Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (14): 2180-2185.doi: 10.12307/2024.296
Previous Articles Next Articles
Melatonin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced injury of human nucleus pulposus cells
Xie Wenguan, Liu Yutao, Cui Wenbo, Kuang Mingye
- Department of Orthopedics, Dongguan Eighth People’s Hospital, Dongguan Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523320, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-04-04Accepted:2023-05-08Online:2024-05-18Published:2023-07-28 -
Contact:Kuang Mingye, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Dongguan Eighth People’s Hospital, Dongguan Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523320, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Xie Wenguan, Master, Department of Orthopedics, Dongguan Eighth People’s Hospital, Dongguan Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523320, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Dongguan City Social Science and Technology Development Project, No. 202050715028791 (to KMY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Wenguan, Liu Yutao, Cui Wenbo, Kuang Mingye. Melatonin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced injury of human nucleus pulposus cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2180-2185.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
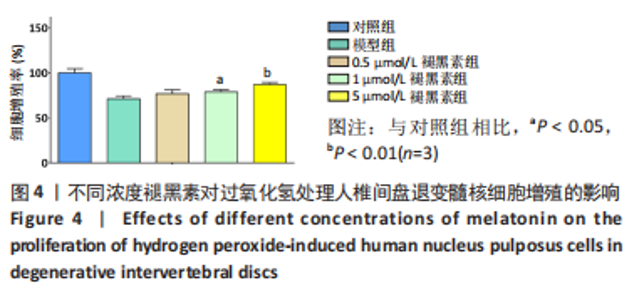
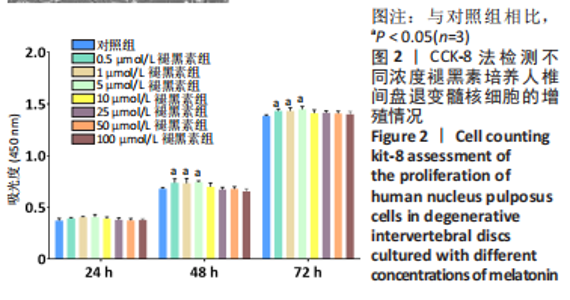
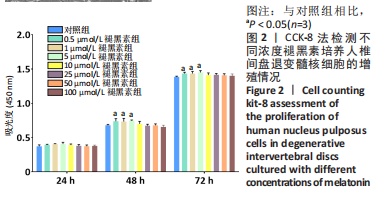
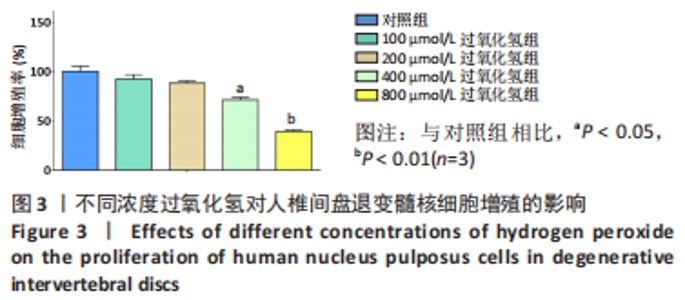
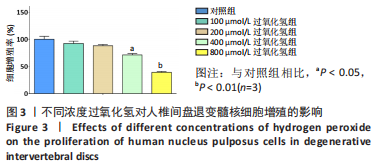
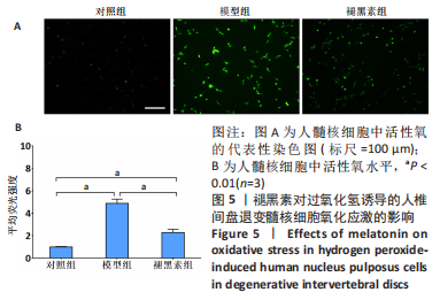
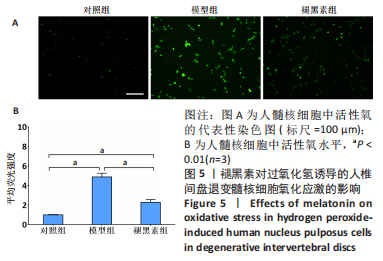
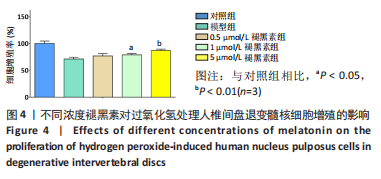
2.4 不同浓度褪黑素对过氧化氢处理人髓核细胞增殖的影响 图4为经过氧化氢处理的人髓核细胞在不同浓度褪黑素干预下的增殖情况,结果表明,在褪黑素干预24 h后,人髓核细胞的抗氧化作用表现出不同程度提升,且呈浓度依赖性。当过氧化氢干预浓度为400 μmol/L时,单纯模型组的人髓核细胞存活率为(71.00±3.37)%,而当褪黑素干预浓度为1 μmol/L时,人髓核细胞存活率则为(78.84±2.59)%,差异有显著性意义(P=0.020 < 0.05)。当褪黑素干预浓度为5 μmol/L时,人髓核细胞存活率则为(86.93±2.48)%,差异有非常显著性意义(P=0.000 < 0.01),说明褪黑素能减轻过氧化氢对人髓核细胞的氧化作用,增强对人髓核细胞的保护作用,最佳抗氧化浓度为5 μmol/L。"
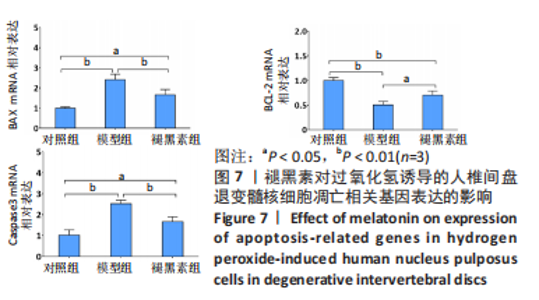
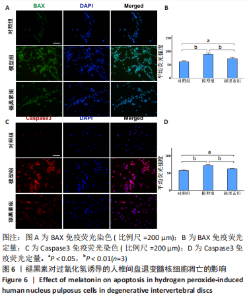
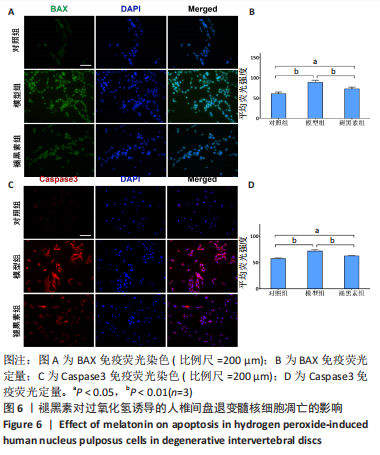
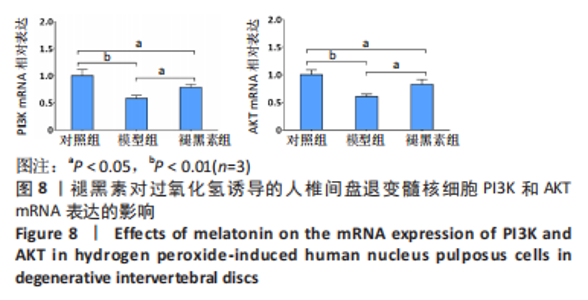
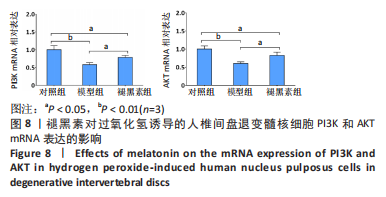
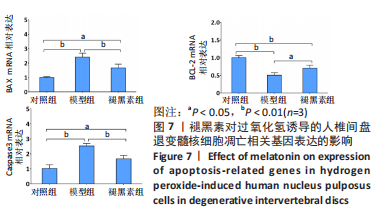
2.7 褪黑素抑制Bax、caspase3基因的表达,促进Bcl-2基因的表达 Bax、caspase3基因的高表达可以促进细胞凋亡。如图7所示,模型组人髓核细胞中Bax和Caspase3的mRNA表达水平均显著高于对照组(P=0.000,0.000 < 0.01),Bcl-2的mRNA表达水平显著低于对照组(P=0.000 < 0.01)。与模型组相比,褪黑素组Bax和Caspase3的mRNA表达水平显著降低(P=0.006,0.003 < 0.01)。此外,与模型组相比,褪黑素组Bcl-2的mRNA表达水平升高(P=0.015 < 0.05)。因此,褪黑素可以抑制过氧化氢诱导的人髓核细胞凋亡。"
