Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (14): 2139-2145.doi: 10.12307/2023.117
Previous Articles Next Articles
Rutin attenuates the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration in rats
Xu Dayong, Li Yunpeng, Wei Jingmei, Liu Ruyin
- Department of Spine Surgery, Henan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-24Accepted:2022-04-29Online:2023-05-18Published:2022-09-30 -
About author:Xu Dayong, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Henan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Henan Provincial Project for Traditional Chinese Medicine Top-notch Talents Training, No. 2019ZYBJ18 (to LRY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Dayong, Li Yunpeng, Wei Jingmei, Liu Ruyin. Rutin attenuates the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2139-2145.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
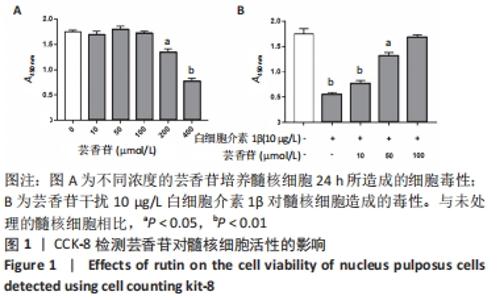
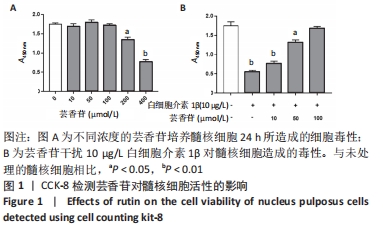
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用大鼠36只,分为3组,实验过程中无脱失,36只大鼠全部用于结果分析。 2.2 芸香苷对髓核细胞活性的影响 结果显示,芸香苷在10-100 μmol/L范围内对髓核细胞活性不影响,浓度增大到200 μmol/L时降低髓核细胞的活性(P < 0.05),当浓度进一步增大到400 μmol/L时,对髓核细胞产生明显的毒性(P < 0.01,见图1A)。因此,确定芸香苷在0-100 μmol/L范围内不会对髓核细胞造成毒性。 用芸香苷干扰白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞发现,芸香苷以剂量依赖性改善白细胞介素1β对髓核细胞造成的毒性,当芸香苷的处理浓度用100 μmol/L时,能够完全缓解10 μg/L的白细胞介素1β对髓核细胞造成的毒性(P > 0.05,见图1B)。因此,浓度为100 μmol/L的芸香苷应用于后续的研究。 "
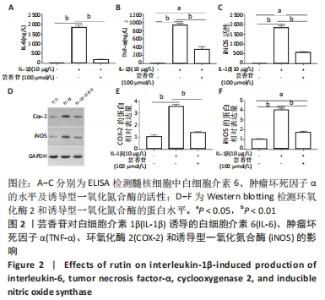
2.3 芸香苷抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞中炎症因子和氧化应激因子的表达 2.3.1 ELISA检测 与未处理的髓核细胞相比,白细胞介素1β诱导了白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达(P < 0.01)。有趣的是,芸香苷处理减少了白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和诱导型一氧化氮合酶的水平,从而消除了白细胞介素1β对髓核细胞的影响(见图2A-C)。 2.3.2 Western blotting检测 结果显示,环氧化酶2和诱导型一氧化氮合酶的蛋白表达水平在白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞中显著升高(见图2D),经芸香苷处理后环氧化酶2恢复正常水平,诱导型一氧化氮合酶的蛋白水平也显著降低(见图2E,F,P < 0.01)。"
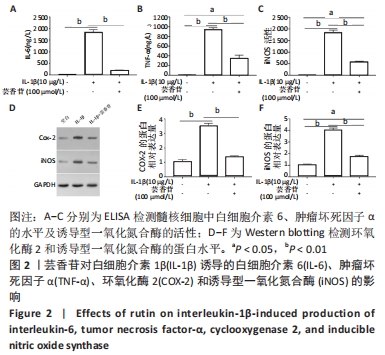
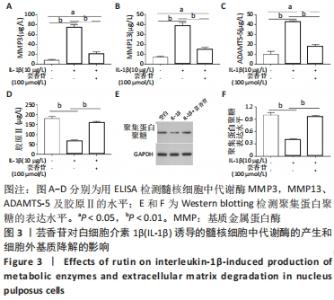
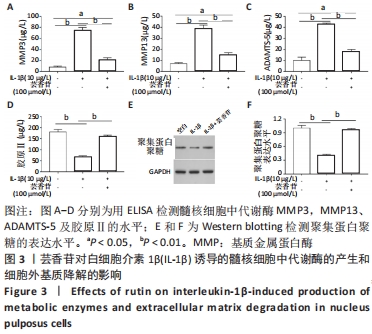
以上结果显示,在髓核细胞中,芸香苷抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的炎症因子和氧化应激因子的表达。因此,推测芸香苷可能通过抑制炎症反应和氧化应激的发生,从而抑制椎间盘退变的发生。 2.4 芸香苷抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞代谢酶的生成和基质降解 结果发现在白细胞介素1β的刺激下,髓核细胞中代谢酶基质金属蛋白酶3、13和ADAMTS-5的水平均显著上调(P < 0.01),胶原Ⅱ的水平显著减少(P < 0.01),经芸香苷处理代谢酶基质金属蛋白酶3(见图3A)、基质金属蛋白酶13(见图3B)和ADAMTS-5(见图3C)的水平均有所下调,胶原Ⅱ的水平显著上调(P > 0.05,见图3D)。此外,芸香苷处理抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞中聚集蛋白多糖的蛋白水平升高(见图3E和F)。这些结果提示,芸香苷能够抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞代谢酶的生成,缓解细胞外基质的降解。因此,推测芸香苷可能通过抑制基质降解缓解椎间盘退变的进展。 "
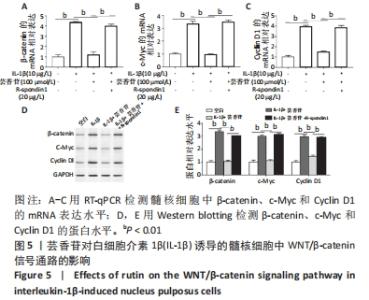
