Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (31): 5064-5070.doi: 10.12307/2023.719
Previous Articles Next Articles
Prevention and treatment of bone-related diseases by regulating macrophages with Chinese medicine
Yang Chaoqiang1, Zhang Hulin2, Wang Xiaomin2, Wang Liang1, Wang Yican1
- 1Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-11Accepted:2022-11-17Online:2023-11-08Published:2023-01-31 -
Contact:Zhang Hulin, Master, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Affiliated Hospital of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Yang Chaoqiang, Master candidate, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, No. 18JR3RA077 (to ZHL); Lanzhou Health Science and Technology Development Project, No. 2019-050 (to ZHL); Lanzhou Talent Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project, No. 2020-RC-67 (to ZHL); Youth Project of Affiliated Hospital of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, No. gzfy-2019-18 (to WXM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Chaoqiang, Zhang Hulin, Wang Xiaomin, Wang Liang, Wang Yican. Prevention and treatment of bone-related diseases by regulating macrophages with Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5064-5070.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
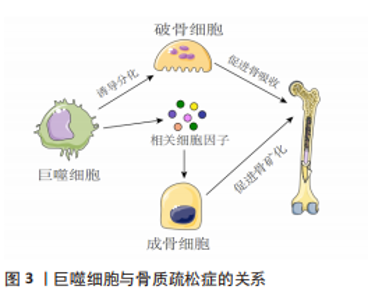
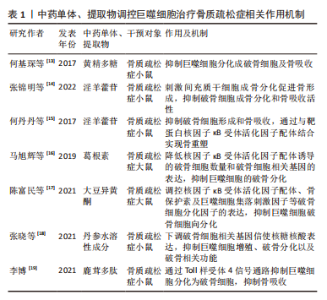
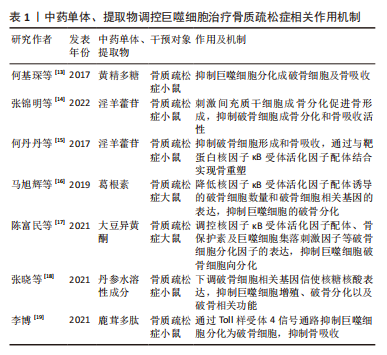
2.1 骨质疏松症与巨噬细胞 骨质疏松症是一种骨稳态失衡为主的全身代谢性疾病,伴有进行性骨丢失[4]。骨丢失是由于破骨细胞骨吸收和成骨细胞骨形成之间的不平衡,引起骨密度下降,致使骨微结构破坏、骨脆性增加。巨噬细胞参与了骨质疏松症的发病机制,激活的巨噬细胞可以分泌促炎细胞因子,并与骨吸收的激活有关。在适当的阶段靶向激活的巨噬细胞可能有助于抑制或减缓骨质疏松症患者骨丢失的进展。 2.1.1 巨噬细胞在成骨细胞中的作用 成骨细胞是负责骨形成的主要细胞,起源于间充质干细胞[5]。成骨细胞生成受不同转录因子的控制。成熟的成骨细胞可分化为骨细胞。在骨重建周期中,巨噬细胞在骨吸收状态下诱导破骨细胞分化中起着重要作用,破骨细胞的分化是成骨细胞形成的调节步骤。成骨细胞在充分激活和增殖的情况下,对骨形成的进展至关重要[6-7]。巨噬细胞极化可能有助于成骨细胞分化,增加骨生成和骨矿化,研究表明M2极化巨噬细胞通过分泌骨形态发生蛋白2、转化生长因子β和胰岛素样生长因子1等诱导成骨细胞分化,并促进骨矿化增加[8-9]。 2.1.2 巨噬细胞在破骨细胞中的作用 多核破骨细胞从造血干细胞的单核破骨前体分化而来,激活的巨噬细胞融合可形成多核破骨细胞,从而通过表达白细胞介素4和白细胞介素13引起骨吸收[10]。核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子可以通过核因子κB受体活化因子受体诱导破骨细胞的增殖和活化。当巨噬细胞受到RNAKL的刺激时,巨噬细胞可能诱导骨质疏松,并导致巨噬细胞M1/M2比率增加[11]。另有研究表明雌激素可以通过雌激素受体α调节下游基因核因子κB p65核转位来保护M2巨噬细胞免受RANKL刺激[12],因此通过降低M1/M2比值阻断雌激素缺乏介导的M2巨噬细胞破骨细胞生成可能是治疗骨质疏松症的潜在治疗靶点。 2.1.3 中医药干预调控巨噬细胞治疗骨质疏松症 随着对中药现代化的研究广泛开展,研究人员陆续发现众多中药单体或中药提取物可以通过调控巨噬细胞进而延缓骨质疏松症的发生发展。天然黄精多糖是中药黄精的主要活性成分之一,何基琛等[13]研究了黄精多糖对RANKL诱导的巨噬细胞向破骨细胞分化和骨吸收的影响,发现黄精多糖对巨噬细胞分化为破骨细胞和骨吸收具有抑制作用。淫羊藿苷是中药淫羊藿的主要活性成分,为8-异戊烯基黄酮苷类化合物,已被广泛证明具有抗骨质疏松活性,可促进骨形成并减少骨吸收。张锦明等[14]研究发现淫羊藿苷对骨细胞具有双重功能,通过刺激间充质干细胞的成骨分化来促进骨形成,同时抑制破骨细胞的成骨分化和骨吸收活性。何丹丹等[15]研究同样发现淫羊藿苷具有抑制破骨细胞的形成和骨吸收活性的能力,其通过与靶蛋白RANKL结合实现骨重塑。葛根素是从中药葛根中分离出来的主要生物活性成分,为单体异黄酮化合物。马旭辉等[16]通过研究葛根素对大鼠骨髓源型巨噬细胞破骨细胞向分化的影响,发现葛根素可降低RANKL诱导的破骨细胞数量和破骨细胞相关基因的表达,从而抑制巨噬细胞的破骨分化能力,进而为为葛根素应用于骨质疏松症的预防与治疗提供了依据。大豆异黄酮是一种与雌激素具有类似结构的黄酮类化合物,从植物中提取,与骨质疏松症的防治密切相关。陈富民等[17]通过分离、培养骨髓源巨噬细胞分析大豆异黄酮对巨噬细胞破骨细胞向分化的影响,发现大豆异黄酮可调控RANKL、骨保护素及巨噬细胞集落刺激因子等破骨细胞分化因子的表达,进而抑制巨噬细胞破骨细胞向分化。