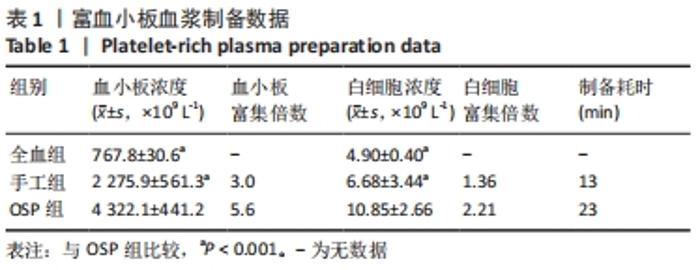
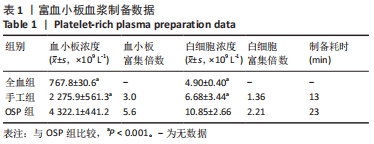
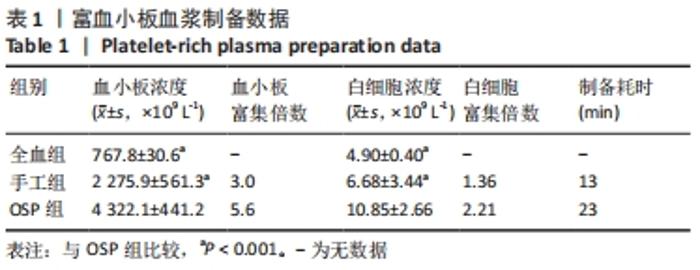
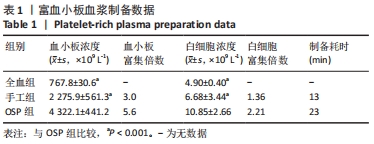
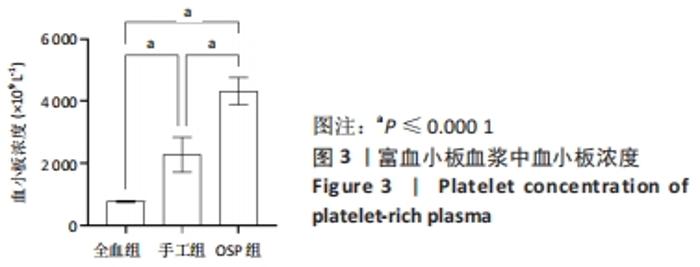
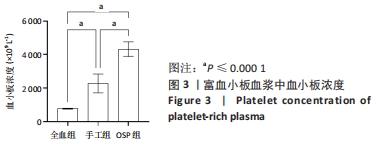
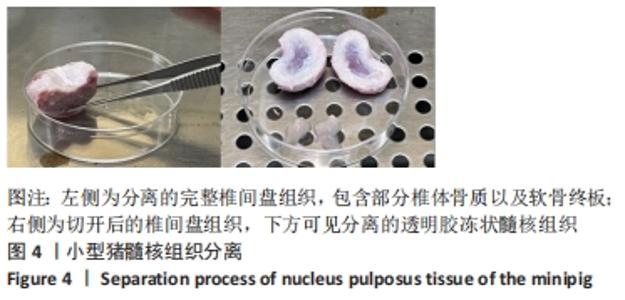
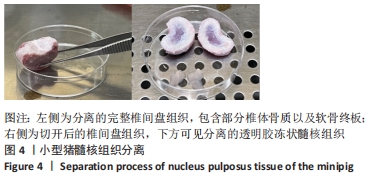
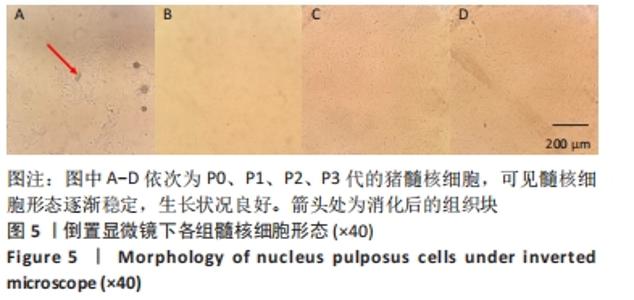
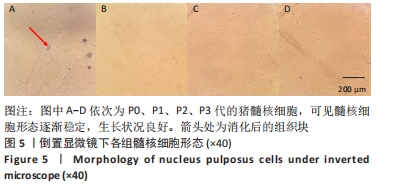
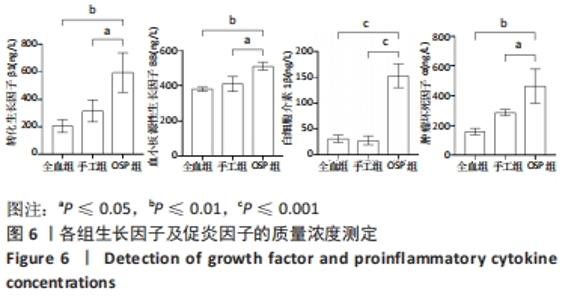
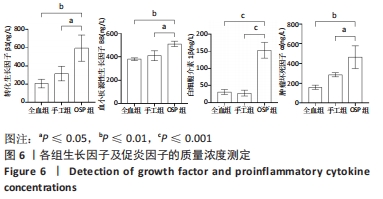
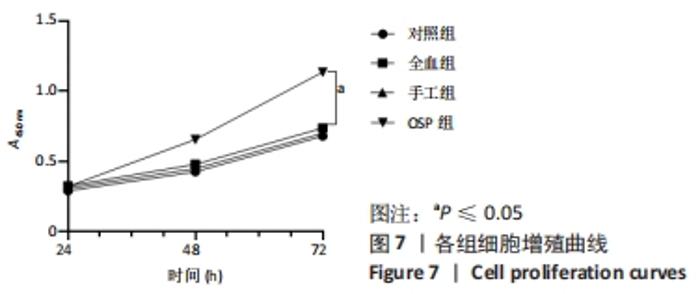
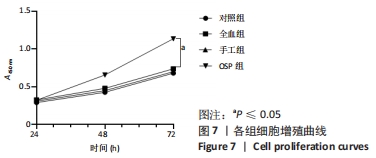
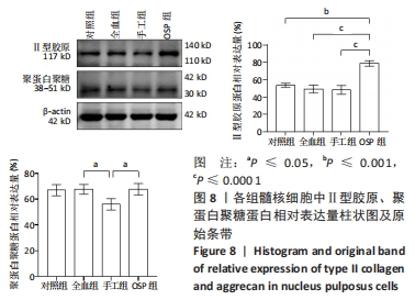
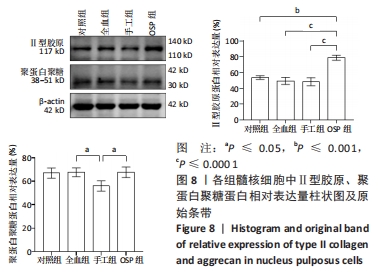
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 1199-1204.doi: 10.12307/2023.061
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells
Lian Shilin1, 2, Zhang Yan2, Jiang Qiang2, Zhang Hanshuo2, Li Tusheng2, Ding Yu1, 2
- 1School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 2Orthopedics of TCM Senior Department, the Sixth Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China
-
Received:2022-02-07Accepted:2022-03-17Online:2023-03-18Published:2022-07-28 -
Contact:Ding Yu, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; Orthopedics of TCM Senior Department, the Sixth Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China -
About author:Lian Shilin, Master candidate, School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; Orthopedics of TCM Senior Department, the Sixth Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China -
Supported by:Capital Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment Technology Research and Demonstration Application Project, No. Z191100006619028 (to DY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lian Shilin, Zhang Yan, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Li Tusheng, Ding Yu. Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1199-1204.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] LI Z, LI Z, CHEN X, et al. Comparison between modified facet joint fusion and posterolateral fusion for the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):29. [2] TOBERT DG, ANTOCI V, PATEL SP, et al. Adjacent Segment Disease in the Cervical and Lumbar Spine. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(3):94-101. [3] ETULAIN J. Platelets in wound healing and regenerative medicine. Platelets. 2018; 29(6):556-568. [4] CHENG J, SANTIAGO KA, NGUYEN JT, et al. Treatment of symptomatic degenerative intervertebral discs with autologous platelet-rich plasma: follow-up at 5-9 years. Regen Med. 2019;14(9):831-840. [5] EVERTS P A, VAN ERP A, DESIMONE A, et al. Platelet Rich Plasma in Orthopedic Surgical Medicine. Platelets. 