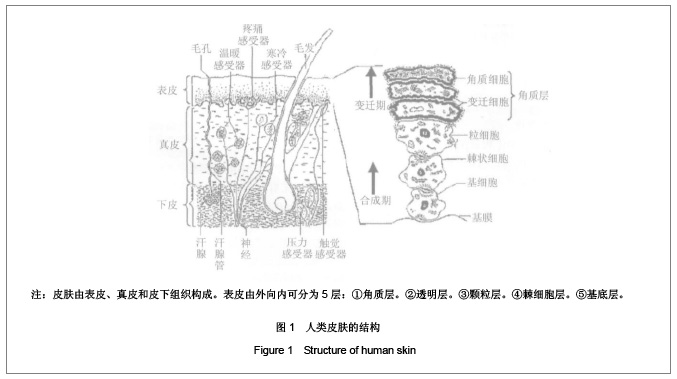
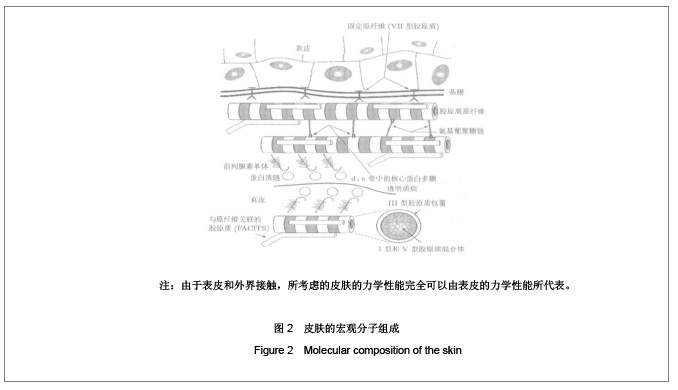
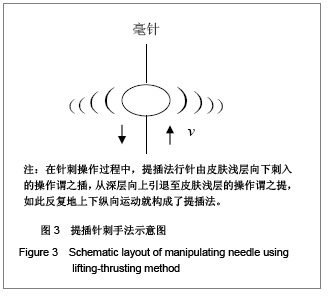
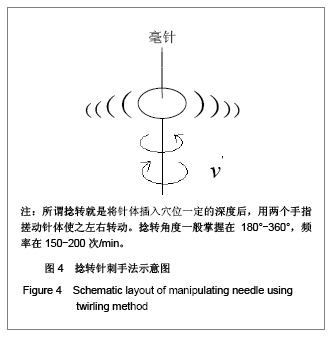
| [1] Fei L, Cheng HS, Cai DH, et al. Kexue Tongbao. 1988;43(6): 658. 费伦,承焕生,蔡得亨,等.经络物质基础及其功能性特征的实验探索和研究展望[J].科学通报,1988,43(6):658.[2] Dung HC. Anatomical features contributing to the formation of acupuncture. Brookline MA:Paradigm,1991.[3] Langevin HM, Churchill DL, Fox JP, et al. Biomechanical response to acupuncture needling in humans. J Appl Physical. 2001;91:2471.[4] Kolodney MS, Wysolmersky RB. Isometric contraction by fibroblasts and endothelial cells in tissue culture:a quantitative study. J Cell Biol. 1992;117:73.[5] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zhenjiu. 2009;29(3):223-226. 王西明.针刺次声能量治病机制的分析[J].中国针灸,2009,29(3):223-226.[6] Yuan L, Yao DW, Tang L, et al. Jiepou Xuebao. 2004;35(4): 337-343. 原林,姚大卫,唐雷,等. 针灸经穴的数字解剖学研究[J].解剖学报,2004,35(4):337-343.[7] Maurel W, Wu Y, Magnenat Thalmann N, et al. Biomechanical Models for Soft Tissue Simulation.Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1998.[8] North JF, Gibson F. Volume compressibility of human abdominal skin. J Biomech.1978;11(4): 203-207.[9] Sivamani RK, Goodman J, Gitis NV, et al. Coefficient of friction: tribological studies in man-an overview. Skin Res Technol. 2003;9(3):227-234.[10] Sivamani RK, Goodman J, Gitis NV, et al. Friction coefficient of skin in real-time. Skin Res Technol. 2003;9(3):235-239.[11] Ding GH, Shen XY, Dai JH, et al. Shengwu Yixue Gongchengxue Zazhi. 2003;20(1):121-124. 丁光宏,沈雪勇,戴建华,等.中医针刺过程中针体受力的动态监测系统研制[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2003,20(1):121-124.[12] Feng YZ. Beijing: Science Press. 1983: 124-134. 冯元桢. 生物力学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1983: 124-134. [13] Oryan A. Role of collagen in soft connective tissue wound healing. Transplant. 1995;27(5):2759. [14] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(39):7382-7385. 王西明.针刺频率和输入能量的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(39):7382-7385.[15] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(22):4346-4348. 王西明.针刺能量的物理学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(22):4346-4348.[16] Deng YR, Wang XM, Zhang WH. Xianyang Shifan Xueyuan Xuebao. 2010;25(4):24-26. 邓亚荣,王西明,张卫华.针刺能量输入模型及动力学方程[J].咸阳师范学院学报,2010,25(4):24-26.[17] Wang XM. Beijing Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng. 2008;27(2): 202-204. 王西明.针刺过程能量的输入[J]. 北京生物医学工程,2008, 27(2): 202-204.[18] Wang XM. Beijing Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng. 2009;28(3): 309-312. 王西明.针刺治病是次声能量的有效利用[J].北京生物医学工程, 2009,28(3):309-312.[19] Wang XM. Xi′an: Xi′an Jiaotong University Press. 2007: 1372-1375. 王西明.熵变概念的再拓展——对人体系统和外界作用规律的研究.生物医学进展[M]. 西安:西安交通大学出版社, 2007: 1372-1375.[20] Wang XM. Shanxi Shifan Daxue Xuebao. 2003;(3):62-64. 王西明. 熵变概念的拓展[J]. 陕西师范大学学报,2003,(3): 62-64.[21] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zhenjiu: Wangluoban. 2007. 王西明. 人体腧穴和外界交换能量(信息)规律的探讨[J].中国针灸: 网络版,2007.[22] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zhenjiu. 2011;31(1):71-74. 王西明. 提插与捻转手法输入能量的比较分析[J]. 中国针灸,2011,31(1):71-74.[23] Lu TJ, Xu F. Luxue Jinzhan. 2008;38(4):393-426. 卢天健,徐峰. 皮肤的力学性能概述[J]. 力学进展,2008,38(4): 393-426.[24] Ding GH, Shen XY, Dai JH, et al. Zhongguo Zhenjiu. 2002; 22(10):679-681. 丁光宏,沈雪勇,戴建华,等.中医针刺过程中针体受力的动态监测系统研制[J].中国针灸,2002,22(10):679-681. |