张晓等[18]通过研究丹参水溶性成分对小鼠单核巨噬细胞的增殖、破骨细胞分化的影响,发现丹参水溶性成分可以下调体外培养破骨细胞相关基因信使核糖核酸表达的影响,有效抑制小鼠单核巨噬细胞的增殖、破骨分化以及破骨相关功能,进而为丹参及其有效成分防治骨质疏松症及影响骨代谢的作用提供依据。鹿茸多肽是鹿茸的主要活性物质,李博[19]研究发现鹿茸多肽可以通过Toll样受体4信号通路抑制骨髓巨噬细胞分化为破骨细胞,抑制绝经性骨质疏松骨吸收,从而为骨质疏松症的治疗提供了新的策略。综上,中药干预巨噬细胞在骨质疏松症防治中发挥重要作用,但是目前研究还局限于动物实验水平,且其具体的干预机制仍未完全阐明,因此需要更加深入的研究;同时应另辟研究路径、探寻更多可能的干预方式。相信随着中药干预巨噬细胞研究的不断深入,应用中药治疗骨质疏松症的优势会更加凸显。 2.1.4 讨论 作者认为骨质疏松症是一种与慢性炎症密切相关的疾病,可导致骨量减少和骨脆性增加。巨噬细胞极化是巨噬细胞产生特定表型并对微环境刺激作出功能反应的过程。M1巨噬细胞在骨质疏松症中导致骨吸收并增强破骨细胞活性,而M2巨噬细胞在各种细胞因子的帮助下抑制骨吸收并促进成骨,未来需要进一步的体内和临床研究来阐明骨质疏松症中M1/M2比率增加治疗骨质疏松症的潜在机制。此外,随着中药现代化的快速发展,发现其可对多靶点、多通路产生影响进而发挥治疗疾病的作用。中医药与巨噬细胞关系密切,未来中医药与目前骨质疏松症疗法相结合有望改善患者的预后,因此进一步挖掘中药的有效成分并阐明其具体的干预机制,以确定靶向巨噬细胞的最佳策略至关重要。巨噬细胞与骨质疏松症的关系见图 3,中药单体、提取物调控巨噬细胞治疗骨质疏松症相关作用机制见表 1。"
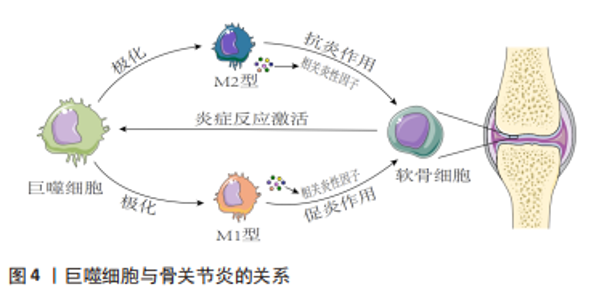
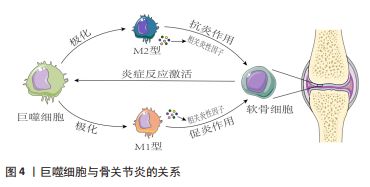
2.2 骨关节炎与巨噬细胞 骨关节炎是一种以关节软骨退化、滑膜和关节脂肪垫炎症以及骨结构改变为特征的关节组织退行性疾病[20]。尽管骨关节炎的病因和发病机制各不相同,但大量证据表明,巨噬细胞可以通过各种分泌介质在调节关节炎症、从而调节骨关节炎严重程度方面发挥重要作用[21-23]。巨噬细胞作为关节滑膜中重要的炎症细胞,通常分为2种表型:具有促炎抗菌作用的M1样巨噬细胞,以及具有抗炎和促分解作用的M2样巨噬细胞,二者之间的失衡可能导致膝关节慢性低度炎症,进而诱发骨关节炎发生发展。 2.2.1 巨噬细胞激活和极化与骨关节炎发生发展 在骨关节炎发展过程中,巨噬细胞失去稳定状态,并以多种方式被激活:一方面通过激活巨噬细胞上的表面模式识别受体进而启动细胞内下游效应,包括核因子κB途径,从而分泌炎性细胞因子和趋化因子[24];另一方面通过核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3(nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3,NLRP3)等炎症小体介导途径,识别各种病原体,产生炎症反应[25]。巨噬细胞是显著的可塑性细胞,分为典型活化的M1巨噬细胞或选择性活化的M2巨噬细胞,它们对微环境刺激的反应不同。M1巨噬细胞被干扰素g、脂多糖等激活极化,可分泌大量促炎细胞因子和介质,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12、环氧化酶2等。M2巨噬细胞由白细胞介素4和白细胞介素13极化,并进一步分为特定亚型,亚型M2a、M2b和M2c显示抗炎表型,有助于组织修复和重塑[26-28]。在骨关节炎发展过程中,巨噬细胞激活状态和M1/M2比率与骨关节炎发展程度高度相关。 2.2.2 巨噬细胞分泌细胞因子和基质金属蛋白酶促进骨关节炎发展 关节炎滑膜中活化和极化的巨噬细胞通过分泌细胞因子、生长因子和基质金属蛋白酶等促进骨关节炎发展。一方面巨噬细胞通过分泌炎性细胞因子诱导软骨细胞衰老和凋亡,并减少关键细胞外基质成分的合成,如蛋白多糖、聚集素和Ⅱ型胶原[29]。此外,它还参与促进关节软骨分解的蛋白水解酶的合成和释放,主要包括基质金属蛋白酶、聚蛋白多糖酶等。另一方面巨噬细胞通过调节刺激骨形成的转化生长因子β、蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原和软骨生成等方面,以促进软骨退化、骨赘形成,并加剧骨关节炎进展[30]。滑膜巨噬细胞产生的血管内皮生长因子被认为会加剧骨关节炎的滑膜血管生成和炎症[31]。巨噬细胞衍生的肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素β可以调节滑膜巨噬细胞中的神经生长因子表达,这可能导致骨关节炎疼痛[32]。此外,研究还表明滑膜巨噬细胞可能通过产生基质金属蛋白酶直接导致软骨损伤[33]。 2.2.3 巨噬细胞和软骨细胞在骨关节炎发展过程中相互作用 骨关节炎进展中巨噬细胞和软骨细胞之间的相互作用十分重要。激活的滑膜巨噬细胞显示较高水平的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素1β、一氧化氮和活性氧等炎性细胞因子,并参与基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶13的合成与释放,它们调节软骨细胞的微环境,促进软骨细胞产生过量金属蛋白酶、聚蛋白多糖酶,导致细胞外基质成分降解,同样,细胞外基质降解成分表达损伤相关分子模式进一步激活巨噬细胞发挥作用,通过刺激巨噬细胞活化并增加滑膜炎症,导致炎症和软骨降解的重复循环[34-35]。 2.2.4 中医药干预调控巨噬细胞治疗骨关节炎 中药单体或复方在骨关节炎治疗中有亦重要价值地位。木犀草素是一种天然黄酮类化合物,作为传统中草药的提取物,具有防治骨关节炎的潜在作用。张纯武[36]通过研究木犀草素对巨噬细胞中相关炎症及血管生成因子影响,发现木犀草素可以通过抑制小鼠单核巨噬细胞血小板衍生生长因子、血管内皮生长因子以及上游因子缺氧诱导因子1α的表达,并且抑制巨噬细胞炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、一氧化氮合酶、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6的表达,从而延缓骨关节炎的发生发展。槲皮素是一种天然存在的类黄酮,广泛存在于中药紫胡、桑叶、槐米和山楂等中。HU等[37]研究发现,槲皮素通过抑制软骨细胞的炎症和凋亡,调节滑膜巨噬细胞对M2巨噬细胞的极化,为软骨细胞创造一个促软骨形成环境来增强骨关节炎环境下的软骨修复,从而发挥软骨保护作用。红景天苷是红景天属最有效的生物活性成分之一。SA等[38]研究发现,红景天苷可缓解大鼠模型骨关节炎急性期疼痛和关节肿胀,降低滑液中白细胞数量、总蛋白含量、促炎递质,下调滑膜促炎基因表达,抑制滑膜中核因子κB的活化和氧化应激反应,促进软骨合成,防止蛋白聚糖和软骨细胞变性的丧失,为预防骨关节炎的发病和进展提供了新的策略。