Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (30): 4812-4818.doi: 10.12307/2022.760
Previous Articles Next Articles
Implantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-loaded platelet-rich plasma combined with extracorporeal shock wave in the repair of bone defects
Huang Gao, Xu Jun, Chen Wenge
- Minda Hospital Affiliated to Hubei University for Nationalities, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-06Accepted:2021-09-04Online:2022-10-28Published:2022-03-29 -
Contact:Chen Wenge, Chief physician, Minda Hospital Affiliated to Hubei University for Nationalities, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Huang Gao, Attending physician, Master, Minda Hospital Affiliated to Hubei University for Nationalities, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the Guiding Project of Hubei Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission, No. WJ2019F140 (to CWG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Gao, Xu Jun, Chen Wenge. Implantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-loaded platelet-rich plasma combined with extracorporeal shock wave in the repair of bone defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4812-4818.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
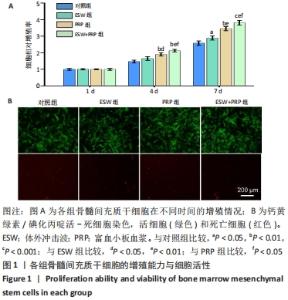
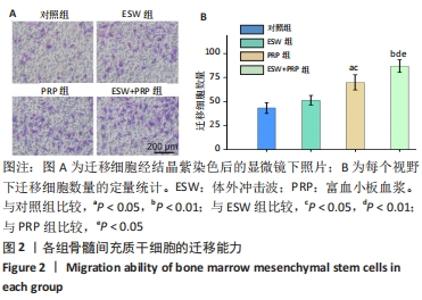
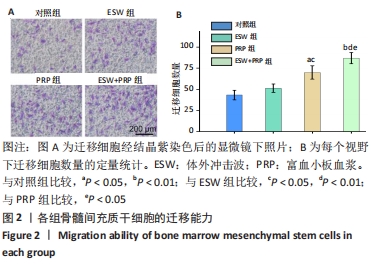
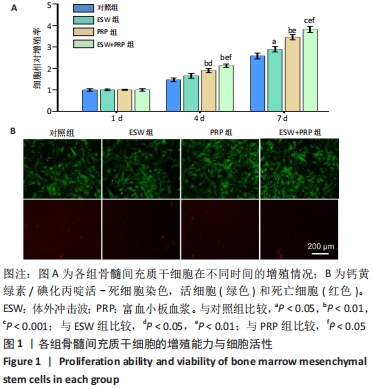
2.1 各组骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖、活性和迁移能力分析 将第4代骨髓间充质干细胞以2.0×104/孔种植在24孔培养板中,分别培养1,4,7 d后使用CCK-8法测定骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖情况,见图1A。结果表明:随着培养时间的延长,各组细胞增殖均发生明显增加。在种植当天(即第1天)时,各组间骨髓间充质干细胞的吸光度值差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。但是,在第4,7天,体外冲击波+富血小板血浆组与其他组比较差异均有显著性意义;富血小板血浆组细胞增殖也均优于对照组和体外冲击波组(P < 0.05)。单纯体外冲击波处理组与未处理对照组相比,在第4天时未见明显变化,但这种差异在第7天时变得显著(P < 0.05)。以上结果提示体外冲击波和富血小板血浆处理均有利于细胞增殖,尤其是联合两种处理方式时可显著促进骨髓间充质干细胞在体外增殖。 在培养3 d后进行钙黄绿素/碘化丙啶活-死细胞染色,见图1B,荧光图片清楚地显示,各组细胞均多为绿染的活细胞,红染的死细胞数量极少。结果显示不管是体外冲击波处理还是与富血小板血浆共培养,均不会降低细胞活性。"
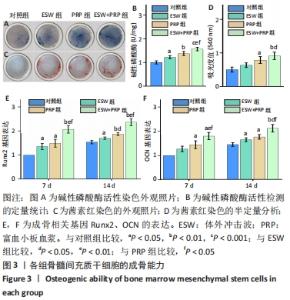
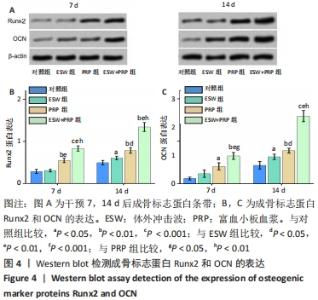
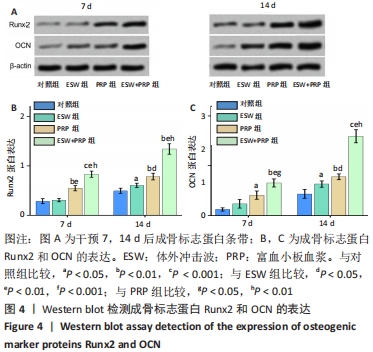
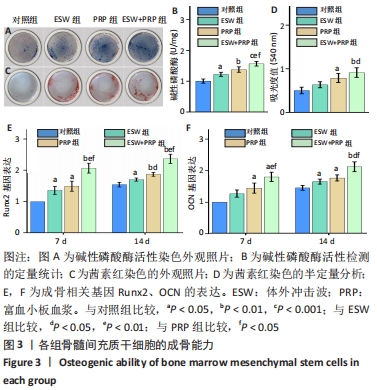
2.2 各组骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨能力 除了影响骨髓间充质干细胞的数量和活性外,成骨分化是骨再生的关键指标。经体外成骨诱导培养14 d后,体外冲击波+富血小板血浆组的碱性磷酸酶活性显著高于对照组(P < 0.001)、体外冲击波组(P < 0.01)和富血小板血浆组(P < 0.05)。同时,体外冲击波组和富血小板血浆组的碱性磷酸酶活性也显著高于对照组,说明不管是体外冲击波还是富血小板血浆处理都可以显著上调骨髓间充质干细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性,见图3A,B。茜素红染色是一种用于矿化的组织学染色,它可以识别沉积的钙结节。大体图像显示体外冲击波和/或富血小板血浆处理组的钙沉积斑点较对照组更明显。对茜素红染色结果进行半定量分析进一步证实了这一变化:即在富血小板血浆组和体外冲击波+富血小板血浆组检测到明显的钙沉积量,见图3C,D。 成骨诱导培养7,14 d后,体外冲击波 +富血小板血浆组的Runx2和OCN基因表达量均较其他组明显上调,差异有显著性意义;而体外冲击波组和富血小板血浆组Runx2和OCN的基因表达量也显著高于对照组;成骨相关基因表达的差异仅在第14天时富血小板血浆组高于体外冲击波组 (P < 0.05),以上研究结果说明体外冲击波和/或富血小板血浆处理可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨相关基因的表达,见图3E,F。"
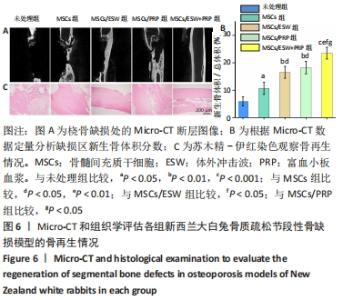
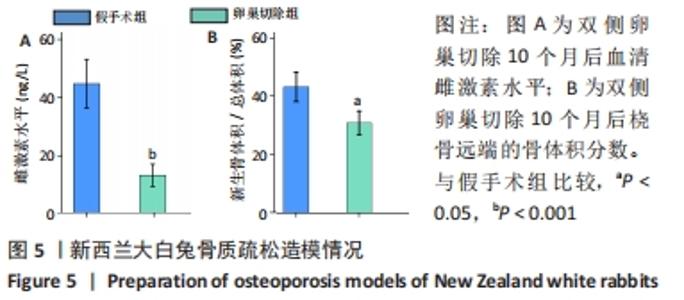
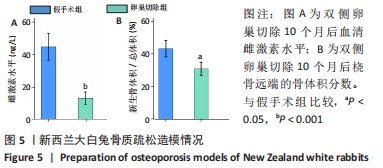
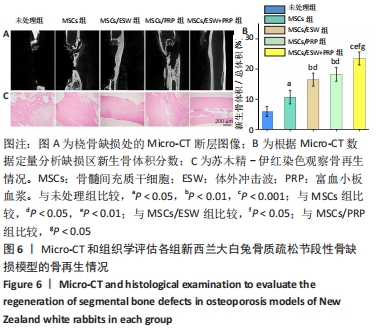
