Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 1669-1674.doi: 10.12307/2022.349
Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification and expression analysis of mouse nucleus pulposus specific markers
Zhang Lei1, Xiu Chunmei1, Ni Li2, Chen Jianquan1, 2
- 1Institute of Orthopedics, Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215008, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-02Revised:2021-03-04Accepted:2021-04-28Online:2022-04-18Published:2021-12-11 -
Contact:Chen Jianquan, MD, Professor, Institute of Orthopedics, Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215008, Jiangsu Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Ni Li, MD, Associate researcher, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhang Lei, Master candidate, Institute of Orthopedics, Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215008, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81902248 (to NL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Lei, Xiu Chunmei, Ni Li, Chen Jianquan. Identification and expression analysis of mouse nucleus pulposus specific markers[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1669-1674.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
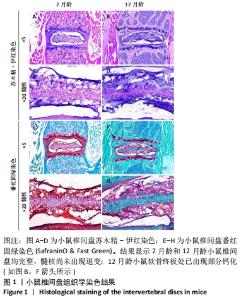
2.1 实验动物数量分析 2月龄及12月龄两组小鼠各5只,饲养过程至收取样本的过程中,未出现小鼠死亡的情况,即2月龄和12月龄两组结果各包括5个样本。 2.2 小鼠椎间盘组织学染色 首先通过组织学染色分析年轻小鼠(2月龄)和老年(12月龄)小鼠椎间盘组织的形态结构。苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,2月龄和12月龄小鼠椎间盘结构完整且大体相同,纤维环和髓核界限均清楚,见图1A-D;但两组小鼠也出现一些不同之处:①2月龄小鼠软骨终板无骨性结构,而12月龄小鼠软骨终板处已出现部分钙化,见图1B(箭头所示);②2月龄小鼠髓核细胞呈圆形和椭圆形,含囊泡样结构;而12月龄小鼠髓核细胞多为细长型,见图1C,D。番红固绿染色结果显示,2月龄和12月龄小鼠椎间盘均含有丰富的细胞外基质,见图1E-H。"

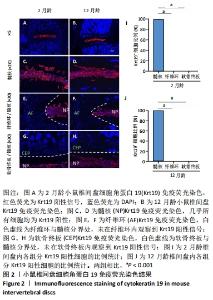
2.3 细胞角蛋白19在小鼠椎间盘中的表达情况 为了观察细胞角蛋白19在小鼠椎间盘内的表达情况,对2月龄和12月龄小鼠分别进行了免疫荧光染色,结果见图2。2 月龄小鼠椎间盘中,细胞角蛋白19阳性信号(红色荧光信号)仅出现于椎间盘中间髓核位置,见图2A,C;而在纤维环和软骨终板内未观察到任何细胞角蛋白19阳性信号,见图2E,G;定量结果进一步显示约99%的髓核细胞表现为细胞角蛋白19阳性,见图2I。与2 月龄小鼠类似,12 月龄小鼠椎间盘内,约99%的髓核组织细胞表达细胞角蛋白19阳性,见图2B,D, J;而在纤维环和软骨终板内仍未见明显的细胞角蛋白19阳性信号,见图2F,H。综上,细胞角蛋白19可特异性识别年轻及老龄小鼠的髓核细胞。"
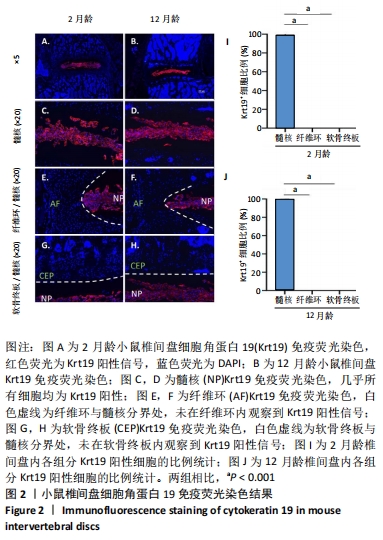
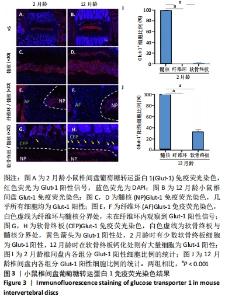
2.4 葡萄糖转运蛋白1在小鼠椎间盘中的表达情况 为了检测葡萄糖转运蛋白1在小鼠髓核中的特异性表达情况,随后对其进行了免疫荧光染色,见图3。免疫荧光结果显示,2月龄小鼠椎间盘内,葡萄糖转运蛋白1阳性信号主要位于椎间盘中间髓核组织处,见图3A,C;而在纤维环和软骨终板处则无明显的葡萄糖转运蛋白1表达,见图3A,E,G,统计结果进一步显示,葡萄糖转运蛋白1阳性细胞在髓核、纤维环和软骨终板中的占比分别为100%,0%和2%,见图3I。而12月龄小鼠椎间盘内,葡萄糖转运蛋白1仍大量表达在髓核内,见图3B,D;但在软骨终板钙化处也可观察到葡萄糖转运蛋白1阳性信号的出现,见图3H;而纤维环处始终未有阳性信号,见图3F,统计结果进一步确认了上述观察,见图3J。因此综上,葡萄糖转运蛋白1可特异性识别年轻小鼠的髓核细胞,但在老龄小鼠中,其髓核特异性有所下降。"

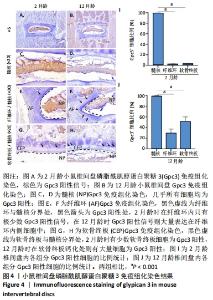
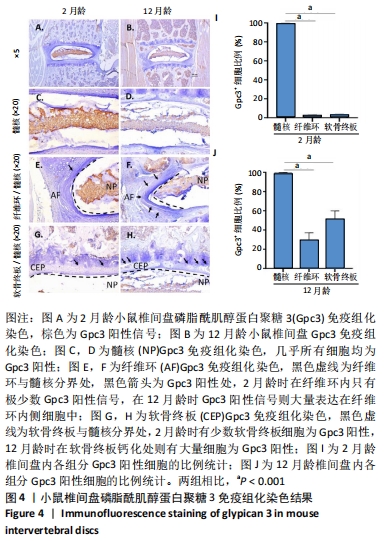
2.5 Gpc3在小鼠椎间盘中的表达情况 同样地,也利用免疫组化的方法观测了Gpc3的表达情况,见图4。2月龄小鼠椎间盘内,Gpc3阳性信号主要位于椎间盘中间髓核组织处,见图4A,C;而在纤维环和软骨终板处则无明显的Gpc3表达,见图4E,G;统计结果进一步显示,Gpc3阳性细胞在髓核、纤维环和软骨终板中的占比分别为99%,2%和2%,见图4I。12月龄小鼠椎间盘内,Gpc3仍大量表达在髓核内,见图4B,D;且在纤维环内侧细胞和软骨终板钙化处细胞中也有大量表达,见图4F,H;定量分析结果显示,Gpc3阳性细胞在髓核、纤维环和软骨终板中的占比分别为99%,29%和51%,见图4J。上述结果表明,Gpc3阳性可特异性识别年轻小鼠的髓核细胞,但在老龄小鼠中,其髓核特异性有所下降。"
| [1] GBD 2019 DISEASES AND INJURIES COLLABORATORS. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet (London, England). 2020;396(10258):1204-1222. [2] KIM HJ, GREEN DW. Adolescent back pain. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2008;20(1): 37-45. [3] LAVELLE WF, BIANCO A, MASON R, et al. Pediatric disk herniation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(11):649-656. [4] SÄÄKSJÄRVI S, KERTTULA L, LUOMA K, et al. Disc Degeneration of Young Low Back Pain Patients: A Prospective 30-year Follow-up MRI Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(19):1341-1347. [5] MAHER C, UNDERWOOD M, BUCHBINDER R. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet (London, England). 