异补骨脂素是中药补骨脂主要的有效成分。田展松[39]研究发现异补骨脂素能通过激活巨噬细胞中CD9/GP130蛋白信号通路,并促进转录激活因子3磷酸化调节M1/M2巨噬细胞比例和功能,进而延缓关节炎的进展。陈博鉴等[40]通过构建人巨噬细胞观察威灵仙提取物对巨噬细胞极化的影响,发现威灵仙提取物干预后可以抑制M1型巨噬细胞细胞因子的分泌、促进M2型巨噬细胞细胞因子白细胞介素6和转化生长因子β1表达,由此推断威灵仙对人巨噬细胞的增殖、活性具有良好的促进作用,且能够抑制其向M1型极化,促使其向M2型极化,从而发挥抗炎、促软骨修复等作用以治疗骨关节炎。亦有研究发现,威灵仙提取物可能通过抑制核因子κB调节一氧化氮合酶并激活Src/FAK信号通路轴来减弱脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞所引起的炎症反应,进而延缓骨关节炎的发生发展[41]。独药各有所长,群药合方有其妙用。李晓辰[42]研究发现膝痹宁方可能通过抑制瞬时受体电位M7通道、细胞外调节蛋白激酶通路及核因子κB信号通路的活化,从而抑制滑膜巨噬细胞M1型极化,进而有效改善骨关节炎小鼠滑膜炎症、滑膜纤维化和软骨退变。危一飞等[43]研究发现,防己黄芪消肿方可能通过抑制M1巨噬细胞极化影响促炎细胞因子及金属基质蛋白酶的分泌,进而抑制关节内炎症、延缓关节软骨退变,从而缓解滑膜炎症治疗骨关节炎。杨楠等[44]研究发现,三色散可以通过抑制滑膜巨噬细胞焦亡及减少背根神经节细胞瞬时受体电位离子通道蛋白内钙离子内流,进而发挥减轻骨关节炎疼痛的功效。综上,临床实践和动物实验均表明中医药干预巨噬细胞防治骨关节炎疗效显著,中药配方中的活性成分化学结构多样,并且涉及多种调控途径。中药配方中的活性成分可以组合开发为强效药物,与单个化合物相比,将为开发新型防治骨关节炎药物提供巨大的潜力。 2.2.5 讨论 作者认为巨噬细胞作为免疫细胞在骨关节炎的症状学和结构进展中至关重要,活化的巨噬细胞产生促炎递质以及多种组织降解酶,这些酶使炎症环境升级,并加速软骨破坏。巨噬细胞和软骨细胞之间的旁分泌作用导致额外的反馈回路,并加速滑膜炎症和软骨退化。因此靶向滑膜巨噬细胞可以减轻疼痛,并减缓骨关节炎发展过程中滑膜炎、软骨损伤和骨赘形成。此外需要进一步研究巨噬细胞潜在功能,阐明导致骨关节炎中M1和M2巨噬细胞失衡的潜在机制,探索巨噬细胞重编程的合适方法,以便对骨关节炎患者进行有效治疗。同时,了解免疫细胞水平与关节组织之间的串扰,以及不同进展阶段对疾病过程的影响,寻求一种对巨噬细胞重编程具有免疫调节作用的药物或生物材料将是治疗骨关节炎和其他免疫疾病的潜在治疗方法。巨噬细胞与骨关节炎的关系见图 4,中药单体、提取物或复方调控巨噬细胞治疗骨关节炎的相关作用机制见表2。"
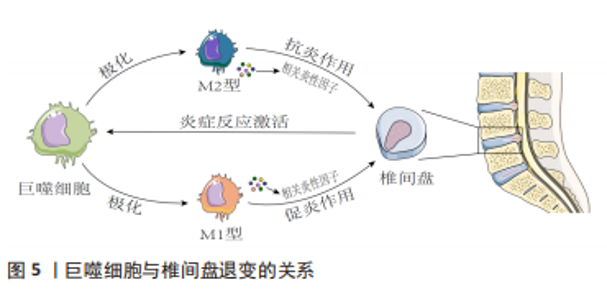
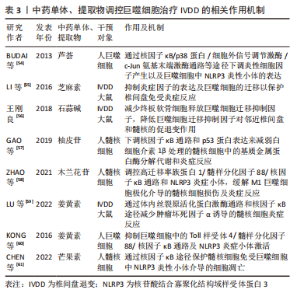
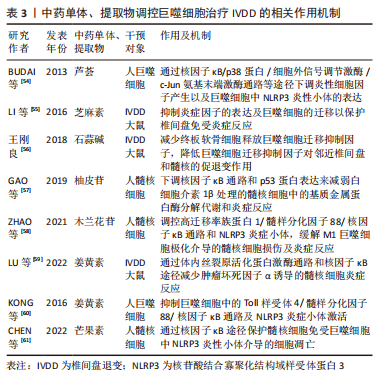
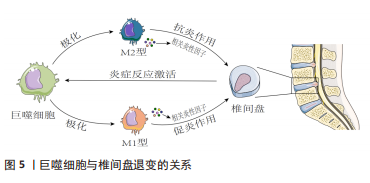
2.3 椎间盘退变与巨噬细胞 IVDD是一种以髓核细胞凋亡减少、细胞外基质降解加速为主要病理特征,常伴随慢性腰痛或下肢神经根性疼痛等临床表现的脊柱疾病[45]。研究显示巨噬细胞作为机体内的主要吞噬细胞,是唯一能够进入闭合髓核的炎症细胞,在椎间盘的各种结构中表达,其数量与IVDD的程度呈正相关。作为炎症细胞的巨噬细胞可能直接发挥吞噬作用或通过神经-免疫机制协同调节椎间盘的代谢,而巨噬细胞功能失衡将导致更多炎性因子趋化和聚集,进而导致椎间盘细胞外基质降解,从而加重椎间盘退变。 2.3.1 退变椎间盘内巨噬细胞的定位与识别 椎间盘退变过程中巨噬细胞或巨噬细胞样细胞扮演了非常重要的角色,随着IVDD的加重,巨噬细胞进一步向椎间盘浸润。NAKAZAWA等[46]通过检测退行性椎间盘并证明受损髓核、纤维环、软骨终板区域中巨噬细胞标志物的表达随着椎间盘恶化程度而显著增加,并且在健康椎间盘中未发现这些标志物。研究证实,大量巨噬细胞存在于退行性椎间盘中并且可能通过循环系统释放到组织中[47-48]。 在炎症环境下,髓核细胞分泌相关促炎趋化因子(CCL2、CCL3、CXCL10等)介导巨噬细胞极化、募集和迁移,产生更多白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α,促进基质金属蛋白酶的合成,最终加重IVDD。上述研究均表明巨噬细胞与IVDD密切相关。 2.3.2 巨噬细胞表型与椎间盘退变 巨噬细胞M1极化可分泌白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎因子,加重椎间盘退变,而巨噬细胞M2极化可分泌白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10等抗炎因子[49-50]。巨噬细胞表型的平衡对于维持内环境稳态具有重要作用,该平衡一旦失衡将会导致内环境稳态破坏,当椎间盘处于持续炎症状态时,细胞外基质的降解增强;炎症微环境促使巨噬细胞向M1极化,分泌更多促炎因子,形成恶性循环,诱发椎间盘退变。巨噬细胞的表型平衡在正常的椎间盘微环境中起着重要作用,一旦表型失衡就会导致椎间盘微环境遭到破坏,进而在巨噬细胞和炎症因子的不断作用下,逐渐出现一系列椎间盘退行性变,同时由于组织修复功能的缺失致使椎间盘退变成为不可逆转的病理情况。 2.3.3 巨噬细胞迁移与椎间盘退变 巨噬细胞发挥其功能作用的基础是迁移到闭合的髓核中。研究表明,髓核、纤维环、终板细胞均可组成性表达在Toll样受体4,且其基础表达取决于细胞类型[51-52]。Toll样受体4的表达受其配体(如脂多糖)的调节,配体与Toll样受体4结合会导致一系列相关促炎递质上调相关的信号级联反应(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子等),进而抑制细胞外基质的表达。巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子是一种高度保守且具有多种功能的细胞因子,不仅在巨噬细胞迁移中具有重要作用,而且对其他促炎因子具有正向调节作用,二者同时作用导致椎间盘退变[53]。 2.3.4 中医药干预调控巨噬细胞治疗椎间盘退变 中医药以其疗效高、副反应小、伤害少、成本低的特点占据椎间盘退变治疗的重要地位。芦荟已被用于传统草药中,作为诱导抗炎作用的免疫调节剂。BUDAI等[54]研究发现,芦荟可以通过核因子κB/p38蛋白/细胞外信号调节激酶/c-Jun氨基末端激酶通路等途径,下调脂多糖诱导的炎性细胞因子产生以及巨噬细胞中NLRP3炎性小体的表达,进而延缓椎间盘退变的发生发展。