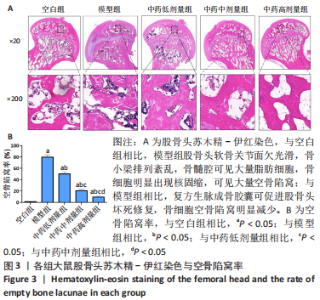
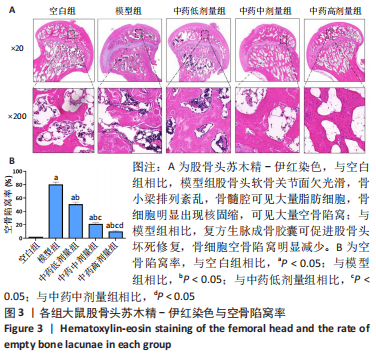
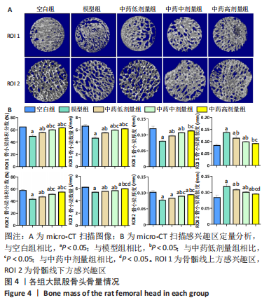
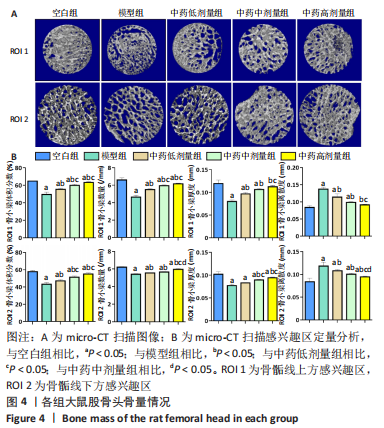
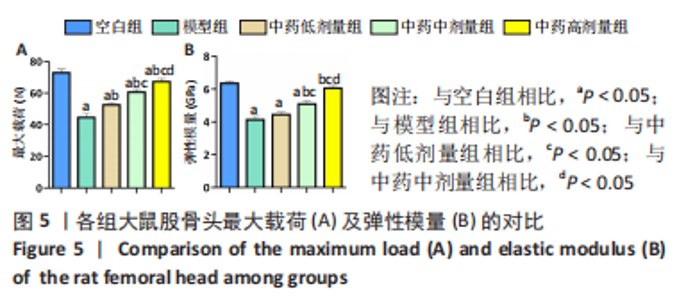
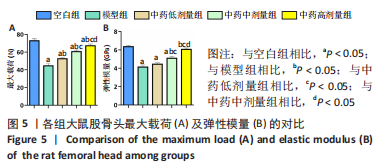
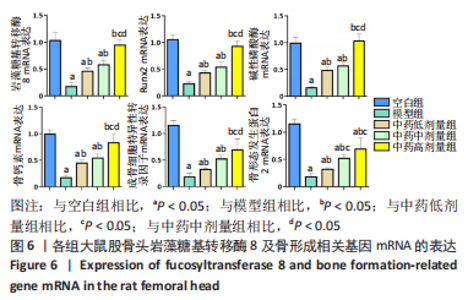
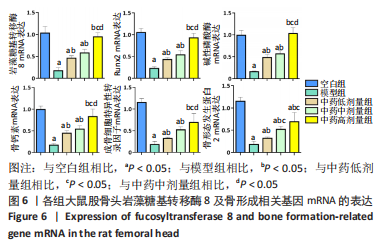
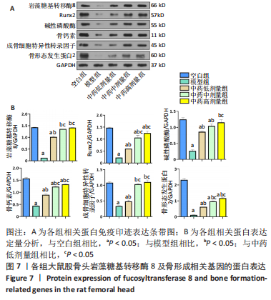
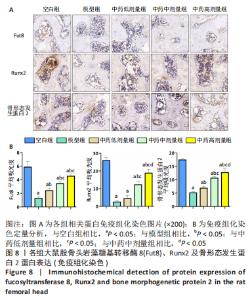
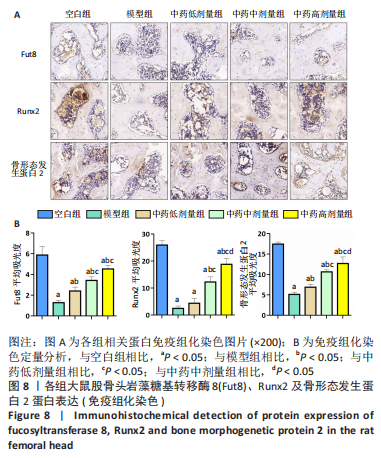
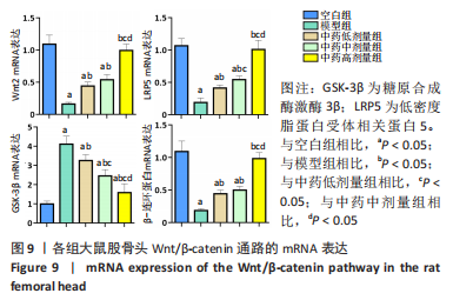
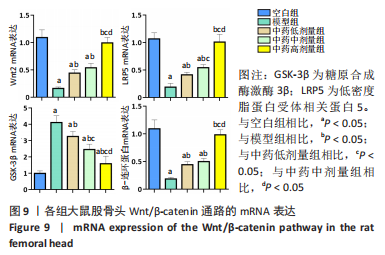
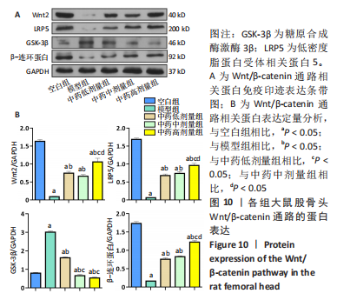
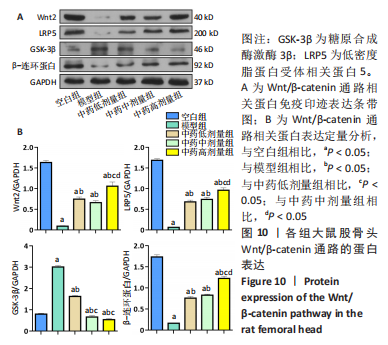
[1] 武瑞骐,崔伟,杨启培,等.激素性股骨头坏死的中医药治疗机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(17):2763-2771.
[2] ZHANG S, WANG C, SHI L, et al. Beware of Steroid-Induced Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head in the Treatment of COVID-19-Experience and Lessons from the SARS Epidemic. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:983-995.
[3] 田心保,林瑞珠,朱宁.激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的发病机制[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(10):915-919.