2021;32(2):163-174. [6] PADILLA S, SÁNCHEZ M, VAQUERIZO V, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Applications for Achilles Tendon Repair: A Bridge between Biology and Surgery. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):824. [7] FEIGIN K, SHOPE B. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Dentistry and Oral Surgery: Introduction and Review of the Literature. J Vet Dent. 2019;36(2):109-123. [8] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110660. [9] EVERTS P, ONISHI K, JAYARAM P, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(7794):7794. [10] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1):44-56. [11] ZHANG Y, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin modulates IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2019; 11(22):10499-10512. [12] LIAN C, GAO B, WU Z, et al. Collagen type II is downregulated in the degenerative nucleus pulposus and contributes to the degeneration and apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):4730-4736. [13] BECKETT MC, RALPHS JR, CATERSON B, et al. The transmembrane heparan sulphate proteoglycan syndecan-4 is involved in establishment of the lamellar structure of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. Eur Cell Mater. 2015;30:69-88. [14] KIRCHNER F, PINAR A, MILANI I, et al. Vertebral intraosseous plasma rich in growth factor (PRGF-Endoret) infiltrations as a novel strategy for the treatment of degenerative lesions of endplate in lumbar pathology: description of technique and case presentation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):72. [15] GULLUNG G, WOODALL W, TUCCI M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma effects on degenerative disc disease: analysis of histology and imaging in an animal model. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2011;2(4):13-18. [16] 卢正操, 蒋强, 付本升, 等. 经皮脊柱内镜联合富血小板血浆注射治疗青壮年腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 转化医学杂志,2021,10(1):30-34. [17] XU J, XIE G, YANG W, et al. Platelet-rich plasma attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration via delivering miR-141-3p-containing exosomes. Cell Cycle. 2021; 20(15):1487-1499. [18] 王乙. TGF-β通路在椎间盘退变分子生物学进程中作用机制的研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版),2020,46(5):1105-1110. [19] 李大鹏, 吴燕, 岳佳伟, 等. 胰岛素样生长因子1通过PI3K/Akt信号通路促进髓核细胞聚集蛋白聚糖及Ⅱ型胶原的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(8):1202-1208. [20] SZÖŐR Á, UJLAKY-NAGY L, TÓTH G, et al. Cell confluence induces switching from proliferation to migratory signaling by site-selective phosphorylation of PDGF receptors on lipid raft platforms. Cell Signal. 