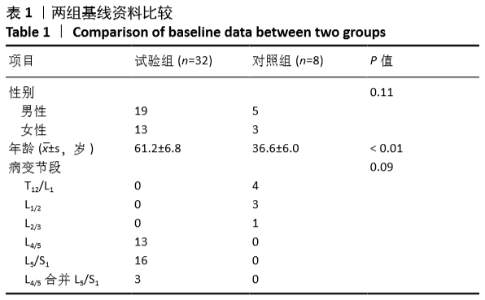
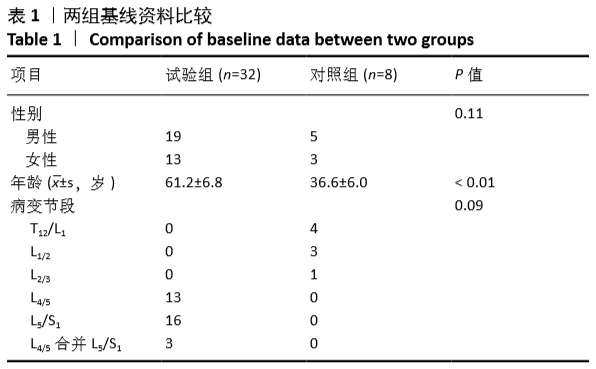
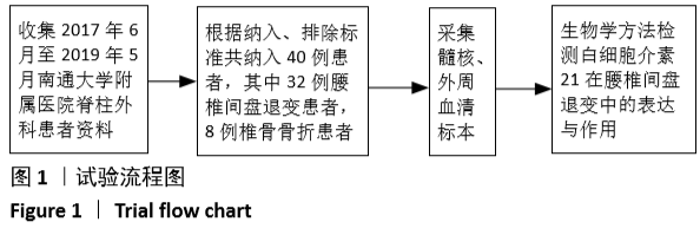
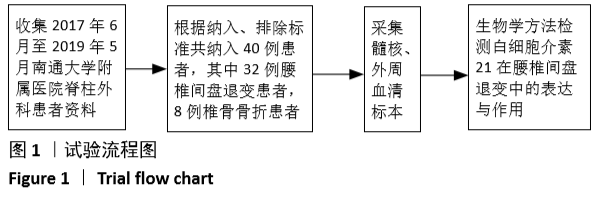
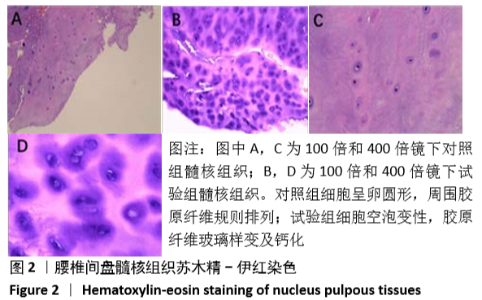
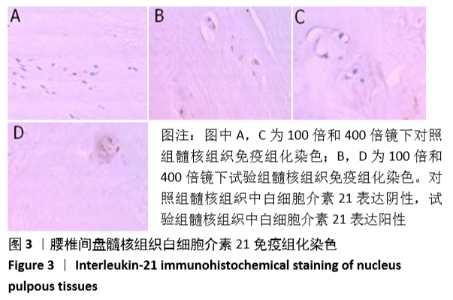
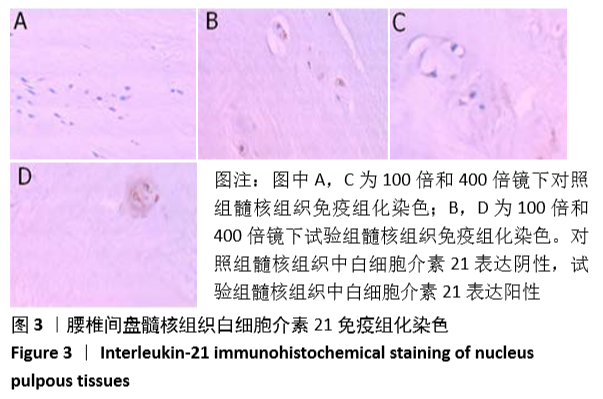
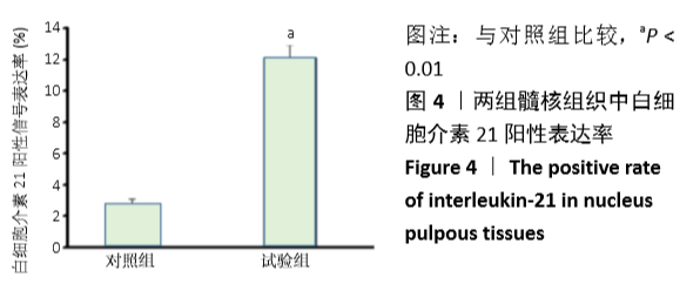
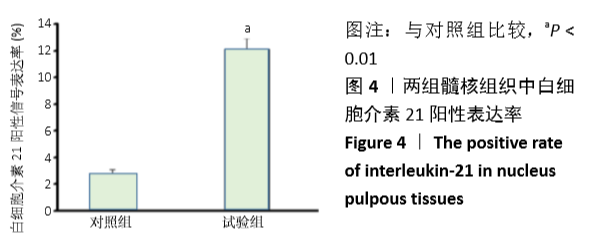
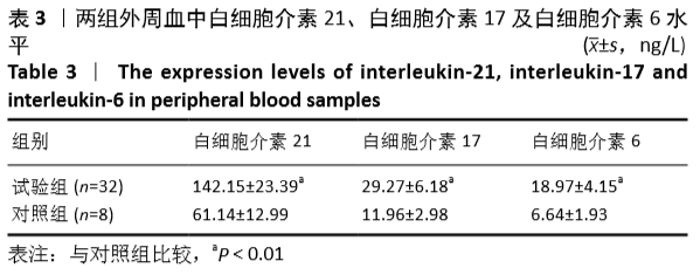
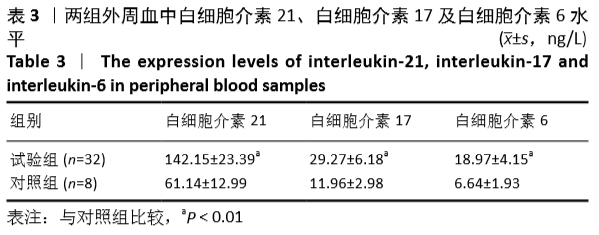
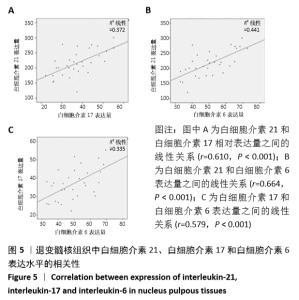
[1] LUOMA K, RIIHIMAKI H, LUUKKONEN R, et al. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine.2000;25(4):487-492.
[2] LAWSON LY, HARFE BD. Developmental mechanisms of intervertebral disc and vertebral column formation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol.2017;6(6): e283-e296.
[3] CAPOOR MN, RUZICKA F, MACHACKOVA T, et al. Prevalence ofpropionibacterium acnes in intervertebral discs ofpatients undergoing lumbar microdiscectomy:A Prospective Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e0161676.
[4] SOLLE JF, BIHIN B, KIRSCHVINK N, et al. Prevalence of age-related changes in ovine lumbar intervertebral discs during computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Comp Med.2016;66(4):300-307.
[5] LV X, LIU Y, ZHOU S, et al. Correlations between the feature of sagittal spinopelvic alignment and facet joint degeneration:a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2016;17(1):341.
[6] TANG P, ZHU P, JI WP. The NLRP3/Caspase-1/Interleukin-1βAxis Is Active in Human Lumbar Cartilaginous Endplate Degeneration. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2016;474(8):1827-1829.
[7] WANG YX, WANG JO, KAPLAR Z. Increased low back pain prevalence in females than in males after menopause age:evidences based on synthetic literature review. Quant Imaging Med Surg.2016;6(2):199-206.
[8] SHAO J, YU M, JIANG L, et al. Differences in calcification and osteogenic potential of herniated discs according to the severity of degeneration based on Pfirrmann grade:a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2016;17:191.
[9] WU X, LIU W, DUAN Z, et al. The Involvement of Protease Nexin-1 (PN1) in the Pathogenesis of Intervertebral Disc (IVD) Degeneration. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30563.