[4] 郭成龙,汪小敏,张晓刚,等.激素性股骨头坏死的中医病因病机及其治疗进展[J].中医临床研究,2021,13(23):143-146.
[5] 赫龙,高爽,李志刚,等.基于三大组学探讨从“痰、虚、瘀”论治SANFH的可行性[J].时珍国医国药,2022,33(8):1947-1949.
[6] HE XM, HE MC, YANG P, et al. The Therapeutic Effect of Huo Xue Tong Luo Capsules in Association Research Circulation Osseous (ARCO) Stage II Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Clinical Study With an Average Follow-up Period of 7.95 Years. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:773758.
[7] 房佳,王金胜.岩藻糖基转移酶8在胃癌中的表达及对预后影响的相关性分析[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2022,43(5):401-406.
[8] SONG T, CHEN P, STROBLE C, et al. Serum glycosylation characterization of osteonecrosis of the femoral head by mass spectrometry. Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2018; 24(1):178-187.
[9] 程经纬,柳杨青,汪艳芳,等.Mstn基因敲除通过上调Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响骨代谢并减轻2型糖尿病小鼠骨质疏松[J].中国病理生理杂志,2022,38(7):1246-1252.
[10] 袁灵青,颜春鲁,安方玉,等.长链非编码RNA介导Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(3):296-303.
[11] 张帆,梁清洋,韩超,等.Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控成骨细胞、破骨细胞在骨质疏松中的作用探讨[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(10):1540-1544.
