| [1]Kirkland RA, Saavedra GM, Franklin JL. Rapid activation of antioxidant defenses by nerve growth factor suppresses reactive oxygen species during neuronal apoptosis: evidence for a role in cytochrome c redistribution. J Neurosci. 2007; 27(42):11315-11326.[2]Colafrancesco V, Villoslada P. Targeting NGF pathway for developing neuroprotective therapies for multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. Arch Ital Biol. 2011;149(2):183-192. [3]Shi ED, Wang BC, Sun QS. Nerve growth factor and injured peripheral nerve regeneration. Neural Negen Res 2008;3(11): 1273-1276 .[4]Urbaniak A. p75NTR receptor--role in cell growth and apoptosis. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012;66:304-310.[5]Allen SJ, Watson JJ, Dawbarn D. The neurotrophins and their role in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011;9(4): 559-573. [6]Takeda A, Loveman E, Clegg A, et al. A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine on cognition, quality of life and adverse events in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2006;21(1): 17-28.[7]Miller DS, Bauer B, Hartz AM. Modulation of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier: opportunities to improve central nervous system pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev. 2008; 60(2): 196-209.[8]Akhlaghi SP, Saremi S, Ostad SN, et al. Discriminated effects of thiolated chitosan-coated pMMA paclitaxel-loaded nanoparticles on different normal and cancer cell lines. Nanomedicine. 2010;6(5):689-697. [9]Xu F, Lu W, Wu H, et al. Brain delivery and systemic effect of cationic albumin conjugated PLGA nanoparticles. J Drug Target. 2009;17(6):423-434. [10]Juillerat-Jeanneret L. The targeted delivery of cancer drugs across the blood-brain barrier: chemical modifications of drugs or drug-nanoparticles? Drug Discov Today. 2008;13 (23-24):1099-1106. [11]Yu DH, Lu Q, Xie J, et al. Peptide-conjugated biodegradable nanoparticles as a carrier to target paclitaxel to tumor neovasculature. Biomaterials. 2010;31(8):2278-2292. [12]Lemoine D, Francois C, Kedzierewicz F, et al. Stability study of nanoparticles of poly(epsilon-caprolactone), poly(D,L-lactide) and poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide). Biomaterials. 1996;17(22):2191-2197.[13]Hu S, Zhang Y. Endostar-loaded PEG-PLGA nanoparticles: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2010;5: 1039-1048. [14]Mainardes RM, Evangelista RC. PLGA nanoparticles containing praziquantel: effect of formulation variables on size distribution. Int J Pharm. 2005;290(1-2):137-144. [15]Xie S, Wang S, Zhao B, et al. Effect of PLGA as a polymeric emulsifier on preparation of hydrophilic protein-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2008;67(2): 199-204. [16]Mei L, Long DH, Huang WD. Jiepo Xue Yanjiu. 2010;32(1): 1-5. 梅林,龙大宏,黄婉丹,等.载牛血清蛋白的PLGA纳米粒制备工艺的优化及特性研究[J].解剖学研究.2010;32(1):1-5.[17]Liu FF,Long DH. Jiepo Xue Yanjiu. 2011;33(2):95-100.刘菲菲,龙大宏.阳离子载基因Me PEG-PLGA纳米粒的制备及优化处方的筛选[J].解剖学研究.2011;33(2):95-100. [18]Clavreul A, Sindji L, Aubert-Pouëssel A, et al. Effect of GDNF-releasing biodegradable microspheres on the function and the survival of intrastriatal fetal ventral mesencephalic cell grafts. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2006;63(2):221-228.[19]Duan Y, Xu J, Lin Y, et al. A preliminary study on MeO-PEG-PLGA-PEG-OMe nanoparticles as intravenous carriers. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;87(2):515-523. [20]Cu Y, Saltzman WM. Controlled surface modification with poly(ethylene)glycol enhances diffusion of PLGA nanoparticles in human cervical mucus. Mol Pharm. 2009; 6(1):173-181. [21]Xu HB. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004. 徐辉碧.纳米医药[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2004.[22]Yang A, Yang L, Liu W, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha blocking peptide loaded PEG-PLGA nanoparticles: preparation and in vitro evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2007;331 (1):123-132. |

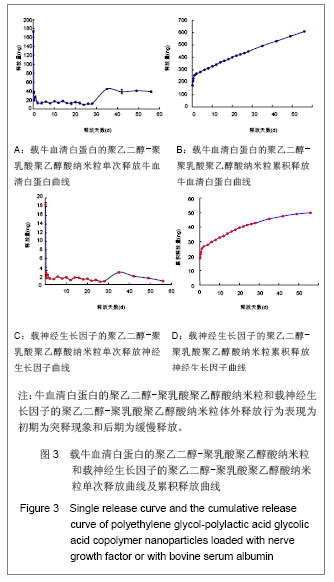
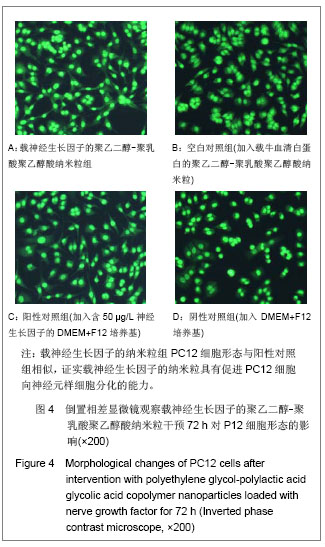
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)