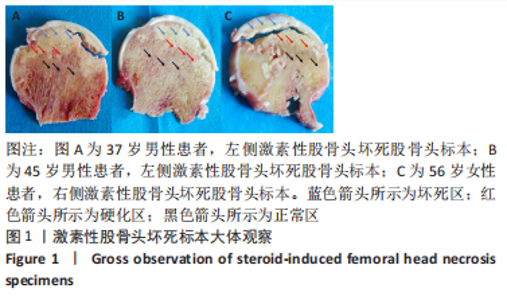
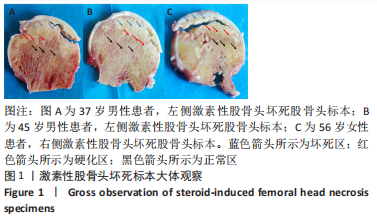
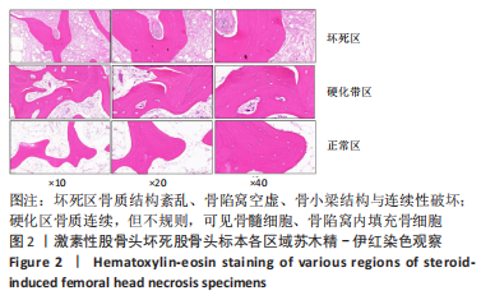
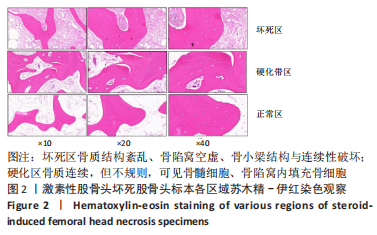
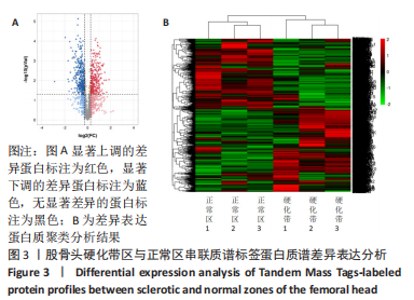
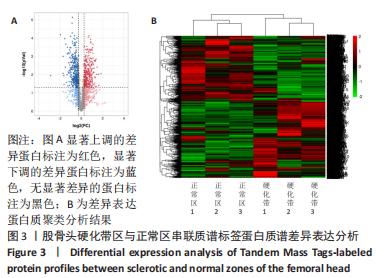
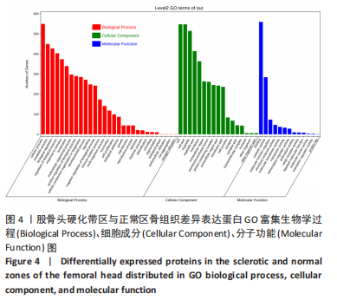
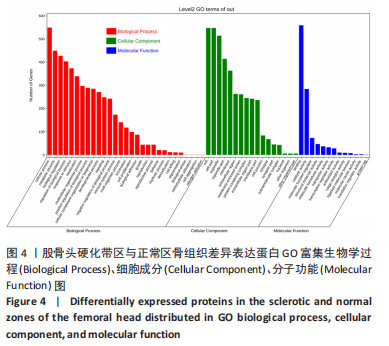
[1] MONT MA, SALEM HS, PIUZZI NS, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today?: A 5-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(12):1084-1099.
[2] LIN T, CHEN W, YANG P, et al. Bioinformatics analysis and identification of genes and molecular pathways in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):327.
[3] 魏秋实,何伟,张庆文,等. 岭南袁氏中医药防治股骨头坏死传承文化研究[J]. 新中医,2022,54(23):216-220.
[4] 何伟,刘予豪,周驰,等. 非手术保髋治疗非创伤性股骨头坏死的临床研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2020,40(2):176-181.
[5] CHEN WH, GUO WX, LI JX, et al. Application of protective weight-bearing in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. Front Surg. 2022;9: 1000073.
[6] CHEN W, LI J, GUO W, et al. Outcomes of surgical hip dislocation combined with bone graft for adolescents and younger adults with osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a case series and literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):499.