| [1] MADIGAN L, VACCARO AR, SPECTOR LR, et al. Management of symptomatic lumbar degenerative disk disease. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17(2):102-111. [2] SUN K, JIANG J, WANG Y, et al. The role of nerve fibers and their neurotransmitters in regulating intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;81:101733. [3] ZEHRA U, TRYFONIDOU M, IATRIDIS JC, et al. Mechanisms and clinical implications of intervertebral disc calcification. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022; 18(6):352-362. [4] LYU FJ, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7. [5] LI Z, LI X, CHEN C, et al. Melatonin inhibits nucleus pulposus (NP) cell proliferation and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling via the melatonin membrane receptors mediated PI3K-Akt pathway. J Pineal Res. 2017;63(3). doi: 10.1111/jpi.12435. [6] CHENG Z, XIANG Q, WANG J, et al. The potential role of melatonin in retarding intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: A systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;70:101394. [7] BUONFIGLIO D, HUMMER DL, ARMSTRONG A, et al. Angelman syndrome and melatonin: What can they teach us about sleep regulation. J Pineal Res. 2020;69(4):e12697. [8] CIPOLLA-NETO J, AMARAL FGD. Melatonin as a Hormone: New Physiological and Clinical Insights. Endocr Rev. 2018;39(6):990-1028. [9] CHRUSTEK A, OLSZEWSKA-SŁONINA D. Melatonin as a powerful antioxidant. Acta Pharm. 2020;71(3):335-354. [10] GE J, ZHOU Q, NIU J, et al. Melatonin Protects Intervertebral Disc from Degeneration by Improving Cell Survival and Function via Activation of the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5120275. [11] BOGA JA, CABALLERO B, POTES Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of melatonin related to its role as an autophagy regulator: A review. J Pineal Res. 2019; 66(1):e12534. [12] MAJIDINIA M, REITER RJ, SHAKOURI SK, et al. The role of melatonin, a multitasking molecule, in retarding the processes of ageing. Ageing Res Rev. 2018;47:198-213. [13] ZHAO L, HU C, ZHANG P, et al. Melatonin preconditioning is an effective strategy for mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for kidney disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1):25-33. [14] YAN R, DING J, WEI Y, et al. Melatonin Prevents NaAsO2-Induced Developmental Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish through Regulating Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(7):1301. [15] HWANG SJ, JUNG Y, SONG YS, et al. Enhanced anti-angiogenic activity of novel melatonin-like agents. J Pineal Res. 2021;71(1):e12739. [16] TURGUT M, BAŞALOĞLU HK, YENISEY C, et al. Surgical pinealectomy accelerates intervertebral disc degeneration process in chicken. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(5):605-612. [17] HE R, CUI M, LIN H, et al. Melatonin resists oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 2018;199:122-130. [18] XIE L, ZHAO Z, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin Alleviates Radiculopathy Against Apoptosis and NLRP3 Inflammasomes Via the Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(16):E859-E868. [19] GAO Z, LIN Y, ZHANG P, et al. Sinomenine ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy in vitro and in vivo. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9):5956-5966. [20] LIU L, CAO JX, SUN B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibition of chronic ethanol-induced oxidative damage via upregulation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt and modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation in PC12 cells and neurons. Neuroscience. 