[10] GRANT MP, EPURE LM, Bokhari R,et al. Human cartilaginous endplate degeneration is induced by calcium and the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in the intervertebral disc. Eur Cell Mater.2016;32:137-151.
[11] ANITUA E, PADILLA S. Biologic therapies to enhance intervertebral disc repair. Regen Med.2018;13(1):55-72.
[12] 赵才勇,何东,刘淼,等.腰椎间盘表观弥散系数与肿瘤坏死因子-α、白细胞介素-6的相关性研究[J].功能与分子医学影像学(电子版), 2016,5(3):34-37.
[13] 张潇潇,姜宏,张志刚,等.肿瘤坏死因子与腰椎间盘退变的相关性研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(12):79-82.
[14] 王亮,张照宏.趋化因子CXCL10(IP-10)、MMP-1及TNF-α与腰椎间盘突出症的相关性研究[J].山东医学高等专科学校学报,2015,37(6):445-447.
[15] 安志辉,丁文元,张剑刚,等.退变性腰椎侧凸TNF-α基因多态性和蛋白表达水平的相关研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2012,1(4):381-387.
[16] 朱书涛,刘洋,张明辉,等.去卵巢大鼠骨组织中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β及白细胞介素6水平与骨质疏松的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(15):2206-2211.
[17] 孙中仪,田纪伟.白细胞介素与椎间盘退变的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(3):249-252.
[18] BATISTA MD, TINCATI C, MILUSH JM, et al. CD57 expression and cytokine production by T cells in lesional and unaffected skin from patients with psoriasis. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e52144.
[19] MACDONALD TT, BELL I, MONTELEONE G. The opposing roles of IL-21 and TGFβ1 in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011;39(4):1061-1066.
[20] NIU X, HE D, DENG S, et al. Regulatory immune responses induced by IL-1 receptor antagonist in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. 2011;49(1-2): 290-296.
[21] LAN L, YONGFENG X, JIANGYONG W, et al. Upregulated IL-21 and IL-21 receptor expression is involved in experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU). Molecular Vision.2009;15:2938-2944.
[22] HAEFELI M, KALBERER F, SAEGESSER D, et al. The course of macroscospicdengeration in the human lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine. 2006;31(14):1522-1531.
[23] PHILLIPS FM, SLOSAR PJ, YOUSSEF JA,et al. Lumbar spine fusion for chronic low back pain due to degenerative disc disease:a systematic review. Spine.2013;38(7):E409-422.
[24] KIMURA H, SHIKATA J, ODATE S, et al. Risk factors for cage retropulsion after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: analysis of 1070 cases. Spine.2012; 37(13):1164-1169.
[25] ZIGLER JE, DELAMARTER RB. Five-year results of the prospective, randomized,multicenter,Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption study of the ProDisc-L total disc replacement versus circumferential arthrodesis for the treatment of single-level degenerative disc disease. J Neurosurg Spine.2012;17(6):493-501.
[26] LAWRENCE BD, HILIBRAND AS, BRODT ED, et al. Predicting the risk of adjacent segment pathology in the cervical spine: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(22 Suppl):S52-64.
[27] BASSO M, CAVAGNARO L, ZANIRATO A, et al. What is the clinical evidence on regenerative medicine in intervertebral disc degeneration. Musculoskeletal Surg. 2017;101(2):93-104.
[28] PENG B, WU W, HOU S, et al. The pathogenesis of discogenic low back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2005;87(1):62-67.
[29] YANG SH, WU CC, SHIH TT, et al. In vitro study on interaction between human nucleus pulposus cells and mesenchymal stem cells through paracrine stimulation. Spine.2008;33(18):1951-1957.
[30] STRASSBURG S, RICHARDSON SM, FREEMONT AJ, et al. Co-culmre induces mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and modulation of the degenerate human nucleus pulposus cell phenotype. Regenerative medicine.2010;5(5):701-711.
[31] JIA Z, YANG P, WU Y, et al. Comparison of biological characteristics of nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells derived from non-degenerative and degenerative human nucleus pulposus. Exp Ther Med2017;13(6): 3574-3580.
[32] Hudson KD, Alimi M, Grunert P, et al. Recent advances in biological therapies for disc degeneration: tissue engineering of the annulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus and whole intervertebral discs. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013;24(5):872-879. |