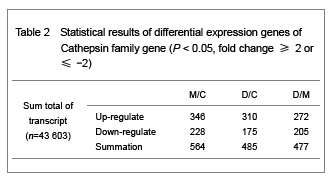
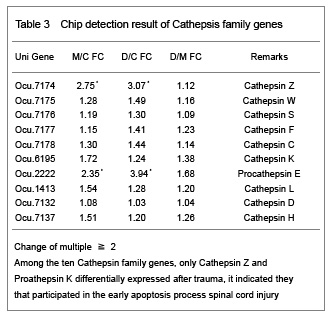
Trauma is the most common reason for acute spinal cord injury and a series of patho-physiological course will happen after spinal cord injury. Allen has divided spinal cord injury into two parts: primary injury and secondary injury. Primary injury refers to a kind of irreversible injury firstly caused by the shift or dislocation of spinal fractures which then leads to intervertebral disc into spinal fractures and fracture fragment pricking into vertebral canal, then resulting in spinal cord compression, shock, laceration, contusion, laceration and cut injuries. While the secondary injury refers to the phenomena that after spinal cord injury, the injured area will inspire a series of neural and biochemical microcirculation disorders and inflammation reactions, which then bring about vascular spasm, blood coagulation and thrombosis. Both can determine the degree and prognosis of spinal cord injury. Mechanism of secondary injury are: (1) Vascular mechanism, namely automatic regulative vascular disorders. Due to vascular endothelial injury, basement membrane exposure, platelet adhesion and thrombosis, that lumen occlusion formation; tissue ischemia and hypoxia leads to edema and bleeding thus results in liquefaction necrosis in the spinal cord tissue. (2) Electrolyte changes, Na+ migrates into neural cells after spinal cord injury, while K+ escapes and gatheres outside the cells, which affects the neighbouring depolarization of adjacent neurons and glial cells, and resulting in nerve conduction block. Inflow of extracellular calcium and the increasing of intracellular calcium activate a variety of protease and phospholipids, which makes the cell membrane break down and lipid peroxide and then resulting in a large number of oxygen free radicals and leading to cell death[3]. (3) Biochemical mechanisms: norepinephrine gathering, increasing of 5-hydroxytryptamine and the production of prostacyclin can damage the blood supply. The production and gathering of dynorphin and other endogenous opioids and excitatory amino acid are considered to be the factors that leading to spinal cord injury[4]. (4) Edema: Biochemical changes of the cellular level causes cytotoxic edema, increasing of local tissue pressure and microcirculation obstruction which further reduce the usage of oxygen. (5) Energy metabolism inhibition: Adenosine triphosphate production decreases.
With regard to the whole organism and the tissue of the injured region, trauma is no doubt a powerful blow to them. Traditionally acknowledged that necrosis is the only result of trauma. However, in recent years, plenty of researches have indicated that hypoxic cells mainly end in necrosis, and at the same time, the number of apoptosis also increased. Ischemic hypoxic cells generate a great deal of oxygen free radicals and also lead to severe calcium overload, both of which will result in the peroxidation of lipid and protein and the damage of DNA. The damage of DNA will lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, disruption of cytoskeleton and activating phospholipase[5-6]. Both of them were successively considered as the main causes to the injury even death of the ischemic hypoxic cells. However, the elimination of oxygen free radicals and calcium blocking cannot totally prevent the death of cells which already are oxygen-deficient and ischemia. Moreover, oxygen free radicals and calcium-overload can not fully explain the fact that after being oxygen-deficient and ischemia, the apoptosis of cells are increased[7]. Recent researches indicate that oxygen free radicals and calcium-overload may be the incentive of cell death rather than the direct cause of the death of oxygen-deficient and ischemia cells. Mitochondrial damage maybe the crucial juncture which contributes to the necrosis and death of oxygen-deficient and ischemia cells[8]. Oxygen deficient and ischemia may result two main consequences of mitochondrion: calcium overload and oxidative stress. Either the combined action or separate action of them can cause necrosis. The mechanism is related with the inducement of mitochondrial permeability transition. At present, it acknowledges that mitochondrial permeability transition is the common result of cells which has been affected by toxic material, and the essence of mitochondrial permeability transition is high-permeation status of permeability transition pore[9-10]. Both Mitochondrial calcium overload and oxidative stress can accelerate adenine nucleotide translocase, voltage-dependent anion channel and cyclophilin