[7] 魏秋实,何晓铭,何伟,等. 非手术保髋治疗ARCO Ⅱ期股骨头坏死的临床疗效及影响因素分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022,15(6):424-430.
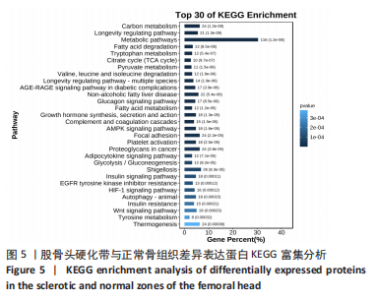
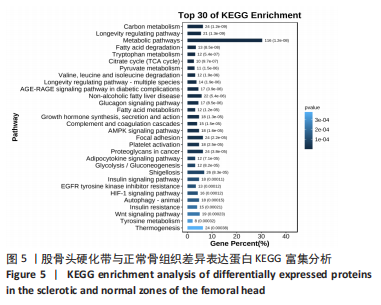
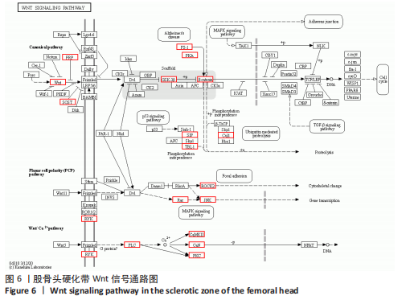
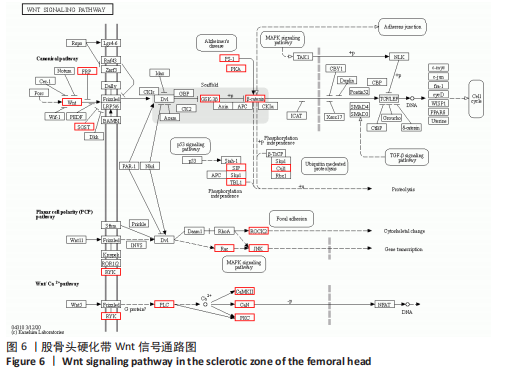
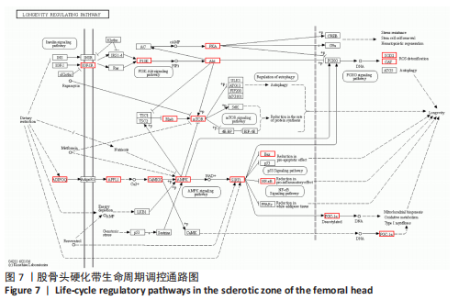
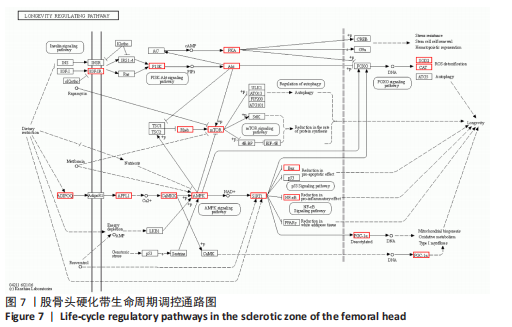
[8] 石少辉. 股骨头坏死硬化带的观察[D]. 北京:中国协和医科大学,2009.
[9] 陈玥,刘敏,铁位有. 基于CT影像的形态学对双侧股骨头坏死塌陷的危险因素分析[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2020,18(7):158-161.
[10] 牟永莹,顾培明,马博,等.基于质谱的定量蛋白质组学技术发展现状[J].生物技术通报,2017,33(9):73-84.
[11] PAGEL O, KOLLIPARA L, SICKMANN A. Quantitative Proteome Data Analysis of Tandem Mass Tags Labeled Samples. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2228:409-417.
[12] PAPPIREDDI N, MARTIN L, WÜHR M. A Review on Quantitative Multiplexed Proteomics. Chembiochem. 2019;20(10):1210-1224.