2010;167(4): 1115-1124. [21] LUO C, YANG Q, LIU Y, et al. The multiple protective roles and molecular mechanisms of melatonin and its precursor N-acetylserotonin in targeting brain injury and liver damage and in maintaining bone health. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;130:215-233. [22] HARTVIGSEN J, HANCOCK MJ, KONGSTED A, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2356-2367. [23] XIN J, WANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(7):1271-1280. [24] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110660. [25] YANG RZ, XU WN, ZHENG HL, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced annulus fibrosus cell and nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(4):2725-2739. [26] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al. Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: The antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978. [27] CHEUNG KM, KARPPINEN J, CHAN D, et al. Prevalence and pattern of lumbar magnetic resonance imaging changes in a population study of one thousand forty-three individuals. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(9):934-940. [28] TORDJMAN S, CHOKRON S, DELORME R, et al. Melatonin: Pharmacology, Functions and Therapeutic Benefits. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(3): 434-443. [29] LOW TL, CHOO FN, TAN SM. The efficacy of melatonin and melatonin agonists in insomnia - An umbrella review. J Psychiatr Res. 2020;121:10-23. [30] MARKOWSKA M, NIEMCZYK S, ROMEJKO K. Melatonin Treatment in Kidney Diseases. Cells. 2023;12(6):838. [31] SAMANTA S. Physiological and pharmacological perspectives of melatonin. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(5):1346-1367. [32] LI J, WANG C, XUE L, et al. Melatonin Suppresses Apoptosis of Nucleus Pulposus Cells through Inhibiting Autophagy via the PI3K/Akt Pathway in a High-Glucose Culture. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:4604258. [33] CHEN Y, WU Y, SHI H, et al. Melatonin ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via the potential mechanisms of mitophagy induction and apoptosis inhibition. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(3):2136-2148. [34] ZHANG Z, LIN J, TIAN N, et al. Melatonin protects vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and calcification via the Sirt1-autophagy pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(1):177-193. [35] TAN DX, MANCHESTER LC, ESTEBAN-ZUBERO E, et al. Melatonin as a Potent and Inducible Endogenous Antioxidant: Synthesis and Metabolism. Molecules. 2015;20(10):18886-18906. [36] COYOY-SALGADO A, SEGURA-URIBE JJ, GUERRA-ARAIZA C, et al. The Importance of Natural Antioxidants in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury in Animal Models: An Overview. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:3642491. [37] DADSENA S, KING LE, GARCÍA-SÁEZ AJ. Apoptosis regulation at the mitochondria membrane level. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021; 1863(12):183716. [38] ROBERTS JZ, CRAWFORD N, LONGLEY DB. The role of Ubiquitination in Apoptosis and Necroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(2):272-284. [39] OUYANG ZH, WANG WJ, YAN YG, et al. The PI3K/Akt pathway: a critical player in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oncotarget. 2017;8(34):57870-57881. [40] WANG W, LI P, XU J, et al. Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and senescence through activating the ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(2):BSR20171454. [41] SUN K, WANG X, ZHANG X, et al. The antagonistic effect of melatonin on TBBPA-induced apoptosis and necroptosis via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in swine testis cells. Environ Toxicol. 2022;37(9):2281-2290. [42] GU H, LI J, ZHANG R. Melatonin upregulates DNA-PKcs to suppress apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via inhibiting miR-101 under H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(2):1283-1292. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [3] | Wan Lingling, Wu Mengying, Zhang Yujiao, Luo Qingqing. Inflammatory factor interferon-gamma affects migration and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells through pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [4] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [5] | Liu Zhezhe, Yu Meiqing, Wang Tingting, Zhang Min, Li Baiyan. Troxerutin modulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway to inhibit brain injury and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1137-1143. |
| [6] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [7] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [8] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [9] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [10] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [11] | Ding Zhili, Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Liu Jiang, Ding Yu. Constructing rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration models by different methods under X-ray guidance: a comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 995-1002. |
| [12] | Xu Fei, Yan Jinqiang, Chai Shoudong. Mechanical stress regulates apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1064-1072. |
| [13] | Gao Xilin, Wu Si Zhang Chao Zhu Liguo, Fu Bifeng, Wang Ping. Mechanotransduction proteins in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 579-589. |
| [14] | Wu Ao, Yu Peng, Teng Jiawen, Kong Peng, Bian Sishan. Analysis of oxidative stress-related genes and immune infiltration in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 302-311. |
| [15] | Liu Zhongyuan, Li Yang, Zhang Zhiwen . Mechanism by which KRT18 interacts with mRNA and long non-coding RNA to regulate intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cell injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 312-321. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||