2.4 影像学和组织学评估节段性骨缺损的再生情况 术后12周采用Micro-CT进行影像学检查,未处理组骨再生情况最差,出现明显节段性骨不连;单纯骨髓间充质干细胞组骨再生也相对受限,出现部分再生后两断端髓腔封闭,也出现骨不连情况;骨髓间充质干细胞/体外冲击波组一侧骨皮质连续再生,另一侧皮质再生不完全;骨髓间充质干细胞/富血小板血浆组的节段性骨缺损修复较好,仅残留少量缺损;而骨髓间充质干细胞/体外冲击波+富血小板血浆组几乎完全修复,并实现髓腔再通,见图6A。各组的骨体积/总体积比值分别为(5.93±1.67)%,(10.72±2.24) %,(16.52±2.16)%,(18.26±2.27)%和(23.53±2.15)%,见图6B。 苏木精-伊红染色组织学评价显示,未处理组和单纯骨髓间充质干细胞组的骨缺损断端间隙被纤维组织填充,术后12周原始骨与纤维组织的界面清晰可见;相比之下,骨髓间充质干细胞/体外冲击波组和骨髓间充质干细胞/富血小板血浆组缺损处再生的皮质骨部分连续,可见缺损部位少量成熟骨痂;而骨髓间充质干细胞/体外冲击波+富血小板血浆组双侧皮质骨再生明显,形成连续结构,缺损区见完全骨性愈合,骨组织成熟,与周围原始骨组织结构相似,实现较好的再生,见图6C。这些结果表明,骨髓间充质干细胞、体外冲击波和富血小板血浆均可部分促进骨质疏松节段性骨缺损的再生,3者的联合使用能获得一个较为满意的骨愈合效果。"
| [1] WANG J, YIN Q, GU S, et al. Induced membrane technique in the treatment of infectious bone defect: A clinical analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(3):535-539. [2] ANGERAME MR, JENNINGS JM, HOLST DC, et al. Management of Bone Defects in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty with Use of a Stepped, Porous-Coated Metaphyseal Sleeve. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2019;9(2):e14. [3] QIAO S, SHENG Q, LI Z, et al. 3D-printed Ti6Al4V scaffolds coated with freeze-dried platelet-rich plasma as bioactive interface for enhancing osseointegration in osteoporosis. Materials & Design. 2020; 194:108825. [4] HA CW, PARK YB. Underestimation and undertreatment of osteoporosis in patients awaiting primary total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(8):1109-1114. [5] POLYZOS SA, ANASTASILAKIS AD, EFSTATHIADOU ZA, et al. Postmenopausal osteoporosis coexisting with other metabolic diseases: Treatment considerations. Maturitas. 2021;147:19-25. [6] WU D, MAO F, YUAN B, et al. Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPPO) Combined with Onionskin-Like Autologous Bone Grafting: A New Technique for Treatment of Tibial Nonunion. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:5997-6006. [7] LENG Y, REN G, CUI Y, et al. Platelet-rich plasma-enhanced osseointegration of decellularized bone matrix in critical-size radial defects in rabbits. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(5):198. [8] BALDWIN P, LI DJ, AUSTON DA, et al. Autograft, Allograft, and Bone Graft Substitutes: Clinical Evidence and Indications for Use in the Setting of Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33(4):203-213. [9] ALSHIHRI A, NIU W, KÄMMERER PW, et al. The effects of shock wave stimulation of mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, and differentiation in an injectable gelatin matrix for osteogenic regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(11):1630-1640. [10] CHEN Y, XU J, HUANG Z, et al. An Innovative Approach for Enhancing Bone Defect Healing Using PLGA Scaffolds Seeded with Extracorporeal-shock-wave-treated Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BMSCs). Sci Rep. 2017;7:44130. [11] YAMAKAWA J, HASHIMOTO J, TAKANO M, et al. The Bone Regeneration Using Bone Marrow Stromal Cells with Moderate Concentration Platelet-Rich Plasma in Femoral Segmental Defect of Rats. Open Orthop J. 2017;11:1-11. [12] WALMSLEY GG, RANSOM RC, ZIELINS ER, et al. Stem Cells in Bone Regeneration. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):524-529. [13] LU Z, KLEINE-NULEND J, LI B. Bone Microenvironment, Stem Cells, and Bone Tissue Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:1315243. [14] NWEKE CE, STEGEMANN JP. Modular microcarrier technologies for cell-based bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(18):3972-3984. [15] BAI H, ZHAO Y, WANG C, et al. Enhanced osseointegration of three-dimensional supramolecular bioactive interface through osteoporotic microenvironment regulation. Theranostics. 2020;10(11):4779-4794. [16] SHANG F, YU Y, LIU S, et al. Advancing application of mesenchymal stem cell-based bone tissue regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):666-683. [17] JU T, ZHAO Z, MA L, et al. Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate-Enhanced Calvarial Regeneration by Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on a Hydroxyapatite/Gelatin Scaffold. ACS Omega. 2021;6(21): 13684-13694. [18] SONG JE, TIAN J, KOOK YJ, et al. A BMSCs-laden quercetin/duck’s feet collagen/hydroxyapatite sponge for enhanced bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(3):784-794. [19] ALBANESE A, LICATA ME, POLIZZI B, et al. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in dental and oral surgery: from the wound healing to bone regeneration. Immun Ageing. 2013;10(1):23. [20] DOS SANTOS RG, SANTOS GS, ALKASS N, et al. The regenerative mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma: A review. Cytokine. 2021;144: 155560. [21] WANG K, LI J, WANG Y, et al. Orchestrated cellular, biochemical, and biomechanical optimizations endow platelet-rich plasma-based engineered cartilage with structural and biomechanical recovery. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):3824-3838. [22] SYAM S, CHANG CW, LAN WC, et al. An Innovative Bioceramic Bone Graft with Platelet-Rich Plasma for Rapid Bone Healing and Regeneration in a Rabbit Model. Model Appl Sci. 2021;11(11):5271. [23] KOGA T, NAKATANI Y, OHBA S, et al. Clinical Safety Assessment of Autologous Freeze-Drying Platelet-Rich Plasma for Bone Regeneration in Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation: A Pilot Study. J Clin Med. 2021; 10(8):1678. [24] LI G, SHEN W, TANG X, et al. Combined use of calcium phosphate cement, mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma for bone regeneration in critical-size defect of the femoral condyle in mini-pigs. Regen Med. 2021;16(5):451-464. [25] KOBAYASHI M, CHIJIMATSU R, YOSHIKAWA H, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy accelerates endochondral ossification and fracture healing in a rat femur delayed-union model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;530(4):632-637. [26] ÖZKAN E, BEREKET MC, ÖNGER ME, et al. The Effect of Unfocused Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Bone Defect Healing in Diabetics. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(4):1081-1086. [27] SILVEIRA A, KOENIG JB, ARROYO LG, et al. Effects of unfocused extracorporeal shock wave therapy on healing of wounds of the distal portion of the forelimb in horses. Am J Vet Res. 2010;71(2):229-234. [28] SATHISHKUMAR S, MEKA A, DAWSON D, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy induces alveolar bone regeneration. J Dent Res. 2008; 87(7):687-691. [29] JEON YR, JUNG BK, ROH TS, et al. Comparing the Effect of Nonactivated Platelet-Rich Plasma, Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on Calvarial Bone Regeneration. J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(2):317-321. [30] ORYAN A, ALIDADI S, MOSHIRI A. Platelet-rich plasma for bone healing and regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(2):213-232. [31] XU JK, CHEN HJ, LI XD, et al. Optimal intensity shock wave promotes the adhesion and migration of rat osteoblasts via integrin β1-mediated expression of phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287(31):26200-26212. [32] SUHR F, DELHASSE Y, BUNGARTZ G, et al. Cell biological effects of mechanical stimulations generated by focused extracorporeal shock wave applications on cultured human bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(2):951-964. [33] HESSELER MJ, SHYAM N. Platelet-rich plasma and its utility in the treatment of acne scars: A systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(6):1730-1745. [34] FERNANDES G, YANG S. Application of platelet-rich plasma with stem cells in bone and periodontal tissue engineering. Bone Res. 2016;4: 16036. [35] LENG Y, YANG F, WANG Q, et al. Material-based therapy for bone nonunion. Mater Design. 2019;183:108161. [36] 左秀芹,尹飒飒,谢惠敏,等.富血小板血浆在肌骨修复领域应用的适用性与相关规范 [J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(20):3239-3245. [37] XIE H, CAO L, YE L, et al. Autogenous bone particles combined with platelet-rich plasma can stimulate bone regeneration in rabbits. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):279. |
| [1] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [2] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [3] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [4] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [5] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [6] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [7] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [8] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [9] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [10] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [11] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [12] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [13] | Peng Kun. Improvement of the treatment effect of osteoporotic fractures: research status and strategy analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 980-984. |
| [14] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [15] | Ou Liang, Kong Dezhong, Xu Daoqing, Ni Jing, Fu Xingqian, Huang Weichen. Comparative clinical efficacy of polymethyl methacrylate and self-solidifying calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 649-656. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||