2.6 芸香苷抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的WNT/β-catenin信号通路的活化 2.6.1 RT-qPCR检测 研究发现,β-catenin、c-Myc和Cyclin D1在髓核细胞中的mRNA表达在白细胞介素1β的诱导下显著升高(P < 0.01),芸香苷处理降低了β-catenin(见图5A)、c-Myc(见图5B)和Cyclin D1(见图5C)的mRNA水平。 2.6.2 Western blotting结果 与白细胞介素1β刺激的髓核细胞相比,芸香苷(100 μmol/L)处理能够显著抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞中β-catenin、c-Myc和Cyclin D1的蛋白表达上调(见图5D,E,P < 0.01)。当芸香苷和WNT/β-catenin通路的激活剂R-spondin1同时处理髓核细胞时,芸香苷的作用被R-spondin1抵消(P > 0.05)。"
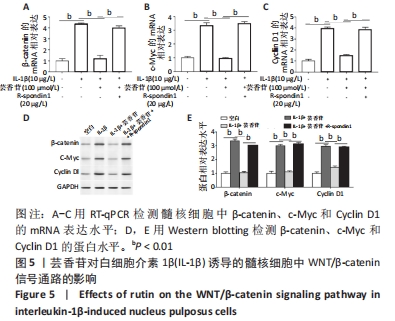
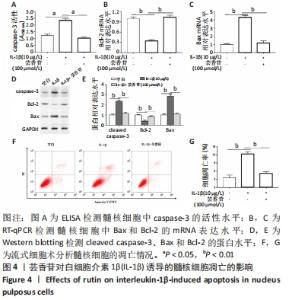
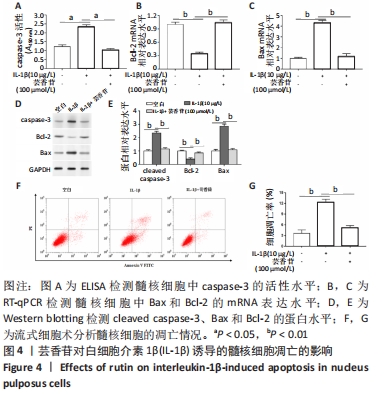
这些结果表明,芸香苷能够抑制髓核细胞中WNT/β-catenin信号通路的活化。 2.7 芸香苷改善针刺诱导的大鼠的椎间盘退变 为了进一步验证芸香苷对椎间盘退变的影响,用芸香苷干预针刺诱导的椎间盘退变模型大鼠,观察大鼠的椎间盘生理生化指标的变化。见图6。 2.7.1 MRI检测 经针刺诱导1周后,MRI观察发现针刺诱导的大鼠髓核组织内部不均匀且呈黑色(见图6A),即针刺诱导了大鼠的椎间盘退变,说明成功构建椎间盘退变大鼠模型。8周后,观察到针刺诱导显著增加了大鼠的Pfirrmann分级(P < 0.01,见图6B)。 2.7.2 ELISA检测 8周后,经检测发现与假手术组大鼠相比,椎间盘退变大鼠的髓核组织中炎症因子白细胞介素6的水平显著升高(见图6C,P < 0.01),细胞外基质发生了一定程度的降解。在芸香苷干预的椎间盘退变大鼠髓核组织中,白细胞介素6的水平表达显著降低(P < 0.01),细胞外基质的组成成分胶原Ⅱ(见图6D)的水平显著升高(P > 0.05);此外,还发现芸香苷能够降低椎间盘退变大鼠的髓核组织中caspase-3的活性(见图6G)。 2.7.3 Western blotting检测 在芸香苷干预的椎间盘退变大鼠髓核组织中,诱导型一氧化氮合酶的蛋白表达均显著降低(P < 0.05),聚集蛋白聚糖的蛋白表达显著升高(见图6E,F,P > 0.05)。 "
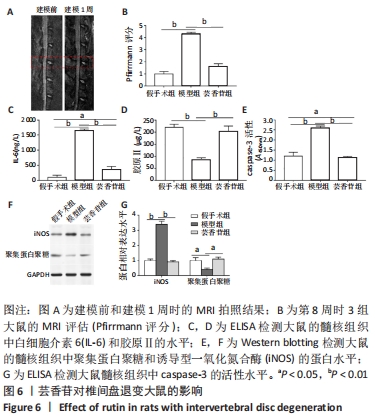
| [1] RIDER SM, MIZUNO S, KANG JD. Molecular Mechanisms of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018;3(1):1-11. [2] JENSEN CE, RIIS A, PETERSEN KD, et al. Economic evaluation of an implementation strategy for the management of low back pain in general practice. Pain. 2017;158(5):891-899. [3] FENG C, LIU H, YANG M, et al. Disc cell senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration: Causes and molecular pathways. Cell Cycle. 2016; 15(13):1674-1684. [4] SAMPARA P, BANALA RR, VEMURI SK, et al. Understanding the molecular biology of intervertebral disc degeneration and potential gene therapy strategies for regeneration: a review. Gene Therapy. 2018;25(2):67-82. [5] ZHANG XB, HU YC, CHENG P, et al. Targeted therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration: inhibiting apoptosis is a promising treatment strategy. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(13):2799-2813. [6] BASSO M, CAVAGNARO L, ZANIRATO A, et al. What is the clinical evidence on regenerative medicine in intervertebral disc degeneration?. Musculoskelet Surg. 2017;101(2):93-104. [7] VAN UDEN S, SILVA-CORREIA J, OLIVEIRA JM, et al. Current strategies for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: substitution and regeneration possibilities. Biomater Res. 2017;21:22. [8] DENT M, MATOBA N. Cancer biologics made in plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2020;61:82-88. [9] GANESHPURKAR A, SALUJA AK. The Pharmacological Potential of Rutin. Saudi Pharm J. 2017;25(2):149-164. [10] ENOGIERU AB, HAYLETT W, HISS DC, et al. Rutin as a Potent Antioxidant: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:6241017. [11] CHUA LS. A review on plant-based rutin extraction methods and its pharmacological activities. