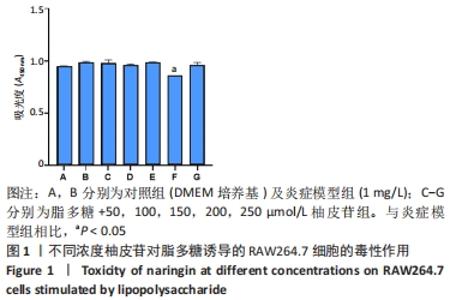
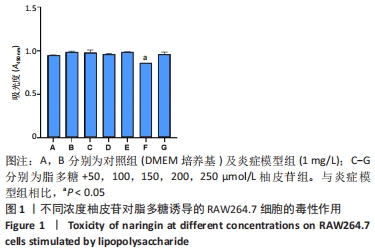
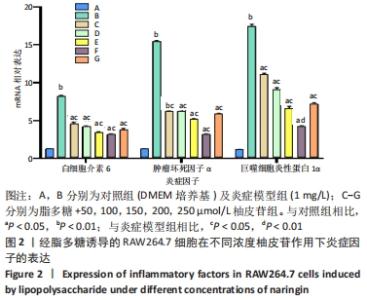
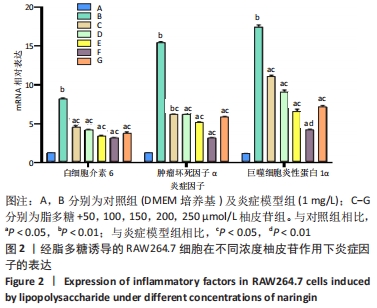
[1] 陆定贵, 林佳杰, 姚顺晗,等. 关节软骨损伤修复的临床研究进展[J]. 微创医学,2021,16(4):538-541.
[2] HUNTER DJ, SCHOFIELD D, CALLANDER E. The individual and socioeconomic impact of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10(7):437-441.
[3] SOLDATOS NK, STYLIANOU P, KOIDOU VP, et al. Limitations and options using resorbable versus nonresorbable membranes for successful guided bone regeneration. Quintessence Int. 2017;48(2):131-147.
[4] GUAN J, GAN L, JIN D, et al. Overexpression of circ_0021739 in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Women with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Is Associated with Reduced Expression of microRNA-194-5p in Osteoclasts. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e929170.
[5] HUANG MY, TU CE, WANG SC, et al. Corylin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response and attenuates the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018;18(1): 221.
[6] YOSHIDA H, SUZUKI M, TANAKA K, et al. Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody prevents loss of bone structure and bone strength in collagen-induced arthritis mice. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018;47(5):384-391.
[7] JERZAK MM. Decreased Production of TNF-α and IL-6 Inflammatory Cytokines in Non-Pregnant Idiopathic RPL Women Immunomodulatory Effect of Sildenafil Citrate on the Cellular Response of Idiopathic RPL Women. J Clin Med. 2021;10(14):3115.
[8] WU AC, RAGGATT LJ, Alexander KA, et al. Unraveling macrophage contributions to bone repair. Bonekey Rep. 2013;2:373.
[9] WU H, CHENG K, GUO Q, et al. Mapping Knowledge Structure and Themes Trends of Osteoporosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:787228.
[10] ZHAO Y, LI Y, QU R, et al. Cortistatin binds to TNF-α receptors and protects against osteoarthritis. EBioMedicine. 2019;41:556-570.
[11] ILCHOVSKA DD, BARROW DM. An Overview of the NF-kB mechanism of pathophysiology in rheumatoid arthritis, investigation of the NF-kB ligand RANKL and related nutritional interventions. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(2):102741.
[12] 丁佩惠, 唐琪, 陈莉丽. 柚皮苷对小鼠成骨细胞MC3T3-E1增殖、分化和矿化的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志,2009,34(13):1712-1716.
[13] 张乐其, 柳毅, 徐高丽,等. 中药柚皮苷诱导成骨作用的研究进展[J]. 口腔医学,2016,36(3):277-280.
[14] KAWAGUCHI K, MARUYAMA H, HASUNUMA R, et al. Suppression of inflammatory responses after onset of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by oral administration of the Citrus flavanone naringin. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2011;33(4):723-729.
