中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (26): 4237-4242.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2769
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
基于数据挖掘技术分析针灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的取穴规律
刘会敏1,冷 军2,郭 文1,房晓磊1,张 晨1,魏方月1
1山东中医药大学康复学院,山东省济南市 250355;2山东中医药大学第二附属医院康复医学科,山东省济南市 250001
The rules of acupoint selection in the treatment of neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury with acupuncture and moxibustion: based on data mining technology
Liu Huimin1, Leng Jun2, Guo Wen1, Fang Xiaolei1, Zhang Chen1, Wei Fangyue1
1School of Rehabilitation, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250001, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
聚类分析:是一组将研究对象分为相对同质群组的统计分析技术。
关联规则分析:从事务数据库、关系数据库和其他信息存储中的大量数据的项集之间发现有趣的、频繁出现的模式、关联和相关性。
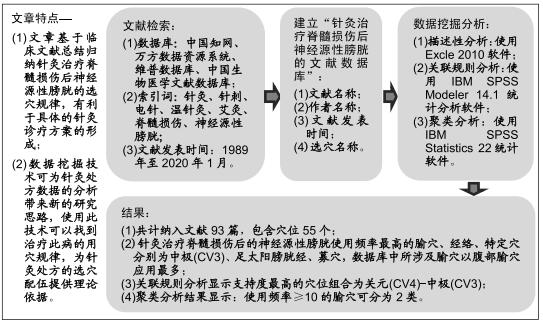
背景:目前,许多的研究表明针灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱具有显著疗效,但对于此病的治疗尚无统一的针灸处方标准。
目的:探究针灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的取穴规律。
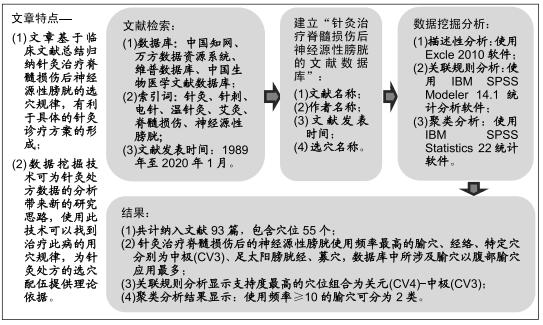
方法:检索1989年至2020年1月发表于中国知网、万方数据资源系统、维普数据库和中国生物医学文献数据库中的有关针灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的相关临床文献,建立数据库对所收集文献的针灸处方进行描述性分析、关联规则分析和聚类分析。
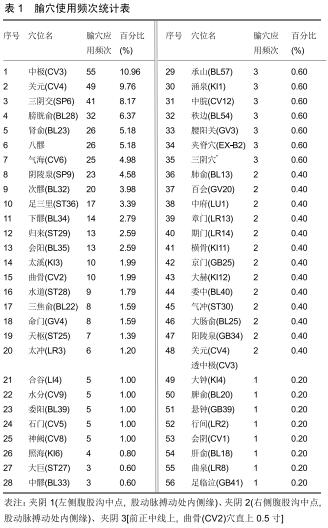
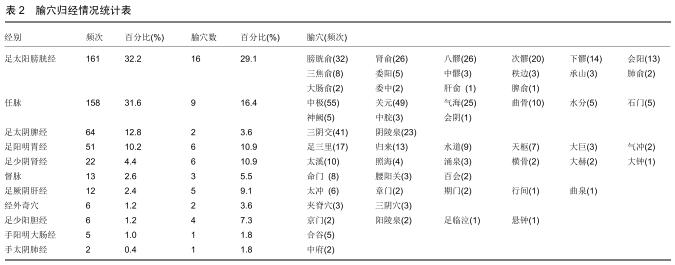
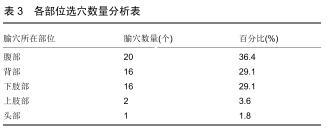
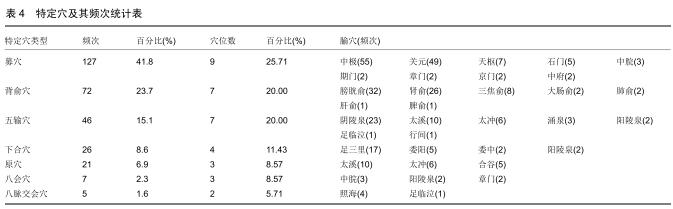
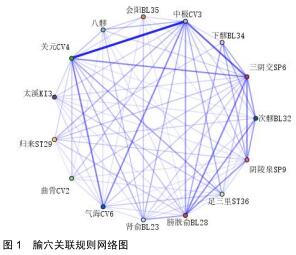
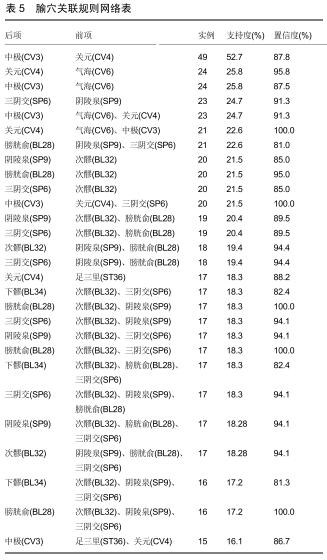
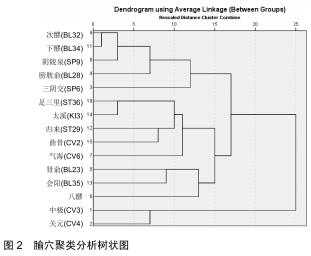
结果与结论:①共计纳入文献93篇,经数据汇总、分析显示针灸治疗脊髓损伤后的神经源性膀胱使用频率最高的腧穴和经络分别为中极(CV3)(频次55)、足太阳膀胱经(频次161);②关联规则分析显示支持度最高的穴位组合为关元(CV4)-中极(CV3);③将使用频率≥10的腧穴进行聚类分析,结果显示腧穴可分为2类;④上述数据证实,针灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱时选穴多为循经选穴和局部选穴,临床治疗可利用数据挖掘得出的关联规则分析和聚类分析结果合理取穴配穴并重用特定穴以提高治病效果。
ORCID: 0000-0001-6928-314X(刘会敏)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: