Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 380-386.doi: 10.12307/2023.883
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration
Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie
- Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical College, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-04Accepted:2022-12-09Online:2024-01-28Published:2023-07-10 -
Contact:Xu Kun, Master, Associate chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical College, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Cao Sheng, Master, Attending physician, Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical College, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Medical Science Research of Hebei Provincial Health Commission, No. 20200386 (to CS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 380-386.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

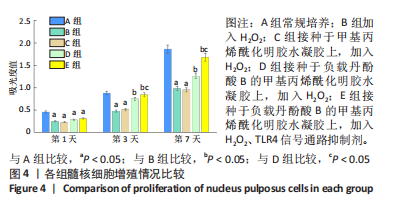
2.4 体外细胞实验结果 2.4.1 各组细胞增殖实验 CCK-8检测结果显示,5组细胞随着培养时间的增加持续增殖,见图4。培养第1天时,与A组比较,B组细胞增殖吸光度值显著降低(P < 0.05);与B组比较,C、D、E组细胞增殖吸光度值无明显变化(P > 0.05)。培养第3天时,与A组比较,B组细胞增殖吸光度值显著降低(P < 0.05);与B组比较,C组细胞增殖吸光度值无明显变化(P > 0.05),D组细胞增殖吸光度值显著升高(P < 0.05);与D组比较,E组细胞增殖吸光度值显著升高(P < 0.05)。培养第7天时,与A组比较,B组细胞增殖吸光度值显著降低(P < 0.05);与B组比较,C组细胞增殖吸光度值无明显变化(P > 0.05),D组细胞增殖吸光度值显著升高(P < 0.05);与D组比较,E组细胞增殖吸光度值显著升高(P < 0.05)。"

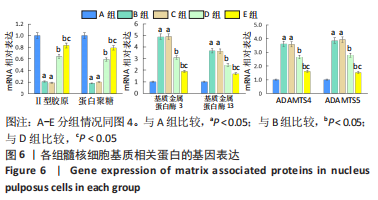
与A组比较,B组Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白聚糖的mRNA表达量明显减少(P < 0.05),基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS4、ADAMTS5的mRNA表达量明显增加(P < 0.05)。与B组比较,C组各基因的mRNA表达量无显著变化(P > 0.05),D、E组Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白聚糖的mRNA表达量明显增加(P < 0.05),基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS4、ADAMTS5的mRNA表达量明显减少(P < 0.05)。与D组比较,E组Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白聚糖的mRNA表达量明显增加(P < 0.05),基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS4、ADAMTS5的mRNA表达量明显减少(P < 0.05)。 2.4.5 Western blot检测各组细胞TLR4/核因子κB 信号通路蛋白的表达 见图7。"
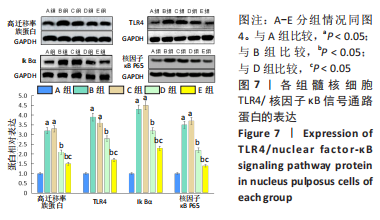

与A组比较,B组高迁移率族蛋白、TLR4、Ik Bα和核因子κB P65的蛋白表达量明显增加(P < 0.05)。与B组比较,C组高迁移率族蛋白、TLR4、Ik Bα和核因子κB P65的蛋白表达量无显著变化(P > 0.05),D、E组高迁移率族蛋白、TLR4、Ik Bα和核因子κB P65的蛋白表达量明显减少(P < 0.05)。与D组比较,E组高迁移率族蛋白、TLR4、Ik Bα和核因子κB P65的蛋白表达量明显减少(P < 0.05)。 2.5 动物体内实验结果 2.5.1 各组大鼠椎间盘X射线片检测 见图8A、B。 术后0周时,针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组椎间盘高度指数均低于正常组(P < 0.05);针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组椎间盘高度指数比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。术后4周时,针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组椎间盘高度指数均低于正常组(P < 0.05);与针刺组比较,针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组椎间盘高度指数升高(P < 0.05);与针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组比较,针刺+载药水凝胶组椎间盘高度指数升高(P < 0.05)。 2.5.2 各组大鼠椎间盘MRI检查 见图8C、D。 术后0周时,针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组MRI指数均低于正常组(P < 0.05);针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组MRI指数比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。术后4周时,针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组MRI指数均低于正常组(P < 0.05);与针刺组比较,针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组MRI指数升高(P < 0.05);与针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组比较,针刺+载药水凝胶组MRI指数升高(P < 0.05)。"


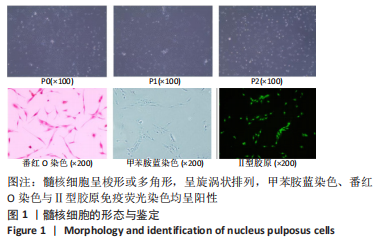
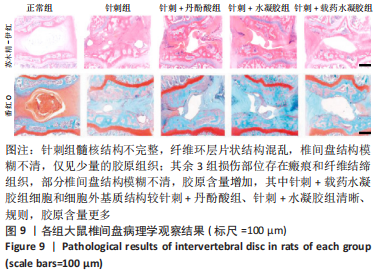
苏木精-伊红染色显示,正常组中细胞和细胞外基质组织良好;针刺组髓核结构不完整,纤维环层片状结构混乱,退变位点被纤维软骨组织和不同细胞形态的细胞所占据,损伤部位存在大量的瘢痕与纤维结缔组织,椎间盘结构模糊不清;其余3组损伤部位存在瘢痕和纤维结缔组织,部分椎间盘结构模糊不清,其中针刺+载药水凝胶组细胞和细胞外基质结构较针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组清晰、规则。番红O染色显示,正常组可见完整的髓核组织,含有丰富的胶原组织;针刺组髓核结构不完整,仅见少量的胶原组织;其余3组髓核组织结构破坏程度均轻于针刺组,胶原含量增加,其中以针刺+载药水凝胶组髓核组织结构更细清晰、规则且胶原含量最多。 椎间盘组织学评分结果显示,正常组、针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组目标椎间盘组织学评分依次为4.39±0.12,13.09±0.13,9.38±0.12,10.54±0.18,7.03±0.22。针刺组、针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组评分高于正常组(P < 0.05),针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组、针刺+载药水凝胶组评分低于针刺组(P < 0.05),针刺+载药水凝胶组评分低于针刺+丹酚酸组、针刺+水凝胶组(P < 0.05)。 2.6 水凝胶的生物相容性 由体外细胞实验与动物体内实验可知,负载丹酚酸B的甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性。"

| [1] DESMOULIN GT, PRADHAN V, MILNER TE. Mechanical Aspects of Intervertebral Disc Injury and Implications on Biomechanics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(8): E457-E464. [2] KAMALI A, ZIADLOU R, LANG G, et al. Small molecule-based treatment approaches for intervertebral disc degeneration: Current options and future directions. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):27-47. [3] KOS N, GRADISNIK L, VELNAR T. A Brief Review of the Degenerative Intervertebral Disc Disease. Med Arch. 2019;73(6):421-424. [4] ZHANG Y, HAN S, KONG M, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis identifies unique chondrocyte subsets and reveals involvement of ferroptosis in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(9):1324-1334. [5] CAZZANELLI P, WUERTZ-KOZAK K. MicroRNAs in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Mechanobiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3601. [6] WU PH, KIM HS, JANG IT. Intervertebral Disc Diseases PART 2: A Review of the Current Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies for Intervertebral Disc Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2135. [7] DU J, XU M, KONG F, et al. CB2R Attenuates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Delaying Nucleus Pulposus Cell Senescence through AMPK/GSK3β Pathway. Aging Dis. 2022;13(2):552-567. [8] LIANG W, HAN B, HAI Y, et al. Mechanism of Action of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in the Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Treatment and Bone Repair and Regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:833840. [9] SABERI M, ZHANG X, MOBASHERI A. Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction with small molecules in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Geroscience. 2021;43(2):517-537. [10] HWANG PY, CHEN J, JING L, et al. The role of extracellular matrix elasticity and composition in regulating the nucleus pulposus cell phenotype in the intervertebral disc: a narrative review. J Biomech Eng. 2014;136(2):021010. [11] 胡琳,叶巧玲,庄和思,等.丹酚酸B对糖尿病肾病db/db小鼠肾纤维化及炎症的影响[J].中草药,2022,53(4):1084-1092. [12] 张一凡,韩向晖,刘萍.丹酚酸B通过抑制MAPKs/NF-κB信号通路减轻动脉粥样硬化模型小鼠肝脏炎症反应[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(4):525-530. [13] 李君,王倩青,郜智慧,等.丹酚酸B抑制AKT的磷酸化诱导子宫内膜癌MFE-280细胞自噬性死亡和细胞衰老[J].中国免疫学杂志,2022,38(6):671-675. [14] SHI M, ZHAO Y, SUN Y, et al. Therapeutic effect of co-culture of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and degenerated nucleus pulposus cells on intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2021;21(9):1567-1579. [15] LIU Y. Hydrogen peroxide induces nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(4):3244-3252. [16] 张贺星,张明,张奕.软骨终板干细胞源性外泌体对椎间盘退变的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(13):1198-1203 [17] FAN Y, YI J, ZHANG Y, et al. Fabrication of curcumin-loaded bovine serum albumin (BSA)-dextran nanoparticles and the cellular antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2018;239:1210-1218. [18] TAVAKOLI S, KLAR AS. Advanced Hydrogels as Wound Dressings. Biomolecules. 2020;10(8):1169. [19] BERNHARD S, TIBBITT MW. Supramolecular engineering of hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;171:240-256. [20] JERVIS PJ, AMORIM C, PEREIRA T, et al. Dehydropeptide Supramolecular Hydrogels and Nanostructures as Potential Peptidomimetic Biomedical Materials. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2528. [21] 刘翔宇,王照东,徐陈,等.载外源性TGF-β1甲基丙烯酰化明胶复合支架促进颅骨缺损修复实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(7):904-912. [22] JIANG G, LI S, YU K, et al. A 3D-printed PRP-GelMA hydrogel promotes osteochondral regeneration through M2 macrophage polarization in a rabbit model. Acta Biomater. 2021;128:150-162. [23] TANG Z, HU B, ZANG F, et al. Nrf2 drives oxidative stress-induced autophagy in nucleus pulposus cells via a Keap1/Nrf2/p62 feedback loop to protect intervertebral disc from degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(7):510. [24] ZHANG X, HUANG Z, XIE Z, et al. Homocysteine induces oxidative stress and ferroptosis of nucleus pulposus via enhancing methylation of GPX4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:552-565. [25] CHE H, LI J, LI Y, et al. p16 deficiency attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration by adjusting oxidative stress and nucleus pulposus cell cycle. Elife. 2020;9:e52570. [26] YANG RZ, XU WN, ZHENG HL, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced annulus fibrosus cell and nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(4):2725-2739. [27] ROSA AC, BRUNI N, MEINERI G, et al. Strategies to expand the therapeutic potential of superoxide dismutase by exploiting delivery approaches. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;168:846-865. [28] MIAO L, ST CLAIR DK. Regulation of superoxide dismutase genes: implications in disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009;47(4):344-356. [29] CALDIROLI A, AUXILIA AM, CAPUZZI E, et al. Malondialdehyde and bipolar disorder: A short comprehensive review of available literature. J Affect Disord. 2020;274:31-37. [30] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110660. [31] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):47-60. [32] FORMAN HJ, ZHANG H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(9):689-709. [33] XIE X, DENG T, DUAN J, et al. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;190:110133. [34] REHMAN SU, ALI T, ALAM SI, et al. Ferulic Acid Rescues LPS-Induced Neurotoxicity via Modulation of the TLR4 Receptor in the Mouse Hippocampus. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(4):2774-2790. |
| [1] | Dai Jing, Liu Shasha, Shen Mingjing. Exosome-loaded injectable hydrogel for repairing bone defects around implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
| [2] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [3] | Chen Pinrui, Pei Xibo, Xue Yiyuan. Function and advantages of magnetically responsive hydrogel in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [4] | Long Zhirui, Huang Lei, Xiao Fang, Wang Lin, Wang Xiaobei. Characteristics of hydrogel microspheres in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| [5] | Xu Jing, Lyu Huixin, Bao Xin, Zhang Yi, Wang Yihan, Zhou Yanmin. Application of near infrared responsive hydrogels in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 486-492. |
| [6] | Zhou Shuliang, Xu Liang, Qian Xuefeng, Zeng Jincai, Zhu Lifan. Correlation between the expression of miRNA-142-3p, mixed lineage kinase 3 and interleukin-1beta in nucleus pulposus and the degree of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 165-171. |
| [7] | Sun Yuan, Wang Qingbo, Pi Yihua, Lu Chunmin, Xu Chuanyi, Zhang Yan. Effects of early and late aerobic exercise on right heart failure induced by monocrotaline in rats with pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 177-185. |
| [8] | Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230. |
| [9] | Chen Simin, Hu Yingjun, Yan Wenrui, Ji Le, Shao Mengli, Sun Ze, Zheng Hongxing, Qi Shanshan. Establishment and evaluation of a streptozotocin-induced diabetic encephalopathy rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 237-241. |
| [10] | Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Liu Tao, Li Yan, He Yuanxu, He Bo, Wang Weiwei, Wei Xiaotao. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in the prevention and treatment of flap necrosis by regulating “autophagy” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 153-158. |
| [11] | Cheng Haotian, Zhao Xiaofeng, Lu Xiangdong, Zhao Yibo, Fan Zhifeng, Qi Detai, Wang Xiaonan, Zhou Runtian, Jin Xinjie, Zhao Bin. Single-cell RNA sequencing and the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 93-99. |
| [12] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [13] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [14] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [15] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||