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;150(3):805-817. [12] CHE YJ, GUO JB, LIANG T, et al. Assessment of changes in the micro-nano environment of intervertebral disc degeneration based on Pfirrmann grade. Spine J. 2019;19(7):1242-1253. [13] NAVONE SE, MARFIA G, GIANNONI A, et al. Inflammatory mediators and signalling pathways controlling intervertebral disc degeneration. Histol Histopathol. 2017;32(6):523-542. [14] 赵赫, 俞兴, 唐向盛, 等. 炎性因子IL-1β、TNF-α与椎间盘退变关系的研究进展[J]. 中国骨伤,2017,30(9):866-871. [15] JIN H, WANG Q, WU J, et al. Baicalein Inhibits the IL-1beta-Induced Inflammatory Response in Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Attenuates Disc Degeneration In vivo. Inflammation. 2019;42(3):1032-1044. [16] SUN K, SUN X, SUN J, et al. Tissue Renin-Angiotensin System (tRAS) Induce Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Activating Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Reaction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021: 3225439. [17] WANG K, CHEN T, YING X, et al. Ligustilide alleviated IL-1beta induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;69:398-407. [18] ZHANG Y, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin modulates IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(22):10499-10512. [19] YANG M, PENG Y, LIU W, et al. Sirtuin 2 expression suppresses oxidative stress and senescence of nucleus pulposus cells through inhibition of the p53/p21 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;513(3): 616-622. [20] CHE H, LI J, LI Y, et al. p16 deficiency attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration by adjusting oxidative stress and nucleus pulposus cell cycle. Elife. 2020;9:e52570. [21] WANG B, KE W, WANG K, et al. Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Activated by Matrix Stiffness Regulates Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence and Apoptosis in Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8884922. [22] CAGLAYAN C, KANDEMIR FM, YILDIRIM S, et al. Rutin protects mercuric chloride-induced nephrotoxicity via targeting of aquaporin 1 level, oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2019;54:69-78. [23] QU S, DAI C, GUO H, et al. Rutin attenuates vancomycin-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis via suppression of apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress. Phytother Res. 2019;33(8):2056-2063. [24] ZHAN S, WANG K, SONG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates intervertebral disc degenerative changes via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):201. [25] WANG JJ, LIU XY, DU W, et al. RBMS3 delays disc degeneration by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(2):499-507. [26] KALITA B, RANJAN R, GUPTA ML. Combination treatment of podophyllotoxin and rutin promotes mouse Lgr5(+ ve) intestinal stem cells survival against lethal radiation injury through Wnt signaling. Apoptosis. 2019;24(3-4):326-340. |