[13] YOON BH, MONT MA, KOO KH, et al. The 2019 Revised Version of Association Research Circulation Osseous Staging System of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(4):933-940.
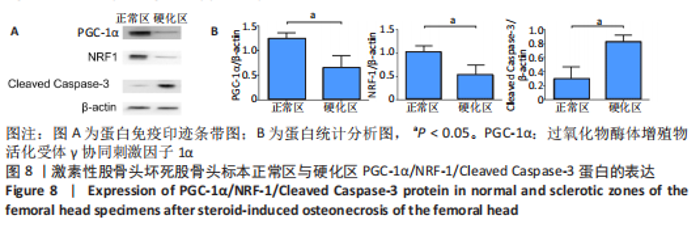
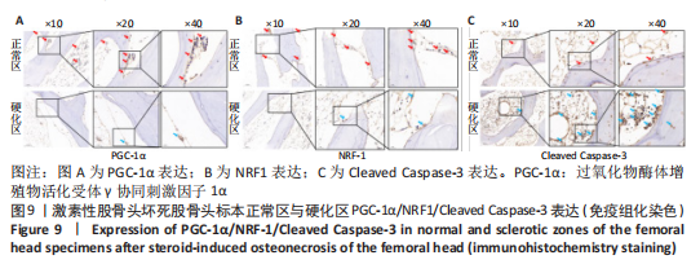
[14] 王慧婷,张岩晨,徐梦怡,等. 能量代谢关键调控因子PGC-1α的研究进展[J].生理学报,2020,72(6):804-816.
[15] 魏秋实,方斌,陈镇秋,等. 股骨头前外侧骨质状态在股骨头坏死塌陷进展中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(16):2516-2522.
[16] TINGART M, BECKMANN J, OPOLKA A, et al. Influence of factors regulating bone formation and remodeling on bone quality in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Calcif Tissue Int. 2008;82(4):300-308.
[17] 于潼,谢利民. 硬化带在股骨头坏死塌陷作用中的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2015,21(1):84-86.
[18] 曾平,陈金龙,李金溢,等. 创伤性股骨头坏死血清差异蛋白质组学的研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(5):453-458.
[19] 胡兆林,常峰. 激素性股骨头坏死发病机制及相关信号通路研究进展[J].医学综述,2022,28(3):466-470.
[20] CHEN XJ, SHEN YS, HE MC, et al. Polydatin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cells by activating the BMP2-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108746.
[21] CHENG CF, KU HC, LIN H. PGC-1α as a Pivotal Factor in Lipid and Metabolic Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3447.
[22] HALLING JF, PILEGAARD H. PGC-1α-mediated regulation of mitochondrial function and physiological implications. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020;45(9):927-936.
[23] KONG S, CAI B, NIE Q. PGC-1α affects skeletal muscle and adipose tissue development by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol Genet Genomics. 2022;297(3):621-633.
[24] 陈黎,张世昌,张国英. 基因过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激因子-1α/雌激素相关受体-α共修饰间充质干细胞对血管化的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2018,35(7):1203-1205.
[25] 闫春雷,黄欣,苏乐群. PGC-1α的转录调节和翻译后修饰[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2015,31(1):12-19.
[26] XIA SR, WEN XY, FAN XL, et al. Wnt2 overexpression protects against PINK1 mutant‑induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(6):2633-2641.
[27] 耿慧霞.李莺歌.石贞玉.等. PGC-1α过表达逆转OGD/R诱导的神经元线粒体功能降低和凋亡[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(11):2078-2083.
[28] WALDMAN M, BELLNER L, VANELLA L, et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids Regulate Adipocyte Differentiation of Mouse 3T3 Cells, Via PGC-1α Activation, Which Is Required for HO-1 Expression and Increased Mitochondrial Function. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(14):1084-1094.
[29] HE Q, WANG T, NI H, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress promoting caspase signaling pathway-dependent apoptosis contributes to bone cancer pain in the spinal dorsal horn. Mol Pain. 2019;15:1744806919876150.
[30] 温宇华,刘培培,宋利格. PGC-1α在骨代谢中的作用[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2021,42(2):266-270. |