2016;28(2):81-93. [21] ZHOU T, LI X, LI G, et al. Injectable and thermosensitive TGF-β1-loaded PCEC hydrogel system for in vivo cartilage repair. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10553. [22] ZHANG J, LI Z, CHEN F, et al. TGF-β1 suppresses CCL3/4 expression through the ERK signaling pathway and inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation-related pain in a rat model. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(9):e379. [23] SEGABINAZZI L, PODICO G, ROSSER MF, et al. Three Manual Noncommercial Methods to Prepare Equine Platelet-Rich Plasma. Animals (Basel). 2021;11(6):1478. [24] GUPTA V, PARIHAR AS, PATHAK M, et al. Comparison of Platelet-Rich Plasma Prepared Using Two Methods: Manual Double Spin Method versus a Commercially Available Automated Device. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2020;11(4):575-579. [25] WEIBRICH G, KLEIS WK. Curasan PRP kit vs. PCCS PRP system. Collection efficiency and platelet counts of two different methods for the preparation of platelet-rich plasma. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13(4):437-443. [26] 陈华, 刘浩. 生物活性因子治疗椎间盘退变性疾病的研究进展[J]. 华西医学, 2017,32(11):1782-1786. [27] ZHU B, CUI G, ZHANG Q, et al. Desumoylation of aggrecan and collagen II facilitates degradation via aggrecanases in IL-1β-mediated osteoarthritis. J Pain Res. 2019;12:2145-2153. [28] WANG SZ, FAN WM, JIA J, et al. Is exclusion of leukocytes from platelet-rich plasma (PRP) a better choice for early intervertebral disc regeneration? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):199. [29] 王书军, 温从吉, 李诗言. 不同套装制备的富血小板血浆中细胞及细胞因子成分的比较[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(6):592-597. [30] DEGEN RM, BERNARD JA, OLIVER KS, et al. Commercial Separation Systems Designed for Preparation of Platelet-Rich Plasma Yield Differences in Cellular Composition. Hss J. 2017;13(1):75-80. [31] DE MELO BAG, MARTINS SHIMOJO AA, MARCELINO PEREZ AG, et al. Distribution, recovery and concentration of platelets and leukocytes in L-PRP prepared by centrifugation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;161:288-295. |
| [1] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [2] | Zheng Hongrui, Zhang Wenjie, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Shen Yajun, Fan Lei. Femoral neck system combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1390-1395. |
| [3] | Li Yue, Lyu Yan, Feng Wanying, Song Yang, Yan Yu, Guan Yongge. Preparation of hyperoside nanoparticles to repair endometrial injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 360-366. |