| [1] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [2] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [3] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [4] | Lian Shilin, Zhang Yan, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Li Tusheng, Ding Yu. Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1199-1204. |
| [5] | Ye Xuwen, Gu Yong, Chen Liang. Curcumin loaded injectable microspheres retard progression of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1884-1891. |
| [6] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [7] | Liu Yapu, Su Yuanyuan, Liu Qi, Yang Zhou, Li Rong, Huang Zucheng, Huang Zhiping, Wu Xiaoliang, Zhu Qingan. Antioxidative stress of trihydroxyethyl rutin on cervical spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(36): 5868-5874. |
| [8] | Huang Fan, Di Anqi, Qiu Mingwang, Huang Chuyu, Li Xiaohui, Zhao Siyi, Fan Zhiyong, Wu Shan. Establishing a rat model of intervertebral disc degeneration using X-ray guidance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5652-5657. |
| [9] | Zhao Yunan, Zhang Haobo, Sun Tao, Yang Xuejun. Hydrogel-based growth factors and drugs in the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: problems and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5525-5533. |
| [10] | Guo Xiaopeng, Liu Yingsong, Shang Hui. Silk fibroin/nano hydroxyapatite composite combined with icariin can promote the proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into nucleus pulposus like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3528-3534. |
| [11] | Xiong Yang, Yang Yingli, Gao Yushan, Wang Xiumei, Yang Yongdong, Zhao Dingyan, Zhao He, Li Chuanhong, Yang Kaitan, Yu Xing. Histological changes of cervical disc tissue and underlying ossification mechanism in patients with cervical degenerative ossification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2868-2873. |
| [12] | Yin Xunlu, Jin Zhefeng, Zhu Liguo, Feng Minshan, Yu Jie, Wei Xu, Zhan Jiawen, Gao Chunyu, Yin He, Liang Long, Han Tao, Sun Kai, Xie Rui . Effect and mechanism of mechanical factors on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1816-1821. |
| [13] | Zhang Lei, Xiu Chunmei, Ni Li, Chen Jianquan. Identification and expression analysis of mouse nucleus pulposus specific markers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1669-1674. |
| [14] | Yu Dong, Liu Kan, Shi Zongting, Yang Xiaoxia, Liu Hengping, Zhang Qingfeng. Pathological changes of the cervical intervertebral discs and rules of migration and apoptosis in endplate chondrocytes in a rabbit model of dynamic disequilibrium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1675-1679. |
| [15] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||