芝麻素是一种从芝麻中提取的生物活性成分,具有软骨保护和抗炎作用。LI等[55]通过研究芝麻素对大鼠体外椎间盘的抗炎和抗分解代谢作用,发现芝麻素可以显著抑制脂多糖诱导的分解代谢酶和炎症因子表达,并且可以抑制脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞的迁移以保护椎间盘免受炎症反应,在治疗椎间盘退行性疾病方面具有积极的前景。石蒜碱是存在于石蒜科植物石蒜的鳞茎内的传统的植物药。王刚良[56]通过构建大鼠椎间盘退变模型研究石蒜碱对椎间盘的保护作用,发现石蒜碱可以减少终板软骨细胞释放巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子,从而降低巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对邻近椎间盘和髓核的促退变作用,保护椎间盘和髓核,进而延缓椎间盘退变。GAO等[57]研究发现,中药骨碎补单体柚皮苷可以通过下调核因子κB通路和p53蛋白表达来减弱白细胞介素1β处理的髓核细胞中的基质金属蛋白酶分解代谢和炎症反应,以此改善椎间盘环境,减缓退变,有望成为一种可能治疗椎间盘退变的替代药物。木兰花苷广泛分布于小檗科、木兰科、罂粟科或防己科等几个植物科的代表中。ZHAO等[58]研究发现,木兰花苷通过灭活调控高迁移率族蛋白1/髓样分化因子88/核因子κB通路和NLRP3炎症小体,缓解M1巨噬细胞极化介导的髓核细胞损伤及炎症反应,为IVDD治疗提供了新的参考。姜黄素是一种来自姜黄的黄色素,是一种安全的天然化合物,用于治疗炎症相关疾病。LU等[59]研究发现姜黄素可以通过体内丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路和核因子κB途径减少肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的炎症髓核细胞中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素4和白细胞介素6的产生,以延缓椎间盘退变。KONG等[60]同样发现姜黄素可以通过抑制佛波酯诱导的巨噬细胞中的Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88/核因子κB通路及NLRP3炎症小体激活,进而抑制椎间盘发生发展。芒果素来源于百合科草本植物知母的干燥根茎。CHEN等[61]通过体外细胞模型探索芒果素在椎间盘中的作用发现,芒果素通过核因子κB途径保护脂多糖刺激的髓核细胞免受巨噬细胞中NLRP3炎性小体介导的细胞凋亡以防治椎间盘退变。综上,中药作为一种多组分、多靶点的方法,与系统生物学的整体概念完美契合,适用于椎间盘退变的治疗。中草药的协同联系和相关活性化合物对IVDD的机制增加了中医药的发展前景。然而,一些中草药在临床和临床前研究中也表现出毒性,需要适当设计和良好控制的前瞻性研究来进一步证明这种草药及其成分的骨骼保护作用和安全性,未来IVDD的发病机制及中医药干预巨噬细胞防治IVDD的物质基础值得进一步研究。 2.3.5 讨论 作者认为炎症、免疫反应、机械负荷、缺氧均是影响IVDD的关键因素。巨噬细胞通过神经免疫机制发挥吞噬作用,而巨噬细胞极化失衡会导致更多炎症因子趋化和聚集,加剧IVDD的发展。IVDD的炎症反应是一个复杂的过程,涉及多种细胞类型在多个愈合阶段的相互作用。了解椎间盘内巨噬细胞的积累、定位和表型可以提高对椎间盘病理生理学的了解,并有助于确定未来的治疗目标。此外使用中药干预巨噬细胞并促进其极化为具有抗炎作用的M2型,有望为有效预防延缓IVDD提供新的策略。未来仍需进一步深化巨噬细胞介导的IVDD发病机制和治疗的基础研究,为IVDD的临床治疗提供确切的药物靶点。巨噬细胞与骨关节炎的关系见图 5,中药单体、提取物或复方调控巨噬细胞治疗骨关节炎相关作用机制见表3。"
| [1] KISHORE A, PETREK M. Roles of Macrophage Polarization and Macrophage-Derived miRNAs in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:678457. [2] CHENG Y, YU Y, ZHUANG Q, et al. Bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis is attenuated by Trichinella spiralis through inhibiting M1 monocyte/macrophage polarization. iScience. 2022;25(3):103979. [3] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [4] ZHANG L, XIE H, LI S. LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 controls osteogenic and adipocytic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis through regulating the miR-196a-5p/Hmga2 axis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020;38(6):794-805. [5] YOSHIDA G, KAWABATA T, TAKAMATSU H, et al. Degradation of the NOTCH intracellular domain by elevated autophagy in osteoblasts promotes osteoblast differentiation and alleviates osteoporosis. Autophagy. 2022; 18(10):2323-2332. [6] HU Y, HAO X, LIU C, et al. Acvr1 deletion in osteoblasts impaired mandibular bone mass through compromised osteoblast differentiation and enhanced sRANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(6):4580-4591. [7] LIU J, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosomes derived from macrophages upon Zn ion stimulation promote osteoblast and endothelial cell functions. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(18):3800-3807. [8] OLMSTED-DAVIS E, MEJIA J, SALISBURY E, et al. A Population of M2 Macrophages Associated With Bone Formation. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 686769. [9] BAI X, CHEN D, DAI Y, et al. Bone formation recovery with gold nanoparticle-induced M2 macrophage polarization in mice. Nanomedicine. 2021;38: 102457. [10] BIGHETTI A, CESTARI TM, SANTOS PS, et al. In vitro and in vivo assessment of CaP materials for bone regenerative therapy. The role of multinucleated giant cells/osteoclasts in bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(1):282-297. [11] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107. [12] DOU C, DING N, ZHAO C, et al. Estrogen Deficiency-Mediated M2 Macrophage Osteoclastogenesis Contributes to M1/M2 Ratio Alteration in Ovariectomized Osteoporotic Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):899-908. [13] 何基琛, 宗少晖, 曾高峰, 等. 黄精多糖对RANKL诱导骨髓巨噬细胞向破骨细胞分化及体内骨吸收功能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(20):3117-3122. [14] 张锦明, 田滢舟, 赵玲, 等. 淫羊藿苷促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化缓解小鼠骨质疏松的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(19):2991-2996. [15] 何丹丹, 夏海建, 蒋俊, 等. 淫羊藿素与RANKL蛋白靶点结合抑制破骨细胞分化抗骨质疏松作用研究[J]. 中草药,2017,48(22):4707-4712. [16] 马旭辉, 张鹏, 杨屹羚, 等. 葛根素对大鼠下颌骨骨髓源巨噬细胞破骨细胞向分化的影响[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2019,17(3):193-197. [17] 陈富民, 代庆刚, 邬春兰, 等. 大豆异黄酮对颌骨骨髓源巨噬细胞破骨细胞向分化的影响[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2021,19(3):197-200. [18] 张晓, 杨帆, 徐又佳. 丹参水溶性成分对小鼠单核巨噬细胞的增殖、破骨细胞分化的影响及其机制[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2021,38(2):379-380. [19] 李博. 鹿茸多肽通过TLR4信号通路抑制破骨细胞生成和骨吸收[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2021. [20] FRANCO-TREPAT E, ALONSO-PEREZ A, GUILLAN-FRESCO M, et al. Amitriptyline blocks innate immune responses mediated by toll-like receptor 4 and IL-1 receptor: Preclinical and clinical evidence in osteoarthritis and gout. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(2):270-286. [21] 张虎林, 王亮, 喻琳, 等. 滑膜巨噬细胞在骨性关节炎发病机制中的作用及其潜在性应用研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(4):590-595. [22] WANG D, CHAI XQ, HU SS, et al. Joint synovial macrophages as a potential target for intra-articular treatment of osteoarthritis-related pain. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(3):406-415. [23] ZHANG J, CHENG F, RONG G, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0005567 overexpression promotes M2 type macrophage polarization through miR-492/SOCS2 axis to inhibit osteoarthritis progression. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):8920-8930. [24] VON KAEPPLER EP, WANG Q, RAGHU H, et al. Interleukin 4 promotes anti-inflammatory macrophages that clear cartilage debris and inhibits osteoclast development to protect against osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol. 2021;229:108784. [25] ZHANG B, CHEN H, OUYANG J, et al. SQSTM1-dependent autophagic degradation of PKM2 inhibits the production of mature IL1B/IL-1beta and contributes to LIPUS-mediated anti-inflammatory effect. Autophagy. 2020;16(7):1262-1278. [26] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [27] MA Y, YANG H, ZONG X, et al. Artificial M2 macrophages for disease-modifying osteoarthritis therapeutics. Biomaterials. 2021;274:120865. [28] LIU Q, PIAN K, TIAN Z, et al. Calcium-binding protein 39 overexpression promotes macrophages from ‘M1’ into ‘M2’ phenotype and improves chondrocyte damage in osteoarthritis by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase/sirtuin 1 axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):9855-9871. [29] GAURAV R, MIKULS TR, THIELE GM, et al. High-throughput analysis of lung immune cells in a combined murine model of agriculture dust-triggered airway inflammation with rheumatoid arthritis. PloS one. 2021; 16(2):e0240707. [30] ZHANG H, LIN C, ZENG C, et al. Synovial macrophage M1 polarisation exacerbates experimental osteoarthritis partially through R-spondin-2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(10):1524-1534. [31] ARSHADI D, SHAKIBA Y, RAJABIAN A, et al. Cholinergic agonists inhibit proliferation of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and monocytic cell lines and reduce VEGF and MMPs expression by these cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2020;42(3):246-254. [32] OHASHI Y, UCHIDA K, FUKUSHIMA K, et al. NGF Expression and Elevation in Hip Osteoarthritis Patients with Pain and Central Sensitization. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:9212585. [33] GEORGIEV T, IVANOVA M, VELIKOVA T, et al. Serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-3 as a prognostic marker for progression of cartilage injury in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Acta Reumatol Port. 2020;45(3): 207-213. [34] CHEN X, LIU Y, WEN Y, et al. A photothermal-triggered nitric oxide nanogenerator combined with siRNA for precise therapy of osteoarthritis by suppressing macrophage inflammation. Nanoscale. 2019;11(14):6693-6709. [35] HAMASAKI M, TERKAWI MA, ONODERA T, et al. A Novel Cartilage Fragments Stimulation Model Revealed that Macrophage Inflammatory Response Causes an Upregulation of Catabolic Factors of Chondrocytes In Vitro. Cartilage. 2021;12(3):354-361. [36] 张纯武. 木犀草素对骨关节炎中巨噬细胞相关性炎症及血管生成因子影响的研究[D]. 南京:南京中医药大学,2016. [37] HU Y, GUI Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Quercetin alleviates rat osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes, modulating synovial macrophages polarization to M2 macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019; 145:146-160. [38] SA L, WEI X, HUANG Q, et al. Contribution of salidroside to the relieve of symptom and sign in the early acute stage of osteoarthritis in rat model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;259:112883. [39] 田展松. 