[12] OSUMI D, TAKAHASHI M, MIYOSHI E, et al. Core fucosylation of E-cadherin enhances cell-cell adhesion in human colon carcinoma WiDr cells. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(5):888-895.
[13] 魏伟,吴希美,李元建.药理实验方法学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2010.
[14] 刘予豪龙血竭提取物调控OB/OC体系促进激素性骨坏死修复的研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2019.
[15] HUANG Z, CHENG C, CAO B, et al. Icariin Protects against Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(2):694-706.
[16] 董玉雷,周磊,李玉龙,等.大鼠激素性股骨头坏死模型的建立和评价[J].中国医学科学院学报,2015,37(2):152-156.
[17] 王建忠,高鸿雁,王坤正,等.淫羊藿对激素性股骨头坏死骨组织OPG/RANKL mRNA表达的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2011,31(10):1714-1717.
[18] 苏强,孙天胜,王秋良,等.不同剂量内毒素联合激素建立兔股骨头缺血性坏死模型的影像学评估[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(11):2108-2111.
[19] 张严,申震,李紫阁,等.环形外固定架联合骨膜烧灼构建大鼠胫骨萎缩性骨不连的新模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(29): 4650-4655.
[20] 梁红锁,杨业静,刘雷,等.普伐他汀灌胃与股骨头局部给药对兔激素性股骨头坏死的干预效果比较[J]. 山东医药,2021,61(26):43-46.
[21] 杨丰合,冯桂宇,李晋玉,等.兔激素性股骨头坏死的造模改进及结果评价[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2021. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0558
[22] 胡慧婷,李新宇,陈维毅,等.股骨有限元建模及相应的生物力学分析[J].中北大学学报(自然科学版),2014,35(5):576-580.
[23] MORGAN EF, UNNIKRISNAN GU, HUSSEIN AI. Bone Mechanical Properties in Healthy and Diseased States. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2018;20:119-143.
[24] 申意伟,徐西林,张晓峰,等.从生物力学角度探讨酒精对大鼠股骨干及股骨头影响的实验研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(3):313-317.
[25] OFTADEH R, PEREZ-VILORIA M, VILLA-CAMACHO JC, et al. Biomechanics and mechanobiology of trabecular bone: a review. J Biomech Eng. 2015;137(1):0108021-01080215. doi: 10.1115/1.4029176.
[26] 付志斌,李盛华,周明旺,等.非创伤性股骨头坏死相关信号通路研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(4):555-560.
[27] 赵静,张春雷,房兴堂,等.WNT信号通路的研究进展[J].中国牛业科学,2012, 38(1):33-37.
[28] ZHU C, LV Y, QIAN C, et al. Proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat BMSCs on a novel Ti/SiC metal matrix nanocomposite modified by friction stir processing. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38875.
[29] 胡彦婷,汪瑜,熊德建,等.阿托伐他汀联合葛根素对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的作用机制研究[J].安徽医药,2020,24(6):1070-1074.
[30] HIRANUMA Y, ATSUMI T, KAJIWARA T, et al. Evaluation of instability after transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy for nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Sci. 2009;14(5):535-542.
[31] CHEN S, LI J, PENG H, et al. Administration of erythropoietin exerts protective effects against glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33(4):840-848.
[32] SUN Y, WENG Y, ZHANG C, et al. Glycosylation of Dentin Matrix Protein 1 is critical for osteogenesis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17518.
[33] RAGNI E, LOMMEL M, MORO M, et al. Protein O-mannosylation is crucial for human mesencyhmal stem cells fate. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(2):445-458.
[34] 金鑫.体外岩藻糖基化修饰细胞表面CD44分子促进人脂肪来源干细胞体内迁移成骨的实验研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2014.
[35] AWAN B, TURKOV D, SCHUMACHER C, et al. FGF2 Induces Migration of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells by Increasing Core Fucosylations on N-Glycans of Integrins. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;11(2):325-333.
|