[15] VINCENZI A, GOETTERT I, SOUZA F. An evaluation of the effects of probiotics on tumoral necrosis factor (TNF-α) signaling and gene expression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021;57:27-38.
[16] JIANG J, YAN L, SHI Z, et al. Hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of total flavonoids of Qu Zhi Ke (peel of Citrus changshan-huyou) on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via modulation of NF-κB and MAPKs. Phytomedicine. 2019;64:153082.
[17] LV Z, WU W, GE S, et al. Naringin protects against perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced liver injury by modulating NRF2 and NF-κB in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;65:140-147.
[18] 谈济洲, 聂二民, 张春元,等. 锌离子对炎症微环境下成骨细胞成骨相关蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志,2016,51(8):486-490.
[19] CHEN M, LIU Q, XU Y, et al. The effect of LyPRP/collagen composite hydrogel on osteogenic differentiation of rBMSCs. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(1):rbaa053.
[20] 张勃昕,吉爱红,曹正垚, 等. miR-34a对人颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J]. 口腔生物医学,2019,10(1):1-5.
[21] WANG LM, ZHAO N, ZHANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits osteogenic differentiation of pre-osteoblasts by downregulation of EphB4 signaling via activated nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. J Periodontal Res. 2018;53(1):66-72.
[22] LIU S, ZHOU M, LI J, et al. LIPUS inhibited the expression of inflammatory factors and promoted the osteogenic differentiation capacity of hPDLCs by inhibiting the NF‐κB signaling pathway. J Periodontal Res. 2020;55(1):125-140.
[23] KANESHIRO S, EBINA K, HI K, et al. IL-6 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation through the SHP2/MEK2 and SHP2/Akt2 pathways in vitro. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(4):378-392.
[24] 周旭华, 陈发明, 陆港霞,等. 新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病血清单核细胞趋化蛋白-1与巨噬细胞炎性蛋白-1α的变化及临床意义[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志,2010,18(2):154-156.
[25] CAO Y, CHEN J, REN G, et al. Punicalagin Prevents Inflammation in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages by Inhibiting FoxO3a/Autophagy Signaling Pathway. Nutrients. 2019;11(11):2794.
[26] REN J , SU D , LI L , et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Aureusidin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via suppressing NF-κB and activating ROS- and MAPKs-dependent Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;387:114846.
[27] HAMEISTER R, LOHMANN CH, DHEEN ST, et al. The effect of TNF-α on osteoblasts in metal wear-induced periprosthetic bone loss. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(11):827-839.
[28] YANG C, LIU W, SHAN H, et al. Naringin inhibits titanium particles-induced up-regulation of TNF-α and IL-6 via the p38 MAPK pathway in fibroblasts from hip periprosthetic membrane. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(5):485-494.
[29] 宋囡,何文智,王智民,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在骨向分化的作用及中医药研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(1):95-99.
[30] NAMBI G. Does low level laser therapy has effects on inflammatory biomarkers IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-13 in osteoarthritis of rat models—a systemic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med Sci. 2021; 36(3):475-484.
[31] MADHU LN, KODALI M, ATTALURI S, et al. Melatonin improves brain function in a model of chronic Gulf War Illness with modulation of oxidative stress, NLRP3 inflammasomes, and BDNF-ERK-CREB pathway in the hippocampus. Redox Biol. 2021;43:101973.
[32] TAMAI R, SUZUKI K, MASHIMA I, et al. MPMBP down-regulates Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 ligand-induced proinflammatory cytokine production by inhibiting NF-κB but not AP-1 activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;79:106085.
[33] GIANNONI P, MARINI C, CUTRONA G, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells impair osteoblastogenesis and promote osteoclastogenesis: role of TNFα, IL-6 and IL-11 cytokines. Haematologica. 2021;106(10):2598-2612.
[34] KOMORI T. Functions of Osteocalcin in Bone, Pancreas, Testis, and Muscle. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7513.
[35] CHEN YN, WEI P, YU BS. Higher concentration of serum C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type I collagen is positively related with inflammatory factors in postmenopausal women with H-typehypertension and osteoporosis. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(6):1135-1141.
|