D to combine into adenine nucleotide translocase-voltage-dependent anion channel-cyclophilin D trigeminal composite to stimulate the conformation alteration of adenine nucleotide translocase, voltage-dependent anion channel and then lead to the occurrence of mitochondrial permeability transition. Mitochondrial permeability transition makes permeability transition pore allows materials as high as 5 000 u molecular weight out and in mitochondrion which results in content loss of mitochondrion, decrease even disappearance of membrane potential, large-scale hydrogen entry into mitochondrion, finally leading to the swelling even disintegration of mitochondrion. With regard to cells, mitochondrial permeability transition will results in consequences as follows: (1) Disturbance will happen in the process of cellular oxidation and phosphorylation and the main energy resource of cells will disappear which make all vital movement of cells hard to continue. (2) The entry of mitochondrial cell pigment C apoptosis inducing the factors into hyalomitome can activate Caspase-9 and Caspase-3 and induce the apoptosis. (3) The accumulative Ca2+ obtained from mitochondrial release raise up the Ca2+ of hyalomitome, activate kinds of proteolytic enzyme and phospholipase intra-cellular, damage even disintegrate cell membrane and finally result in cellular necrosis. It can be concluded from the whole analysis that the occurrence of mitochondrial permeability transition is the crucial juncture which contributes to the transformation from reversible injury to irreversible injury[11-12].
The relevant gene expression of mitochondrial apoptosis is mainly analyzed in this experience, and the result turns out that: oryctolagus cuniculus voltage-dependent anion channel 5, pseudogene mRNA and oryctolagus cuniculus solute carrier family 25 member 5 are expressed normally in the spinal cord injury group, and the expression volume is decreased after being treated by large dose of drugs, so obvious differences are displayed on the expression between drug group and spinal cord injury group. However, voltage-dependent anion channel 1, voltage-dependent anion channel 2, B-cell lymphoma 2, B-cell lymphoma 1, cytochrome b5 and RABEST086T-like cytochrome cxidase Va, Caspase 2, Caspase 3, Caspase 7, Caspase 9 and Caspase 14 appears no difference on expression between drug group and spinal cord injury group. Oryctolagus cuniculus voltage-dependent anion channel 5 pseudogene mRNA is the nuclear gene encoding which is voltage-dependent. Oryctolagus cuniculus solute carrier family 25 member 5 nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein mRNA is the nuclear gene encoding of mitochondrial bearer protein-adenine mononucleotide translocator. Supra citato, voltage-dependent anion channel pseudogene mRNA and solute carrier family 25 member 5 are the main components of permeability transition pore, adenine nucleotide translocase, voltage-dependent anion channel and cyclophilin D will combine into adenine nucleotide translocase-voltage-dependent anion channel-cyclophilin D trigeminal composite to stimulate adenine nucleotide translocase and voltage-dependent anion channel to change conformation and result in the occurrence of mitochondrial permeability transition which finally leads to cell death by mitochondrial mechanism. It is known to all, necrosis and apoptosis of partial histiocytes will occur after severe spinal cord injuries, and paralysis is the clinical manifestation of it. Large dose of methylprednisolone has the function of protecting neuromechanism if being applied prophase.
During this experiment, adenine nucleotide translocase and voltage-dependent anion channel increase their expressions at the prophase but decrease their expressions after being impacted by large dose of methylprednisolone. The experimental result indicates that apart from the functions of inhibiting inflammatory reaction, alleviating tissue water, repressing peroxidatic reaction of lipide and regulating the level of Ca2+, large dose of methylprednisolone also possibly producing a marked effect of anti-cell death by means of regulating the permeability of mitochondrial transformation hole. Obviously, this explaination just from the aspect of gene transcription level, and other gene function can be reflected on the regulation of translation or post-translation. The most important thing is that the ion permeation status of mitochondrial transformation hole essentially contributes to the occurrence of mitochondrial permeability transition. Therefore, more experiments are needed to further validate this phenomenon.