2017; 389(10070):736-747. [6] LONGO UG, LOPPINI M, DENARO L, et al. Rating scales for low back pain. Br Med Bull. 2010;94:81-144. [7] CIEZA A, CAUSEY K, KAMENOV K, et al. Global estimates of the need for rehabilitation based on the Global Burden of Disease study 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet (London, England). 2021;396(10267):2006-2017. [8] DIELEMAN JL, CAO J, CHAPIN A, et al. US Health Care Spending by Payer and Health Condition, 1996-2016. JAMA. 2020;323(9):863-884. [9] WUERTZ K, HAGLUND L. Inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disk degeneration and discogenic pain. Global Spine J. 2013;3(3):175-184. [10] LYU FJ, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7. [11] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组. 腰椎间盘突出症诊疗指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(8):477-487. [12] ZHAO L, MANCHIKANTI L, KAYE AD, et al. Treatment of Discogenic Low Back Pain: Current Treatment Strategies and Future Options-a Literature Review. Curr Pain Head Rep. 2019;23(11):86. [13] KREINER DS, MATZ P, BONO CM, et al. Guideline summary review: an evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. Spine J. 2020;20(7):998-1024. [14] Hanley EN Jr, Herkowitz HN, Kirkpatrick JS, et al. Debating the value of spine surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(5):1293-1304. [15] ADAMS MA, DOLAN P, MCNALLY DS. The internal mechanical functioning of intervertebral discs and articular cartilage, and its relevance to matrix biology. Matrix Biol. 2009;28(7):384-389. [16] DALY C, GHOSH P, JENKIN G. A Review of Animal Models of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Pathophysiology, Regeneration, and Translation to the Clinic. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:5952165. [17] LI Z, CHEN X, XU D, et al. Circular RNAs in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(6):e12704. [18] ZHANG Y, YANG B, WANG J, et al. Cell Senescence: A Nonnegligible Cell State under Survival Stress in Pathology of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:9503562. [19] CHOI H, JOHNSON ZI, RISBUD MV. Understanding nucleus pulposus cell phenotype: a prerequisite for stem cell based therapies to treat intervertebral disc degeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;10(4):307-316. [20] SUN B, LIAN M, HAN Y, et al. A 3D-Bioprinted dual growth factor-releasing intervertebral disc scaffold induces nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):179-190. [21] WEN T, WANG H, LI Y, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote the repair of intervertebral disc degeneration by transferring microRNA-199a. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex). 2021:1-15. [22] SINKEMANI A, WANG F, XIE Z, et al. Nucleus Pulposus Cell Conditioned Medium Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation into Nucleus Pulposus-Like Cells under Hypoxic Conditions. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:8882549. [23] SAKAI D, NAKAI T, MOCHIDA J, et al. Differential phenotype of intervertebral disc cells: microarray and immunohistochemical analysis of canine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus. Spine. 2009;34(14):1448-1456. [24] LEE C, SAKAI D, NAKAI T, et al. A phenotypic comparison of intervertebral disc and articular cartilage cells in the rat. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(12):2174-2185. [25] RICHARDSON S M, KNOWLES R, TYLER J, et al. Expression of glucose transporters GLUT-1, GLUT-3, GLUT-9 and HIF-1alpha in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;129(4):503-511. [26] ALINI M, EISENSTEIN SM, ITO K, et al. Are animal models useful for studying human disc disorders/degeneration? Eur Spine J. 2008;17(1):2-19. [27] MELROSE J, TESSIER S, RISBUD MV. Genetic murine models of spinal development and degeneration provide valuable insights into intervertebral disc pathobiology. Eur Cell Mater. 2021;41:52-72. [28] XU X, WANG D, ZHENG C, et al. Progerin accumulation in nucleus pulposus cells impairs mitochondrial function and induces intervertebral disc degeneration and therapeutic effects of sulforaphane. Theranostics. 2019;9(8):2252-2267. [29] BIAN Q, MA L, JAIN A, et al. Mechanosignaling activation of TGFβ maintains intervertebral disc homeostasis. Bone Res. 2017;5:17008. [30] NAKAMICHI R, ITO Y, INUI M, et al. Mohawk promotes the maintenance and regeneration of the outer annulus fibrosus of intervertebral discs. 2016;7:12503. [31] KATZ JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(suppl_2): 21-24. [32] KOS N, GRADISNIK L, VELNAR T. A Brief Review of the Degenerative Intervertebral Disc Disease. Med Arch (Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina). 2019;73(6):421-424. [33] VERGROESEN PP, KINGMA I, EMANUEL KS, et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(7):1057-1070. [34] NI L, ZHENG Y, GONG T, et al. Proinflammatory macrophages promote degenerative phenotypes in rat nucleus pulpous cells partly through ERK and JNK signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5362-5371. [35] TAVANA S, MASOUROS S, BAXAN N, et al. The Effect of Degeneration on Internal Strains and the Mechanism of Failure in Human Intervertebral Discs Analyzed Using Digital Volume Correlation (DVC) and Ultra-High Field MRI. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:610907. [36] DUDEK M, YANG N, RUCKSHANTHI JP, et al. The intervertebral disc contains intrinsic circadian clocks that are regulated by age and cytokines and linked to degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(3):576-584. [37] SAKAI D, NAKAMURA Y, NAKAI T, et al. Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1264. [38] JI ML, JIANG H, ZHANG XJ, et al. Preclinical development of a microRNA-based therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5051. [39] SAKAI D, NAKAI T, MOCHIDA J, et al. Differential phenotype of intervertebral disc cells: microarray and immunohistochemical analysis of canine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(14):1448-1456. [40] FUJITA N, MIYAMOTO T, IMAI J, et al. CD24 is expressed specifically in the nucleus pulposus of intervertebral discs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 338(4):1890-1896. [41] RUTGES J, CREEMERS LB, DHERT W, et al. Variations in gene and protein expression in human nucleus pulposus in comparison with annulus fibrosus and cartilage cells: potential associations with aging and degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(3):416-423. [42] MACIVER N, JACOBS S, WIEMAN H, et al. Glucose metabolism in lymphocytes is a regulated process with significant effects on immune cell function and survival. J Leukocyte Biol. 2008;84(4):949-957. [43] XIAO L, DING B, GAO J, et al. Curcumin prevents tension-induced endplate cartilage degeneration by enhancing autophagy. Life Sci. 2020;258:118213. [44] HAN Y, LI X, YAN M, et al. Oxidative damage induces apoptosis and promotes calcification in disc cartilage endplate cell through ROS/MAPK/NF-κB pathway: Implications for disc degeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;516(3):1026-1032. [45] TESSIER S, MADHU V, JOHNSON Z, et al. NFAT5/TonEBP controls early acquisition of notochord phenotypic markers, collagen composition, and sonic hedgehog signaling during mouse intervertebral disc embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 2019;455(2):369-381. [46] YAO G, YIN J, WANG Q, et al. Glypican-3 Enhances Reprogramming of Glucose Metabolism in Liver Cancer Cells. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:2560650. [47] ZHENG Y, FU X, LIU Q, et al. Characterization of Cre recombinase mouse lines enabling cell type-specific targeting of postnatal intervertebral discs. J Cell Physiol. 2019;10.1002/jcp.28166. [48] MOHANTY S, PINELLI R, PRICOP P, et al. Chondrocyte-like nested cells in the aged intervertebral disc are late-stage nucleus pulposus cells. Aging Cell. 2019; 18(5):e13006. [49] MEANS AL, XU Y, ZHAO A, et al. A CK19(CreERT) knockin mouse line allows for conditional DNA recombination in epithelial cells in multiple endodermal organs. Genesis (New York, NY: 2000). 2008;46(6):318-323. |
| [1] | Lu Pan, Zhang Chunlin, Wang Yongkui, Yan Xu, Dong Chao, Yue Yisen, Li Long, Zhu Andi. Volume changes of cervical herniated discs after open-door laminoplasty and conservative treatment as assessed by three-dimensional volume method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1395-1401. |
| [2] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [3] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [4] | Wang Jiajia, Liu Jie, Wang Min. Establishing a murine model of experimental apical periodontitis induced by Fusobacterium nucleatum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 176-181. |
| [5] | Ding Yan, Xiang Guangda, Meng Biying, Xu Xiaoli, Chen Yuefu. Establishment and identification of a myeloid-derived growth factor deficiency model in apolipoprotein E knockout mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2196-2201. |
| [6] | Hu Yihua, Yang Chunhua, Lu Yuanyuan, Sun Deyi. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with triptolide on transforming growth factor beta expression in synovium and synovial fluid in a mouse model of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2252-2258. |
| [7] | Guo Qiqi, Li Yi, Weng Huanze, Wang Qian, Jia Min. Advances in animal models of pulmonary fibrosis induced by biotic and abiotic factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2273-2278. |
| [8] | Yin Xunlu, Jin Zhefeng, Zhu Liguo, Feng Minshan, Yu Jie, Wei Xu, Zhan Jiawen, Gao Chunyu, Yin He, Liang Long, Han Tao, Sun Kai, Xie Rui . Effect and mechanism of mechanical factors on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1816-1821. |
| [9] | Yu Dong, Liu Kan, Shi Zongting, Yang Xiaoxia, Liu Hengping, Zhang Qingfeng. Pathological changes of the cervical intervertebral discs and rules of migration and apoptosis in endplate chondrocytes in a rabbit model of dynamic disequilibrium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1675-1679. |
| [10] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [11] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [12] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [13] | Wang Feng, Zhou Liyu, Saijilafu, Qi Shibin, Ma Yanxia, Wei Shanwen. CaMKII-Smad1 promotes axonal regeneration of peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1064-1068. |
| [14] | Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Expression of interleukin-24 in a mouse model of periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 679-684. |
| [15] | Yang Yang, Yao Yu, Shen Xiaotian, Liu Jiajia, Xue Jianhua. Expression and significance of interleukin-21 in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 690-694. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||