| [4] | Ning Ziwen, Wang Xu, Shi Zhengliang, Qin Yihua, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, Wang Yang, Li Yanlin. Meniscal injury repair methods for non-blood supply area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 420-426. |
| [5] | Zhang Weiye, Zhan Jiawen, Zhu Liguo, Wang Shangquan, Chen Ming, Wei Xu, Feng Minshan, Yu Jie, Han Tao, Cai Chuhao, Zhou Shuaiqi, Shao Chenchen. Effect of nucleus pulposus cells-derived exosomes under cyclic mechanical tension on endplate chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 223-229. |
| [6] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [7] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [8] | Huang Fan, Di Anqi, Qiu Mingwang, Huang Chuyu, Li Xiaohui, Zhao Siyi, Fan Zhiyong, Wu Shan. Establishing a rat model of intervertebral disc degeneration using X-ray guidance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5652-5657. |
| [9] | Zhao Yunan, Zhang Haobo, Sun Tao, Yang Xuejun. Hydrogel-based growth factors and drugs in the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: problems and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5525-5533. |
| [10] | Lyu Yan, Guan Yongge, Song Yang, Li Yue. Hydrogel combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of damaged endometrium in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4940-4945. |
| [11] | Huang Gao, Xu Jun, Chen Wenge. Implantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-loaded platelet-rich plasma combined with extracorporeal shock wave in the repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4812-4818. |
| [12] | Xie Xingqin, Nie Yuqi, Zhang Yi. Application and role of human platelet lysate in tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4553-4561. |
| [13] | Hu Pengyu, Yu Zhiping, Jia Guanghou, Cong Zhichao, Cong Haibo. Adjuvant treatment of nonunion of tibial fractures with platelet-rich plasma evaluated by bone turnover markers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4367-4373. |
| [14] | Liu Chao, Zhang Lijun, Du Xinjie, Xu Qian, Lü Hongjuan, Fan Dongmei, Tian Huanling, Huang Jian, Huang Yuxiang. Mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to promote platelet plasma coagulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4010-4015. |
| [15] | Zhang Jingying, Li Ziyi, Liu Xiaochuan, Li Dan, Wang Yang, Wu zhuguo. Tail vein injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for repair of skull injury in aging mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3944-3950. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||