel insight into circular RNA HECTD1 in astrocyte activation via autophagy by targeting MIR142-TIPARP: implications for cerebral ischemic stroke. Autophagy. 2018; 14(7):1164-1184. [49] Zhou Z, Ma J, Lu J, et al. Circular RNA CircCDH13 contributes to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis via CircCDH13/miR-296-3p/PTEN axis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(5):3521-3535. [50] Wang Q, Luo S, Yang J, et al. Circ_0114876 promoted IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury by targeting miR-671/TRAF2 axis. Biotechnol Lett. 2021;43(4):791-802. [51] Liu Y, Zhang Y. Hsa_circ_0134111 promotes osteoarthritis progression by regulating miR-224-5p/CCL1 interaction. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(16):20383-20394. [52] Ouyang X, Ding Y, Yu L, et al. Circ_SPG11 plays contributing effects on IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and ECM degradation via miR-665 inhibition-mediated GREM1 upregulation. Clin Immunol. 2021;233:108889. [53] Fu Q, Li L, Wang B, et al. CircADAMTS6/miR-431-5p axis regulate interleukin-1β induced chondrocyte apoptosis. J Gene Med. 2021; 23(2):e3304. [54] Zhang J, Cheng F, Rong G, et al. Hsa_circ_0005567 Activates Autophagy and Suppresses IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Apoptosis by Regulating miR-495. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:216. [55] Mouw JK, Ou G, Weaver VM. Extracellular matrix assembly: a multiscale deconstruction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):771-785. [56] Feng M, Jing L, Cheng J, et al. Circ_0020093 ameliorates IL-1β-induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of human chondrocytes by upregulating SPRY1 via targeting miR-23b. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(10):3623-3633. [57] Wu Y, Hong Z, Xu W, et al. Circular RNA circPDE4D Protects against Osteoarthritis by Binding to miR-103a-3p and Regulating FGF18. Mol Ther. 2021;29(1):308-323. [58] Wang T, Hao Z, Liu C, et al. LEF1 mediates osteoarthritis progression through circRNF121/miR-665/MYD88 axis via NF-кB signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(8):689. [59] Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski ŁA, Szukiewicz D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:561459. [60] Chen G, Liu T, Yu B, et al. CircRNA-UBE2G1 regulates LPS-induced osteoarthritis through miR-373/HIF-1a axis. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(13): 1696-1705. [61] Zhang M, Mou L, Liu S, et al. Circ_0001103 alleviates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte cell injuries by upregulating SIRT1 via targeting miR-375. Clin Immunol. 2021;227:108718. [62] Liu W, Yang H, Feng X, et al. Circular RNA circCTNNA1 is downregulated in osteoarthritis and sponges miR-29a to suppress LPS-induced apoptosis of synoviocytes. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(1):1-6. [63] Zhang J, Cheng F, Rong G, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0005567 overexpression promotes M2 type macrophage polarization through miR-492/SOCS2 axis to inhibit osteoarthritis progression. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):8920-8930. [64] Zhang W, Qi L, Chen R, et al. Circular RNAs in osteoarthritis: indispensable regulators and novel strategies in clinical implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):23. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [4] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [5] | Wu Yujie, Wan Xiaofang, Wei Mianxing, Peng Shiyuan, Xu Xiaomei. Correlation between autophagy and the Hippo-YAP protein pathway in periodental ligament cells on the pressure side of a mouse model of orthodontic tooth movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 683-689. |
| [6] | Zhao Siqi, Du Juan, Qu Haifeng, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Effects of enriched environment combined with melatonin on learning and memory function and brain neuron apoptosis in SAMP8 mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 701-706. |
| [7] | Zhang Qing, Gao Chunlan, Yu Feifei, Zhang Zhenghao, Ma Fang, Gao Yuan, Li Guizhong, Jiang Yideng, Ma Shengchao. Ephrin A receptor 2 DNA methylation increases in pancreatic beta cell apoptosis induced by homocysteine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 714-719. |
| [8] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [9] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [10] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [11] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [12] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [13] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [14] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [15] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||