Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (25): 4010-4015.doi: 10.12307/2022.407
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to promote platelet plasma coagulation
Liu Chao1, 2, Zhang Lijun1, Du Xinjie1, Xu Qian3, Lü Hongjuan3, Fan Dongmei3, Tian Huanling2, Huang Jian2, Huang Yuxiang2
- 1Linyi Women and Children Hospital, Linyi 276000, Shandong Province, China; 2Allcare Biomedical Development, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China; 3Qingdao Women and Children’s Hospital, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266011, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2021-02-10Accepted:2021-03-31Online:2022-09-08Published:2022-01-25 -
Contact:Huang Yuxiang, MD, Allcare Biomedical Development, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Chao, Master, Linyi Women and Children Hospital, Linyi 276000, Shandong Province, China; Allcare Biomedical Development, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China Zhang Lijun, Chief physician, Linyi Women and Children Hospital, Linyi 276000, Shandong Province, China Liu Chao and Zhang Lijun contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the Major Research & Development Project of Shandong Province, No. 2018GSF118121 (to ZLJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Chao, Zhang Lijun, Du Xinjie, Xu Qian, Lü Hongjuan, Fan Dongmei, Tian Huanling, Huang Jian, Huang Yuxiang. Mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to promote platelet plasma coagulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4010-4015.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
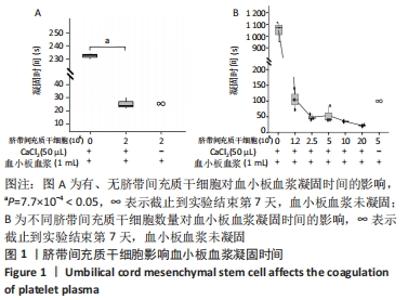
2.1 脐带间充质干细胞促进血小板血浆凝固 血小板血浆形成凝胶样的过程,本质上是凝血反应,其过程由一系列凝血因子共同发挥作用,通过激活凝血酶原将可溶的纤维蛋白原转变成不可溶纤维蛋白,最终交联的纤维蛋白形成凝胶样结构[18],其中Ca2+作为凝血因子Ⅳ在凝血过程中发挥重要作用。体外采集的血小板血浆,在肝素钠、EDTA等抗凝剂的作用下,血浆一般不会发生凝固现象,通过向血浆中添加一定比例的Ca2+可以重新激活凝血反应。利用血小板血浆凝固的这一个特性,可以作为干细胞使用过程的凝胶支持材料。实验过程中发现,将脐带间充质干细胞添加至血小板血浆中,血浆和脐带间充质干细胞都可以稳定保存,但是在CaCl2刺激下,含有脐带间充质干细胞的血浆能够更快地凝固,实验数据表明含有脐带间充质干细胞的血浆凝固速度是单纯血浆组凝固速度的10倍左右,见图1A。通过设置血浆中不同梯度的干细胞数量,发现血小板血浆凝胶形成时间与脐带间充质干细胞数量呈现相关性,见图1B。基于以上实验数据表明,脐带间充质干细胞能够加速血小板血浆的凝固过程。"
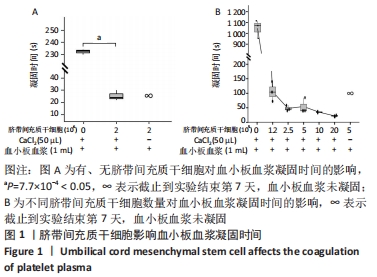
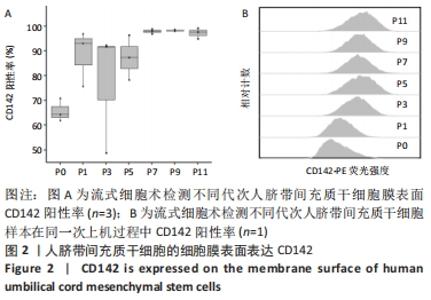
2.2 脐带间充质干细胞随着传代次数的增加高表达CD142 为进一步研究脐带间充质干细胞促进血小板血浆凝固的机制。将凝血机制中已经报道的凝血因子逐个调查,分析发现CD142(Symbol名称F3)作为凝血因子的辅助因子,能够结合凝血因子Ⅶa从而促进凝血过程,通常情况下血管内不含有CD142,当血管破损组织中的CD142进入血管中,进而启动凝血过程。由于CD142 RNA存在可变剪切,可以产生细胞外可溶蛋白和跨膜蛋白这两种蛋白形式,这两种蛋白均具有凝血因子辅酶作用,其中CD142的跨膜蛋白是目前已知的唯一一种定位于细胞膜的凝血因子[19]。由此猜想脐带间充质干细胞可能通过CD142促进凝血。通过流式细胞术检测到脐带间充质干细胞的膜表面表达CD142,见图2。"
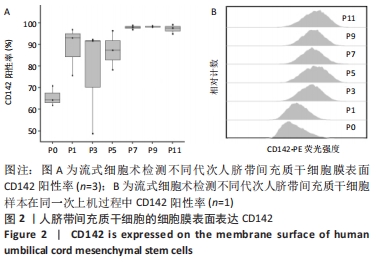
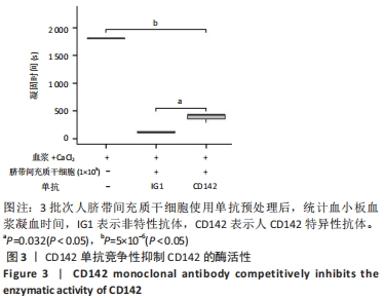
并且当脐带间充质干细胞处于较低代次时,不同人来源间充质干细胞表达CD142存在较大的个体差异,间充质干细胞从P0代到P1代CD142的表达有一个激增过程,之后随着干细胞传代次数增加,干细胞表面的CD142也逐渐趋于稳定高表达,见图2,提示脐带间充质干细胞表达的CD142有可能参与到凝血过程。 2.3 人脐带间充质干细胞表面CD142是加速血小板血浆凝固的主要机制 为验证人脐带间充质干细胞表面的CD142是否是加速血小板血浆凝固的主要原因。在实验中选择CD142抗体靶向人脐带间充质干细胞膜表面的CD142蛋白,由于抗体与CD142蛋白结合,通过空间位阻可能抑制CD142发挥促凝血的功能,实验结果表明CD142单抗可以显著延长人脐带间充质干细胞促进血小板血浆的凝固时间,见图3,由此推测CD142是人脐带间充质干细胞促进血小板血浆凝固的一个主要机制。"
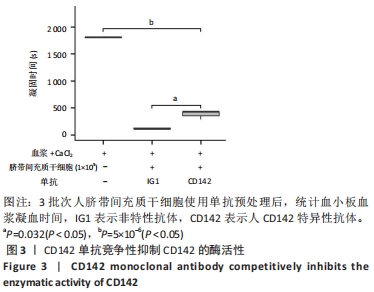

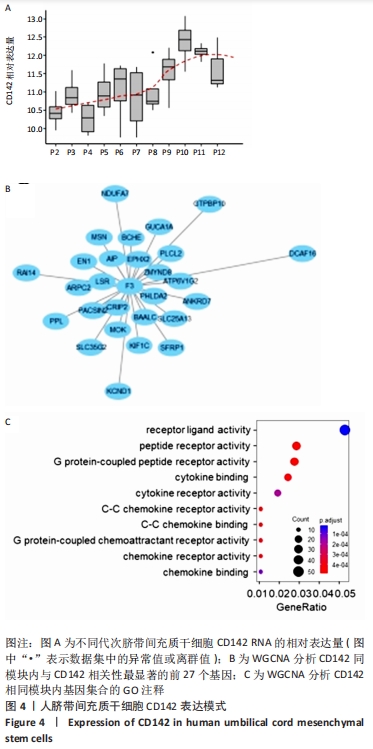
2.4 人脐带间充质干细胞CD142表达调控模式 通过上述研究了解到,人脐带间充质干细胞表达CD142并随着细胞传代而增加,那么体外培养的人脐带间充质干细胞为何趋向于表达CD142,需要进一步研究。 许多研究表明CD142在许多肿瘤中高表达,主要机制是由于肿瘤处于厌氧环境,这种条件能够刺激CD142的转录因子表达[20],但是相对于体内2%-8%的氧分压[21],在体外正常培养的细胞处于一种高氧环境。为探究人脐带间充质干细胞CD142的表达调控模式,检索GEO数据库发现GSE119987数据收集了4例脐带间充质干细胞(男2例,女2例)[22],表达矩阵经过背景矫正以及去除批次效应,剔除未收集足量RNA用于检测的样品P1代和P13代数据,根据表达量和代次拟合回归曲线,可以观察到细胞随着传代次数增加,CD142在基因表达水平整体呈现上调趋势,从P8代开始CD142快速上调,见图4A,这与人脐带间充质干细胞CD142蛋白水平的表达趋势基本一致。 为进一步分析人脐带间充质干细胞表达CD142对干细胞的影响,研究过程选择GEO数据中CD142高表达的P10,P11,P12代次样品,进行WGCNA分析,找到与CD142表达相似的基因集,见图4B,并对模块内的基因集合做GO注释,通过注释发现模块内的基因主要与受体激活以及细胞趋化性相关,见图4C。"
| [1] LENG Z, ZHU R, HOU W, et al. Transplantation of ACE2- Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves the Outcome of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Aging Dis. 2020;11(2):216-228. [2] CHEN J, HU C, CHEN L, et al. Clinical Study of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Induced by Epidemic Influenza A (H7N9) Infection: A Hint for COVID-19 Treatment. Engineering (Beijing). 2020;6(10):1153-1161. [3] GALIPEAU J, SENSÉBÉ L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):824-833. [4] BARBASH IM, CHOURAQUI P, BARON J, et al. Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infarcted myocardium: feasibility, cell migration, and body distribution. Circulation. 2003; 108(7):863-868. [5] JI SZ, XIAO SC, LUO PF, et al. An epidermal stem cells niche microenvironment created by engineered human amniotic membrane. Biomaterials. 2011;32(31):7801-7811. [6] WANG X, JIANG B, SUN H, et al. Noninvasive application of mesenchymal stem cell spheres derived from hESC accelerates wound healing in a CXCL12-CXCR4 axis-dependent manner. Theranostics. 2019;9(21):6112-6128. [7] JUNG HH, PARK K, HAN DK. Preparation of TGF-β1-conjugated biodegradable pluronic F127 hydrogel and its application with adipose-derived stem cells. J Control Release. 2010;147(1):84-91. [8] SU J, DING L, CHENG J, et al. Transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells combined with collagen scaffolds restores ovarian function in a rat model of premature ovarian insufficiency. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(5): 1075-1086. [9] LI L, DUAN X, FAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Combination with Hyaluronic Acid for Articular Cartilage Defects. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9900. [10] MARMOTTI A, ROSSI R, CASTOLDI F, et al. PRP and articular cartilage: a clinical update. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:542502. [11] ABRAMS GD, FRANK RM, FORTIER LA, et al. Platelet-rich plasma for articular cartilage repair. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2013;21(4):213-219. [12] PAVLOVIC V, CIRIC M, JOVANOVIC V, et al. Platelet Rich Plasma: a short overview of certain bioactive components. Open Med (Wars). 2016;11(1):242-247. [13] HERSANT B, SID-AHMED M, BRAUD L, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves the Wound Healing Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Paracrine and Metabolism Alterations. Stem Cells Int. 2019; 2019:1234263. [14] 刘超,张丽君,陶昊,等.基于细胞生物学方法比较5种不同组织来源间充质干细胞的特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(33): 5334-5340. [15] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559. [16] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. ClusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012; 16(5):284-287. [17] OTASEK D, MORRIS JH, BOUÇAS J, et al. Cytoscape Automation: empowering workflow-based network analysis. Genome Biol. 2019; 20(1):185. [18] SCHENONE M, FURIE BC, FURIE B. The blood coagulation cascade. Curr Opin Hematol. 2004;11(4):272-277. [19] MANN KG, KRUDYSZ-AMBLO J, BUTENAS S. Tissue factor controversies. Thromb Res. 2012;129 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S5-7. [20] SUN L, LIU Y, LIN S, et al. Early growth response gene-1 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α affect tumor metastasis via regulation of tissue factor. Acta Oncol. 