异补骨脂素调节巨噬细胞极化在骨关节炎中的抗炎作用机制研究[D]. 重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2021. [40] 陈博鉴, 黄永明, 刘文渤, 等. 威灵仙提取物促使M1型THP-1源巨噬细胞向M2型极化的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2021,32(12):2893-2898. [41] PAN LL, ZHANG QY, LUO XL, et al. (7R,8S)-9-acetyl-dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol inhibits inflammation and migration in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Phytomedicine. 2016;23(5):541-549. [42] 李晓辰. TRPM7介导膝骨关节炎中滑膜巨噬细胞M1型极化的机制研究及膝痹宁方的干预作用[D]. 南京:南京中医药大学,2021. [43] 危一飞, 程桯, 肖潇, 等. 防己黄芪消肿方调控滑膜巨噬细胞极化治疗膝骨关节炎滑膜炎[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(13):112-122. [44] 杨楠, 廖太阳, 张力, 等. 三色散干预滑膜巨噬细胞焦亡影响背根神经节TRPA1治疗KOA疼痛的离体研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2022,33(1):33-38. [45] MCHUGH J. Targeting IL-1beta expression in IVDD. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(4):188. [46] NAKAZAWA KR, WALTER BA, LAUDIER DM, et al. Accumulation and localization of macrophage phenotypes with human intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2018;18(2):343-356. [47] NAKAWAKI M, UCHIDA K, MIYAGI M, et al. Sequential CCL2 Expression Profile After Disc Injury in Mice. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(4):895-901. [48] KAWAKUBO A, UCHIDA K, MIYAGI M, et al. Investigation of resident and recruited macrophages following disc injury in mice. J Orthop Res. 2020; 38(8):1703-1709. [49] YAMAGISHI A, NAKAJIMA H, KOKUBO Y, et al. Polarization of infiltrating macrophages in the outer annulus fibrosus layer associated with the process of intervertebral disc degeneration and neural ingrowth in the human cervical spine. Spine J. 2022;22(5):877-886. [50] LI L, WEI K, DING Y, et al. M2a Macrophage-Secreted CHI3L1 Promotes Extracellular Matrix Metabolic Imbalances via Activation of IL-13Ralpha2/MAPK Pathway in Rat Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Front Immunol. 2021;12:666361. [51] ZHANG Q, WENG Y, JIANG Y, et al. Overexpression of miR-140-5p inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced human intervertebral disc inflammation and degeneration by downregulating toll-like receptor 4. Oncol Rep. 2018; 40(2):793-802. [52] HU S, SHAO Z, ZHANG C, et al. Chemerin facilitates intervertebral disc degeneration via TLR4 and CMKLR1 and activation of NF-kB signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(12):11732-11753. [53] LIANG H, YANG X, LIU C, et al. Effect of NF-kB signaling pathway on the expression of MIF, TNF-α, IL-6 in the regulation of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Int. 2018;18(4):551-556. [54] BUDAI MM, VARGA A, MILESZ S, et al. Aloe vera downregulates LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine production and expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages. Mol Immunol. 