2013;52(4):842-851. [21] MOHYELDIN A, GARZÓN-MUVDI T, QUIÑONES-HINOJOSA A. Oxygen in stem cell biology: a critical component of the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(2):150-161. [22] WIESE DM, RUTTAN CC, WOOD CA, et al. Accumulating Transcriptome Drift Precedes Cell Aging in Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Serially Cultured to Replicative Senescence. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(9):945-958. [23] BEVILACQUA MP, POBER JS, MAJEAU GR, et al. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1984;160(2):618-623. [24] FOLCO EJ, MAWSON TL, VROMMAN A, et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induce Endothelial Cell Activation and Tissue Factor Production Through Interleukin-1α and Cathepsin G. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(8):1901-1912. [25] SASSA Y, HATA Y, MURATA T, et al. Functional role of Egr-1 mediating VEGF-induced tissue factor expression in the retinal capillary endothelium. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2002;240(12):1003-1010. [26] FRIEDMAN R, BETANCUR M, BOISSEL L, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: adjuvants for human cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13(12):1477-1486. [27] 刘婷.脐带间充质干细胞体外扩增研究及其分泌细胞因子的高通量筛查[D].北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院, 2012. [28] XU J, ZGHEIB C, HODGES MM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells correct impaired diabetic wound healing by decreasing ECM proteolysis. Physiol Genomics. 2017;49(10):541-548. [29] ALMALKI SG, AGRAWAL DK. Effects of matrix metalloproteinases on the fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):129. [30] TATSUMI K, OHASHI K, MATSUBARA Y, et al. Tissue factor triggers procoagulation in transplanted mesenchymal stem cells leading to thromboembolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;431(2):203-209. [31] ANTEBI B, RODRIGUEZ LA 2ND, WALKER KP 3RD, et al. Short-term physiological hypoxia potentiates the therapeutic function of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):265. [32] REDONDO-CASTRO E, CUNNINGHAM CJ, MILLER J, et al. Changes in the secretome of tri-dimensional spheroid-cultured human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro by interleukin-1 priming. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018; 9(1):11. [33] TOBITA M, TAJIMA S, MIZUNO H. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma: stem cell transplantation methods that enhance stemness. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:215. [34] MISHRA A, TUMMALA P, KING A, et al. Buffered platelet-rich plasma enhances mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2009;15(3):431-435. [35] MOLL G, ANKRUM JA, KAMHIEH-MILZ J, et al. Intravascular Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cell Therapy Product Diversification: Time for New Clinical Guidelines. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25(2):149-163. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [4] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [5] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [6] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [7] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [8] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [9] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [10] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [11] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [12] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [13] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [15] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