2013;56(4):471-479. [55] LI K, LI Y, XU B, et al. Sesamin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and extracellular matrix catabolism in rat intervertebral disc. Connect Tissue Res. 2016;57(5):347-359. [56] 王刚良. 石蒜碱通过抑制NF-κb通路缓解软骨终板退变和腰椎间盘退变[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2018. [57] GAO G, CHANG F, ZHANG T, et al. Naringin Protects Against Interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta)-Induced Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells Degeneration via Downregulation Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) Pathway and p53 Expression. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9963-9972. [58] ZHAO F, GUO Z, HOU F, et al. Magnoflorine Alleviates “M1” Polarized Macrophage-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Through Repressing the HMGB1/Myd88/NF-kappaB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:701087. [59] LU B, CHEN X, CHEN H, et al. Demethoxycurcumin mitigates inflammatory responses in lumbar disc herniation via MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;108:108914. [60] KONG F, YE B, CAO J, et al. Curcumin Represses NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB and P2X7R Signaling in PMA-Induced Macrophages. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:369. [61] CHEN J, BIAN M, PAN L, et al. alpha-Mangostin protects lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nucleus pulposus cells against NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated apoptosis via the NF-kappaB pathway. J Appl Toxicol. 2022;42(9):1467-1476. |
| [1] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [4] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [5] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [6] | Lian Shilin, Zhang Yan, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Li Tusheng, Ding Yu. Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1199-1204. |
| [7] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [8] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [9] | Yang Yitian, Wang Lu, Yao Wei, Zhao Bin. Application of the interaction between biological scaffolds and macrophages in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [10] | Li Wenjie, You Aijia, Zhou Junli, Fang Sujuan, Li Chun. Effects of different dressings in the treatment of burn wounds: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
| [11] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [12] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [13] | Wang Jinling, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Huang Fujin, Yin Lingwei, Zhong Peirui, Liu Jin, Sun Guanghua, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of exercise training on bone mass and bone microstructure in aged osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 676-682. |
| [14] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [15] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||